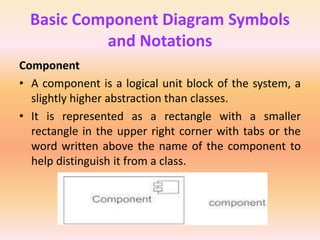
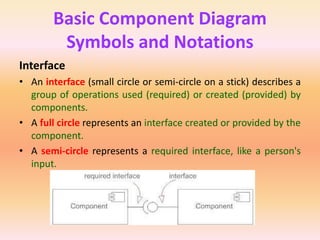
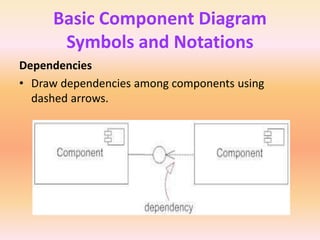
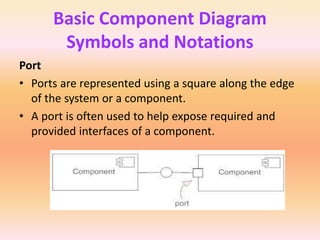
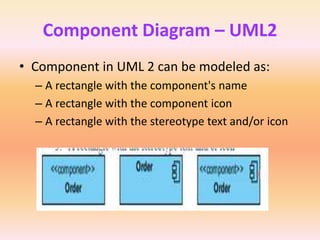
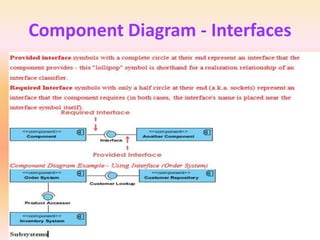
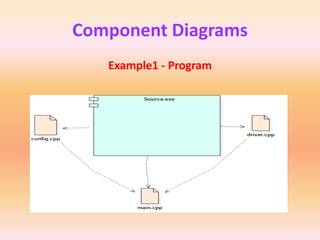
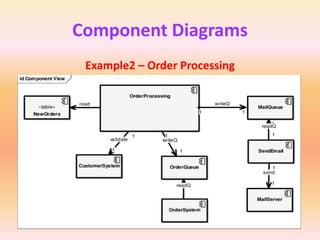
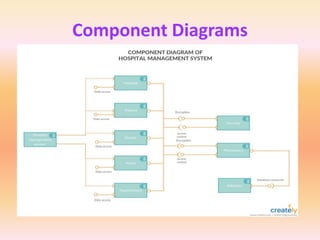
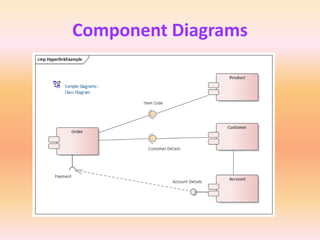
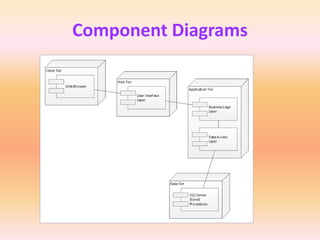
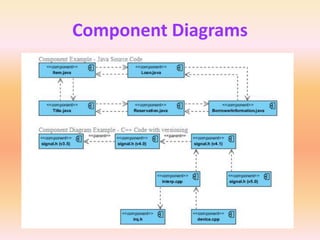
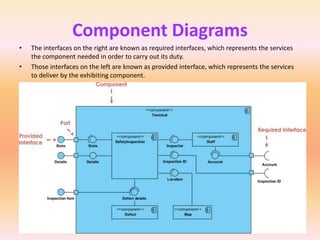
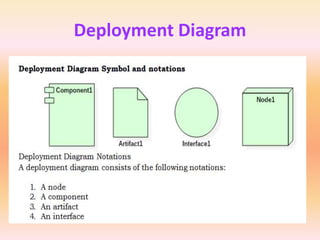
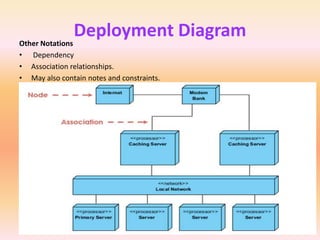
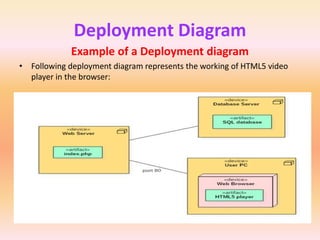
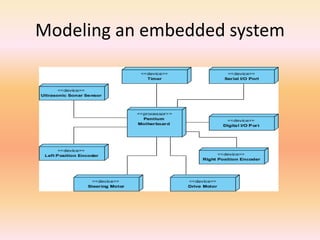
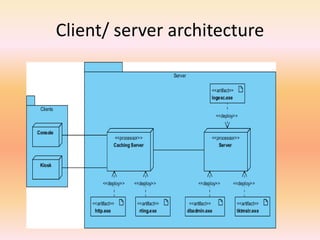
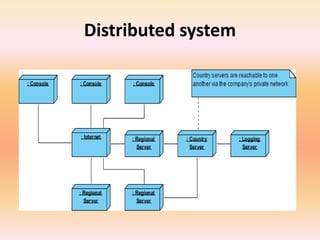
The document describes component diagrams in UML. It defines that a component diagram models the organization and connections between physical components in a system. It notes that component diagrams can help ensure all required system functions are covered in development. The document outlines the basic symbols used in component diagrams like components, interfaces, dependencies, and ports. It provides examples of how component diagrams can model programs and order processing systems.