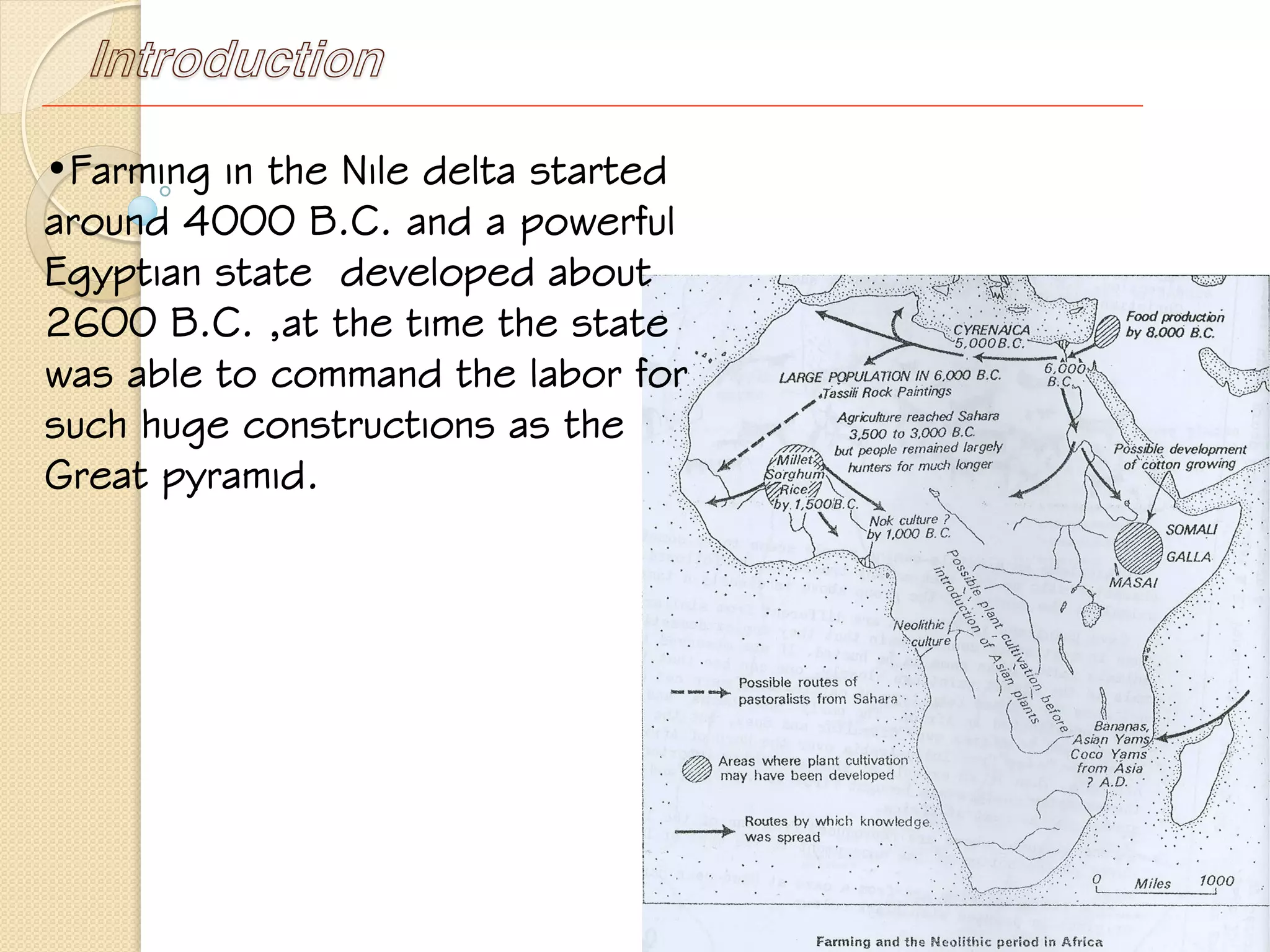
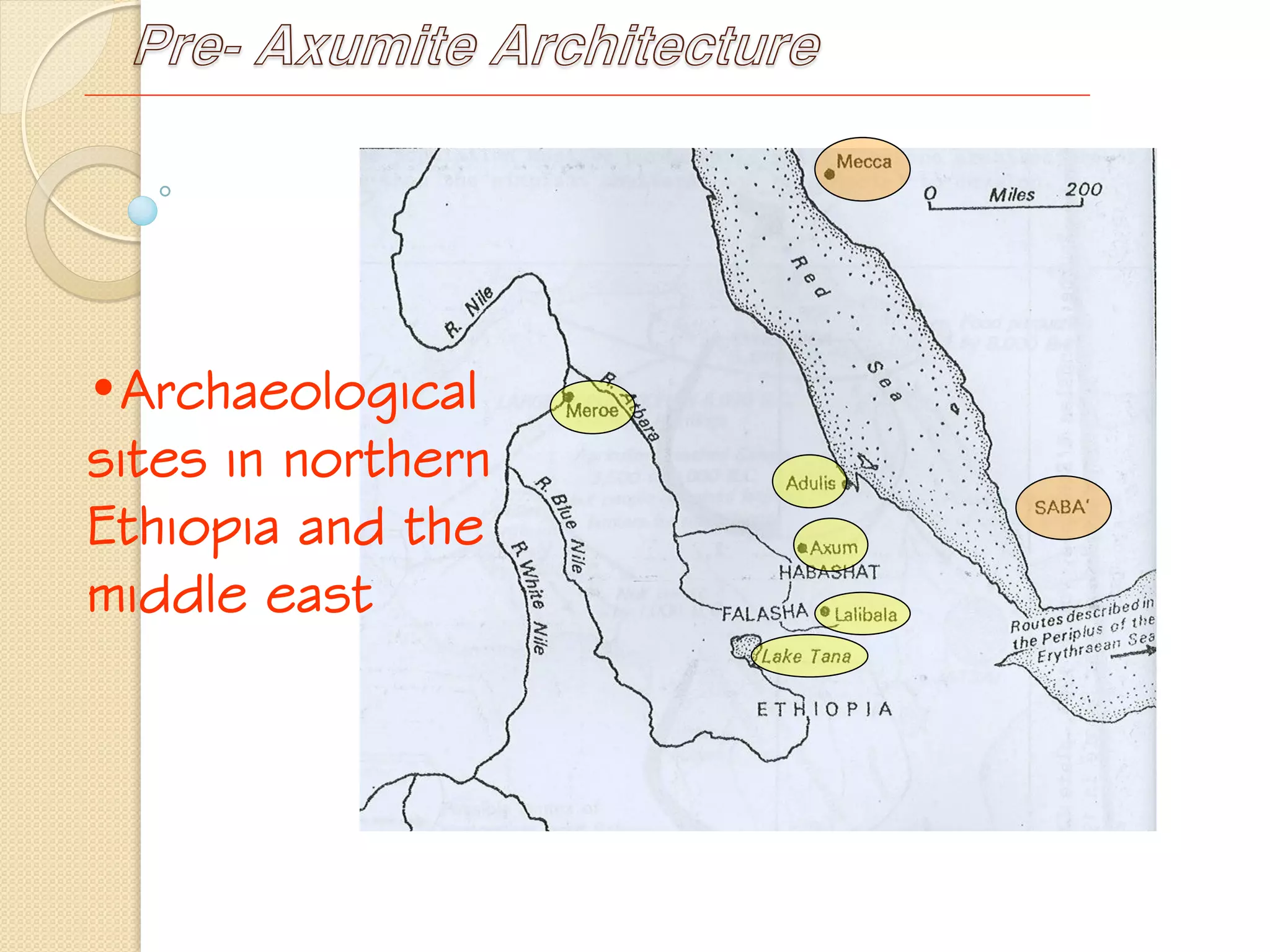
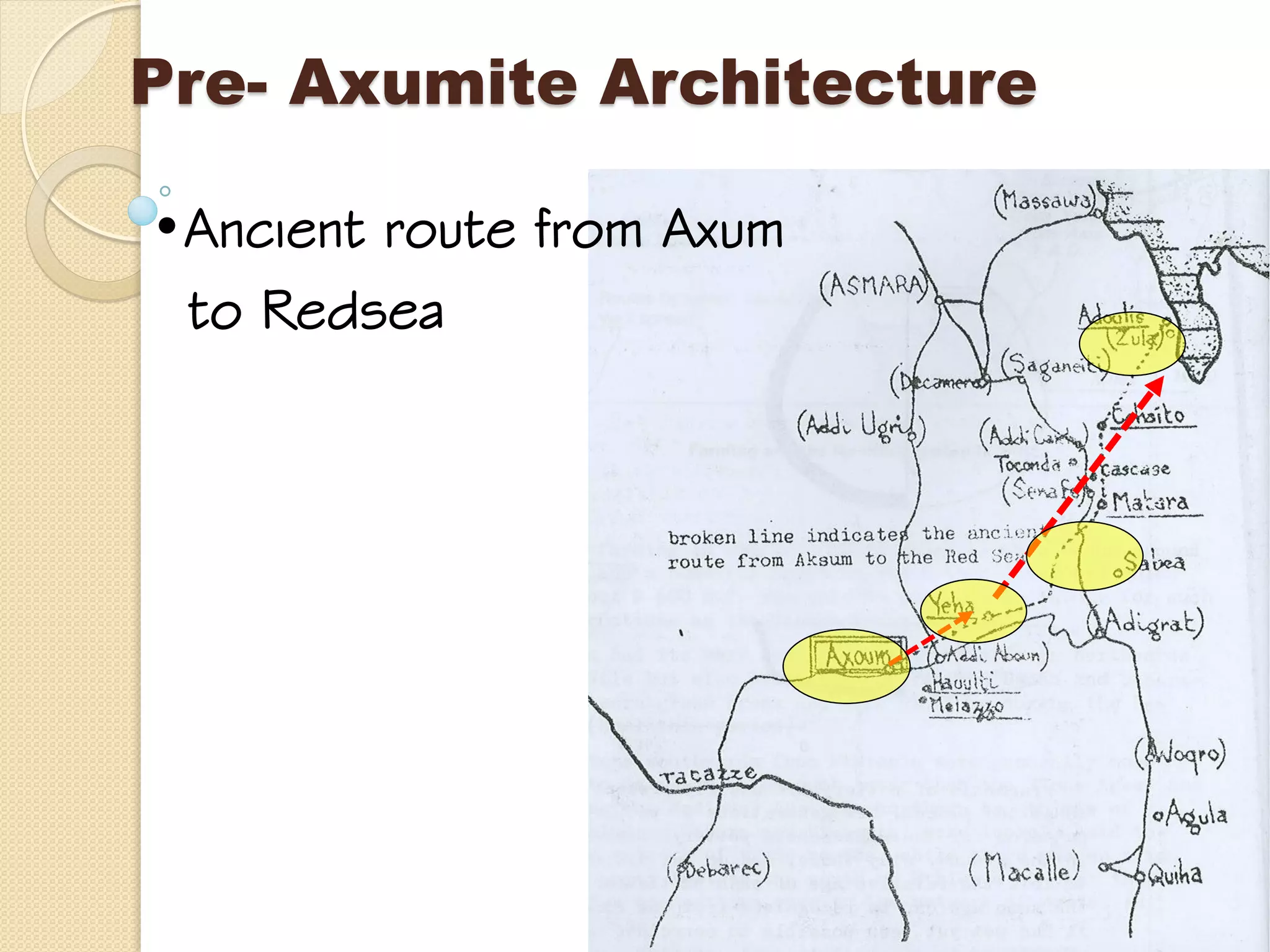
