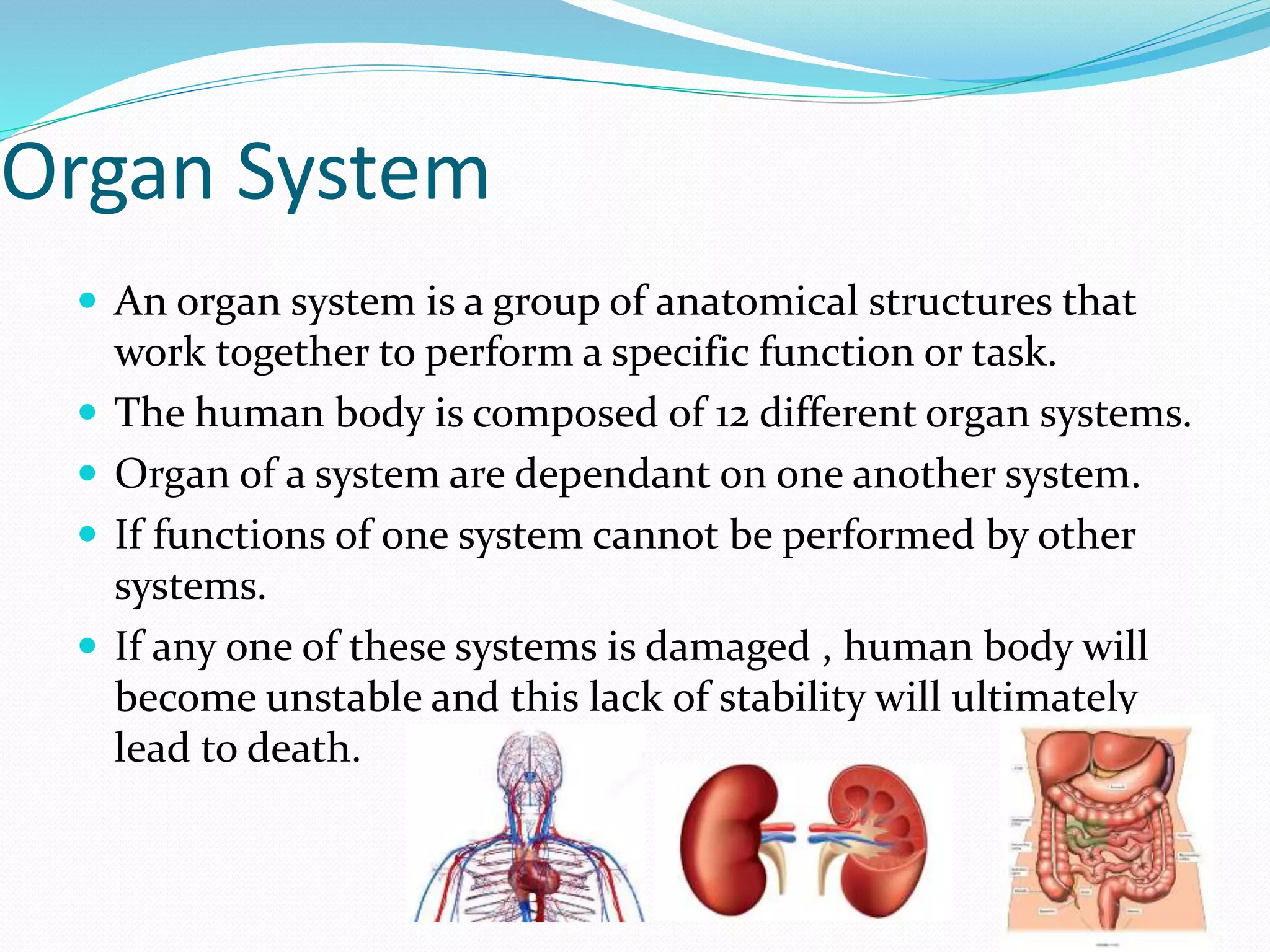
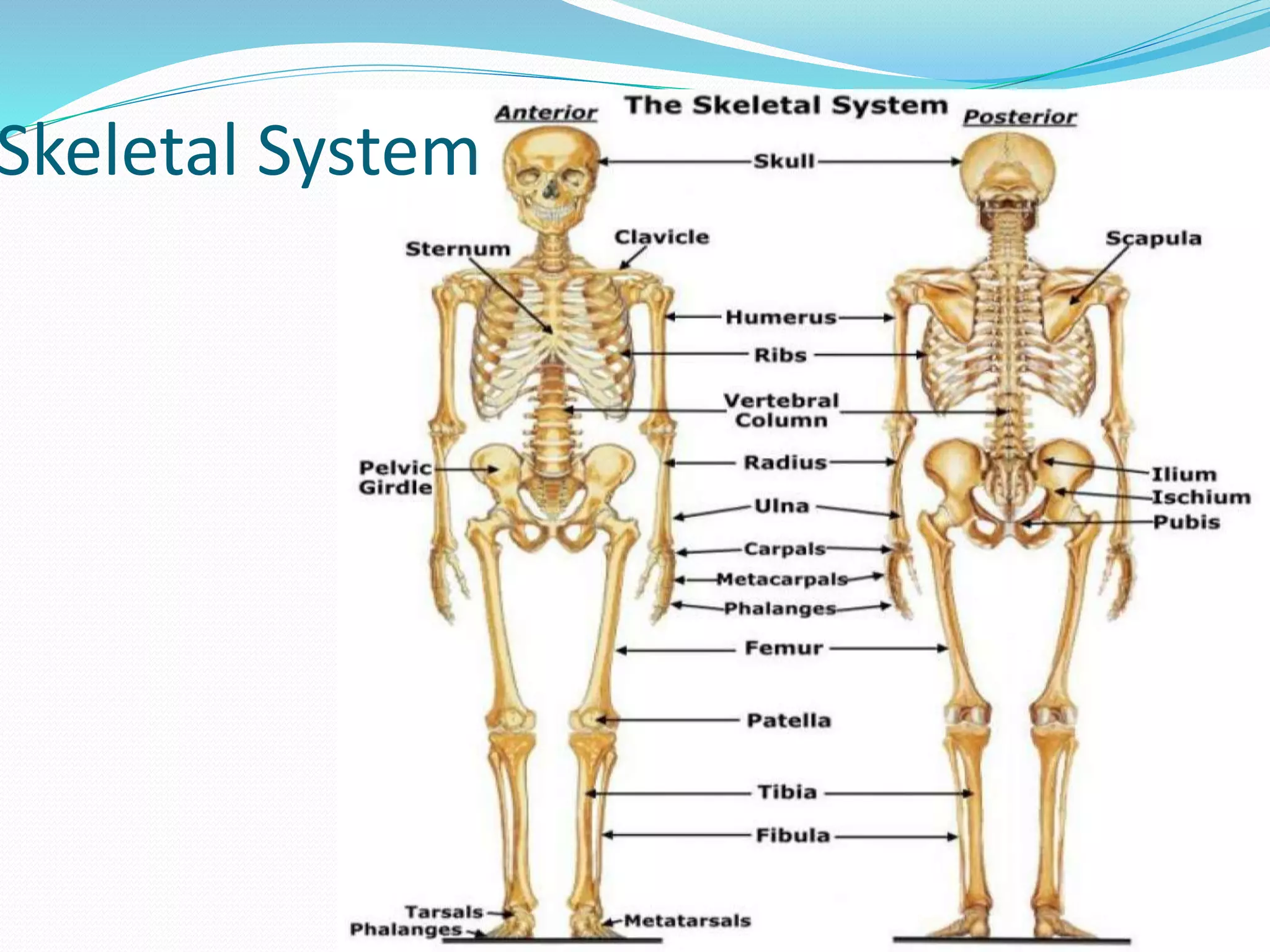
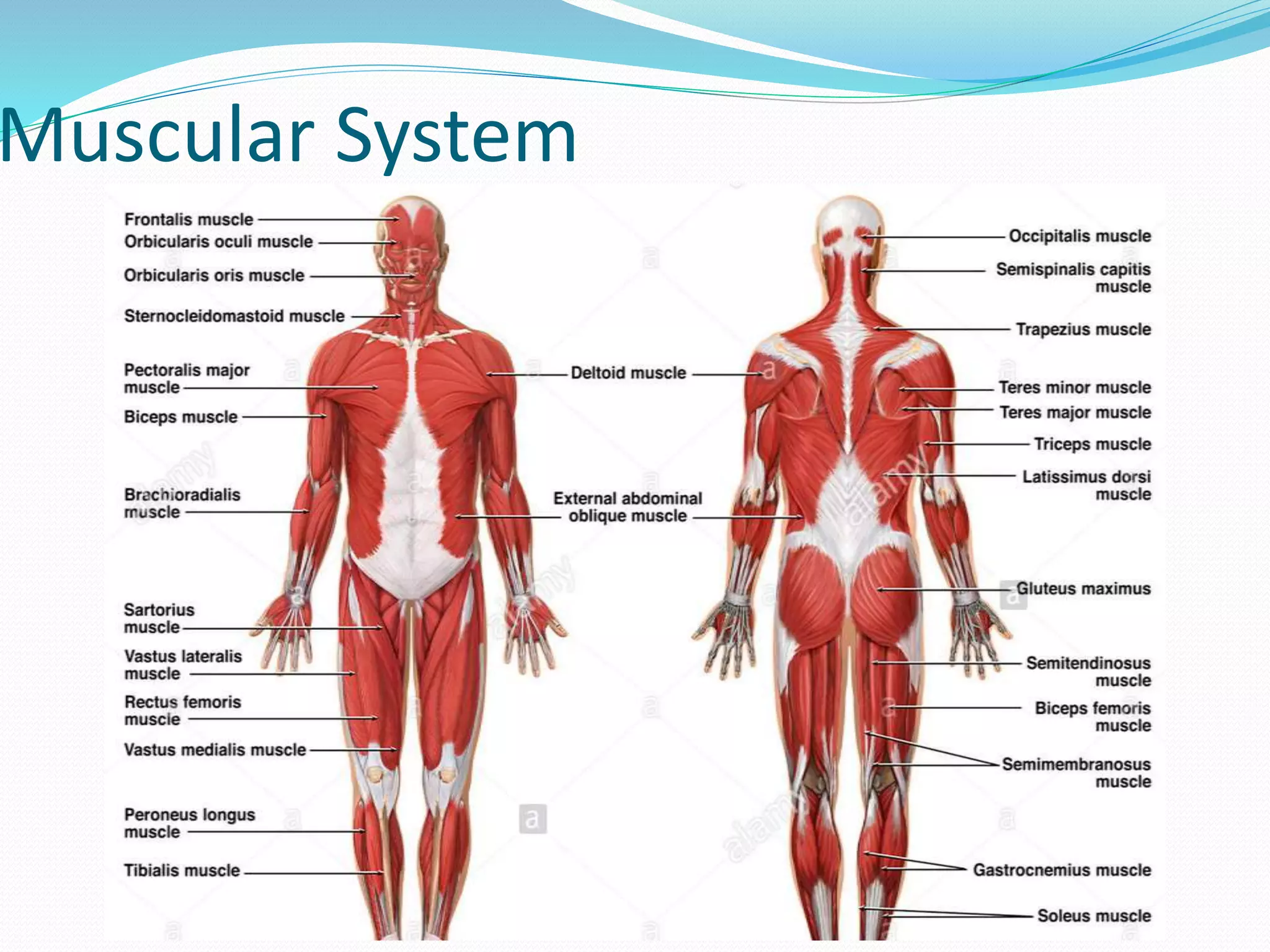
