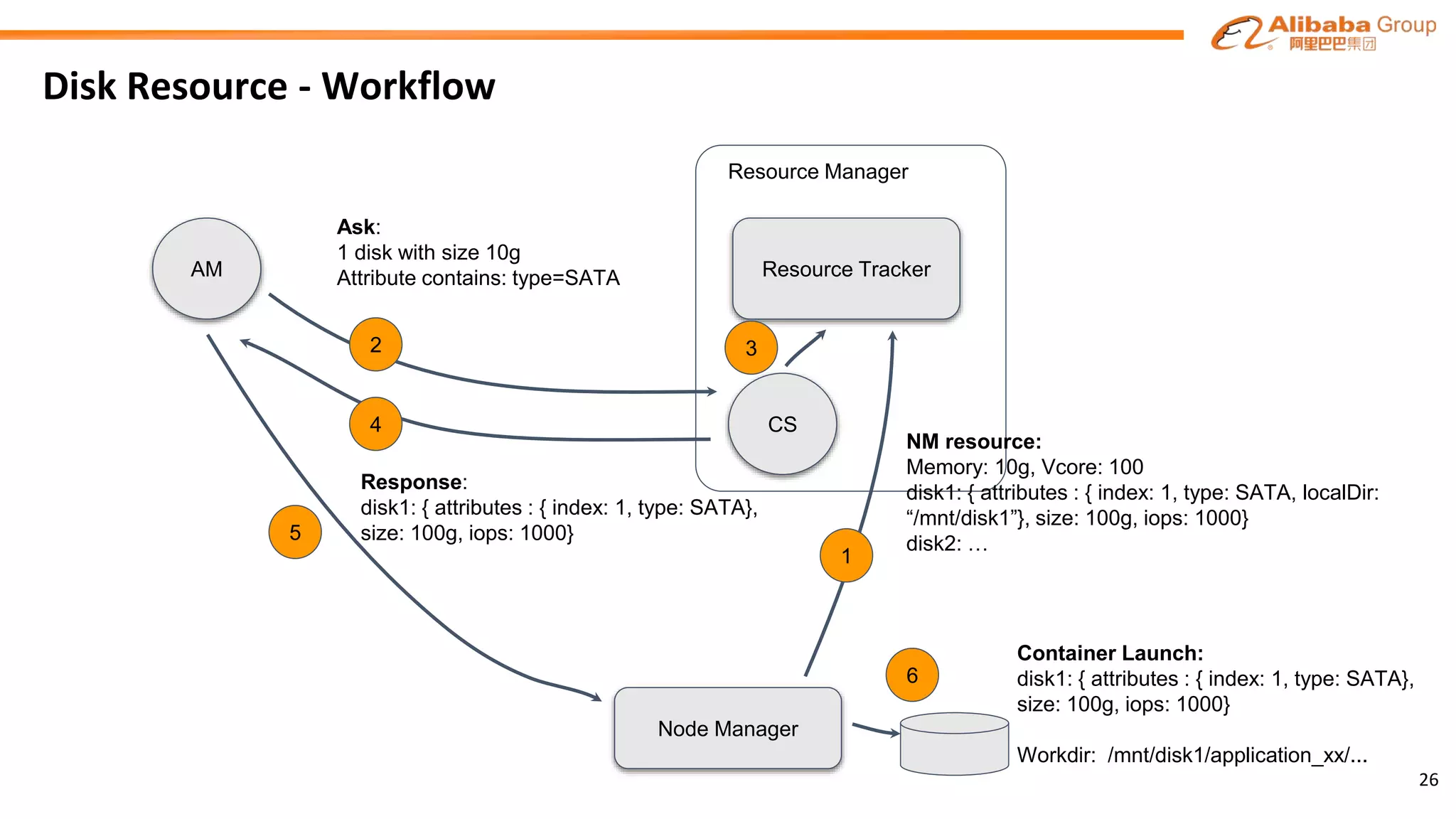
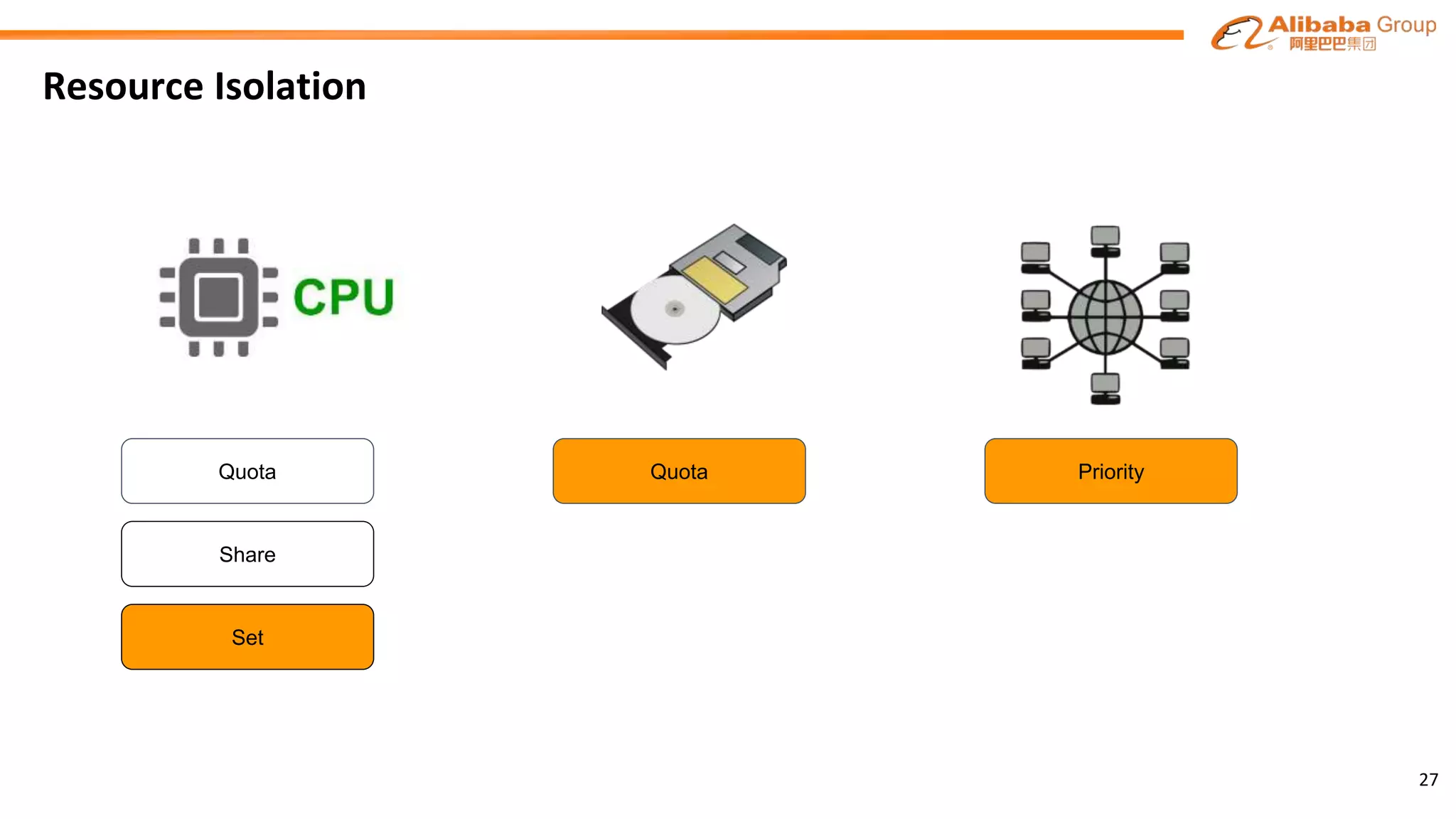
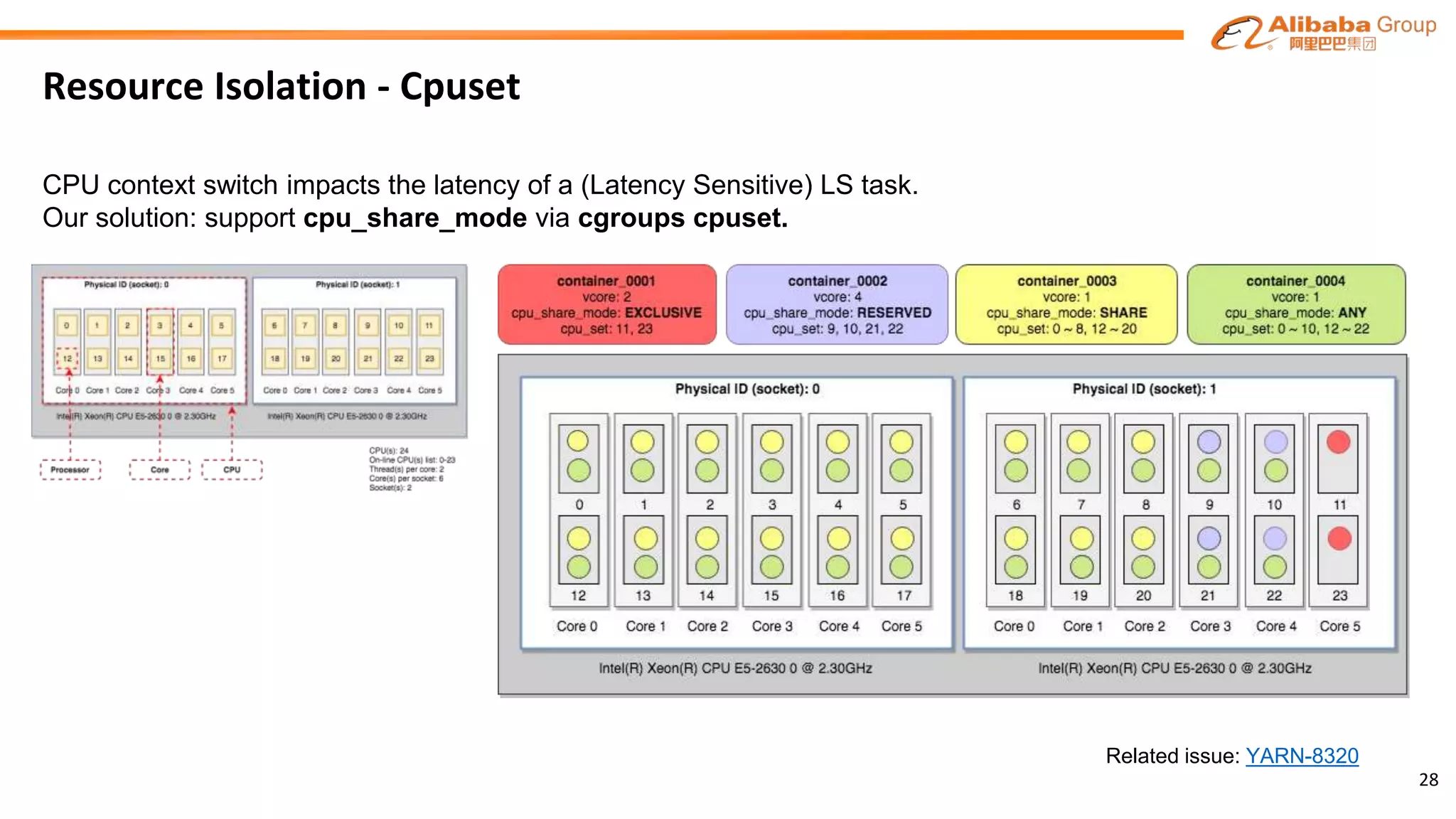
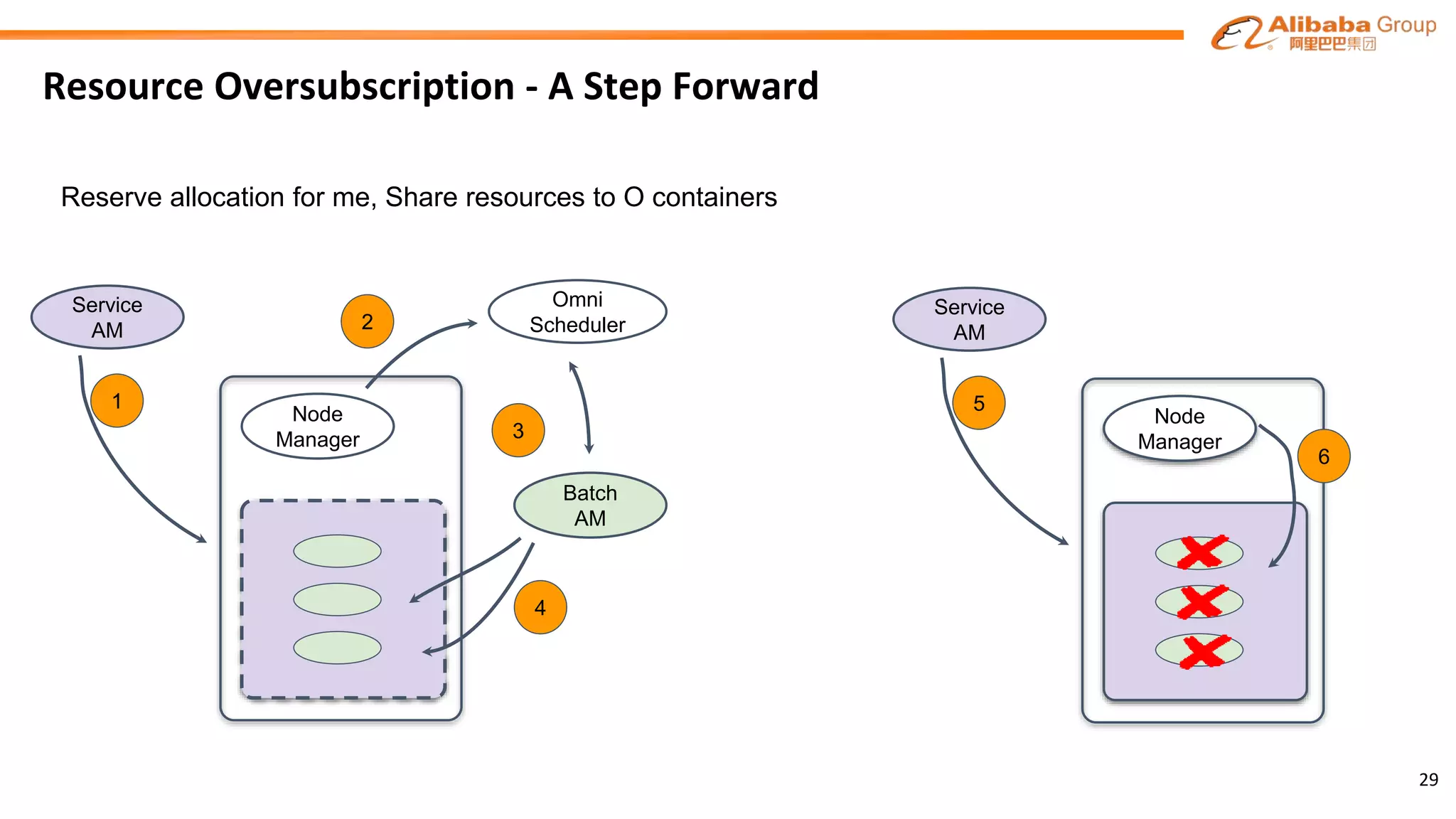