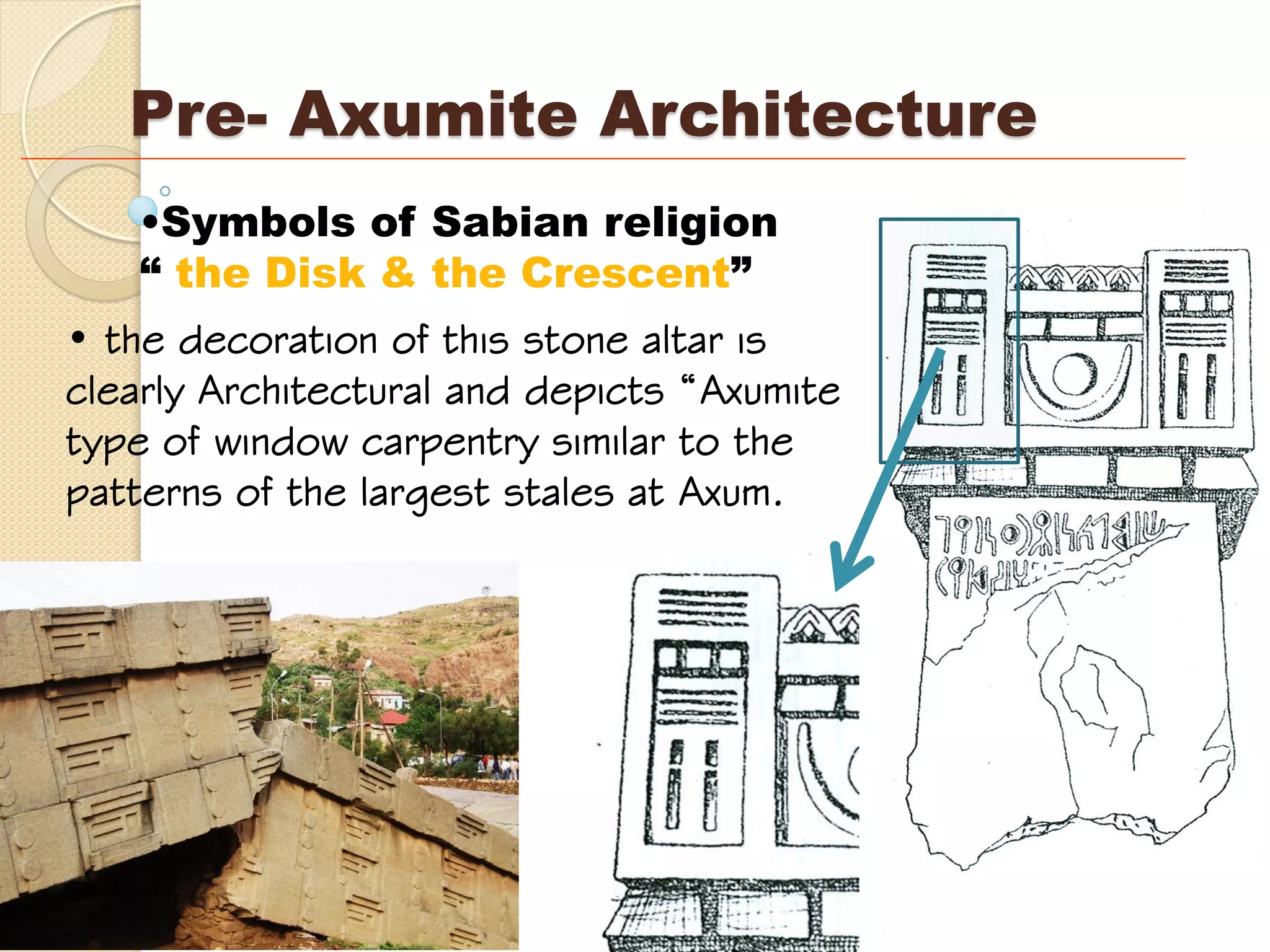
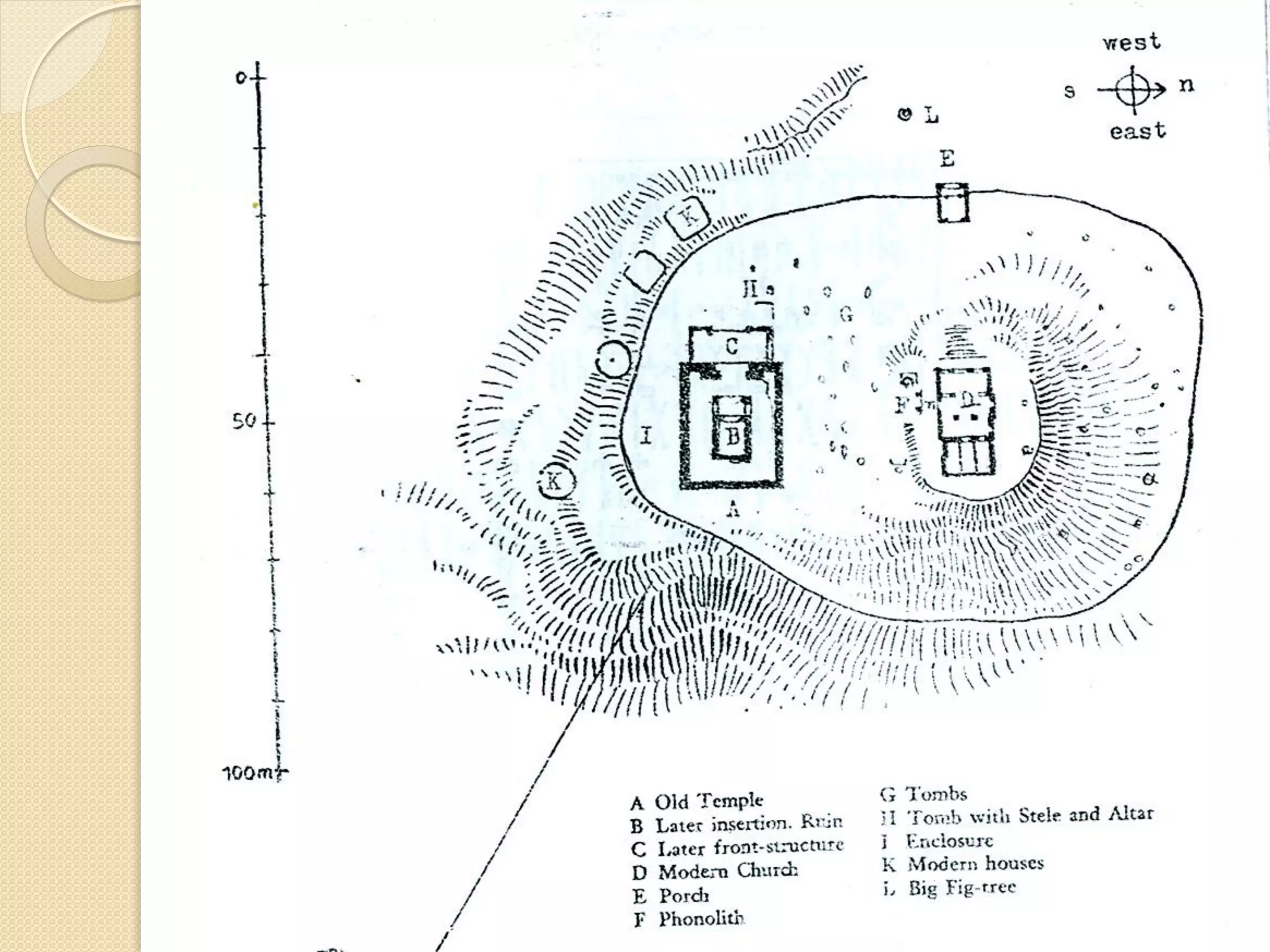
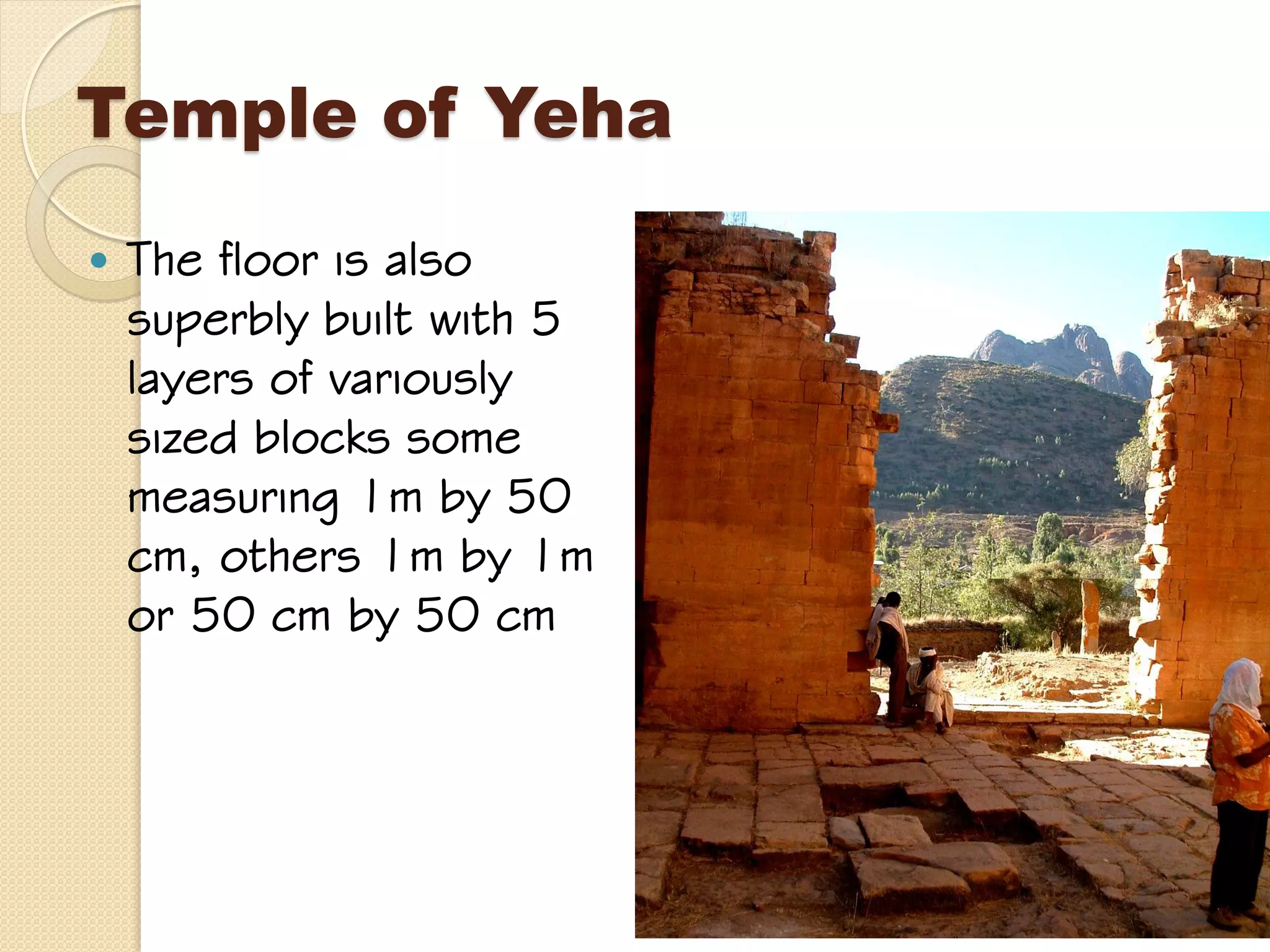