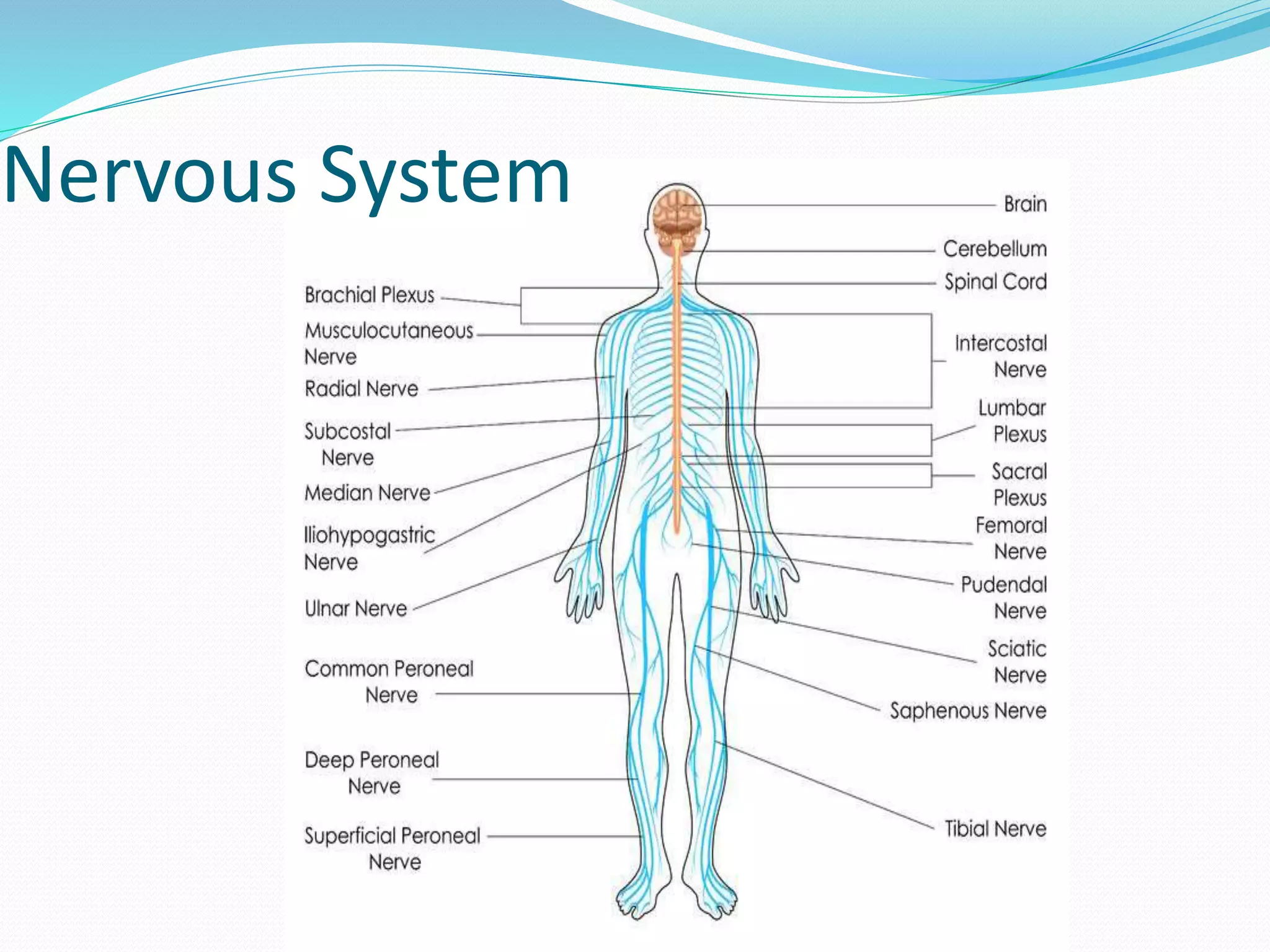
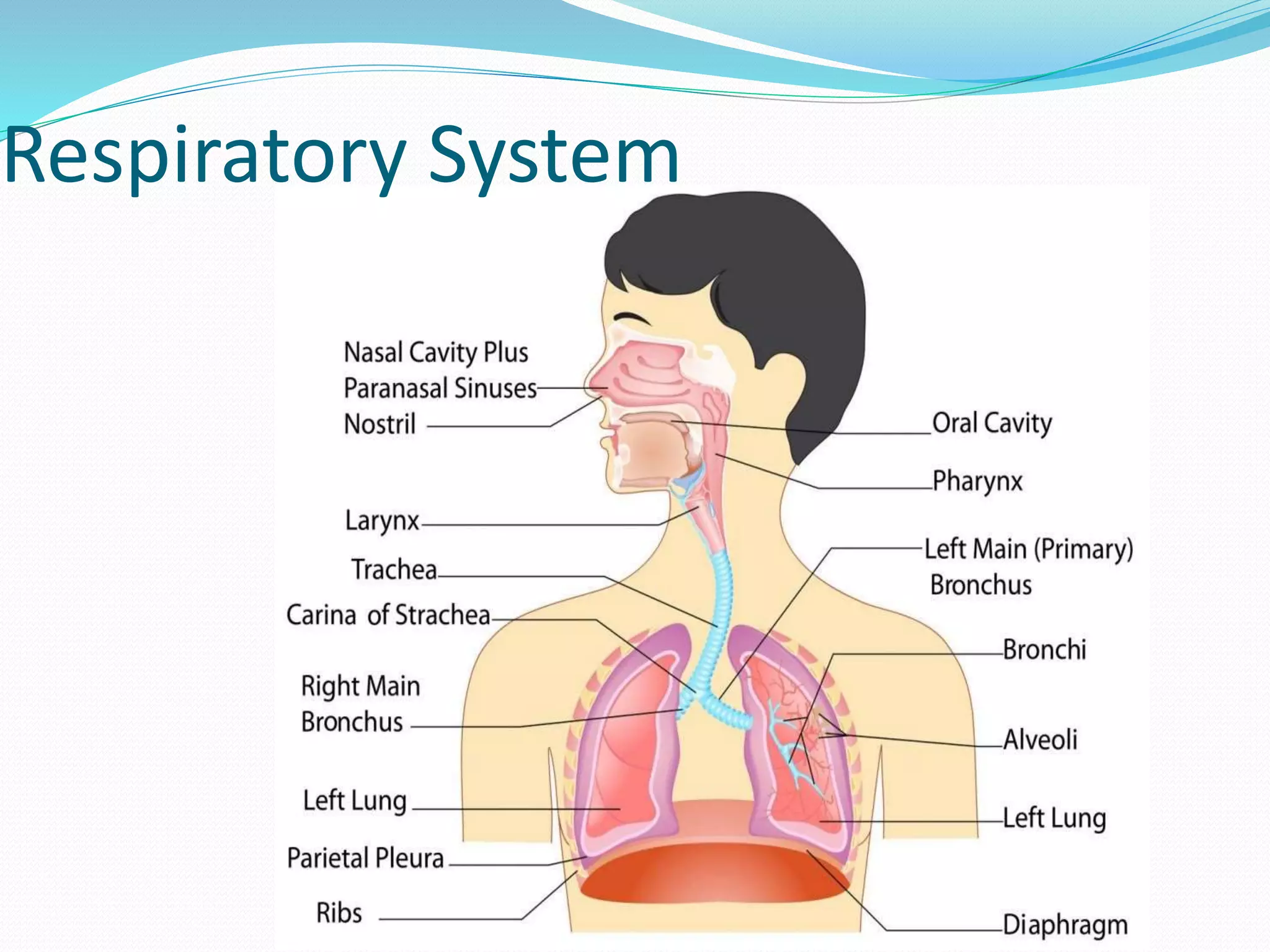
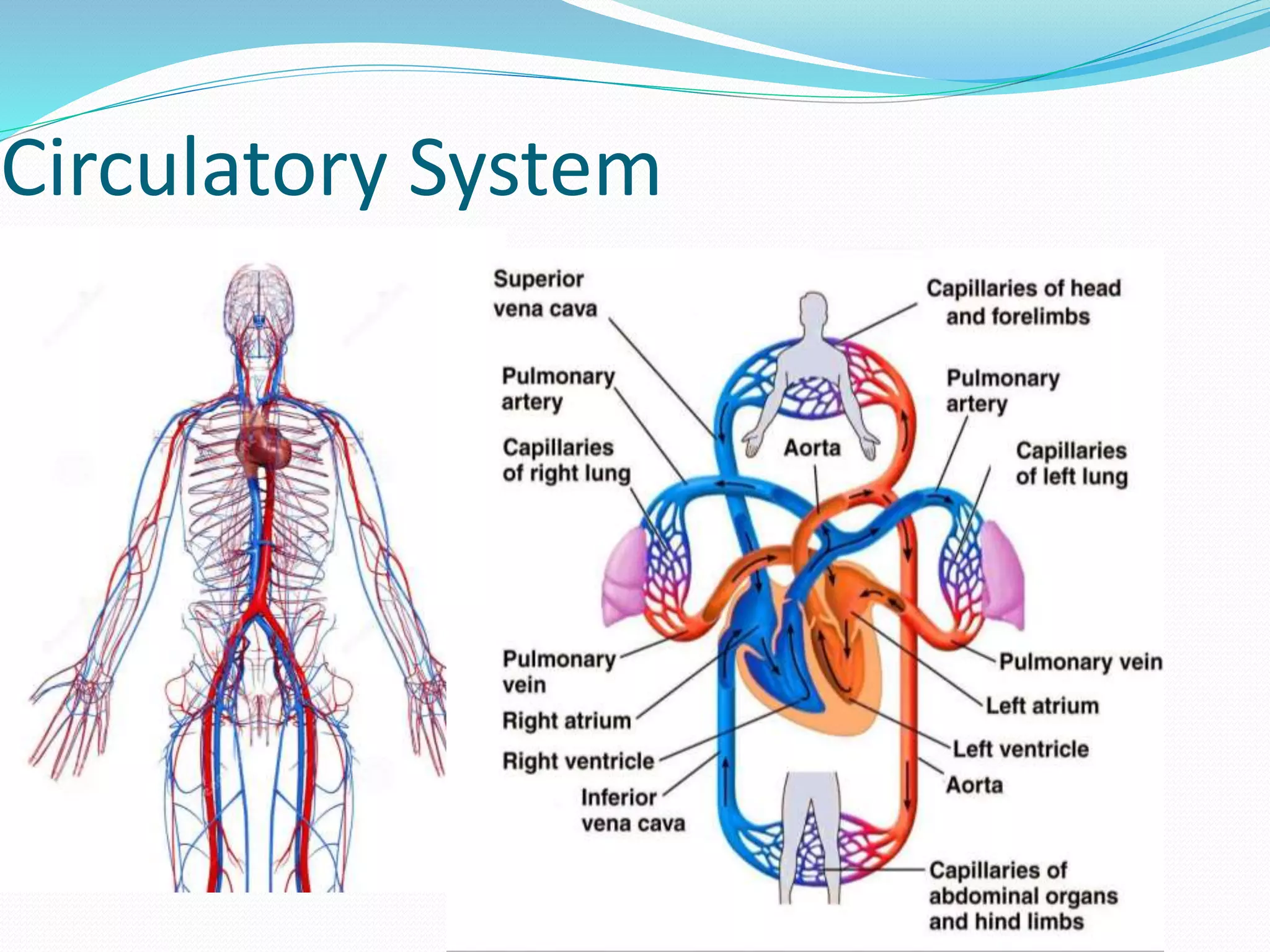
