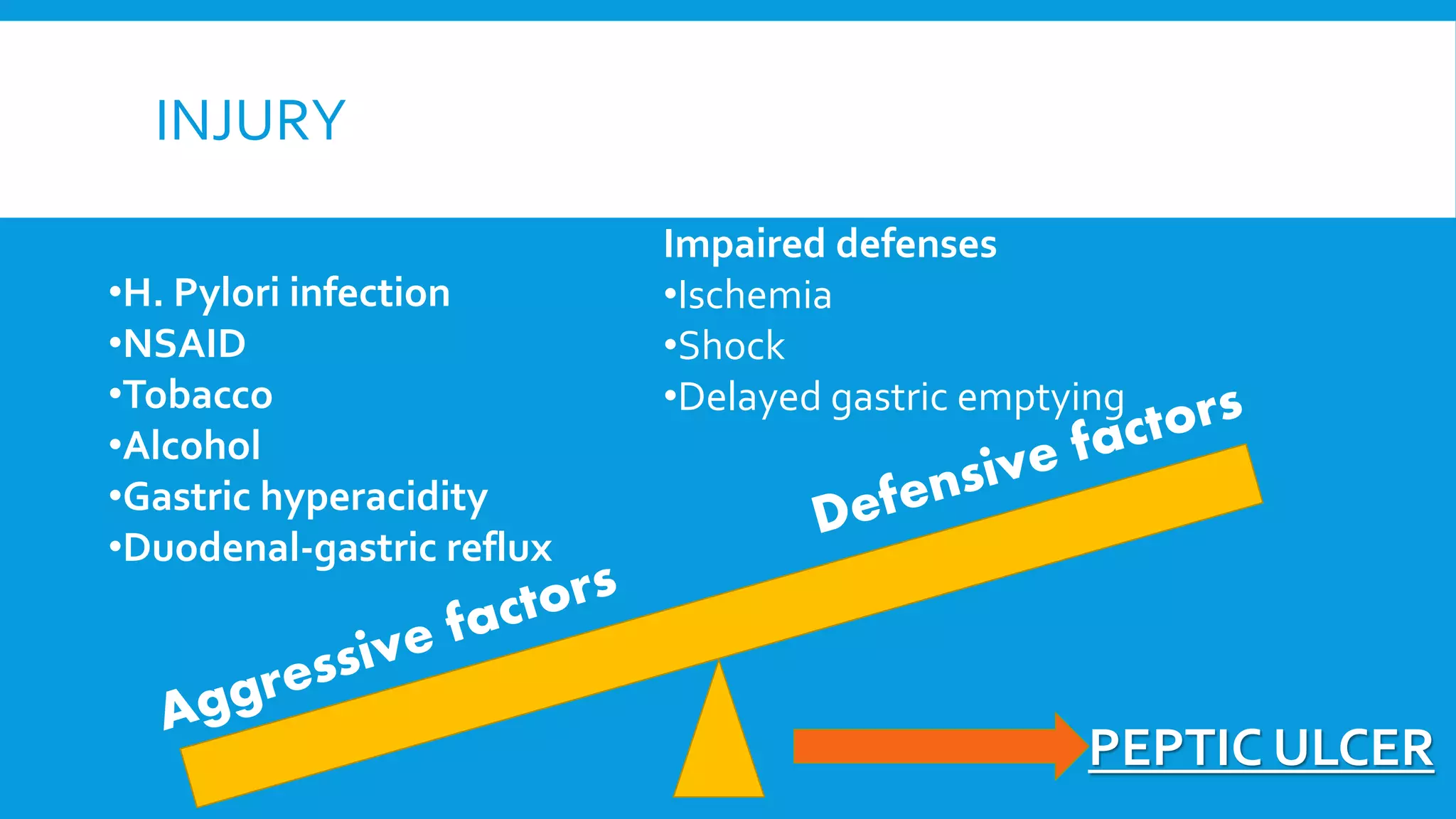
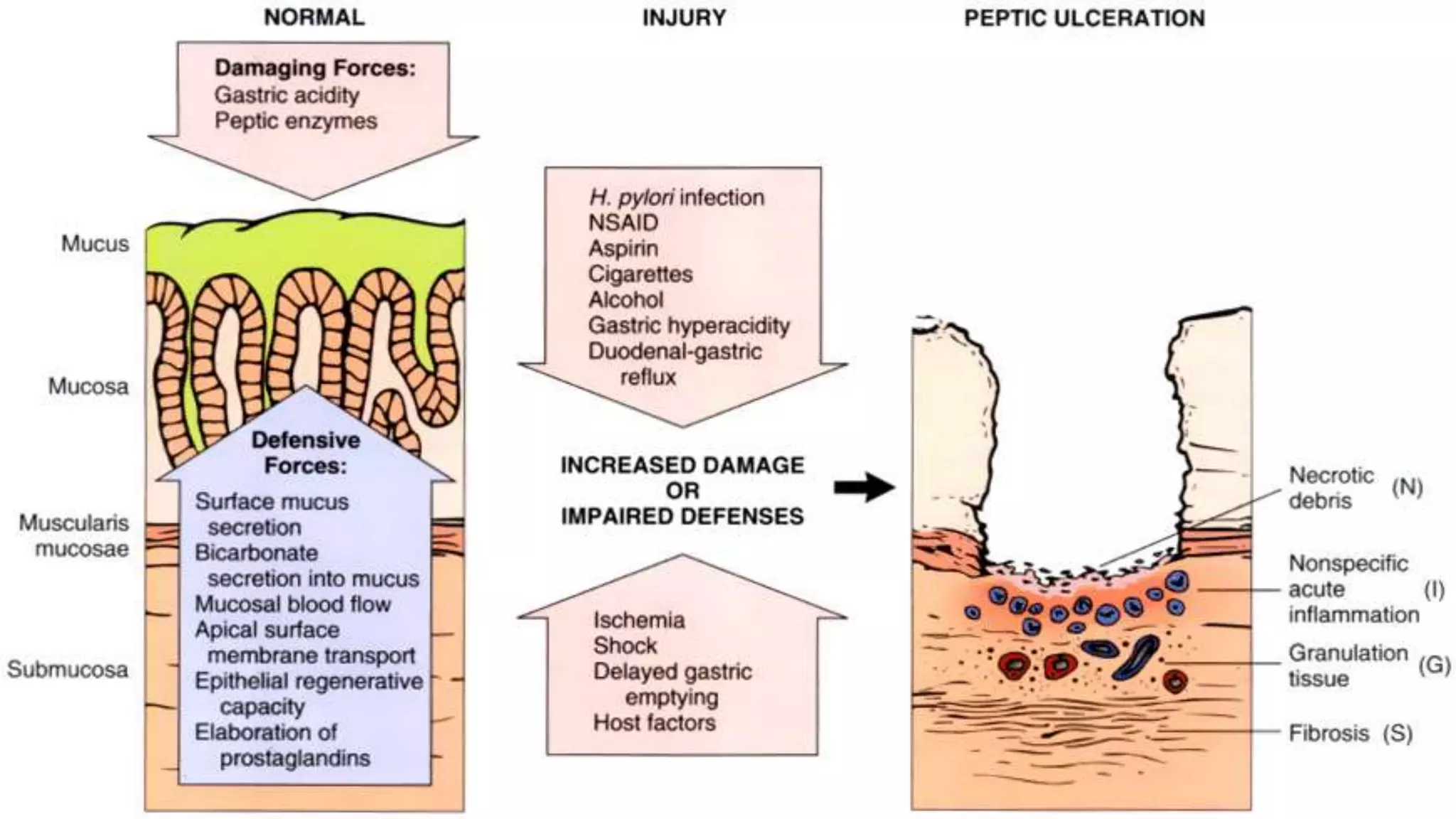
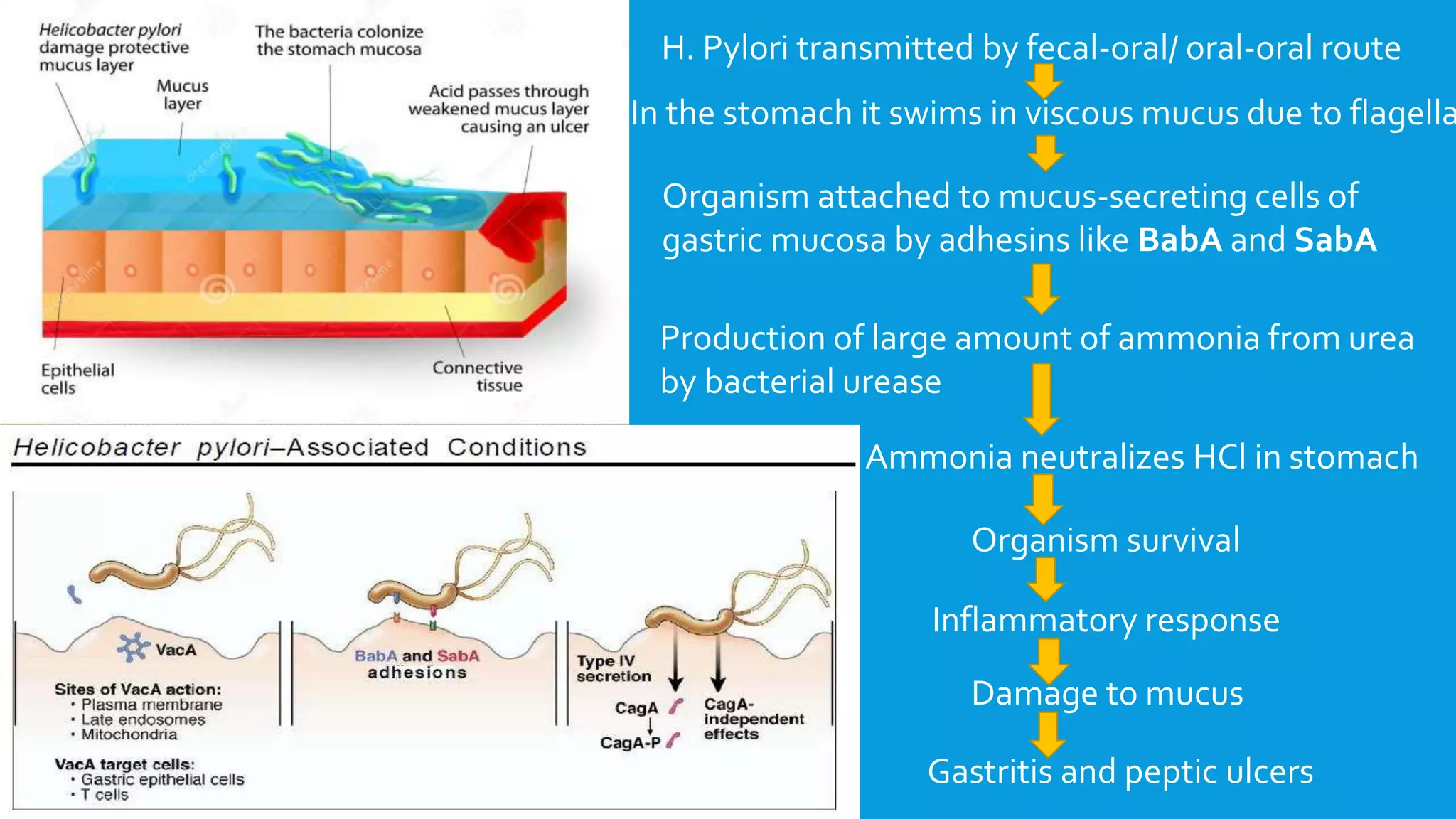
