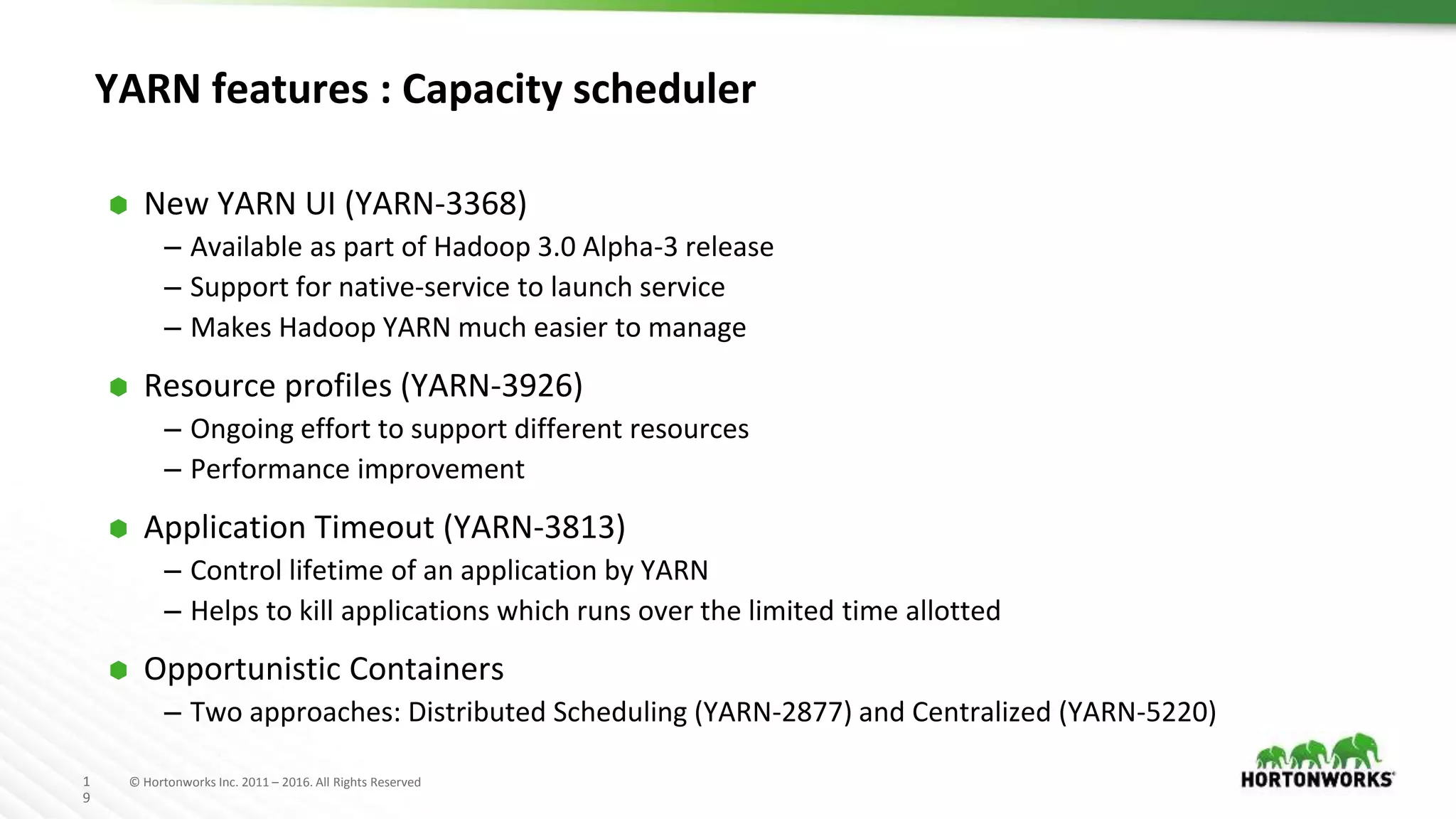
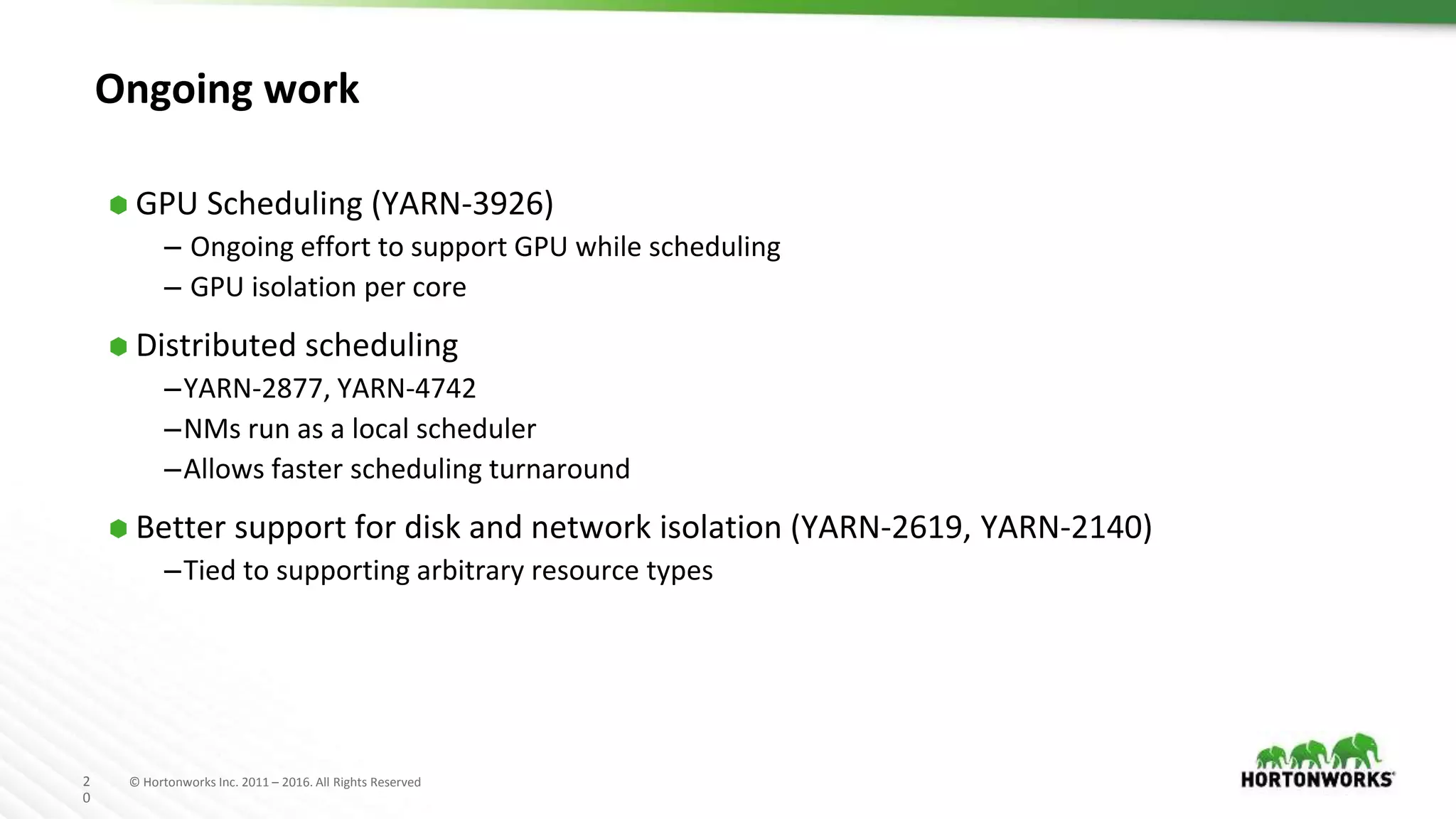
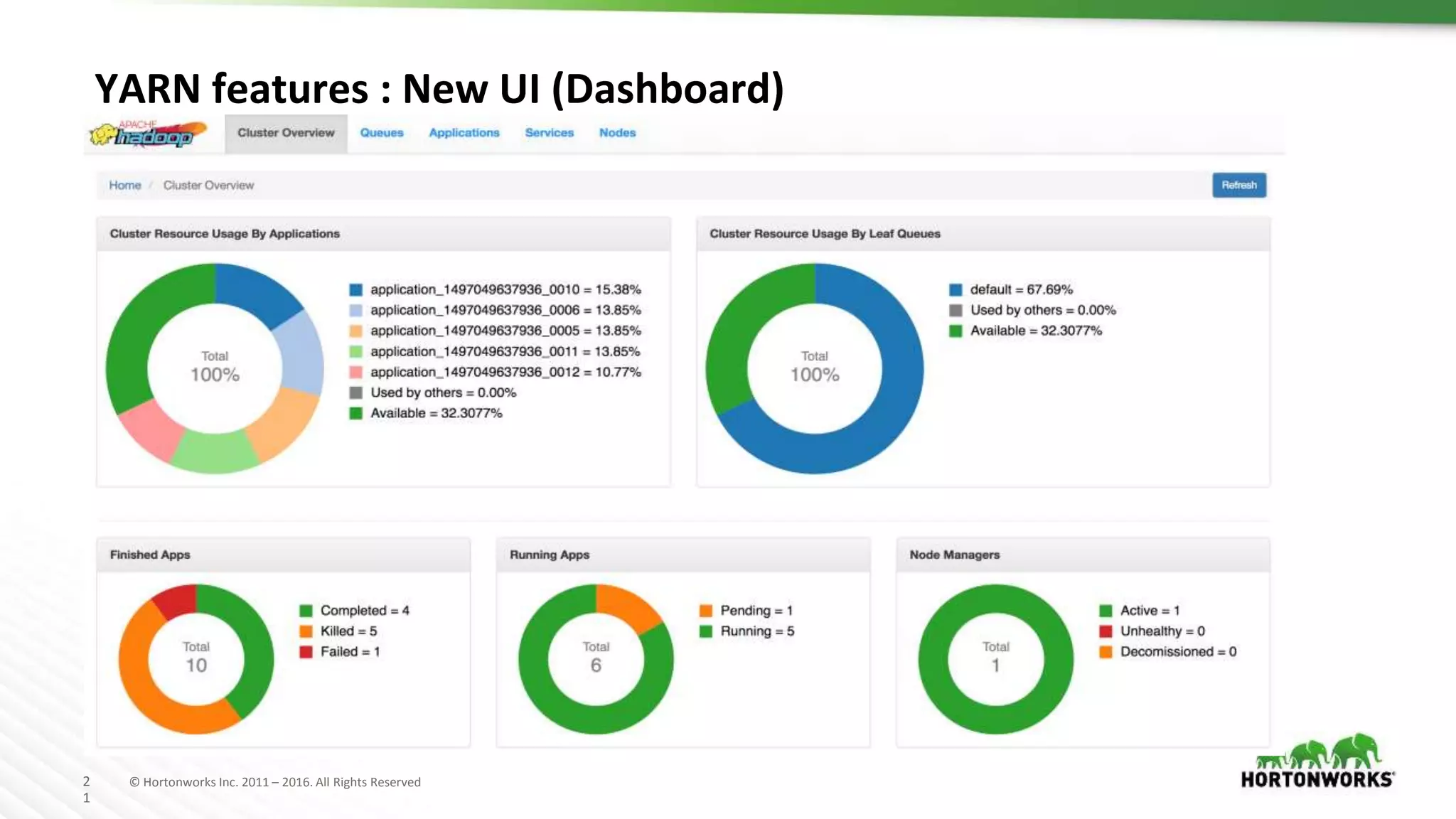