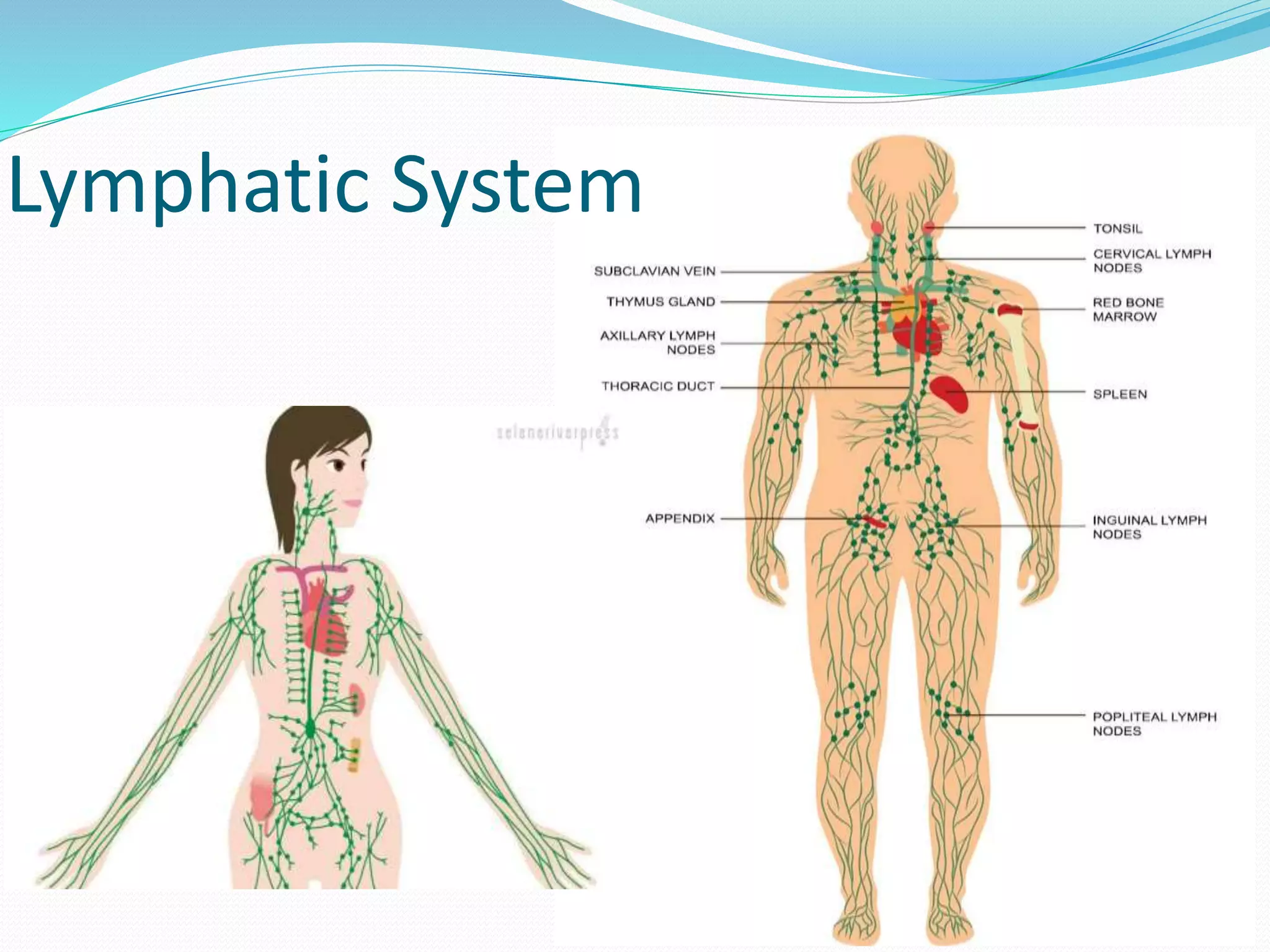
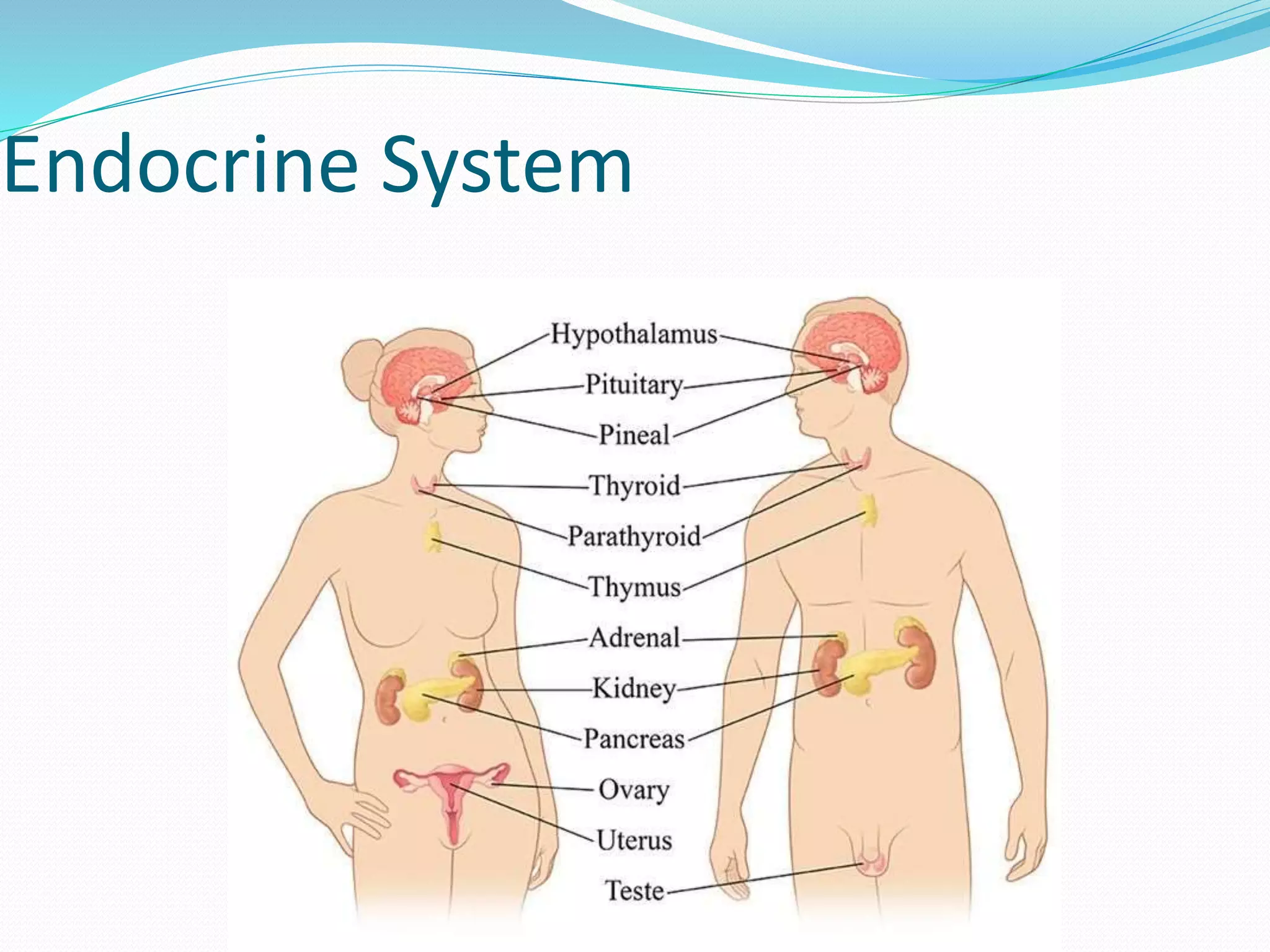