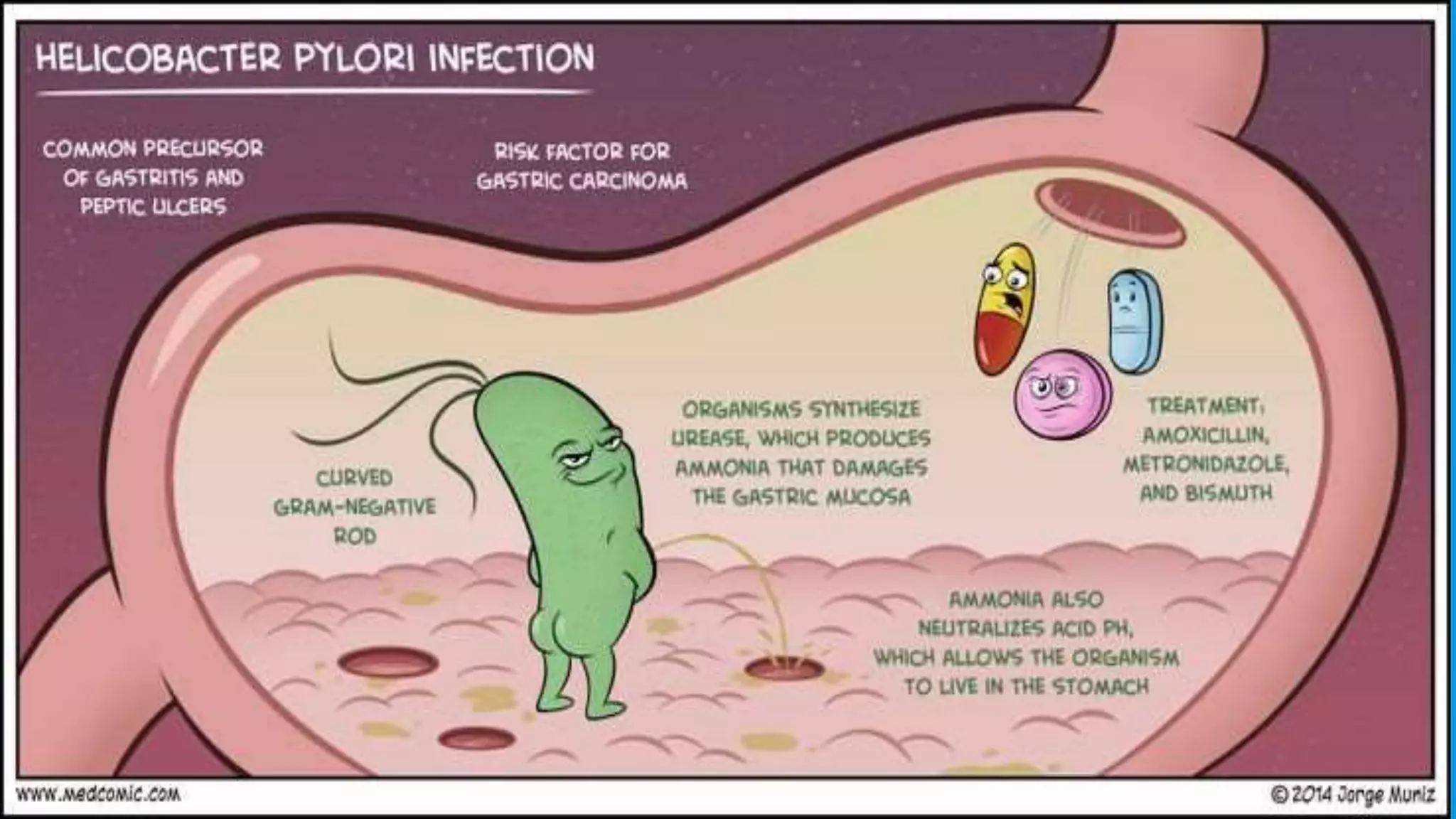
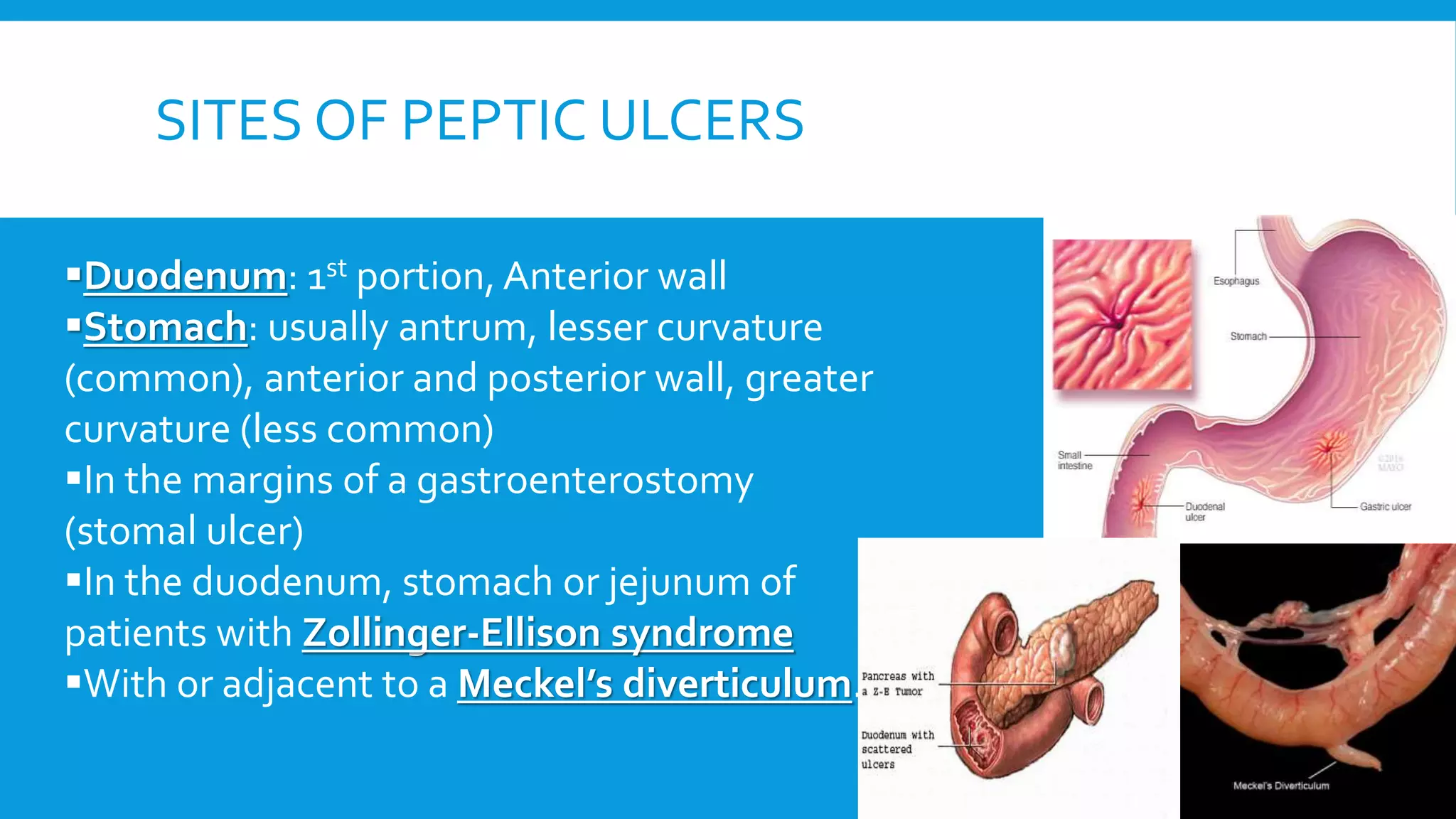
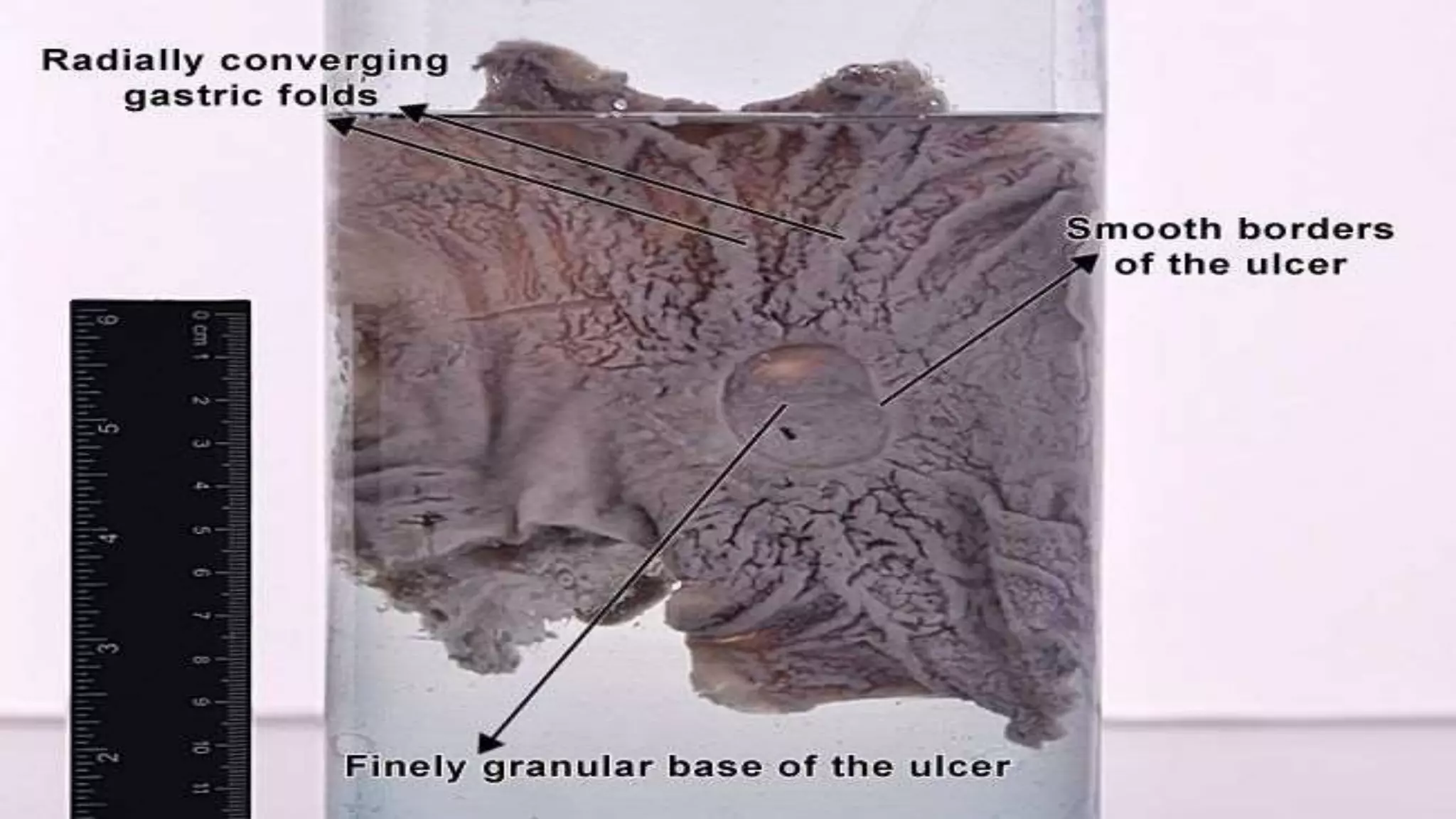
The document provides an overview of peptic ulcers, defining them as disruptions in the mucosal integrity of the stomach and duodenum, with a focus on their pathogenesis, morphology, and complications. Key factors contributing to peptic ulcer development include H. pylori infection, NSAIDs, and lifestyle choices such as smoking and alcohol use. Clinical features include epigastric pain and dyspepsia, with complications potentially leading to hemorrhage, perforation, and gastrointestinal obstruction.