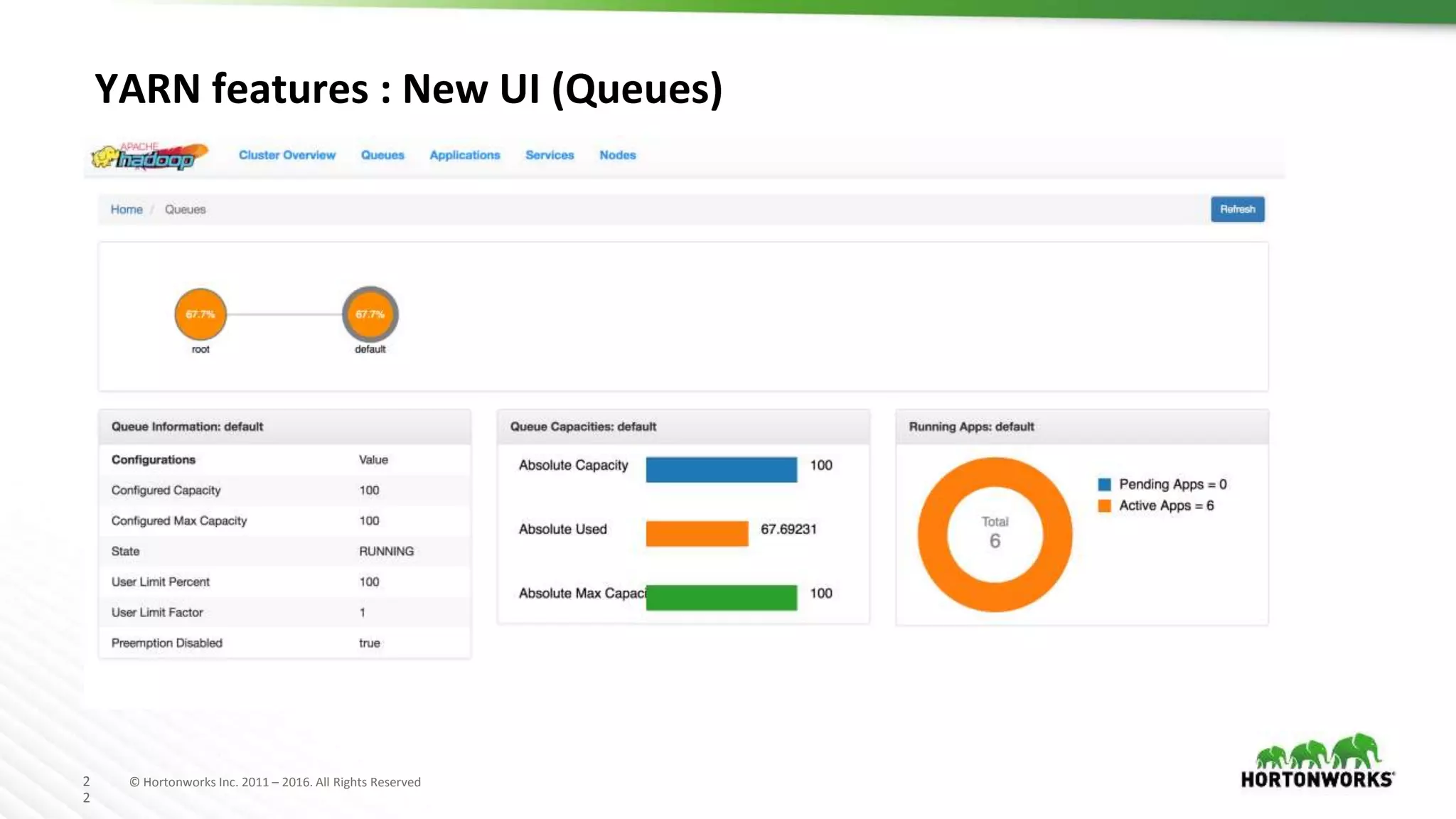
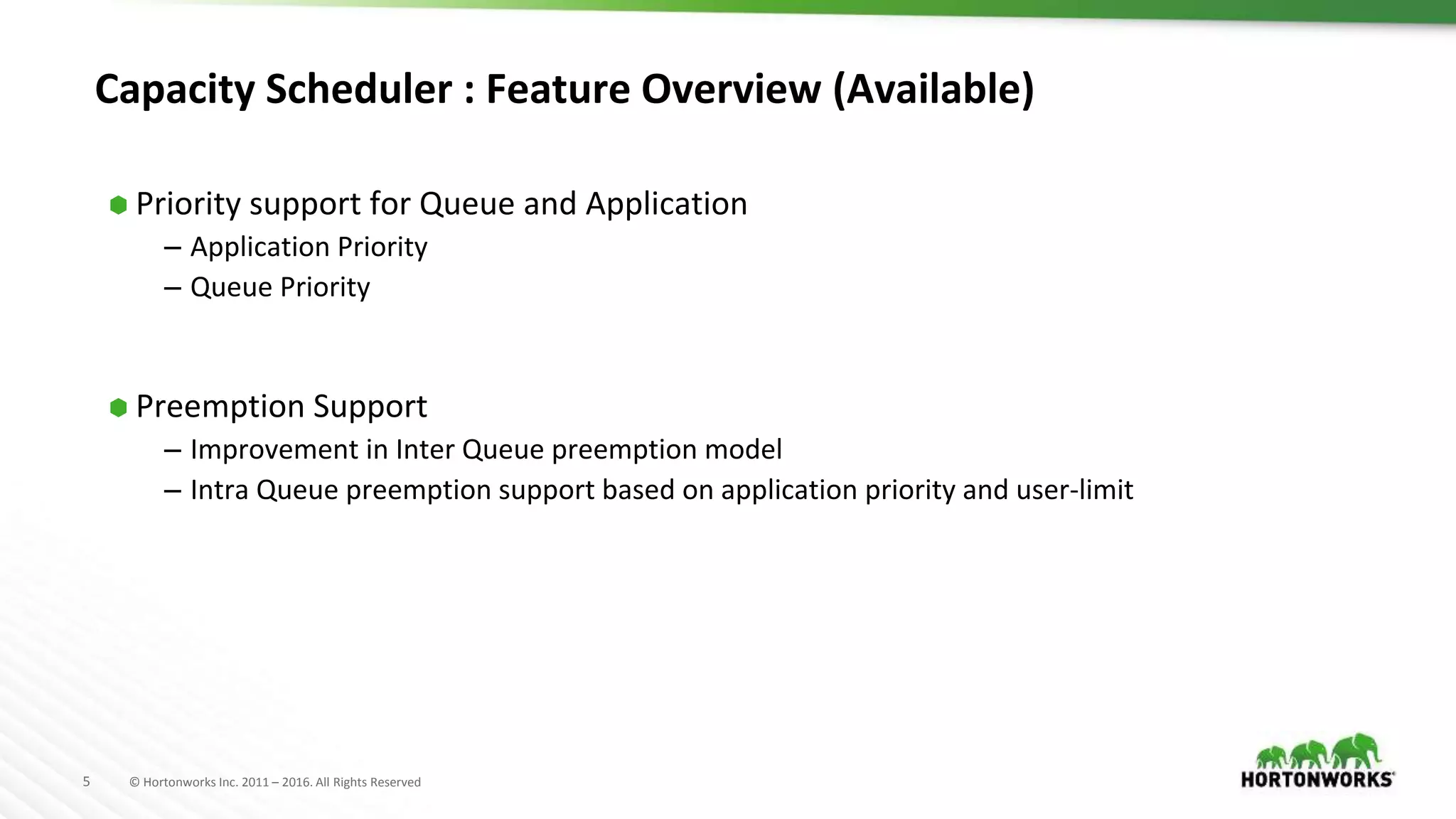
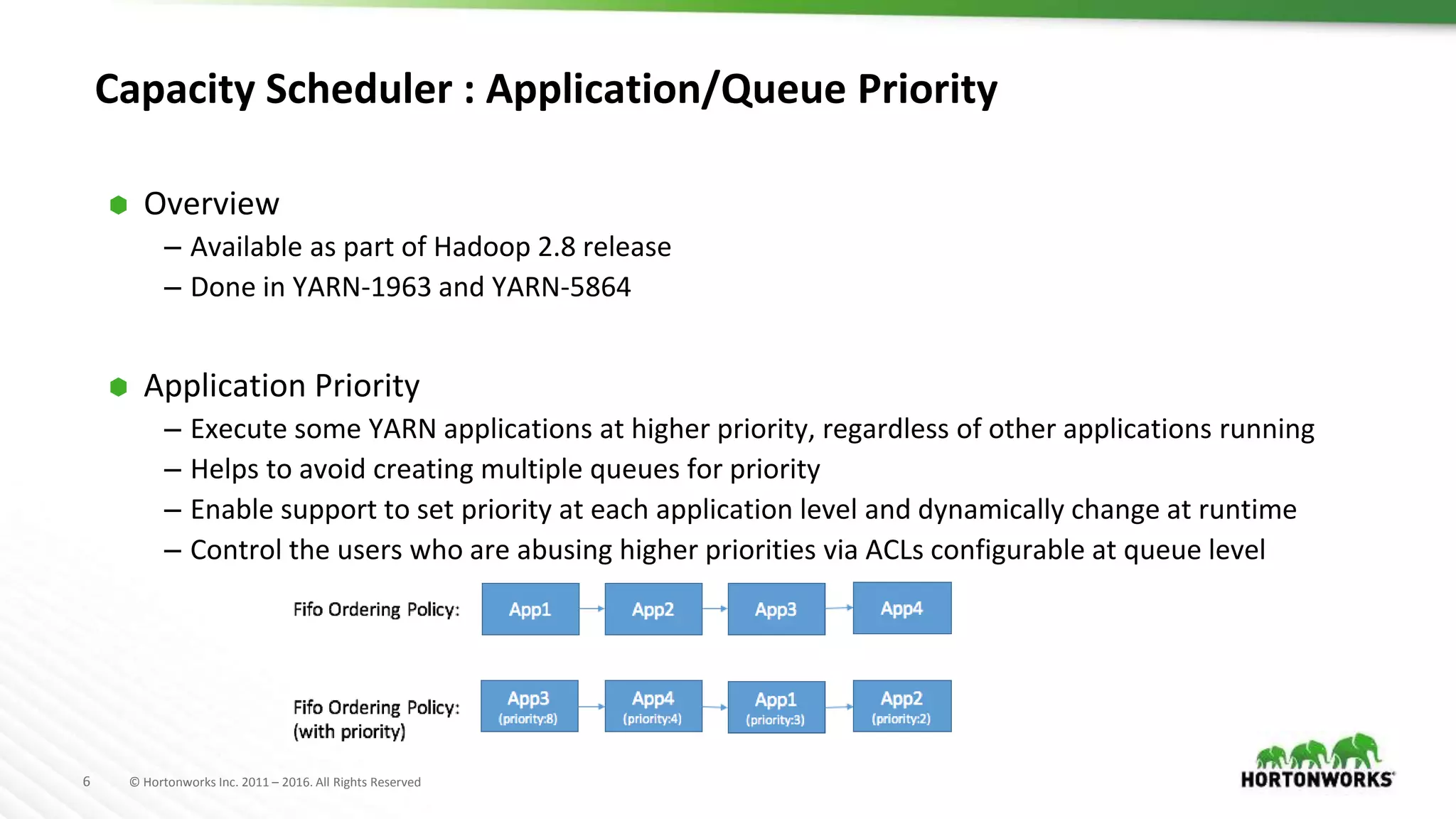
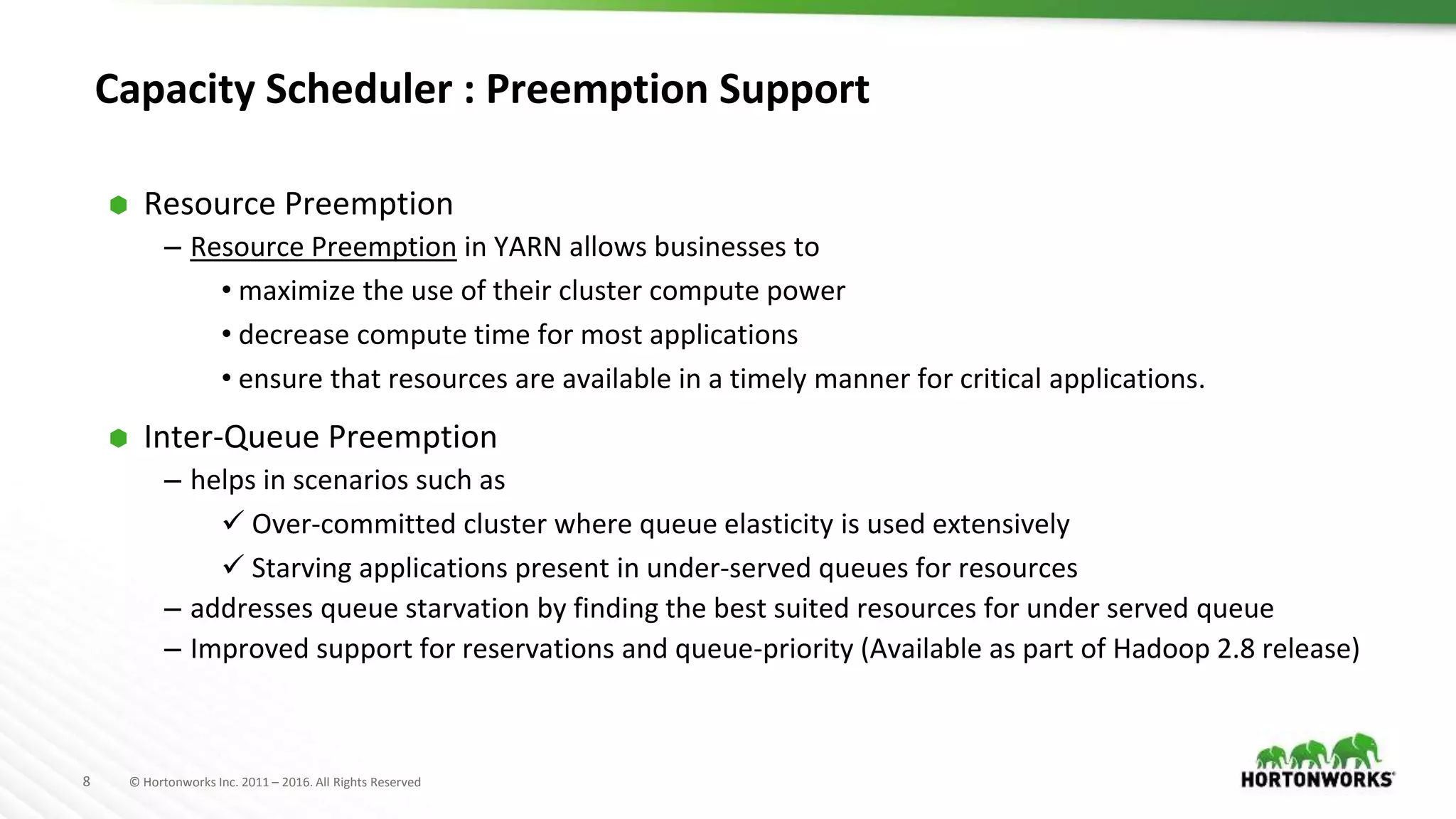
