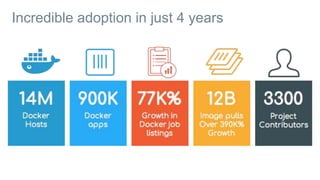
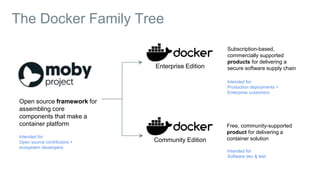
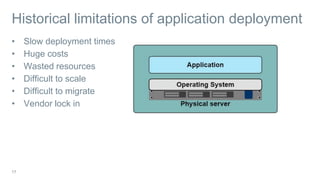
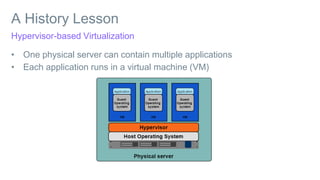
This document provides an introduction to Docker and discusses how it helps address challenges in the modern IT landscape. Some key points:
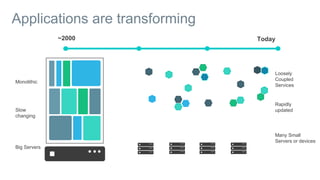
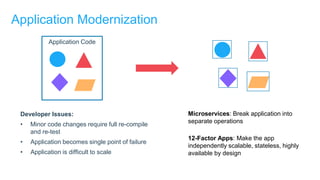
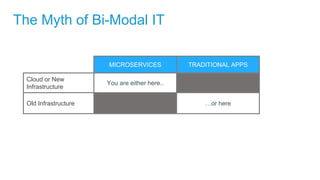
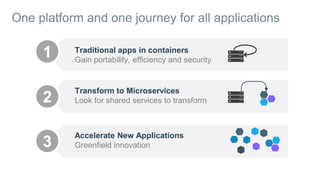
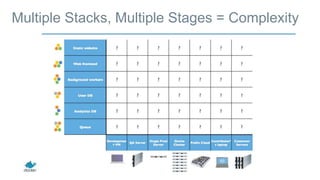
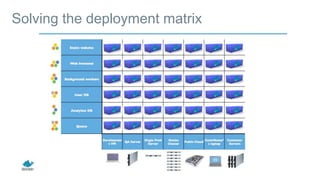
- Applications are increasingly being broken up into microservices and deployed across multiple servers and environments, making portability and scalability important.
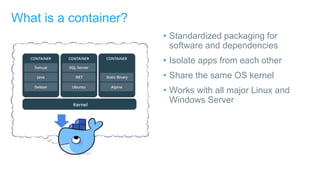
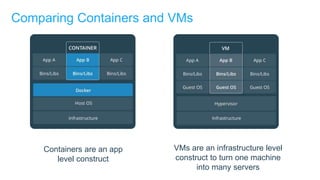
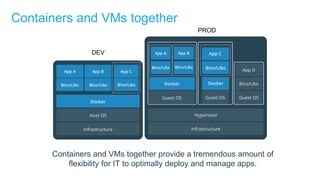
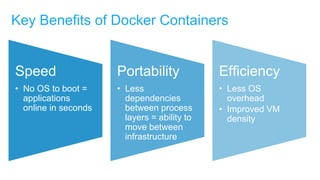
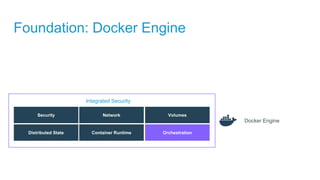
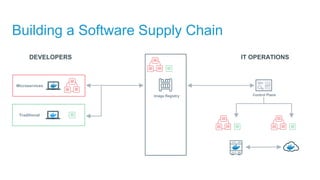
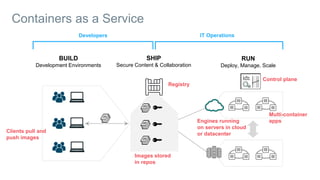
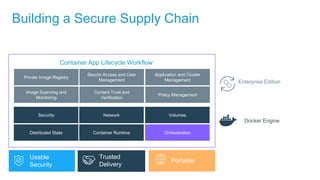
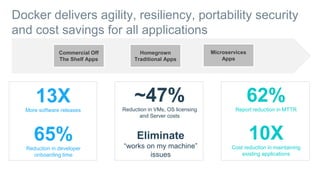
- Docker containers help address these issues by allowing applications to run reliably across different infrastructures through package dependencies and resources together. This improves portability.
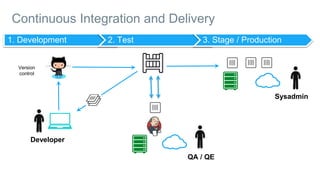
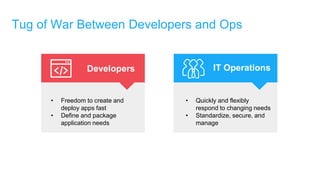
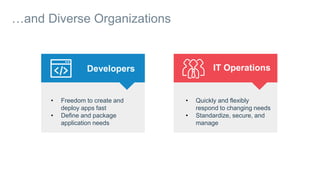
- Docker provides a platform for building, shipping and running applications. It helps bridge the needs of developers who want fast innovation and operations teams who need security and control.