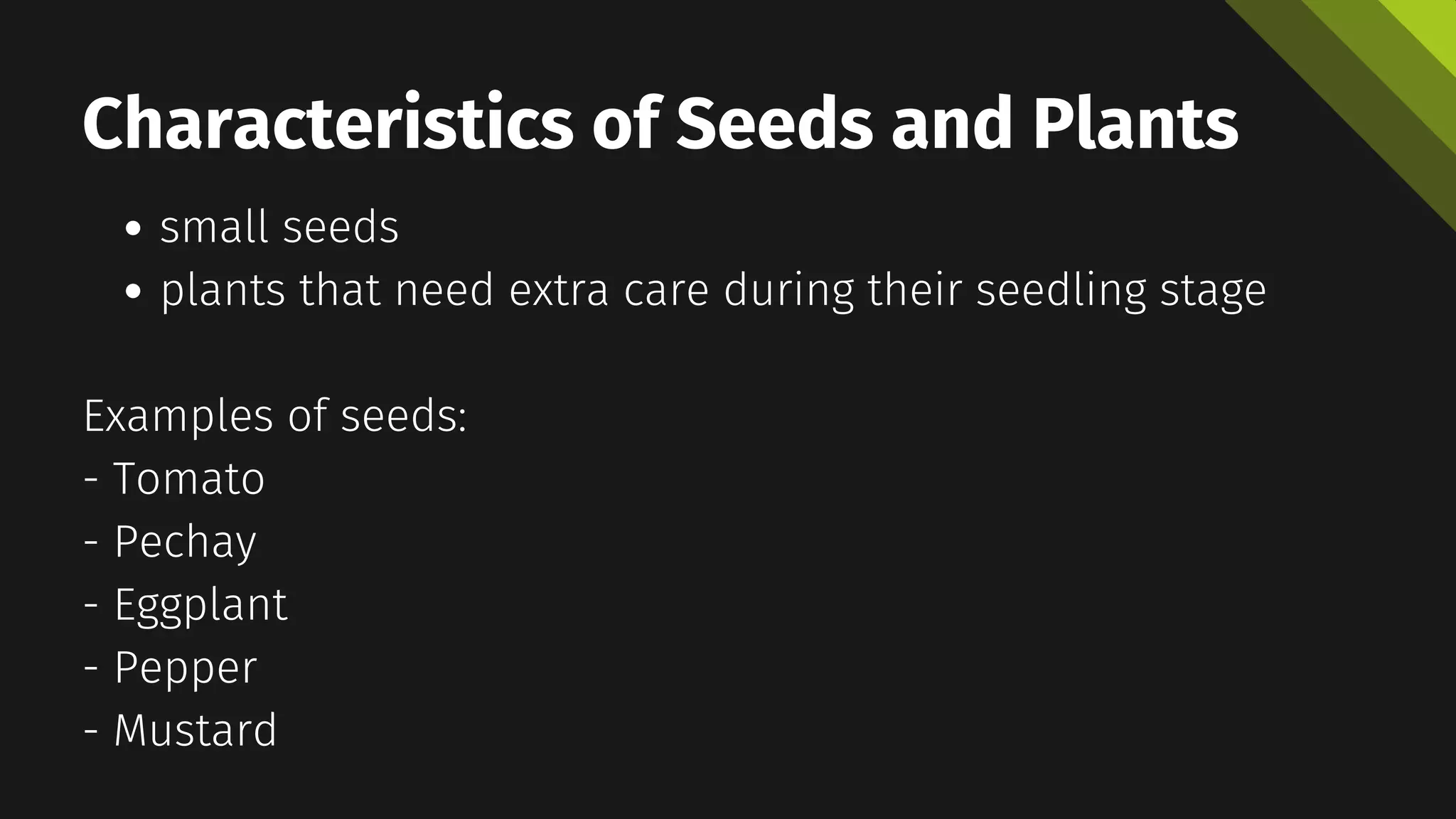
The document discusses two methods of planting: direct seeding and indirect seeding. Direct seeding involves planting seeds directly in the garden soil, and is suitable for seeds that are large and fast-growing. Indirect seeding involves starting seeds in containers like pots and then transplanting the seedlings, which is better for small seeds and plants that need extra care in the seedling stage like tomatoes and peppers. Both methods have advantages like earlier harvest for direct seeding, and higher success rates for indirect seeding, but also disadvantages involving costs, labor and risk of damage to seedlings. The document provides examples of crops suitable for each method and steps for transplanting seedlings.