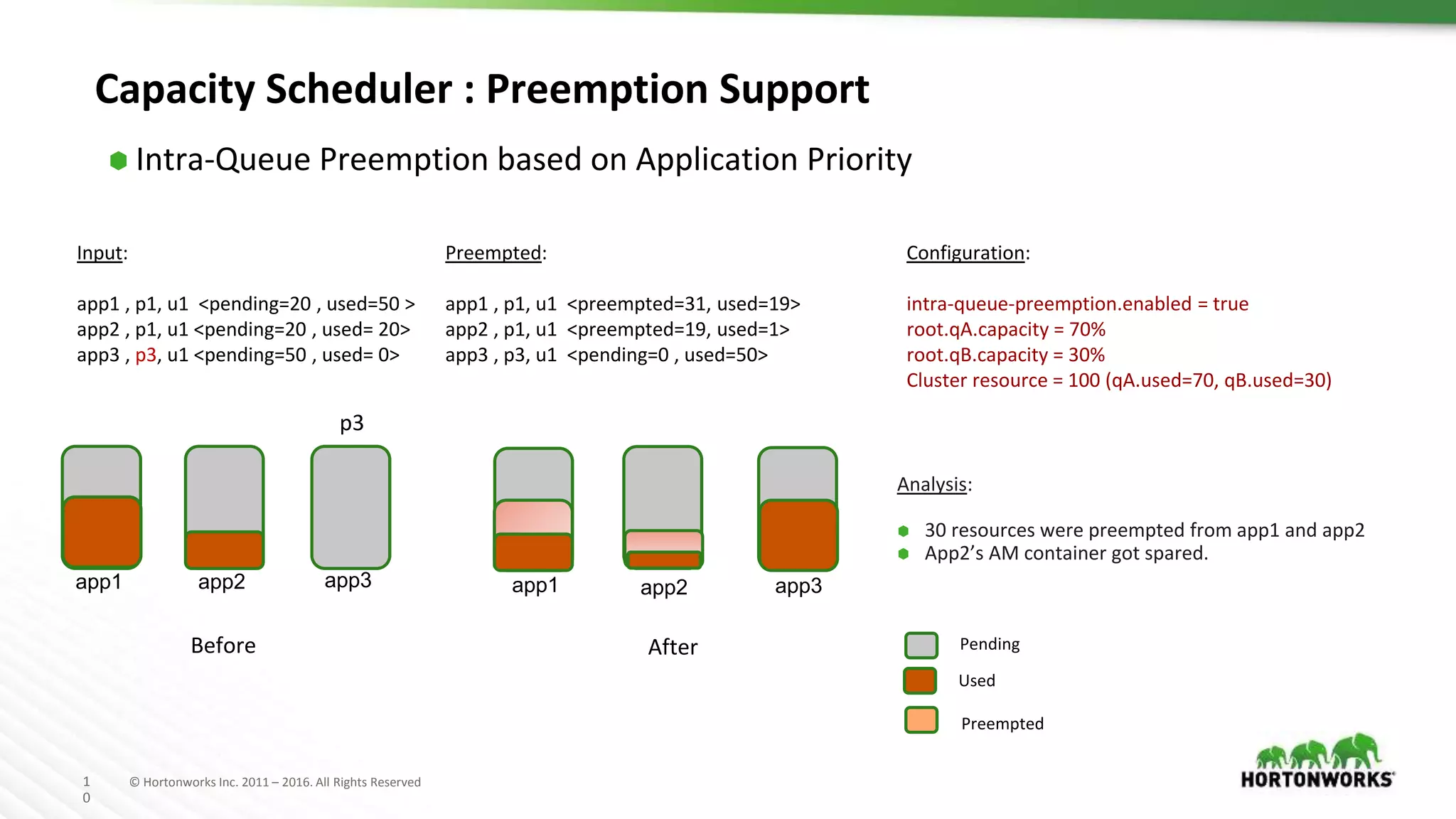
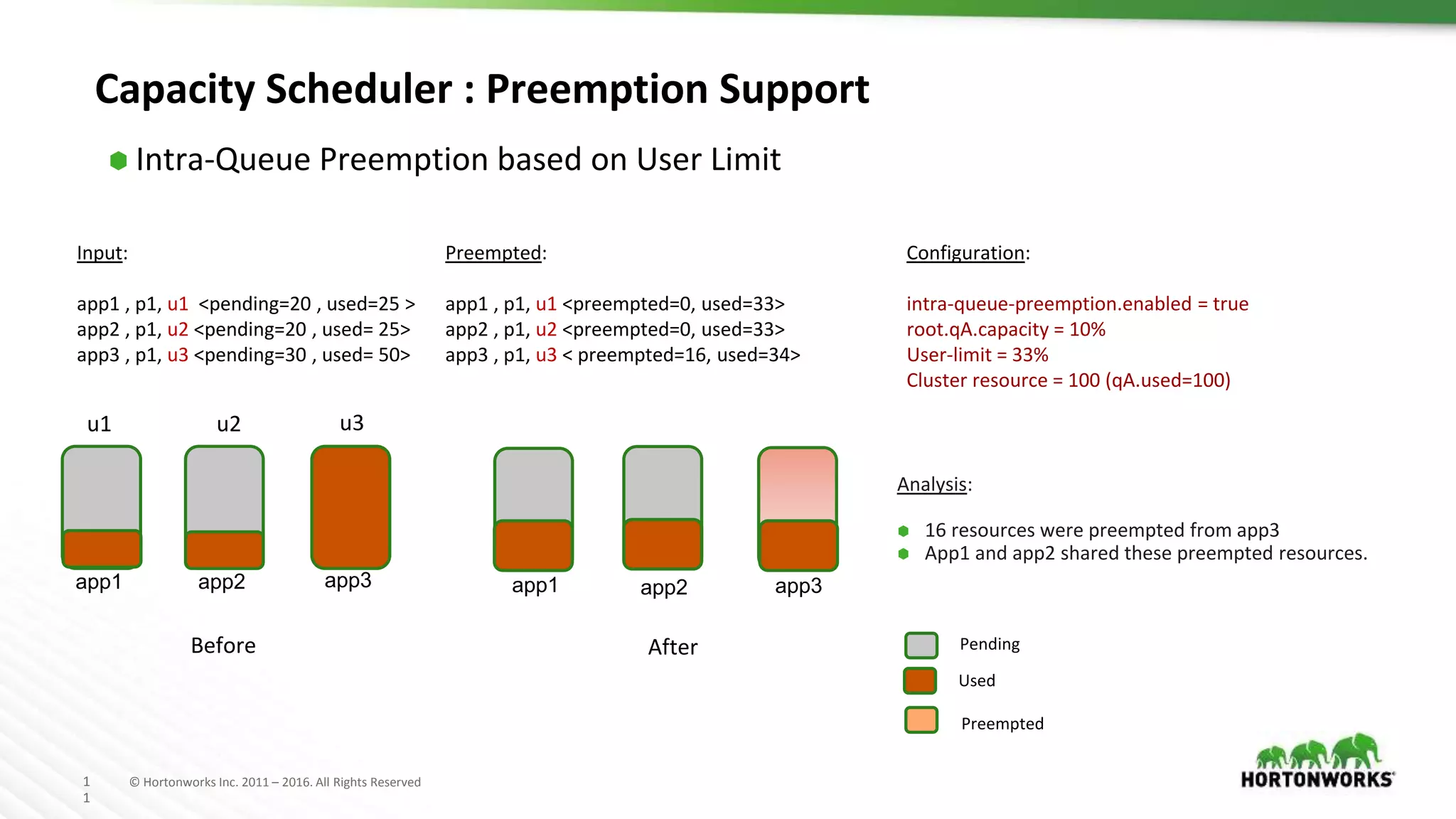
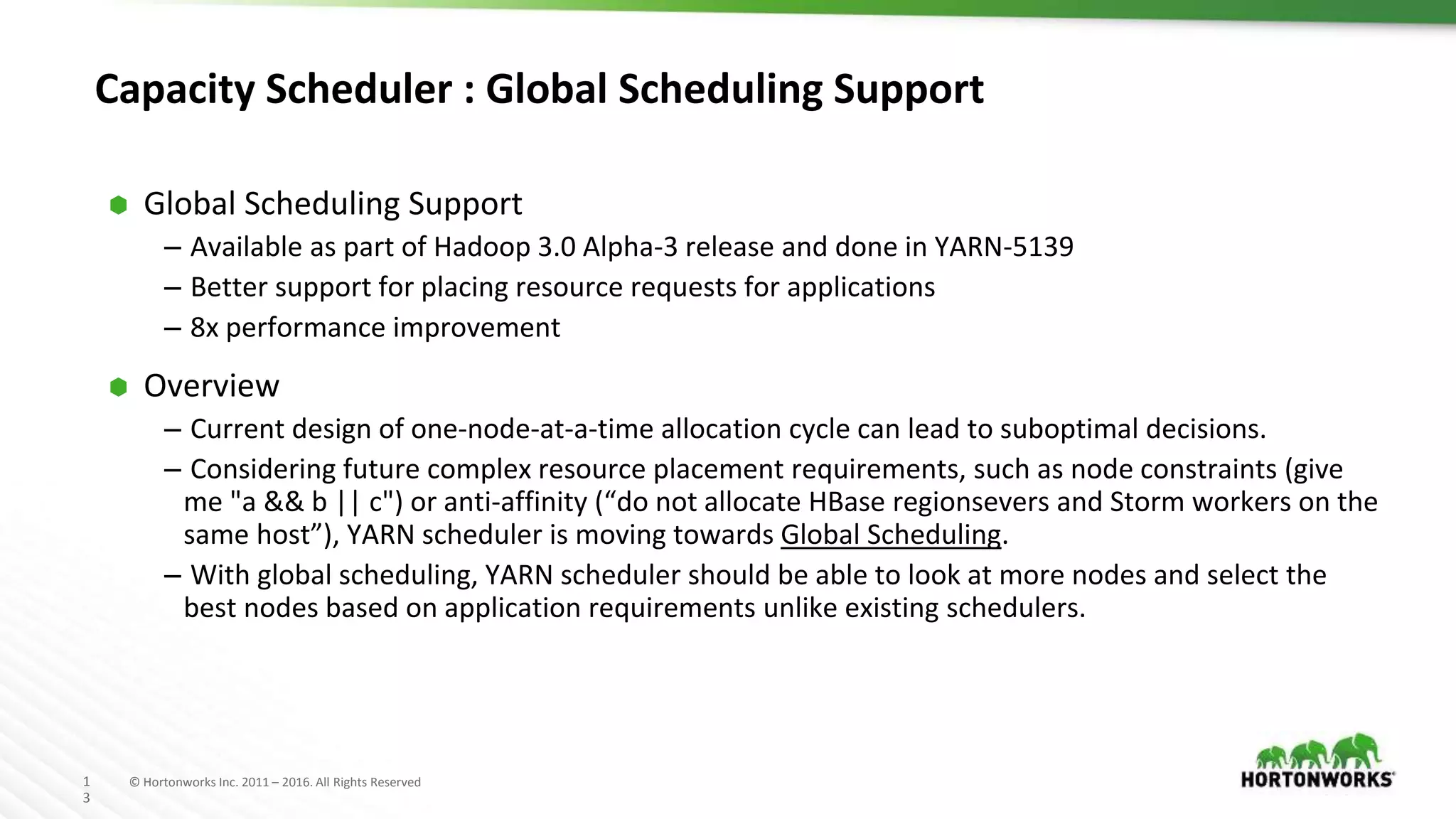
