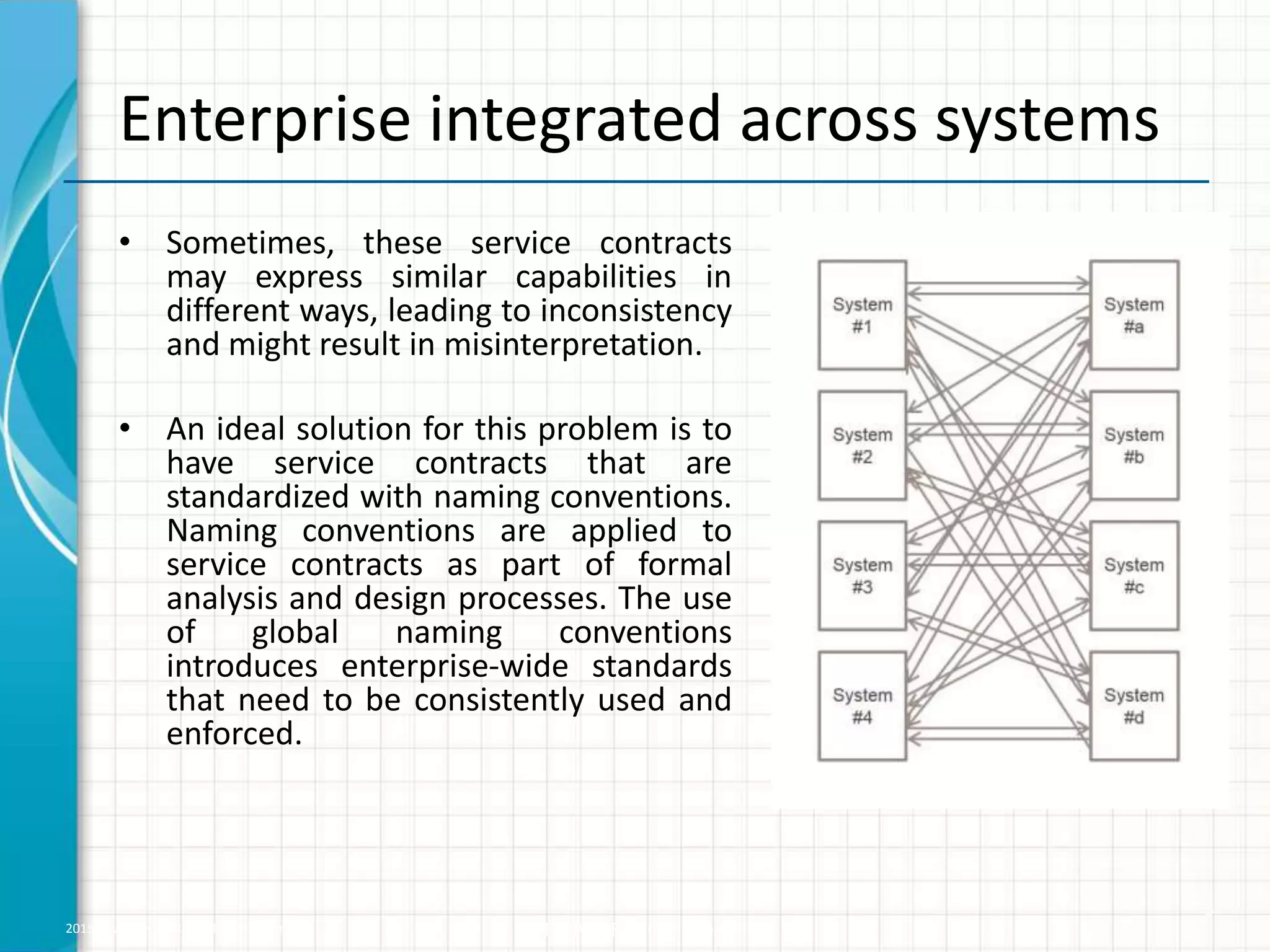
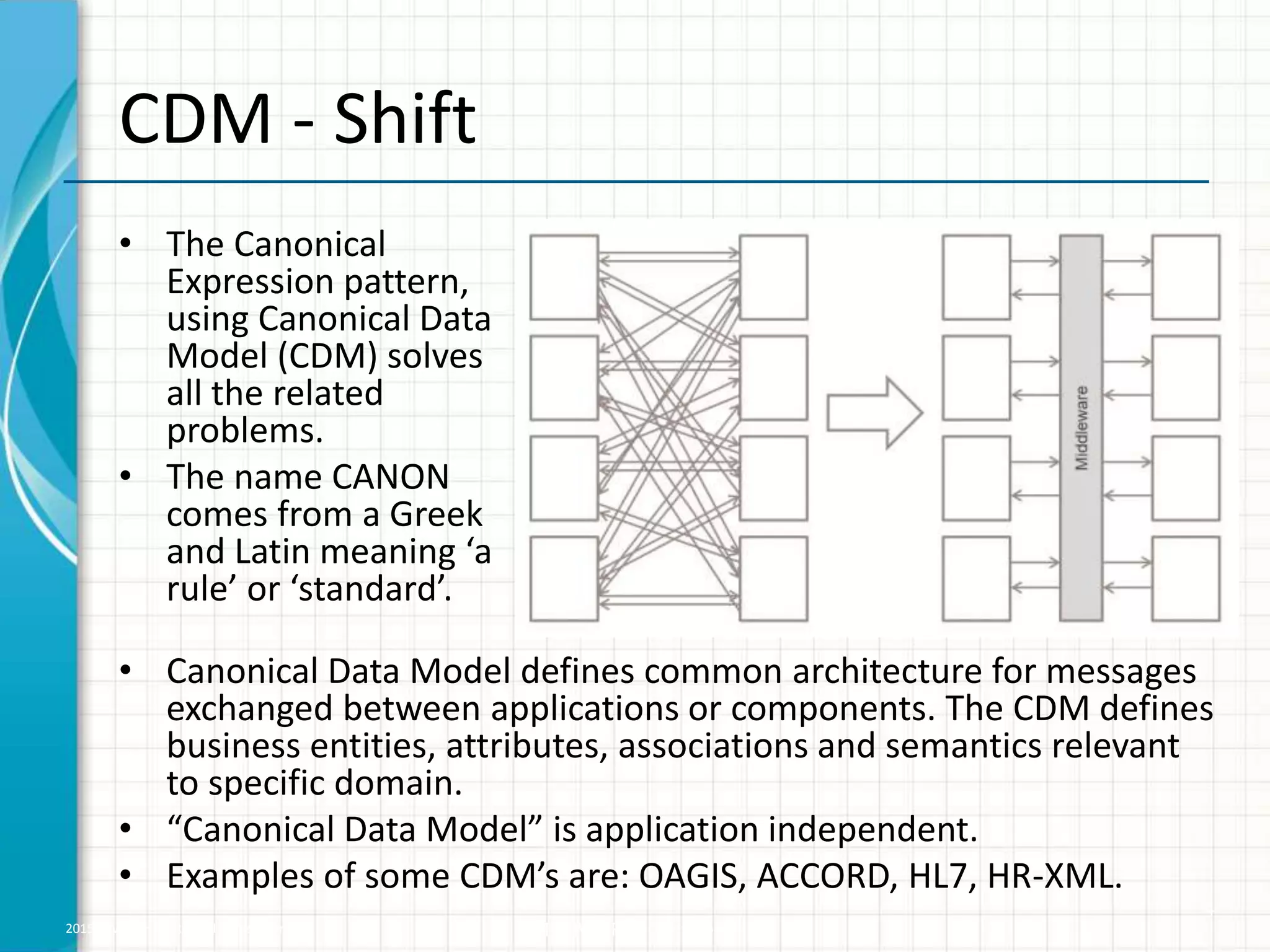
The document discusses the benefits of using a canonical data model (CDM) to standardize terminology and data across business units. A CDM defines common business entities, attributes, and semantics to reduce inconsistencies between different custom data models. This standardization improves business communication, increases software reusability, reduces the number of integration points and transformations needed, and lowers integration time and costs. However, CDMs can be very large and generic, may impact performance, and usually do not contain business validations.