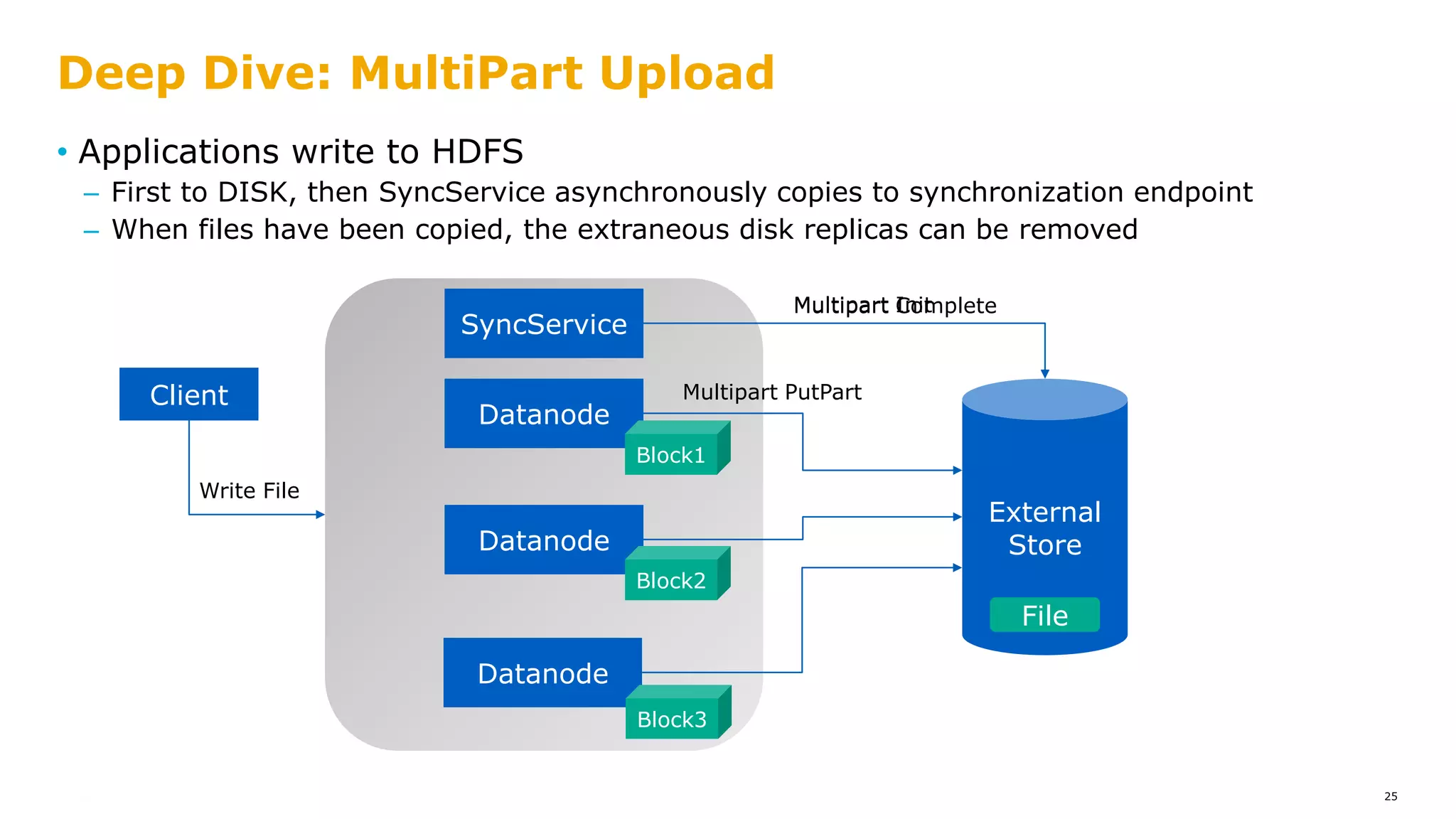
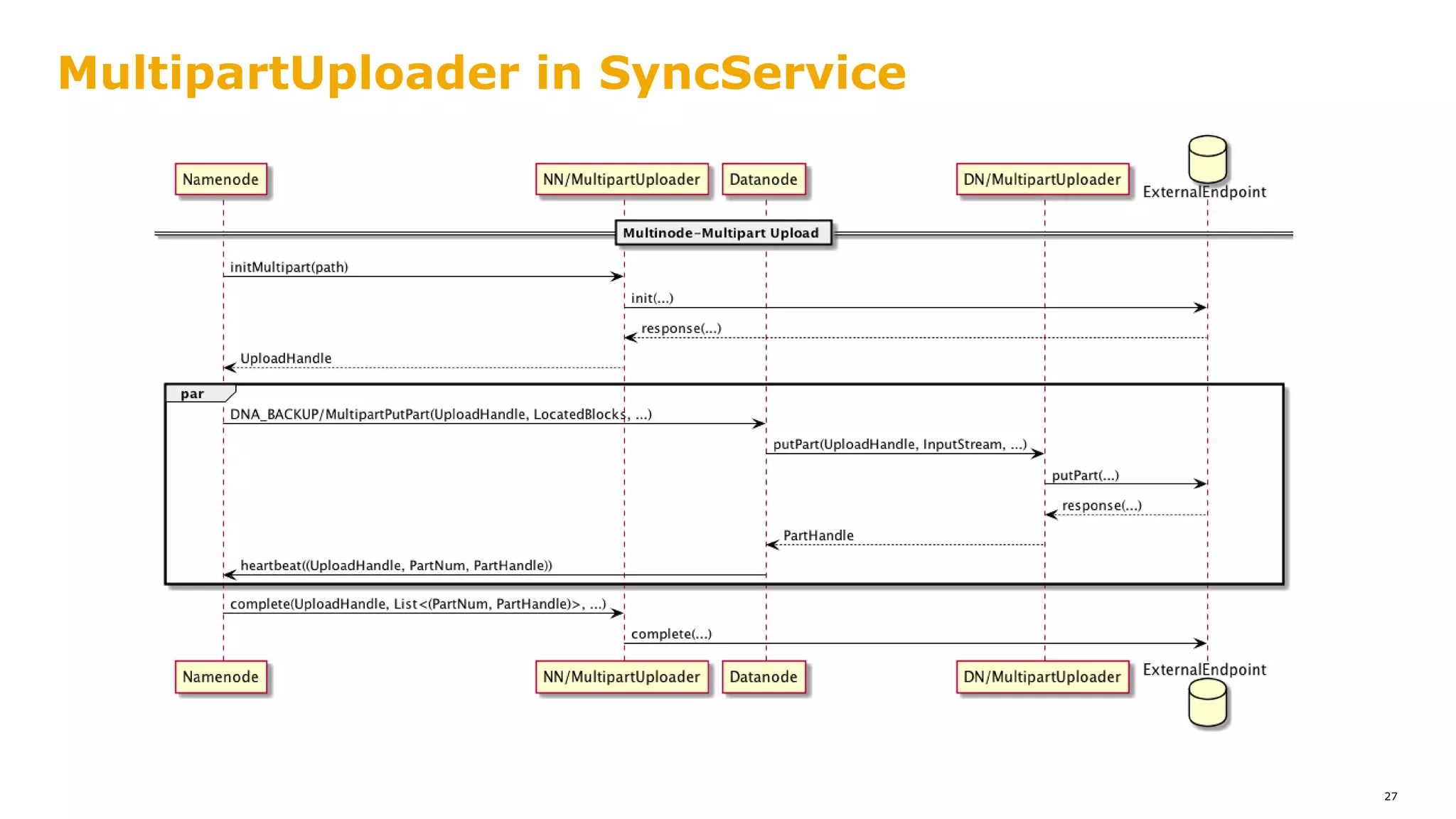
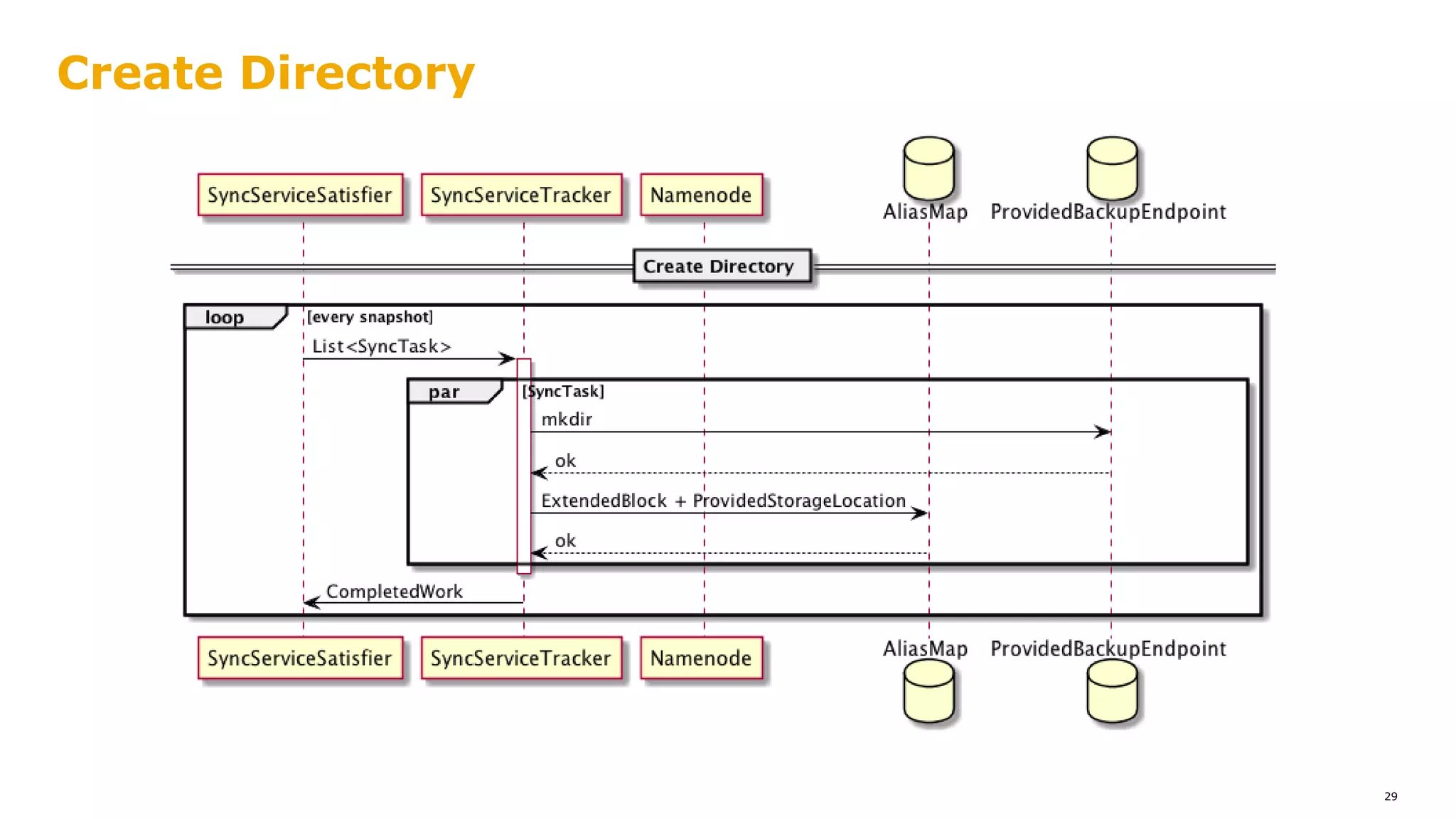
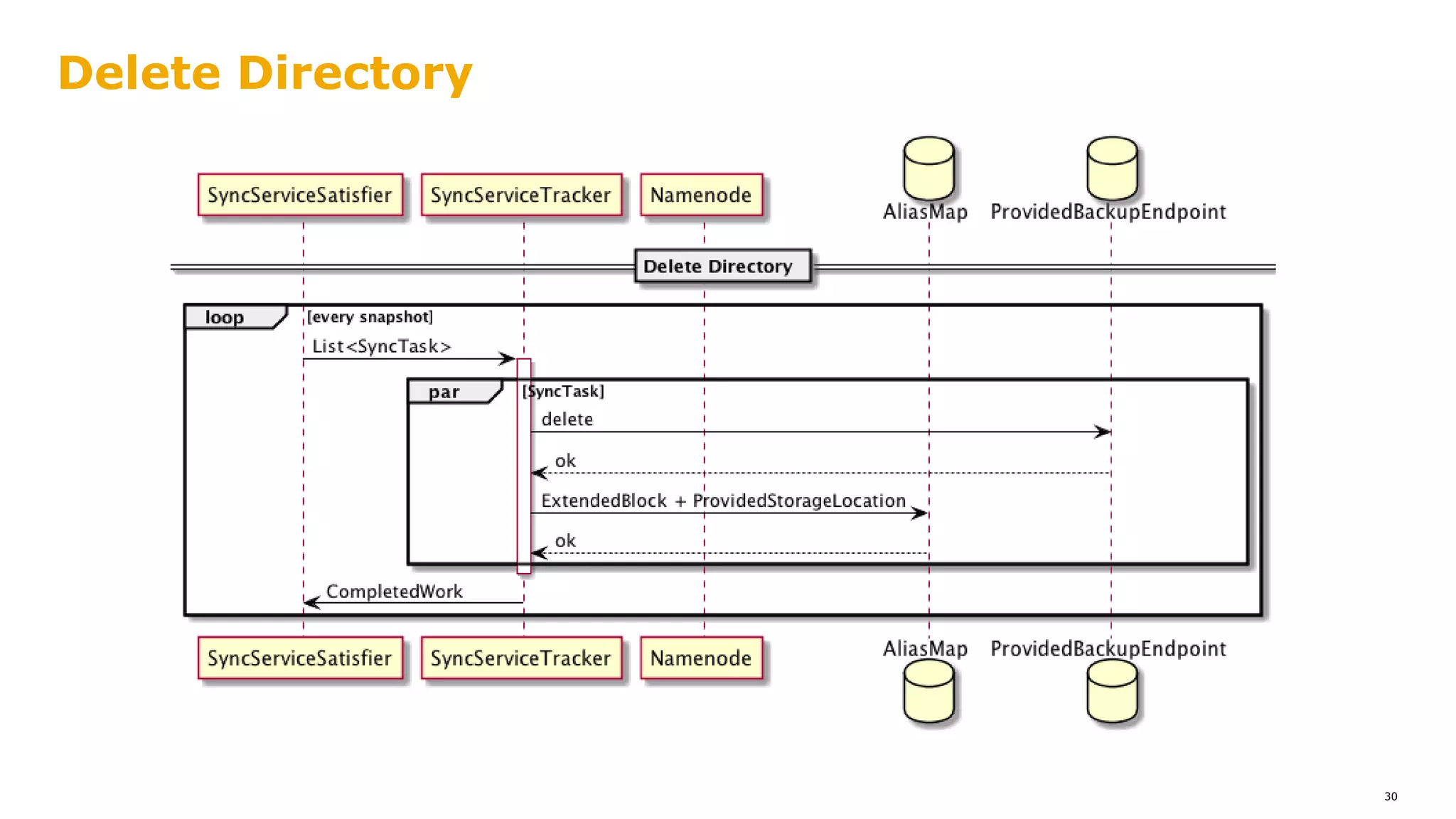
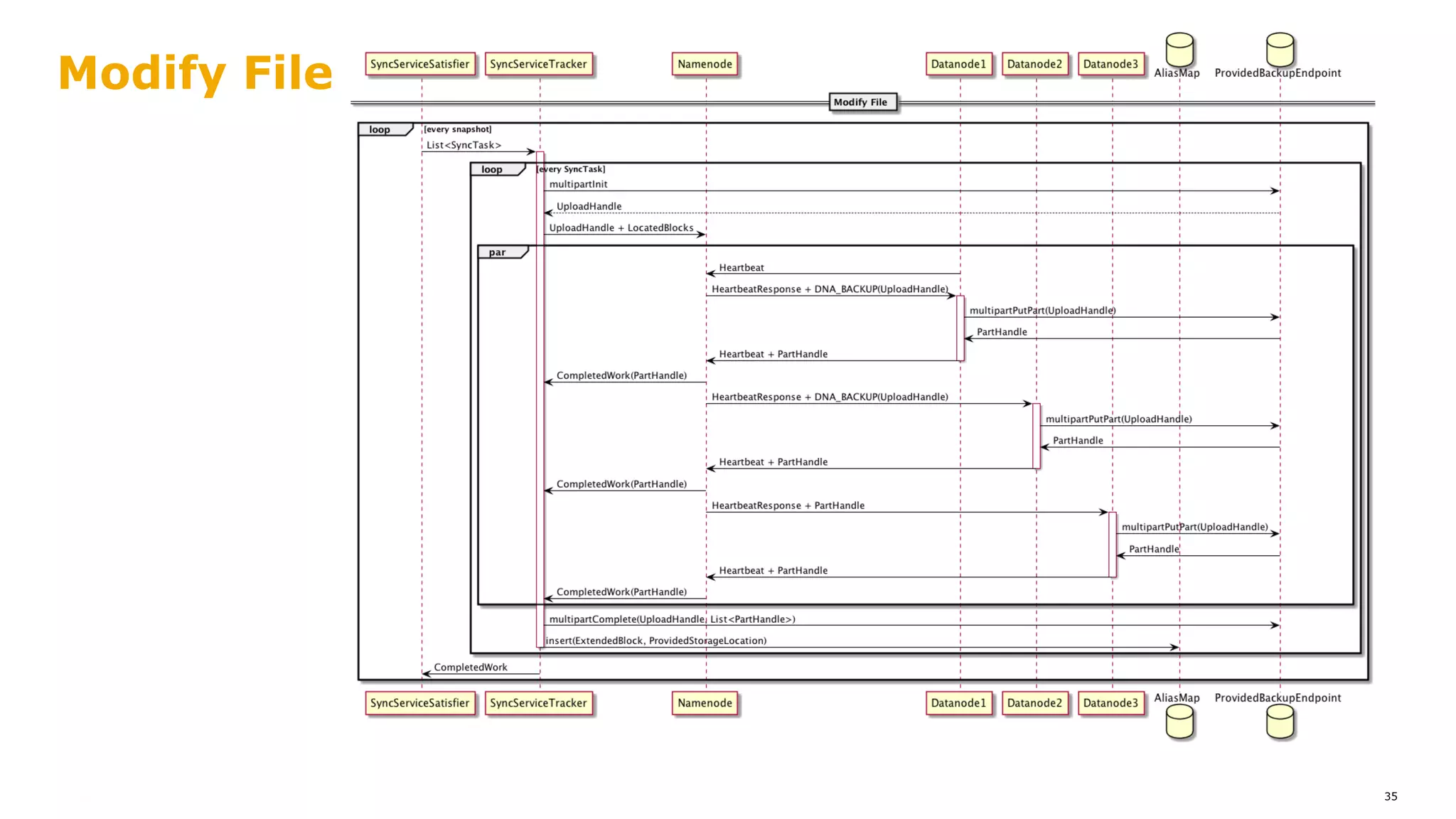
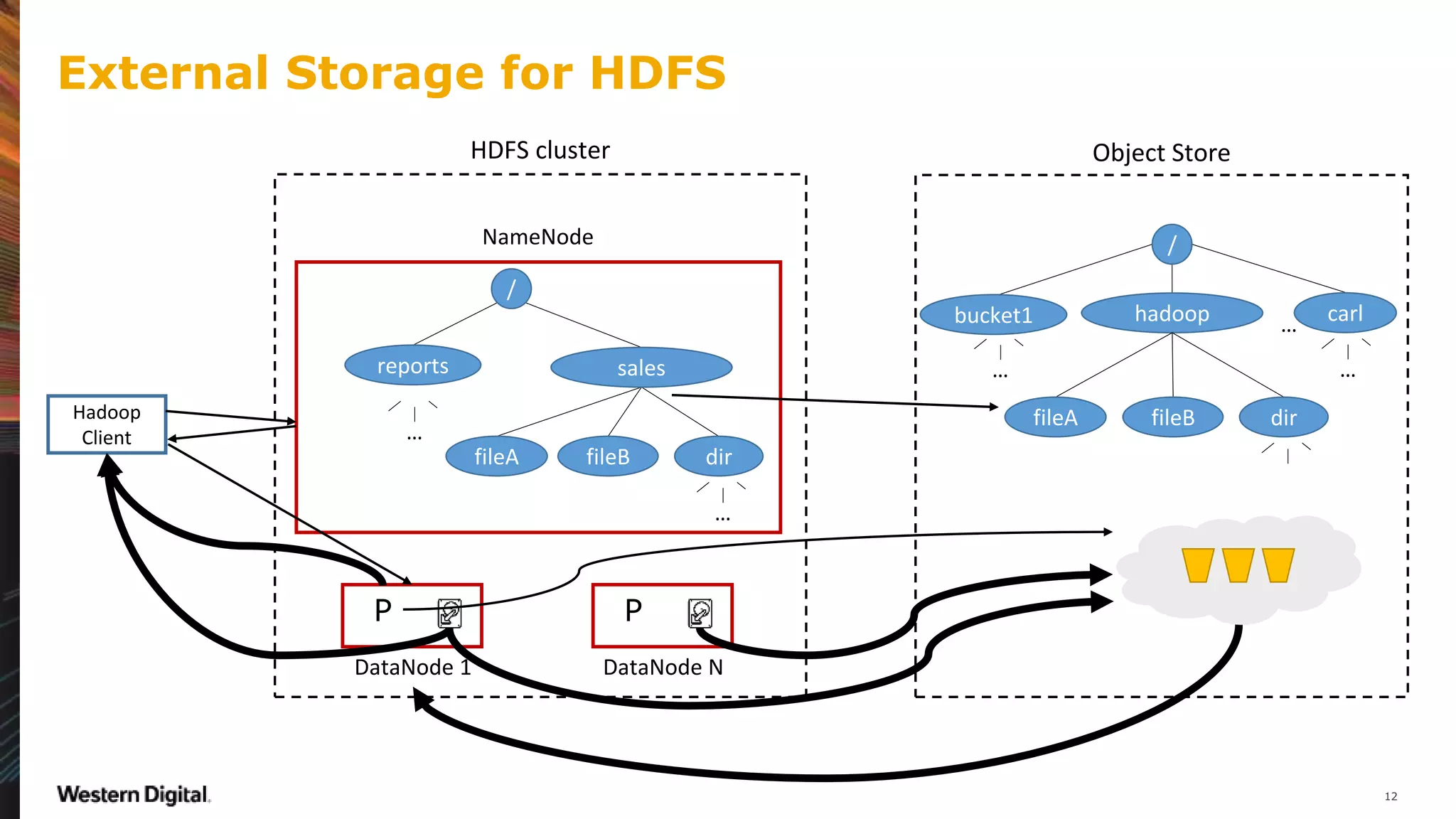
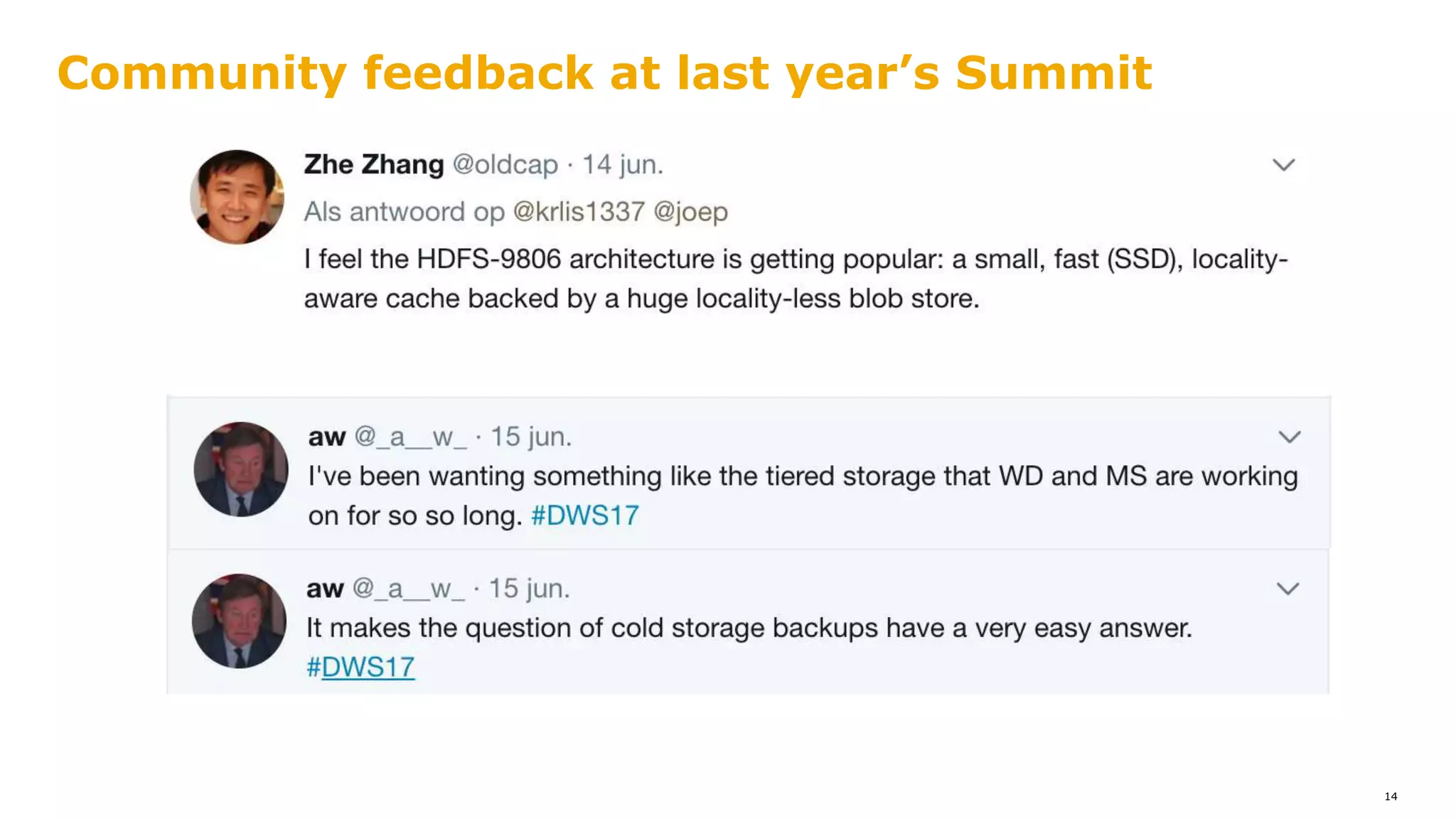
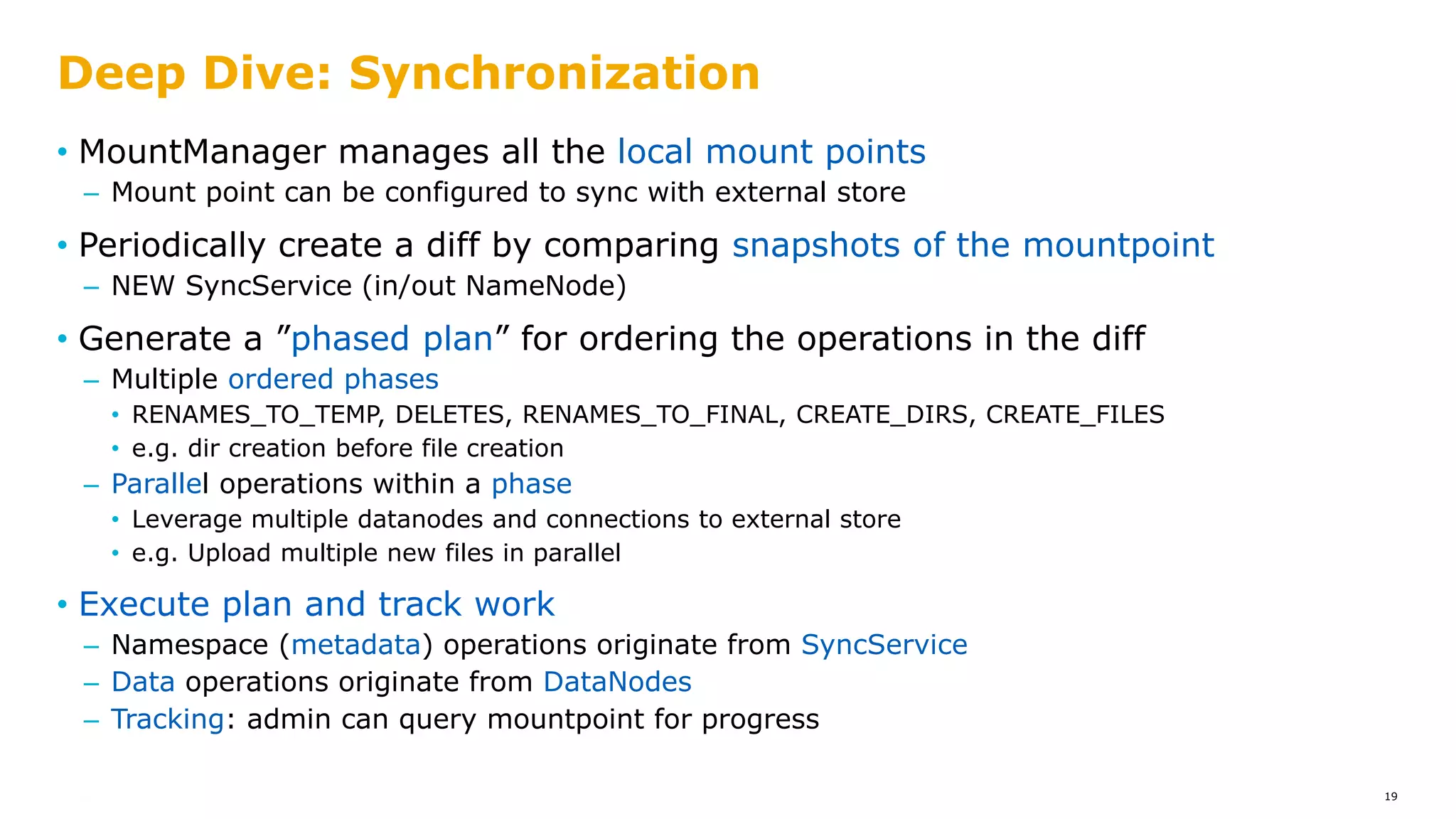
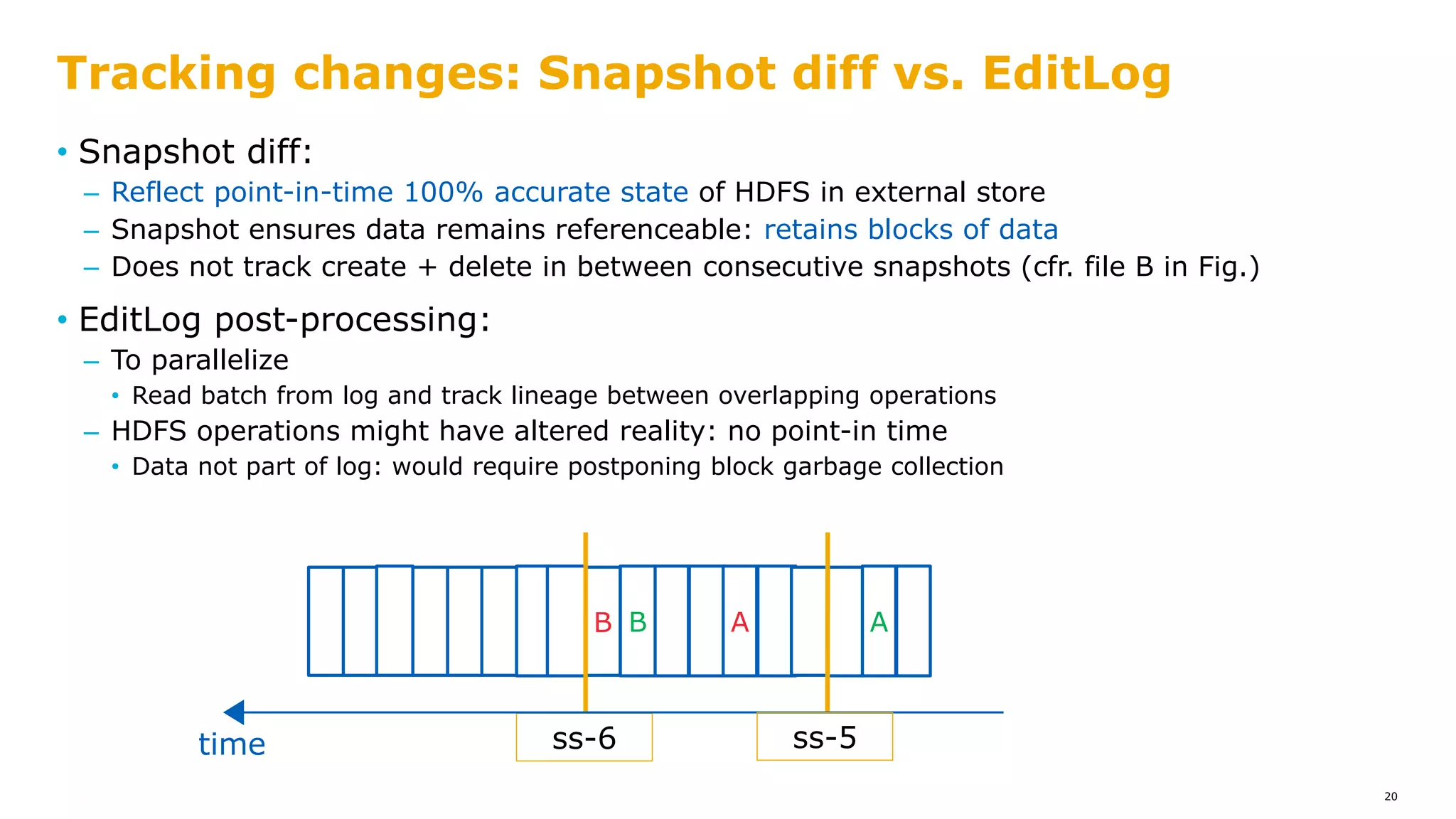
The document outlines a proposal for integrating HDFS with object storage systems to enhance data management and