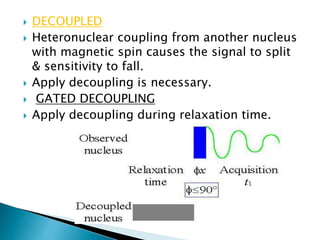
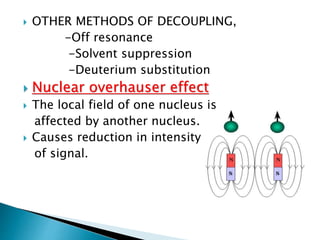
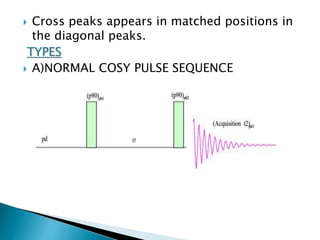
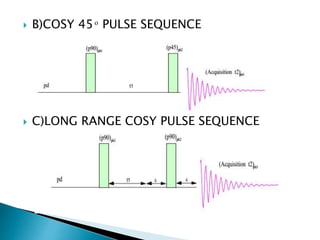
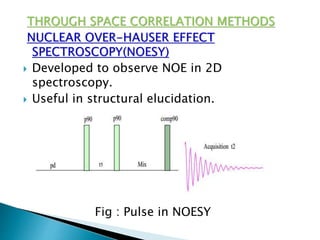
This document discusses 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy techniques. It defines 1D and 2D NMR, and describes their principles and applications. Key types of 1D NMR techniques discussed include regular, decoupled, and gated decoupling NMR. 2D NMR techniques covered include COSY, NOESY, HSQC, and HMBC. Examples are provided to illustrate how these techniques can be used to analyze molecular structure.