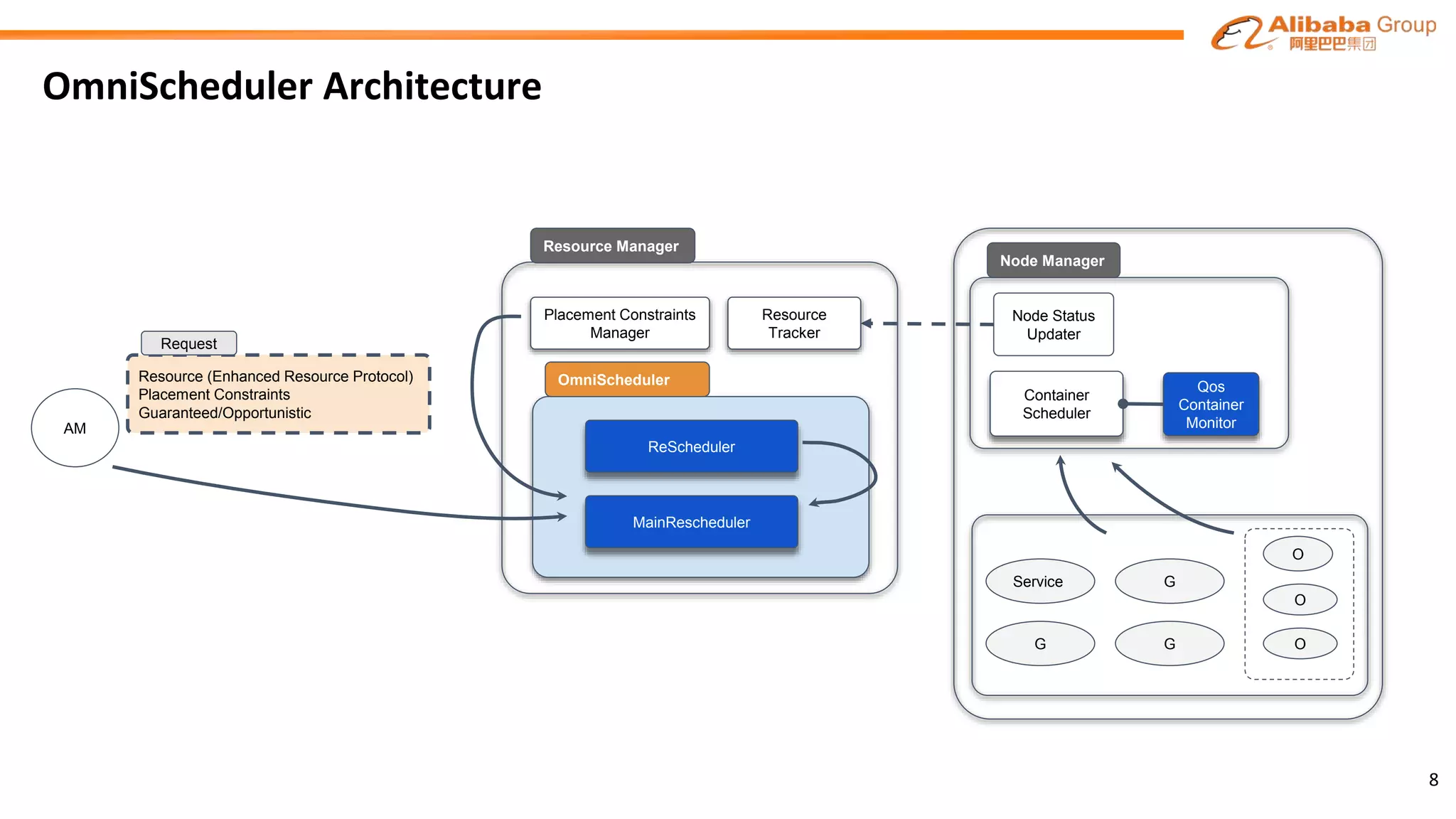
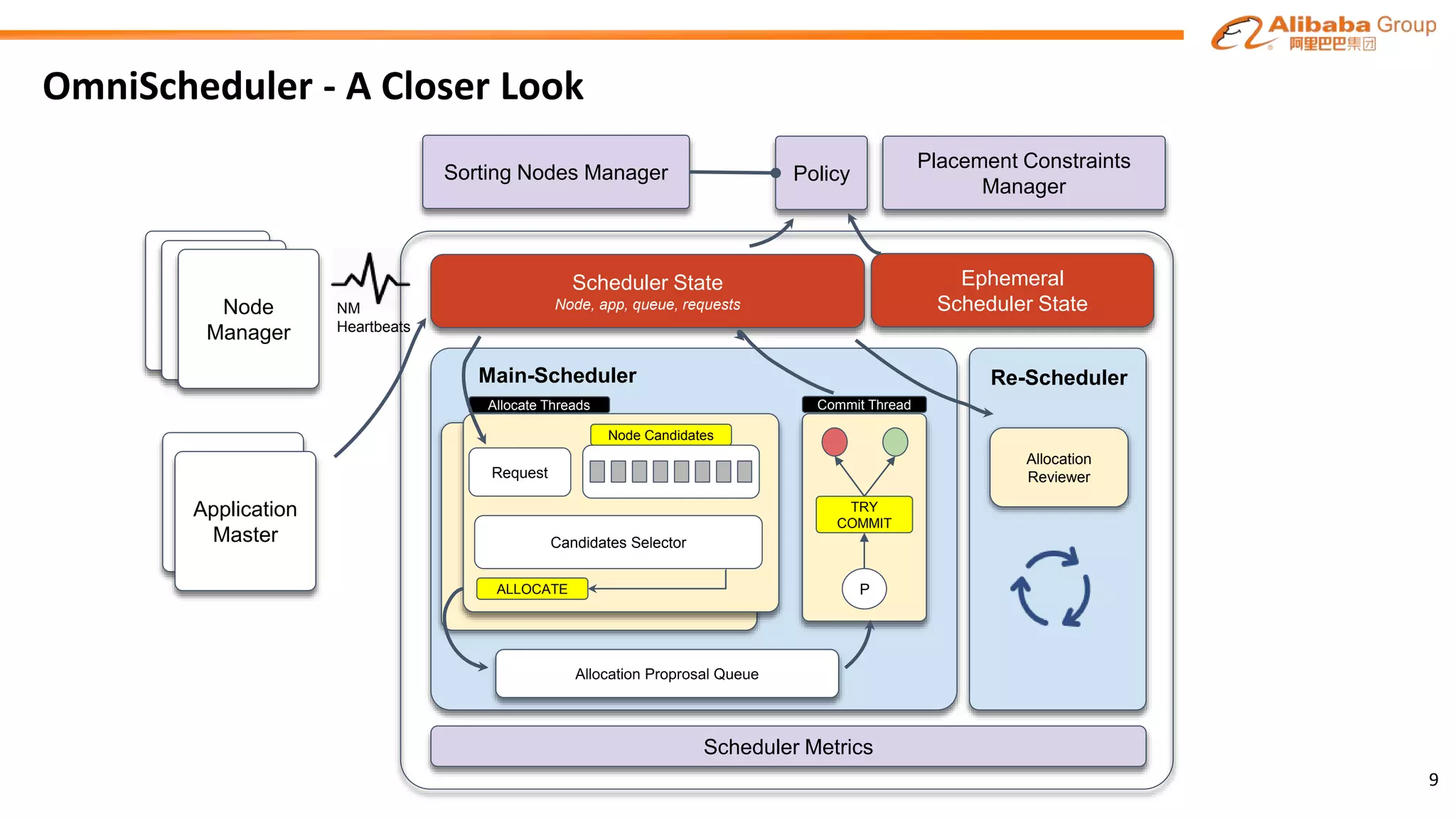
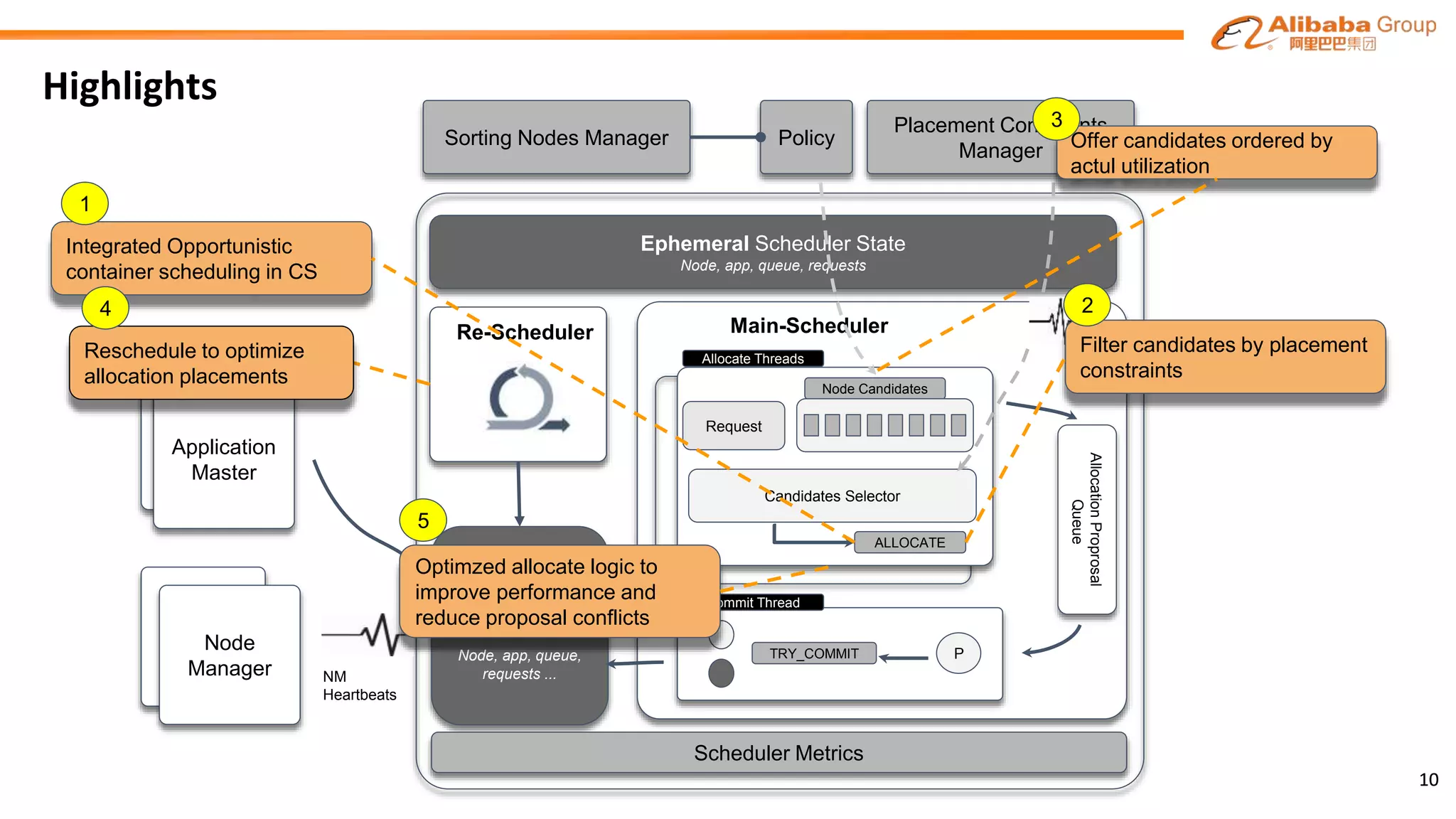
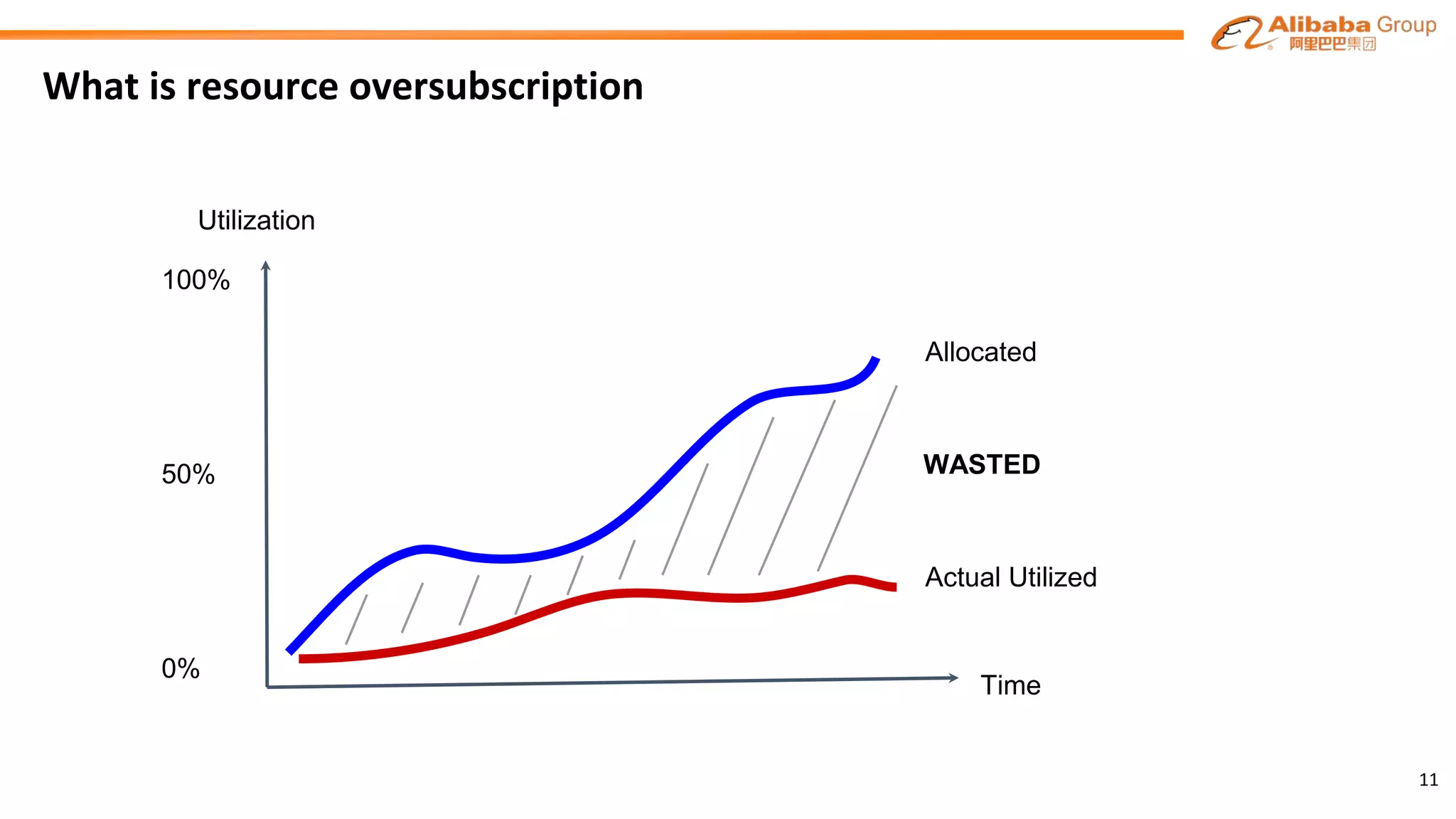