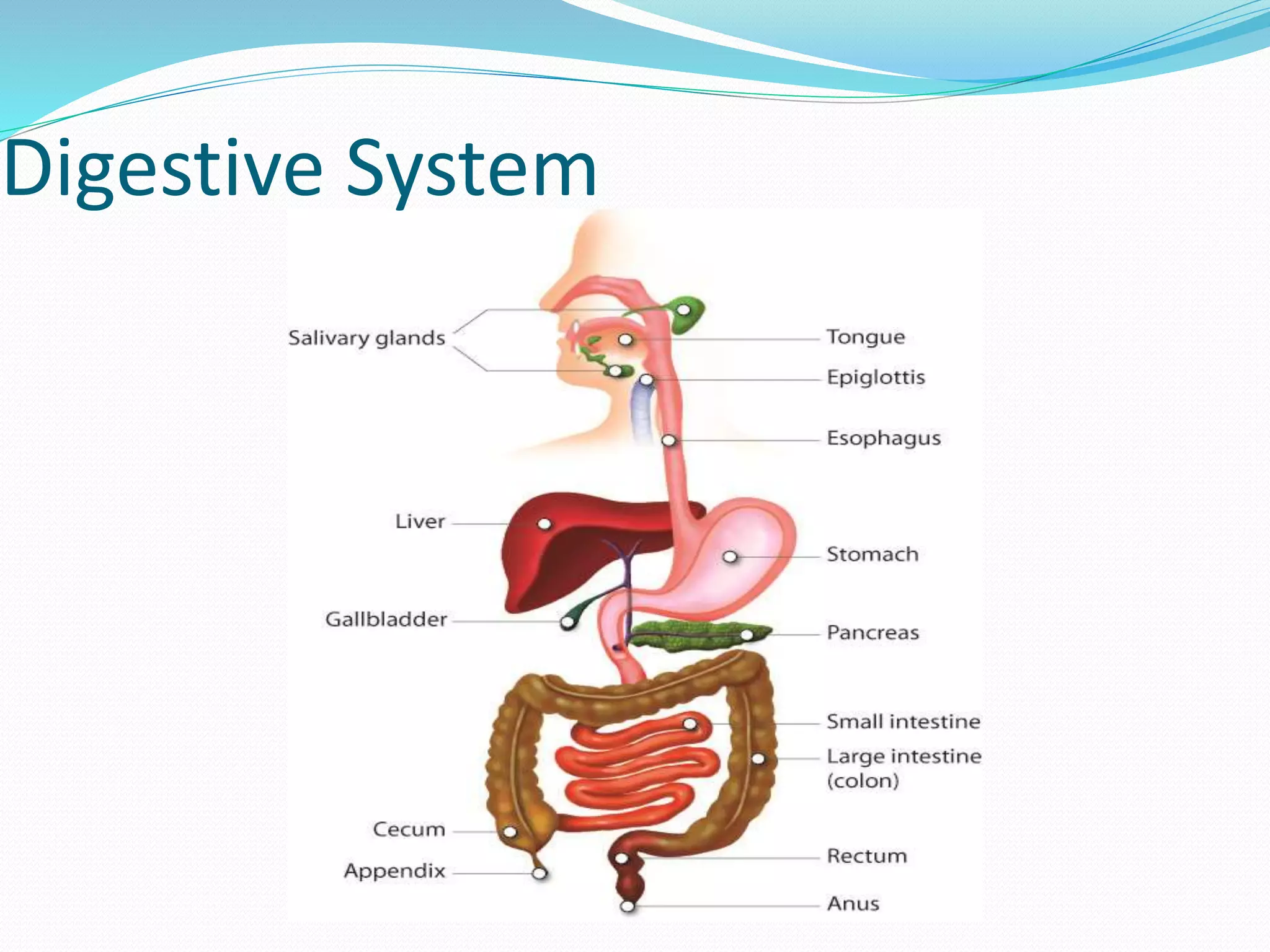
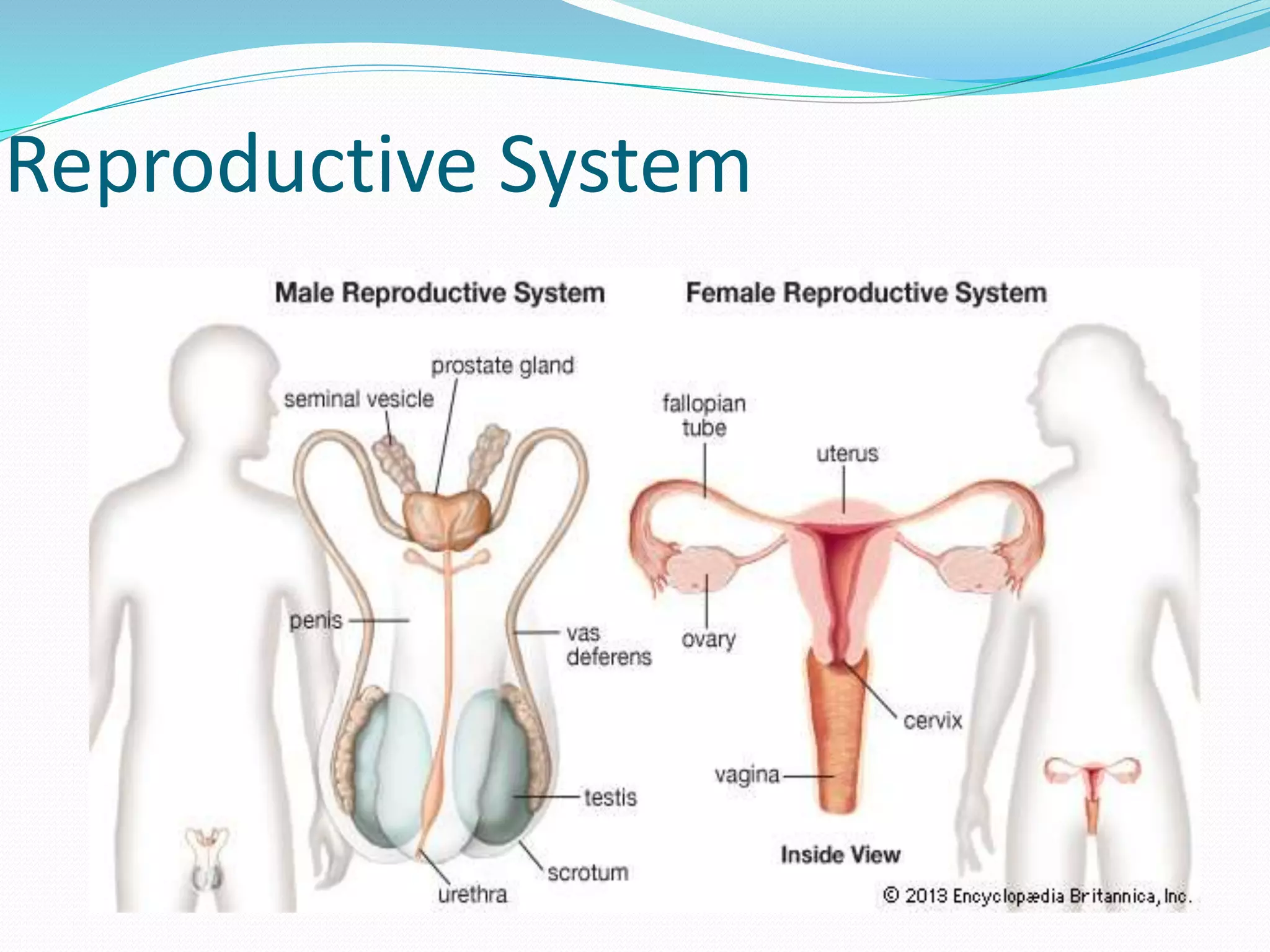
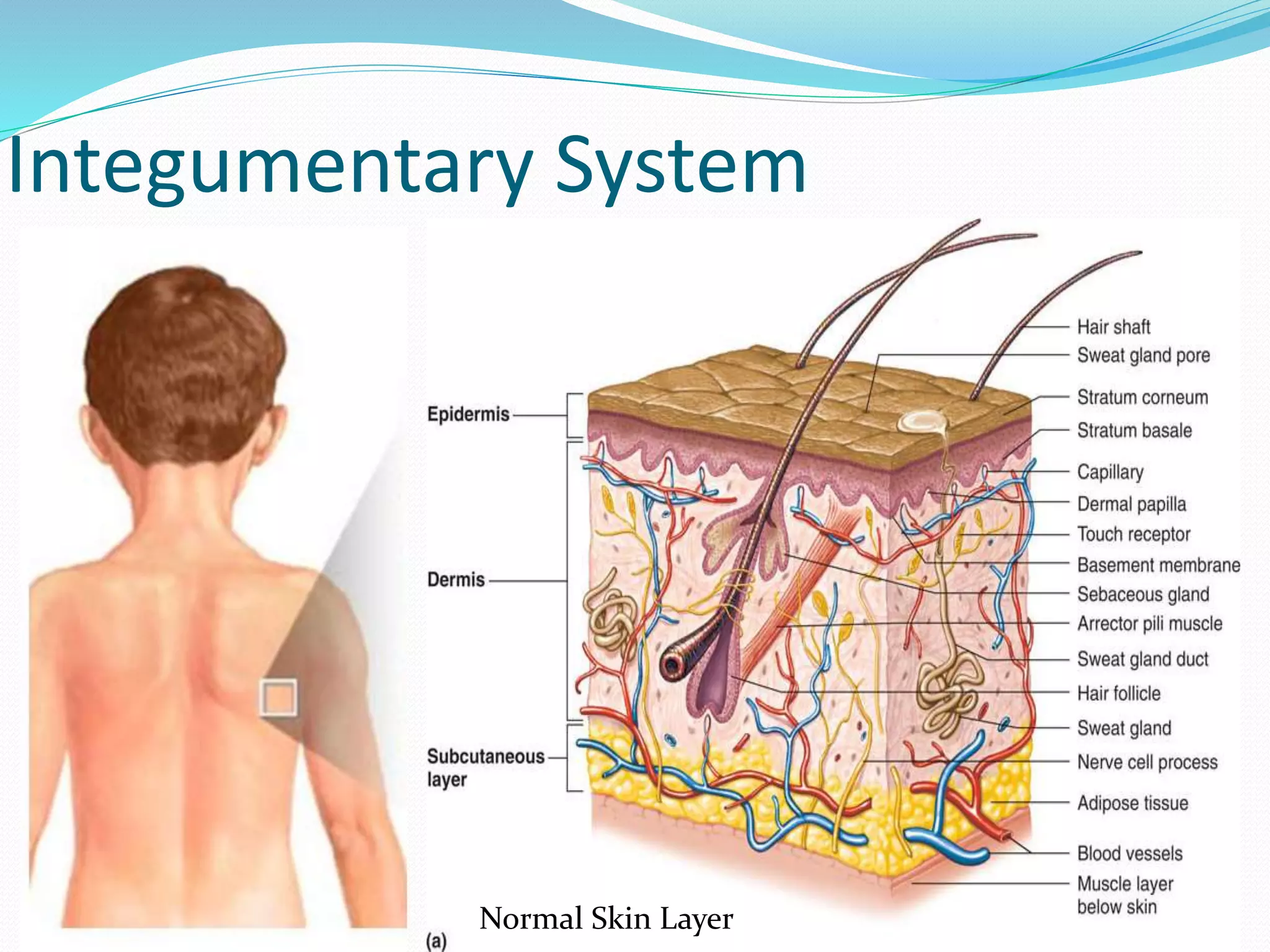
