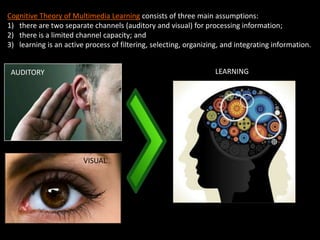
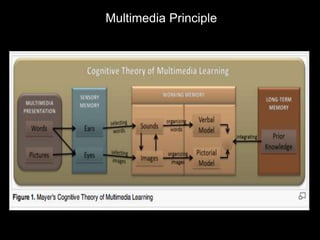
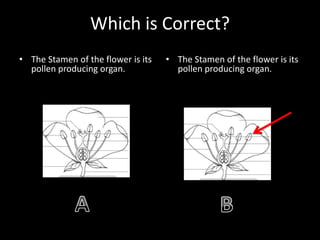
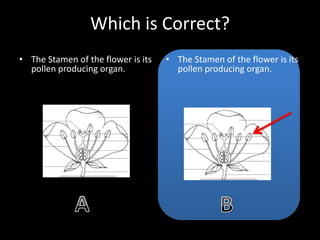
This document summarizes principles of multimedia design for instruction. It discusses cognitive theory, including separate channels for auditory and visual processing and limits on channel capacity. Key principles covered are the multimedia, contiguity, modality, and redundancy principles. Formative and summative assessment examples are provided to evaluate student learning throughout and after instruction.