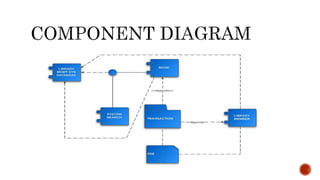
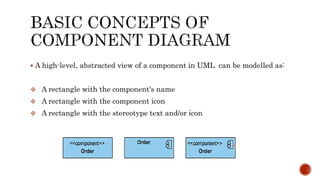
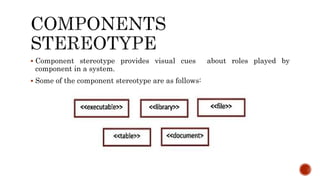
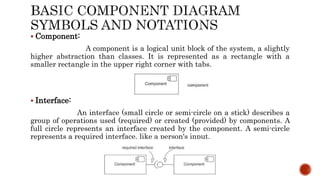
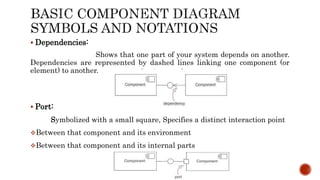
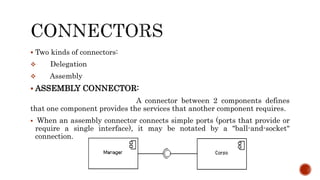
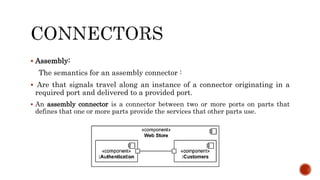
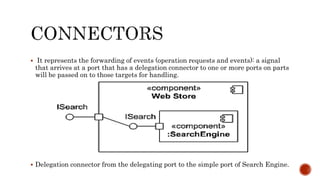
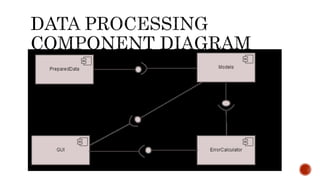
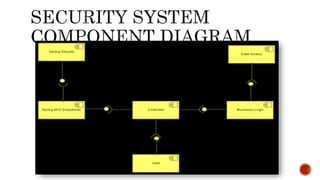
The document discusses UML component diagrams, highlighting their importance for modeling the implementation perspectives of a system, including components, databases, executables, and source code. It explains various notations such as components, interfaces, dependencies, and ports, as well as the types of connectors like assembly and delegation. Overall, component diagrams serve to visualize relationships and interactions within a system, ensuring all required functions are addressed during development.