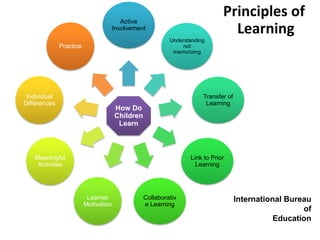
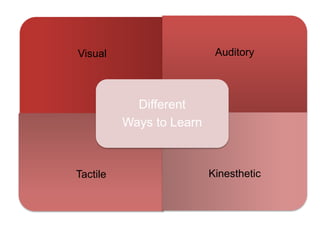
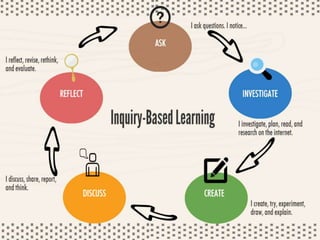
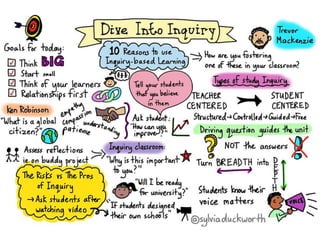
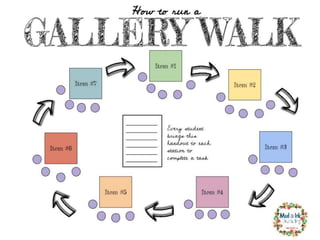
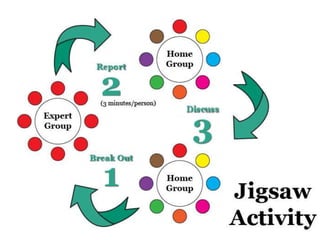
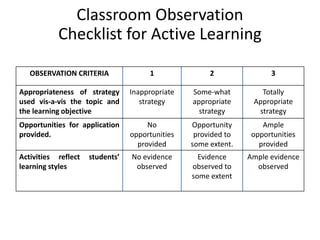
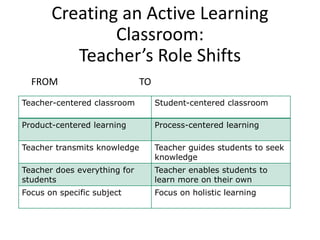
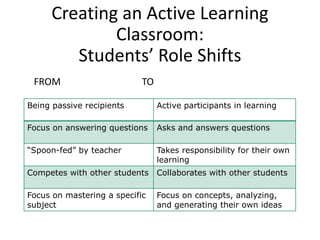
The document outlines strategies for teachers to understand and implement active learning in the classroom, emphasizing the importance of recognizing diverse learning styles. It contrasts teacher-centered and student-centered environments and highlights the roles of teachers and students in fostering active learning. Key strategies discussed include inquiry-based learning, collaboration, and the need for teachers to facilitate rather than dictate learning.