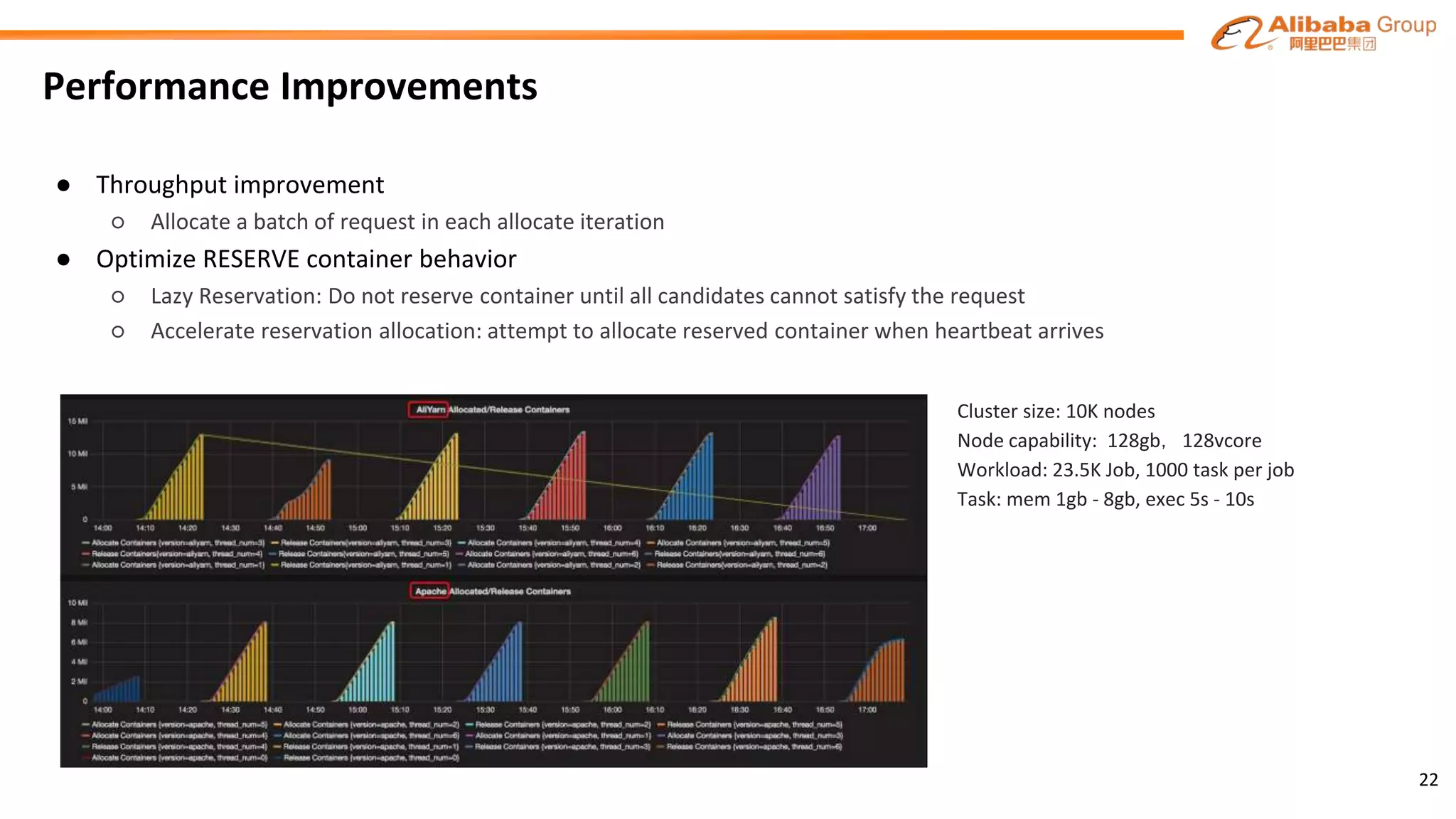
The document outlines the enhancements and future directions of the Apache YARN ecosystem in Alibaba, focusing on the development of the omni scheduler, resource extension and isolation, and multi-dimensional resource management. It details the challenges faced by existing schedulers and introduces new methods for optimizing container allocation, improving utilization rates, and managing resource conflicts, including features like dynamic scheduling and QoS modules. Future work is proposed to further enhance performance, reduce latency, and leverage machine learning for optimizations.







