1. The document provides information on classifying different types of manufacturing costs as direct or indirect, fixed or variable, and product vs period costs.
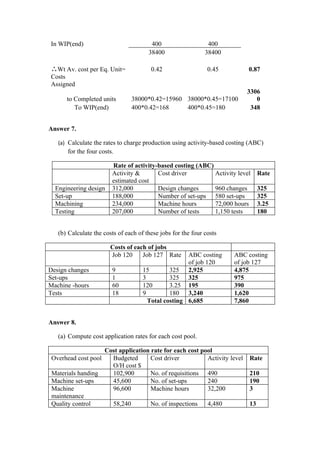
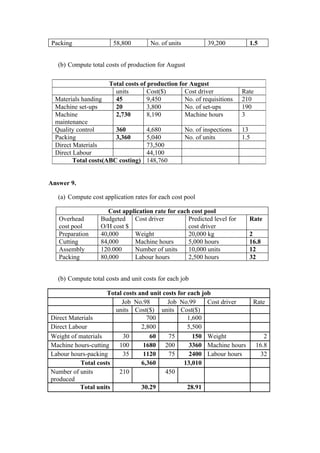
2. It also asks to classify costs using different costing methods like job order costing vs process costing.
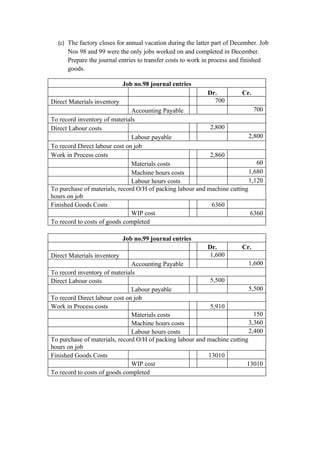
3. Journal entries are provided to record the transfer of costs from work in process to finished goods for two jobs completed in December.