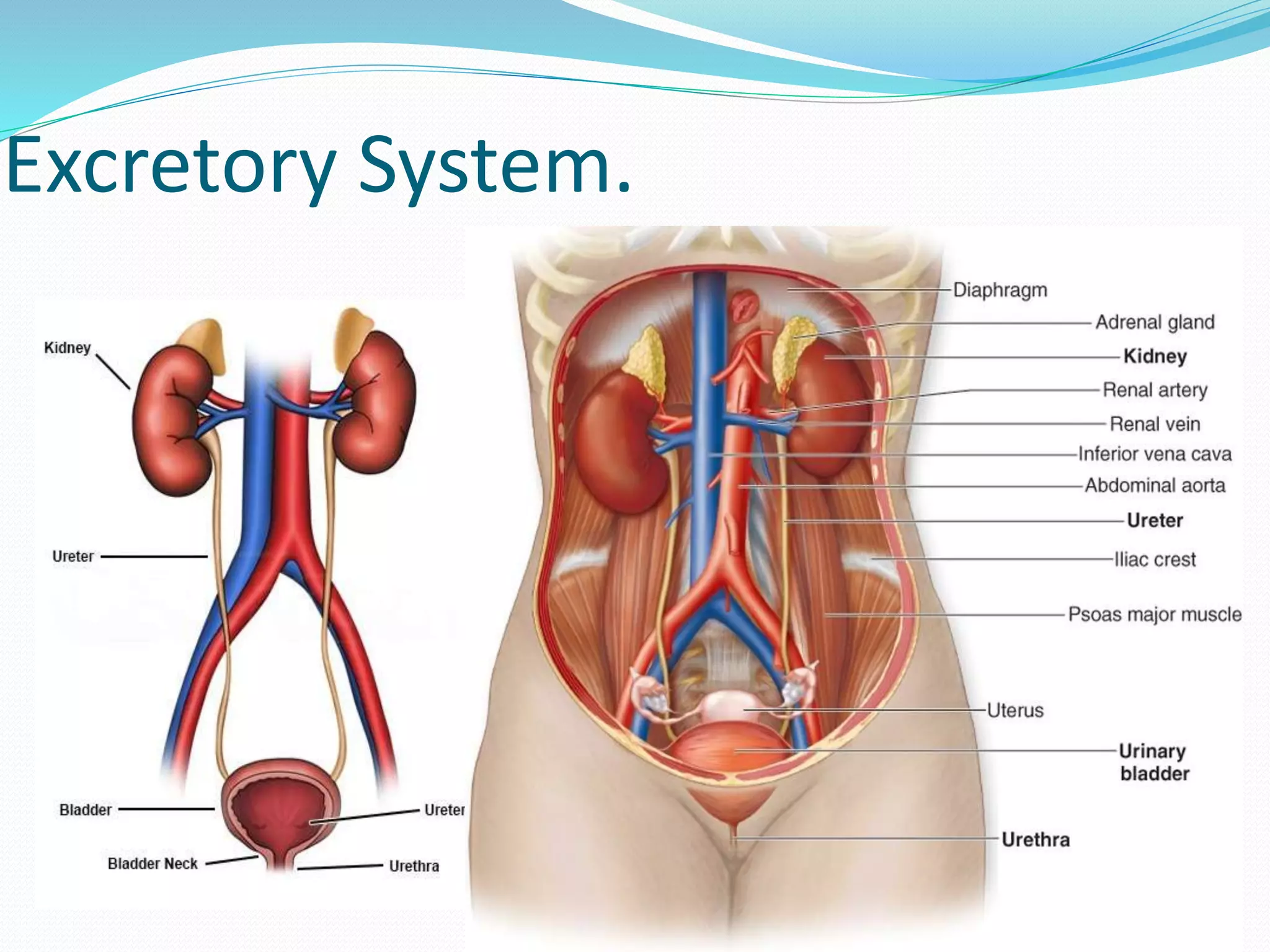
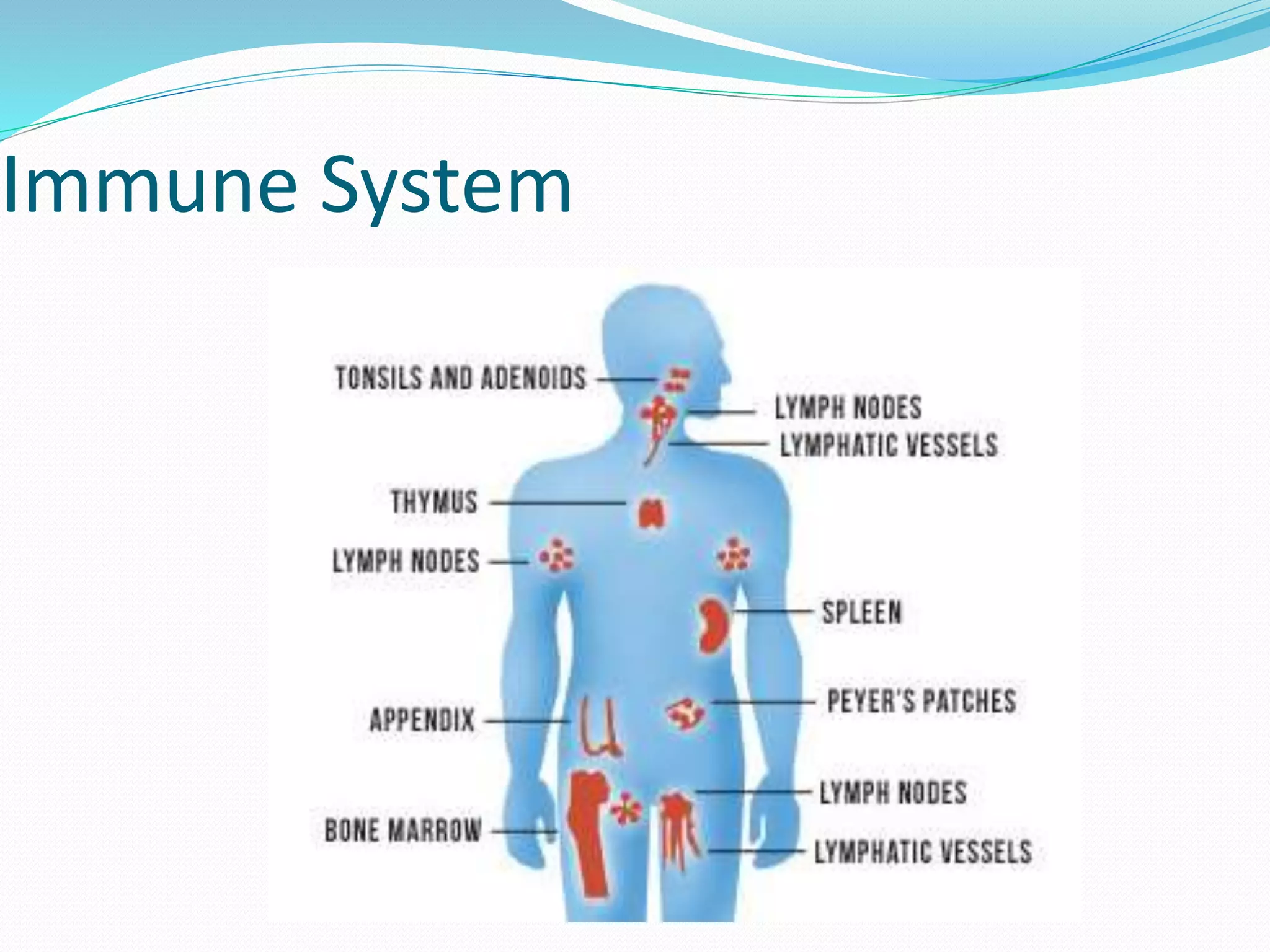
The document outlines the 12 organ systems of the human body, detailing their components and primary functions. Each system depends on others for stability and proper functioning, and damage to any one system can lead to significant health issues or death. Understanding these systems is critical for medical professionals as it forms the foundation of medical science.