![Reduce Allocation Proposal Conflicts
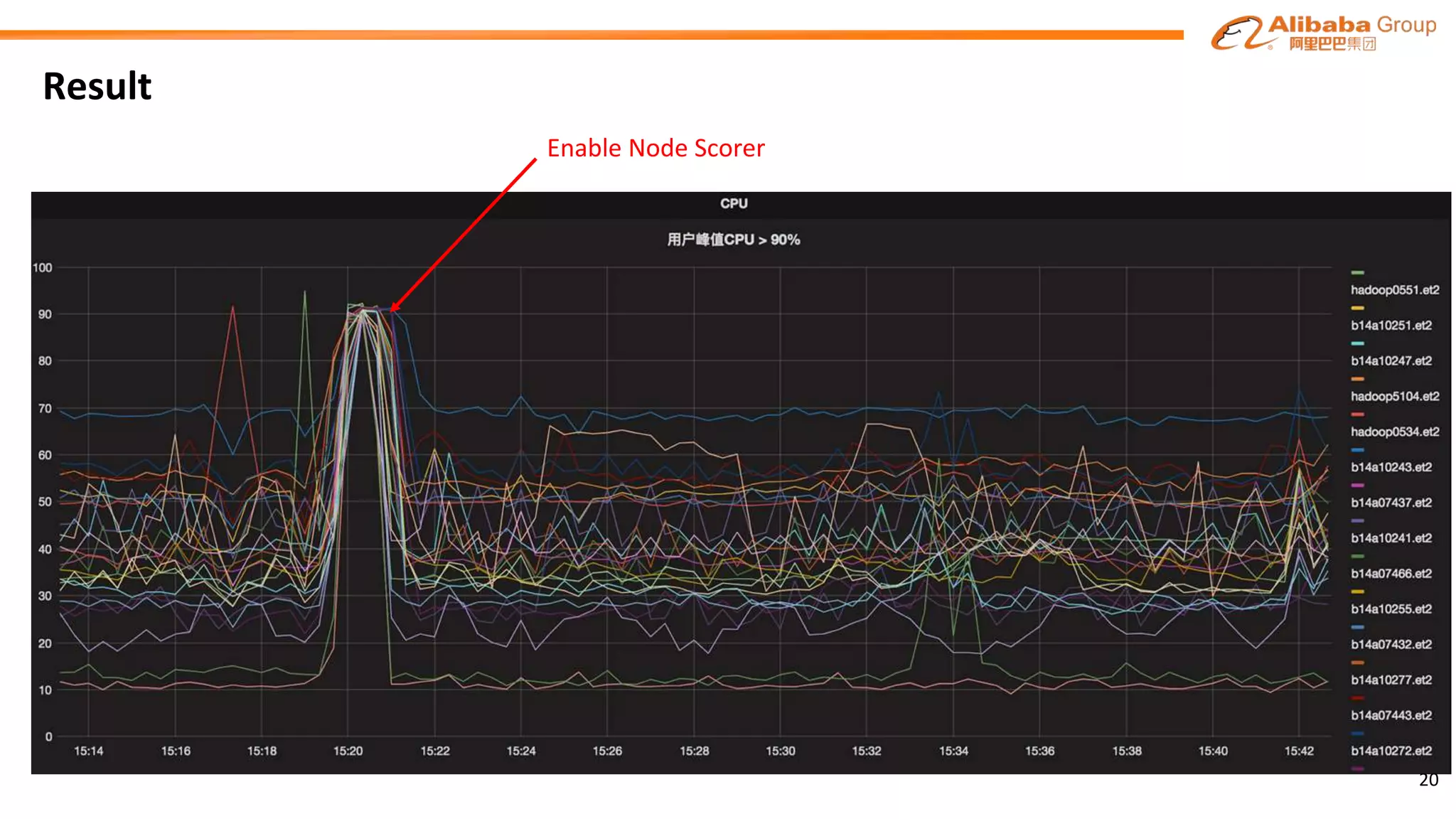
Allocate thread is fast, often tens of milliseconds, sorting is slow (depending on the number of nodes), possibly a large
number of allocate threads will see same sorting result. If they both do allocate in order, that creates a lot of conflicts.
Therefore, we optimized the sorting strategy to “Partition Score Sort”.
N1
[0.0,0.1]
Nx
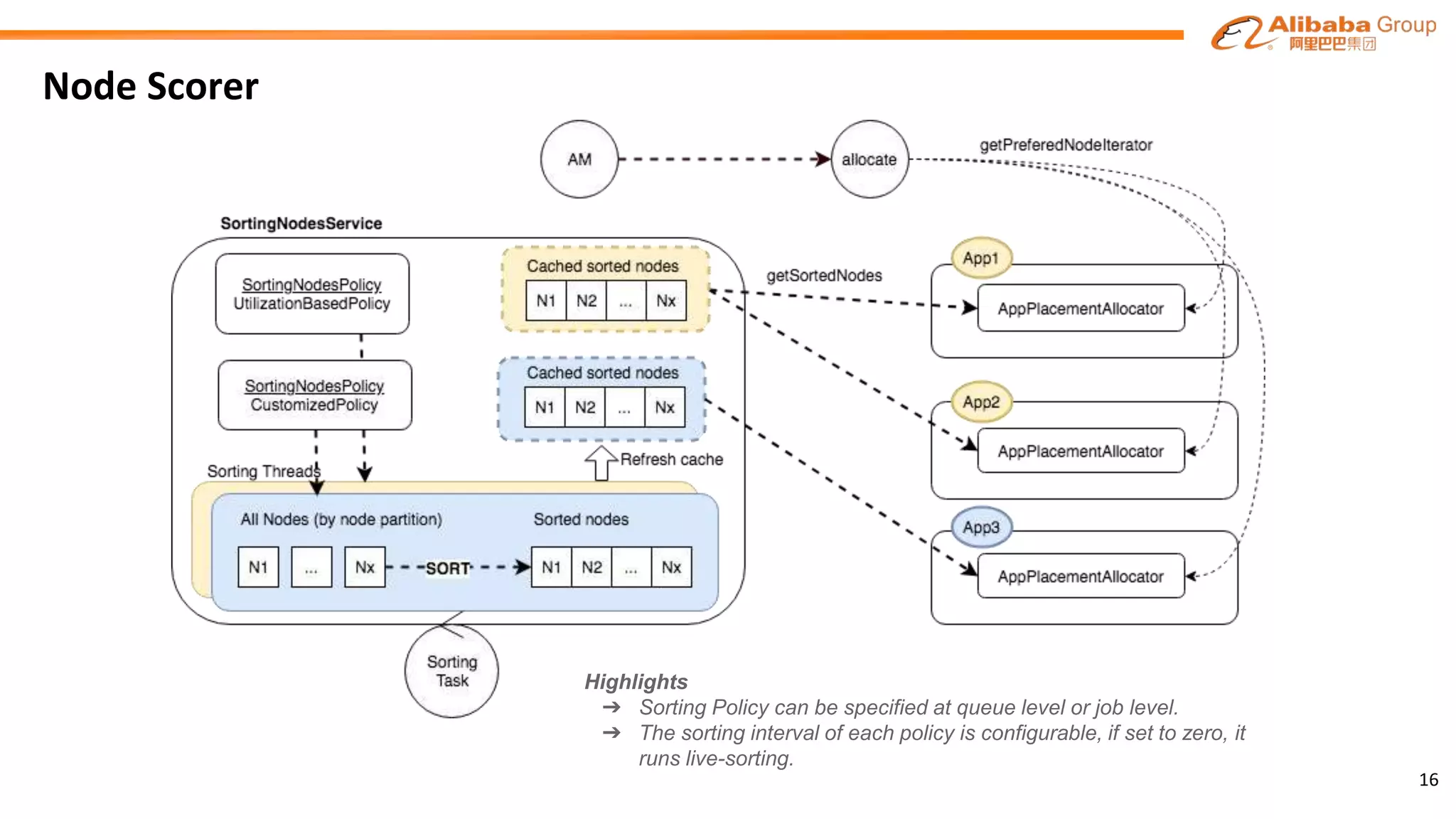
Node
Scorer
(0.1,0.2]
(0.9, 1.0] N1 N3
N2
N4 N5
N6
N2
App1
App2
P1
P9
P0
... (0.9, 1.0] N1 N3 N6P0
Random Pick
(0.9, 1.0] N1 N3 N6P0
(0.1,0.2] N2P1
Unsatisfied
Random Pick