access. It discusses the challenges faced with existing methods, such as latency and lack of filesystem features, and presents a structured approach to enable HDFS to efficiently tier data between local and remote storage. The proposed solution includes using storage policies and synchronization services to maintain seamless workflows, ensuring that HDFS retains its core functionalities while leveraging the benefits of cloud-based object storage.

![• Tiered Storage [issues.apache.org]
– HDFS-9806
– HDFS-12090
Microsoft – Western Digital – Apache Community
2
Virajith Jalaparti
Chris Douglas
…
Ewan Higgs
Kasper Janssens
Thomas Demoor
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdfstieredstoragenew-180622045701/75/HDFS-tiered-storage-2-2048.jpg)
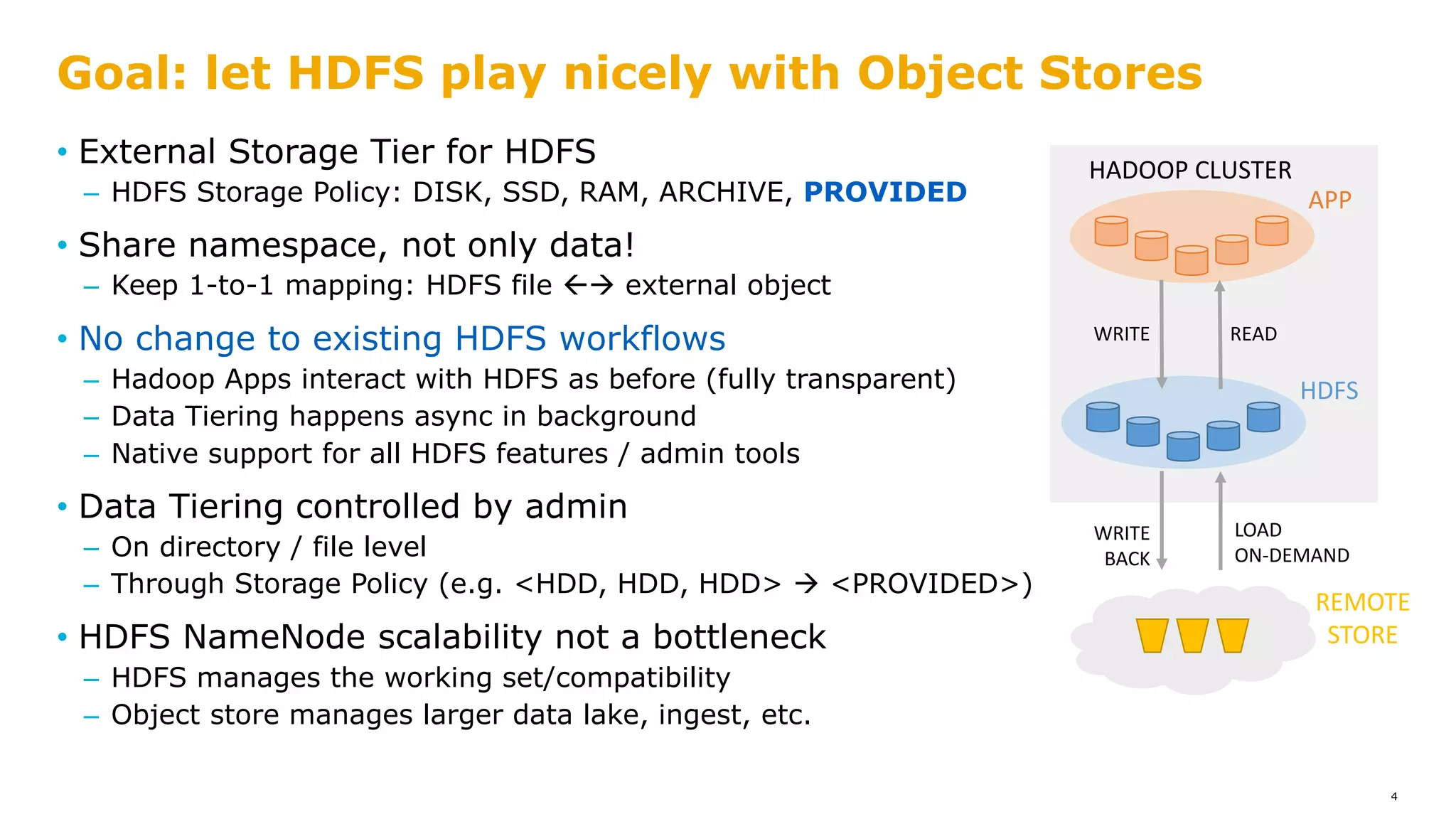
![• Hadoop Compatible FS [1]: s3a://, wasb://, adl://, …
• Direct IO between Hadoop apps and Object Store
• Disaggregated compute & storage
• HDFS NameNode functions taken up by Object Store