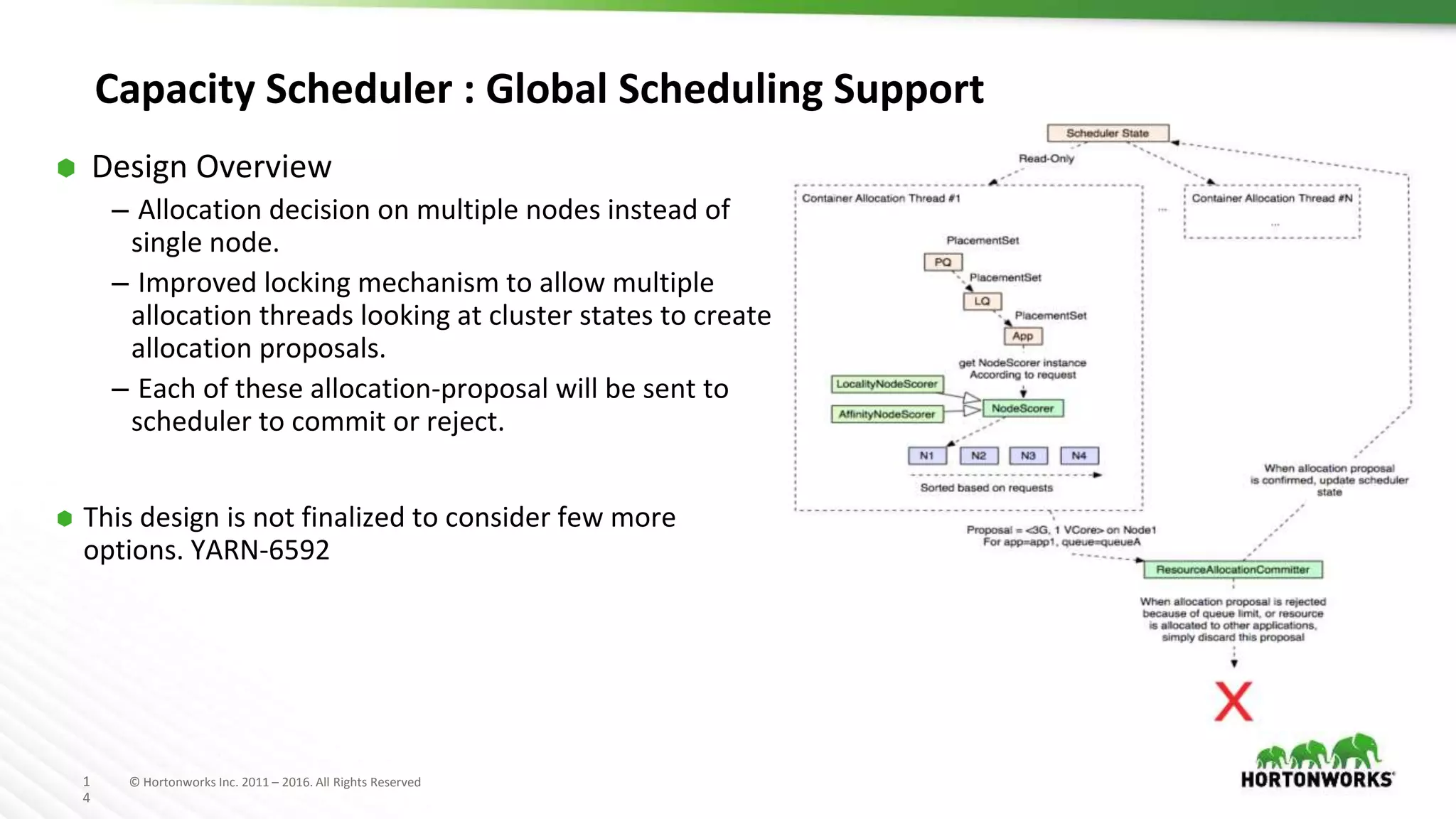
The document discusses improvements in the capacity scheduler of Apache Hadoop YARN, highlighting features like application and queue priority, preemption support, and ongoing enhancements including global scheduling and absolute resource configuration. Key points include the benefits of inter-queue and intra-queue preemption for optimizing resource allocation and the shift toward a more flexible resource management model. Additionally, it touches on ongoing features such as GPU scheduling and a new user interface for better management of YARN.



