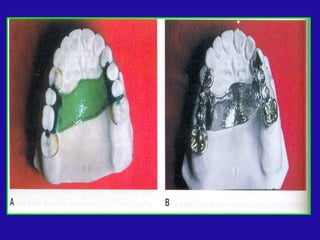
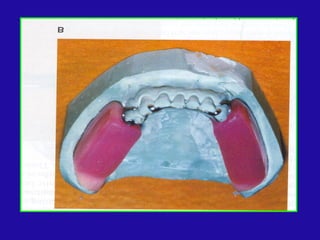
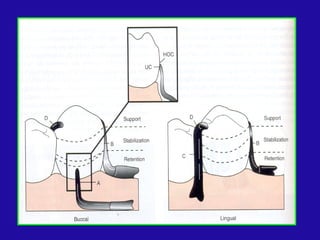
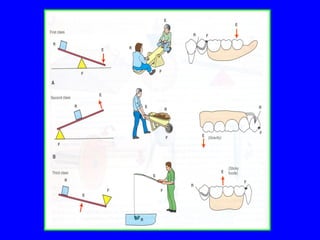
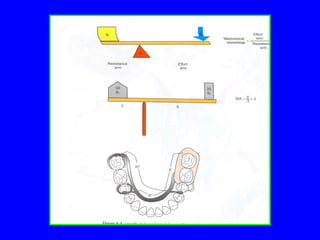
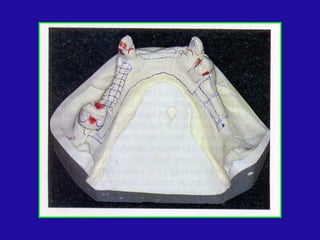
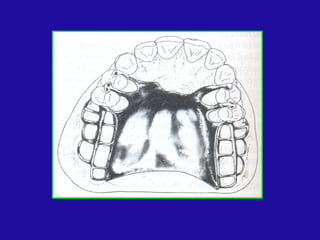
The document discusses distal extension partial dentures, outlining their support mechanisms which mainly rely on abutment teeth and the residual ridge for stability and retention. Various factors influencing support, such as ridge contour, impression accuracy, and denture design, are emphasized, along with the importance of ensuring the denture base effectively contacts oral tissues. The ideal conditions for a supportive residual ridge and the impact of occlusal load on denture performance are also reviewed.