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apacheyarn3-180622213428/75/Apache-Hadoop-YARN-3-x-in-Alibaba-21-2048.jpg)

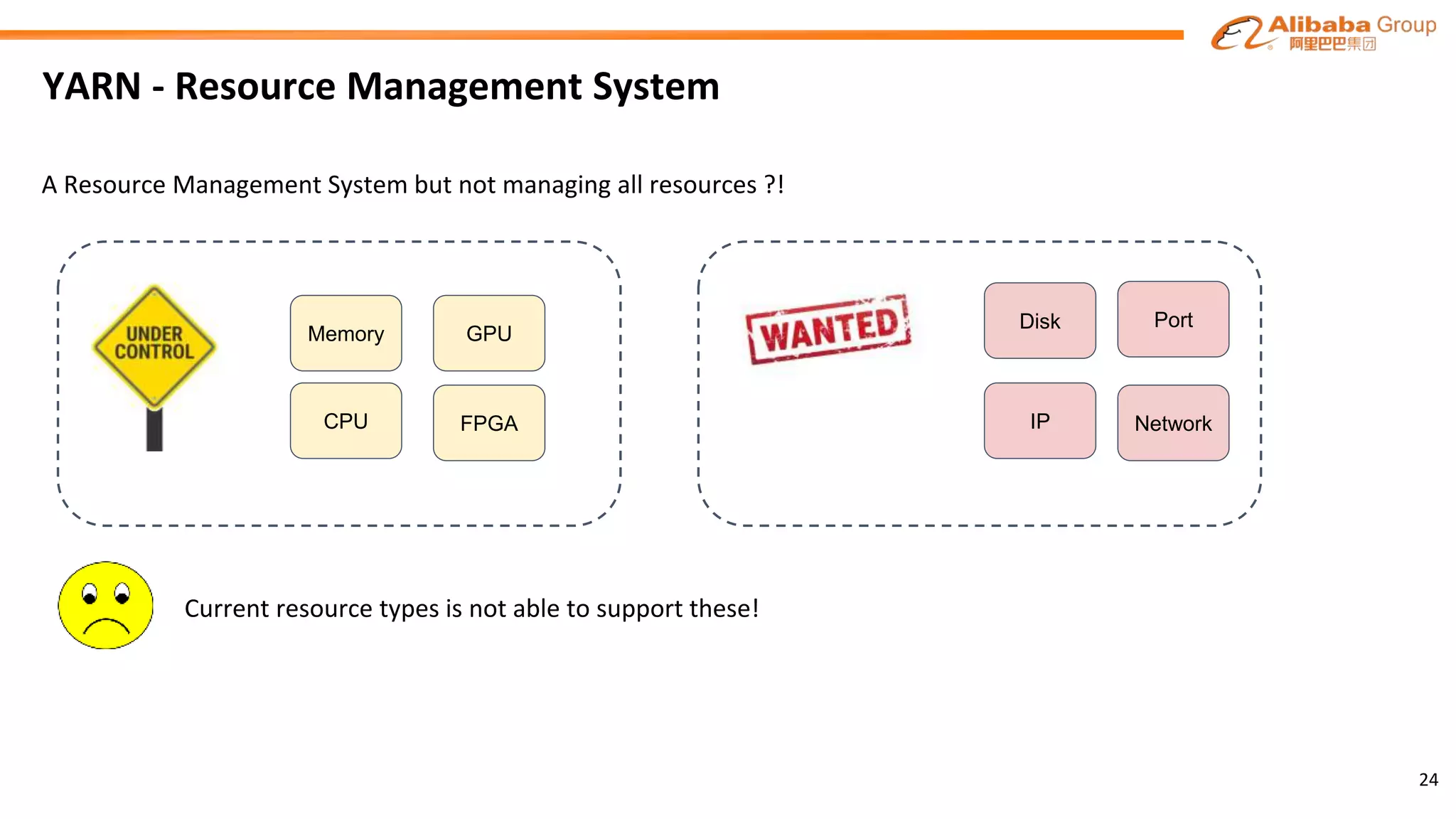
![Multi-dimensional Resources
COUNTABLE
SET
RESOURCE
SET
disks : [ {attributes : {"type":"sata", "index":"1"}, size : 100, iops : 100, ratio : 100},
{attributes : {"type":"ssd", "index":"2"}, size : 100, iops : 100, ratio : 100},
{attributes : {"type":"ssd", "index":"9999"}, size : 40, iops : 40, ratio : 40}]
{
"name": "IP",
"values": ["10.100.0.1", "0.100.0.2", "100.100.0.3"]
}
{
"name" : "memory",
"units" : "mb"
"value" : "1024"
}
Ne
w
Ne
w
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apacheyarn3-180622213428/75/Apache-Hadoop-YARN-3-x-in-Alibaba-25-2048.jpg)