![1
7
© Hortonworks Inc. 2011 – 2016. All Rights Reserved
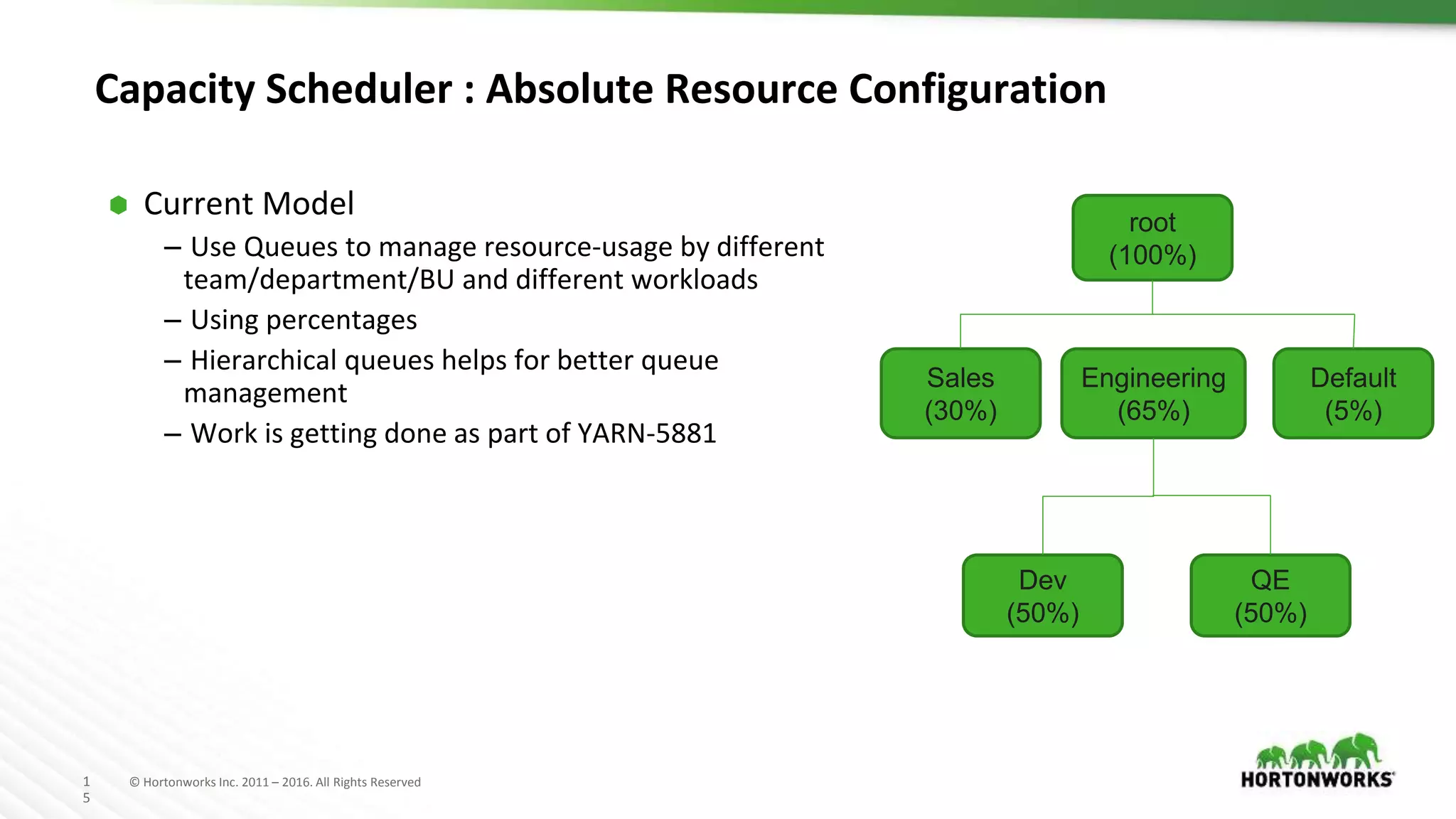
Capacity Scheduler : Absolute Resource Configuration
⬢ New Approach
– Can specify absolute resource values as min-resource to
queues.
– For better elasticity, also can support specify absolute
resource values as max-resource to queues.
– parent.min-resource >= Σ(child.min-resource).
– “relax the exactly-sum-to-100% requirement of today”
⬢ Challenges of Absolute Configuration
– Ensuring SLAs when cluster scales down
– Handling min-resources when cluster scales up
root
[memory=100Gi,vcores=100]
Sales
[memory=30Gi,v
cores=30]
Engineering
[memory=65Gi,
vcores=60]
Default
[memory=1Gi,
vcores=1]
Dev
[memory=30Gi,
vcores=50]
QE
[memory=35Gi,
vcores=10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017junapachehadoopyarn-capacityschedulerimprovements-170622221801/75/Jun-2017-HUG-YARN-Scheduling-A-Step-Beyond-17-2048.jpg)