Hadoop already plays nicely with Object Stores
3
REMOTE
STORE
APP
HADOOP CLUSTER
READWRITE
[1]: https://s.apache.org/Hadoop3FSspec
• Pain points:
– Not really a FileSystem: rename, append, directories, ...
• Even with correct semantics, performance unlike HDFS
• HDFS features unavailable (e.g., hedged reads, snapshots, etc.)
– No locality
• Higher latency than attached storage
• Higher variance in both latency and throughput
– No HDFS integration
• Policies for users, permissions, quota, security, …
• Storage Plugins (e.g. Ranger, Sentry)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdfstieredstoragenew-180622045701/75/HDFS-tiered-storage-3-2048.jpg)

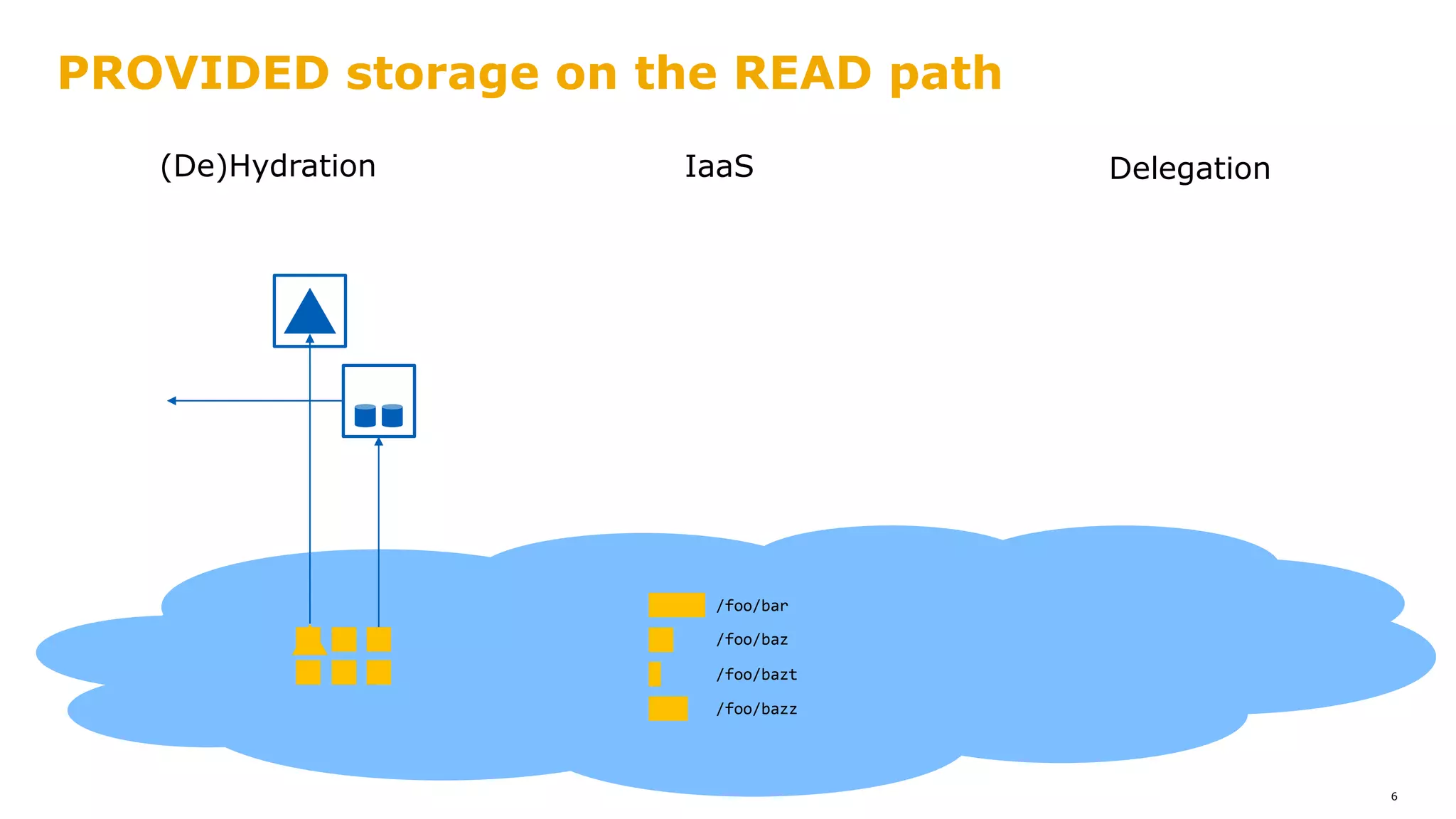
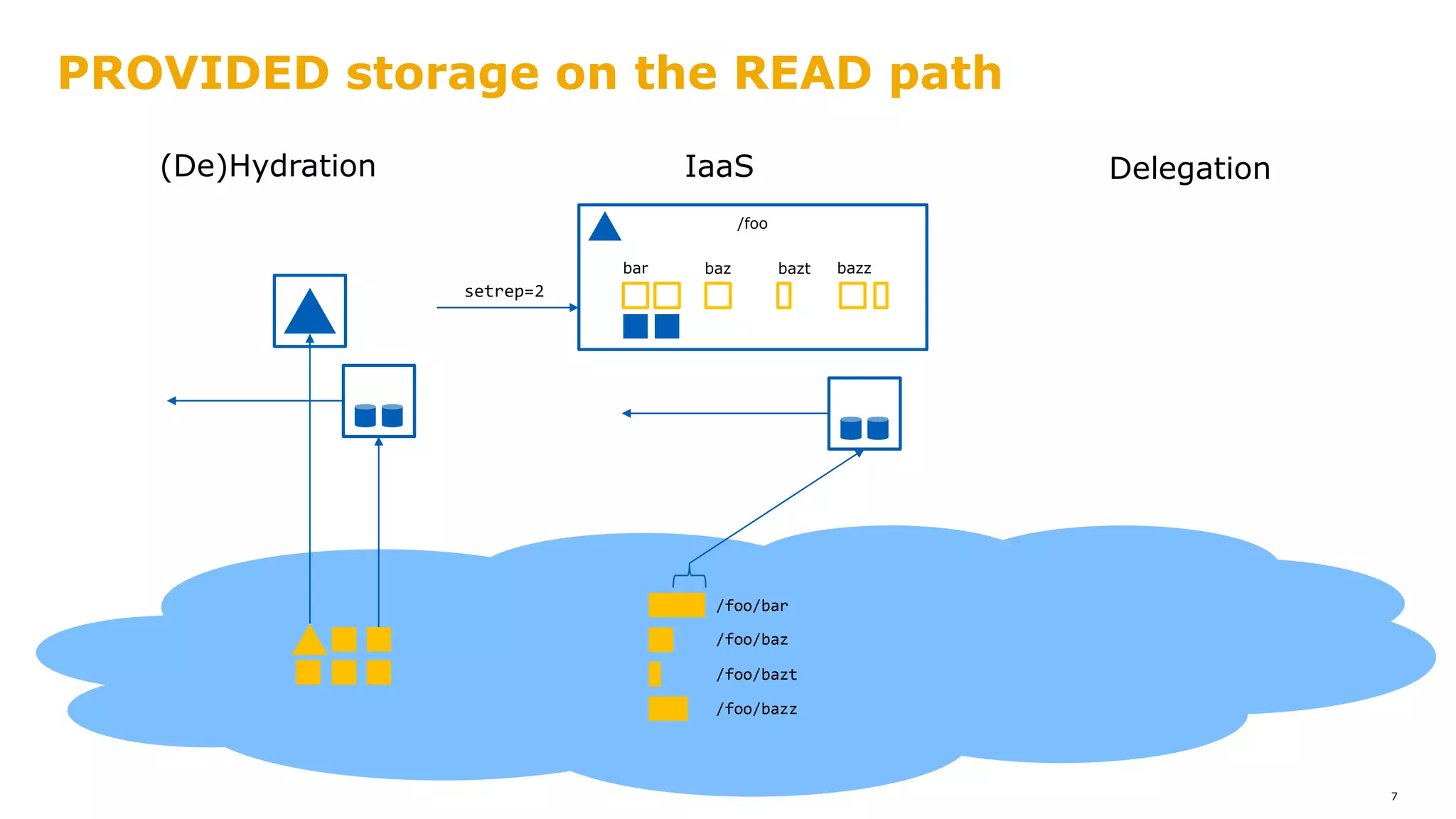
![PROVIDED storage on the READ path
8
/foo/bar
/foo/baz
/foo/bazt
/foo/bazz
/foo
bar baz bazt bazz
[Router-Based]
Federation
/cloud
?
