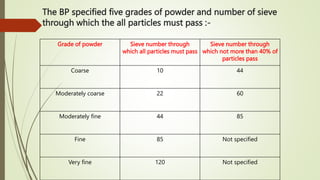
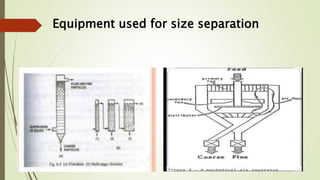
This document discusses size separation techniques used in the pharmaceutical industry. It begins by defining size separation as the process of separating particles into different sizes using screening surfaces. Some common objectives of size separation are to classify materials by size, control size variation, and enhance product performance. Sieves are the most common screening devices and come in various materials and constructions like woven wire, punched plates, and bolting cloth. Key size separation techniques discussed are agitation, brushing, and centrifugal motion, which use vibration, rotation, or air flow to move particles through sieves.