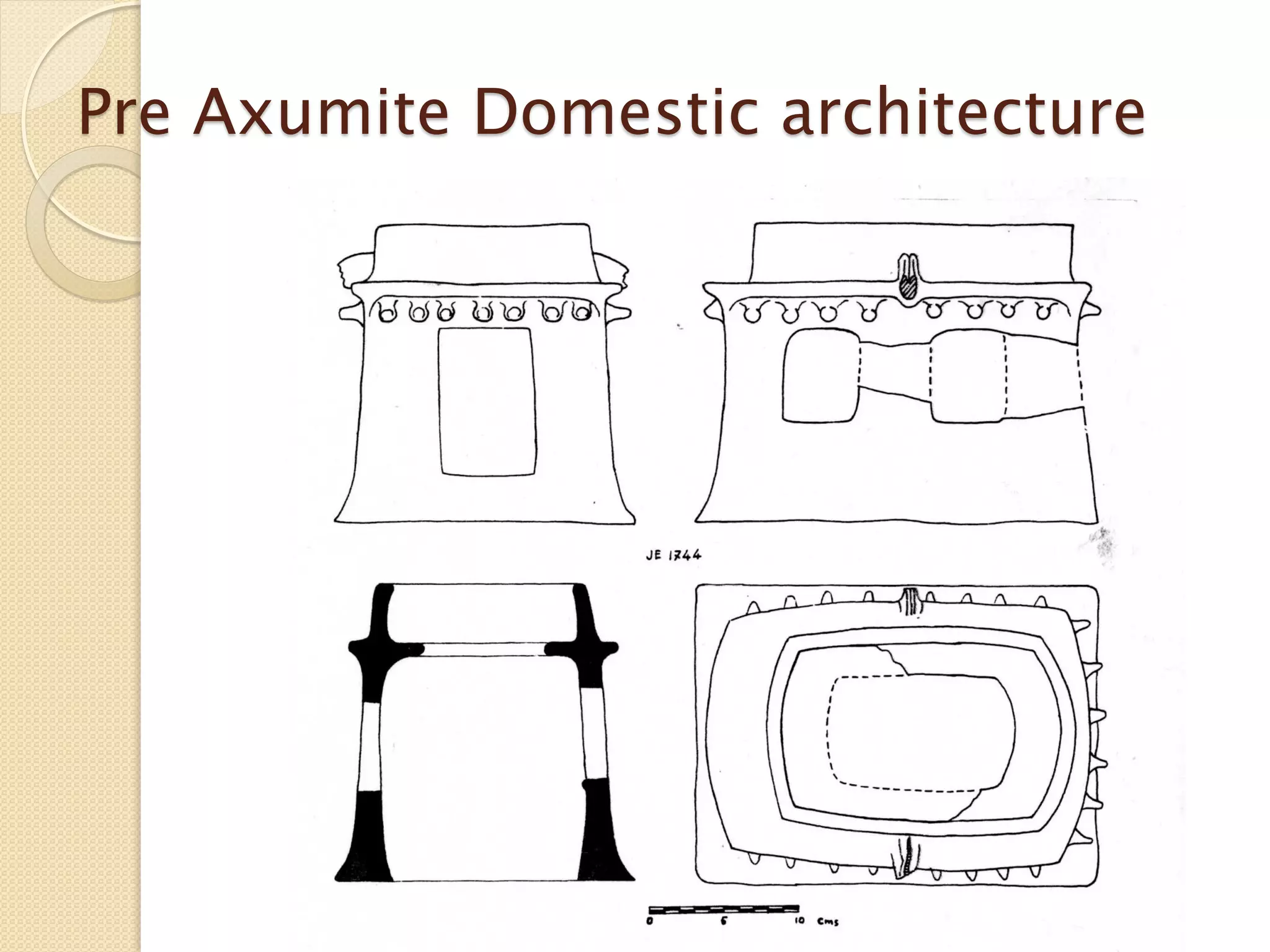
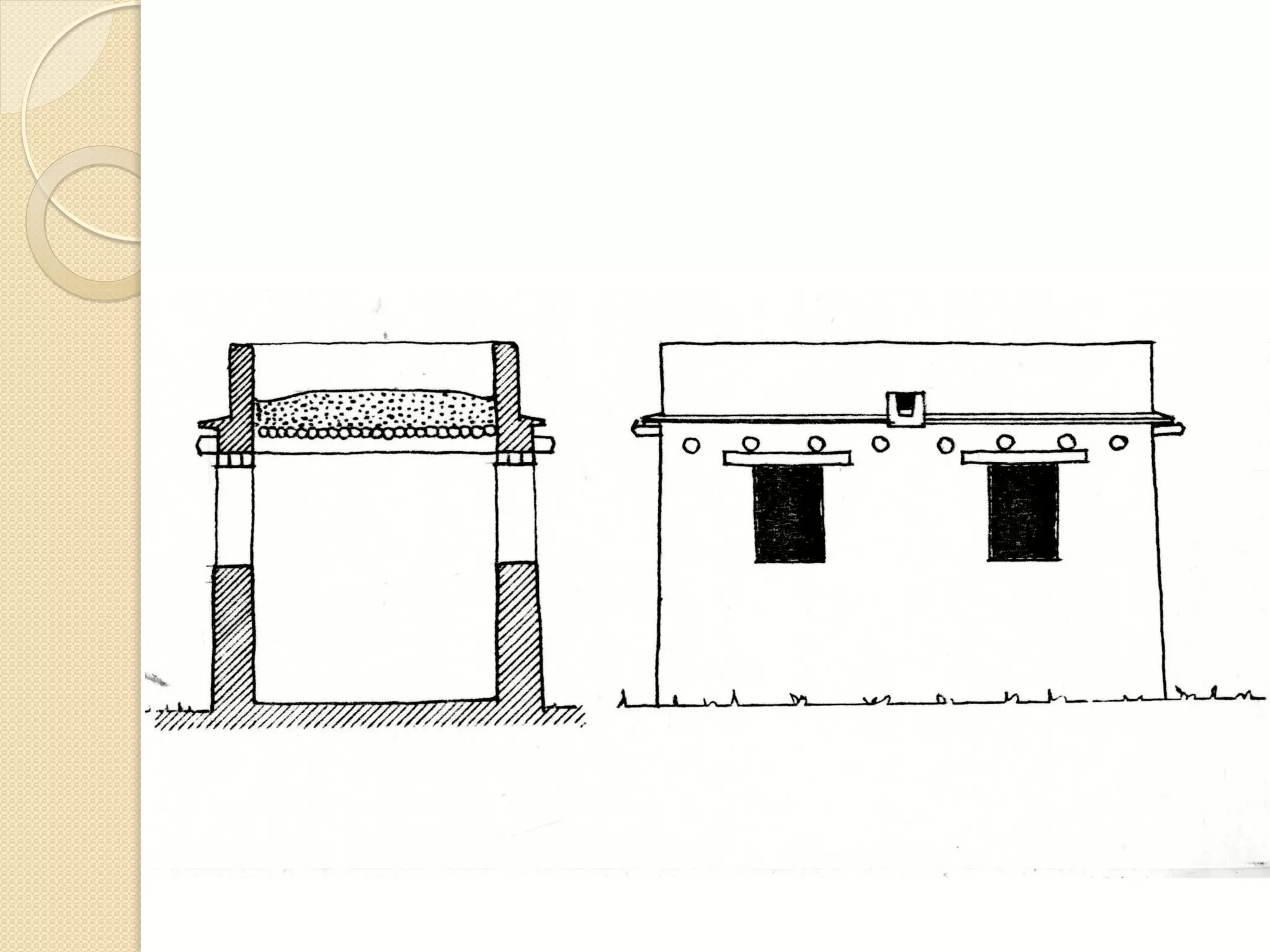
This document provides an overview of ancient Ethiopian art and architecture before the Axumite period. It describes some of the earliest cave paintings in Ethiopia dated to around 400,000 years ago. It discusses the influences of South Arabian culture between 500 BC to 100 AD, including the introduction of the Sabean script. One of the oldest well-preserved buildings in Ethiopia, the Temple of Yeha built around 500 BC, is highlighted for its precision masonry constructed without mortar. Characteristics of Pre-Axumite domestic architecture are also briefly touched on before comparing ancient Ethiopian structures to examples from Egypt, Greece and Rome.