IaaS(De)Hydration Delegation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdfstieredstoragenew-180622045701/75/HDFS-tiered-storage-8-2048.jpg)
![Apache Hadoop 3.1.0
• Generate FSImage from a FileSystem
Start a NameNode serving remote data
Serve from (a subset of) DataNodes in the cluster
• Backported and deployed in production at Microsoft
• Static: namespace changes are not reflected in HDFS NameNode
9
• Prototype code [2] with the PROVIDED abstraction
Read-through caching of blocks (demand paging)
Scheduled, metered prefetch for recurring pipelines with SLOs
Write-through to remote (participant in the HDFS write pipeline)
Wire FSImage to a running NameNode
• Per-application NameNodes; with isolation
• Bidirectional synchronization out of scope
[2]: https://github.com/Microsoft-CISL/hadoop/tree/tieredStore-sig16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdfstieredstoragenew-180622045701/75/HDFS-tiered-storage-9-2048.jpg)








![• Tiered Storage HDFS-12090 [issues.apache.org]
– Design documentation
– List of subtasks, lots of linked tickets – take one!
– Discussion of scope, implementation, and feedback
• Bert Verslyppe, Hendrik Depauw, Íñigo Goiri, Rakesh Radhakrishnan, Uma
Gangumalla, Daryn Sharp, Steve Loughran, Sanjay Radia, Anu Engineer,
Jitendra Pandey, Andrew Wang, Zhe Zhang, Allen Wittenauer, and many
others …
Thanks to the community for feedback & help!
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hdfstieredstoragenew-180622045701/75/HDFS-tiered-storage-23-2048.jpg)