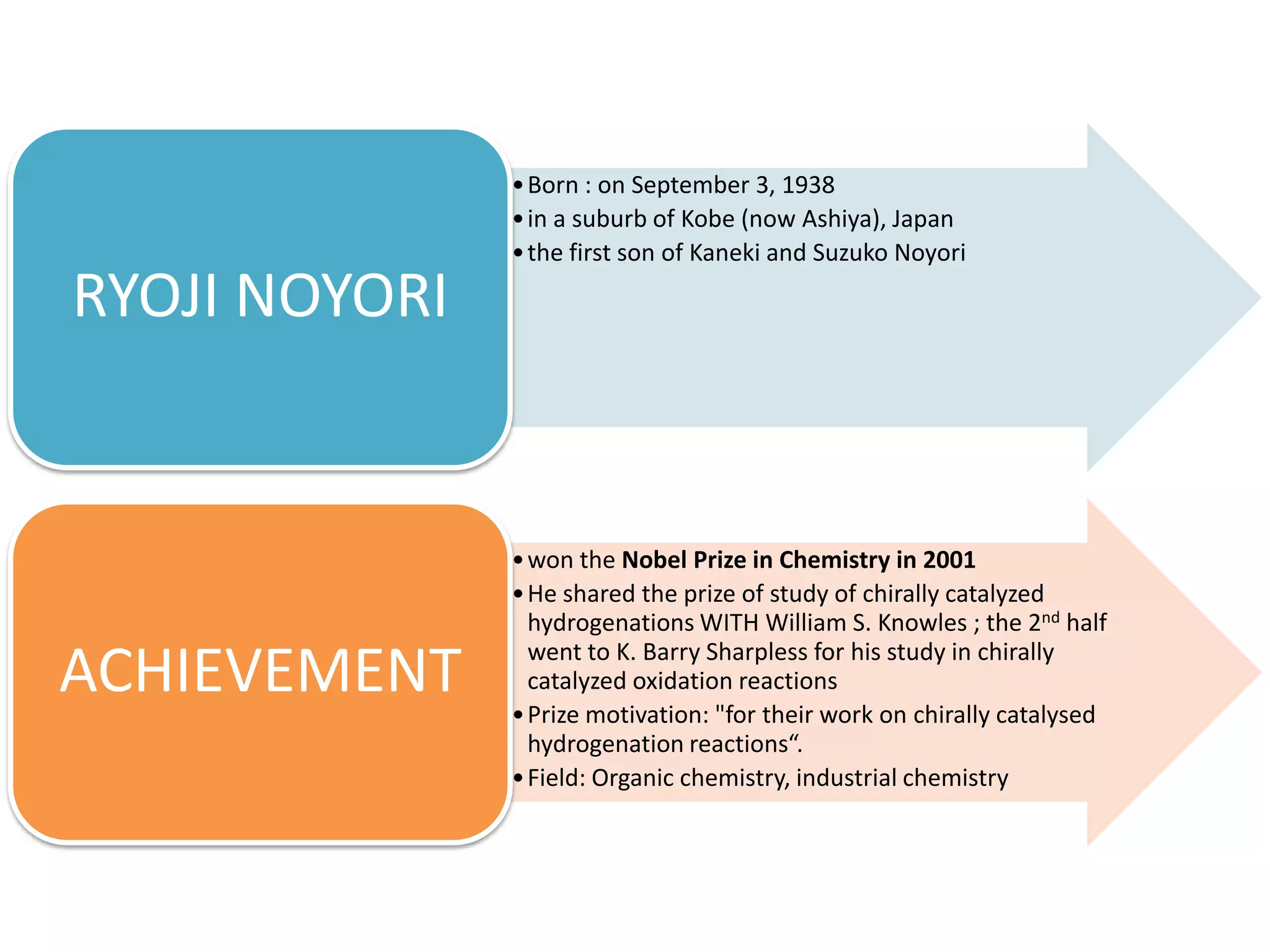
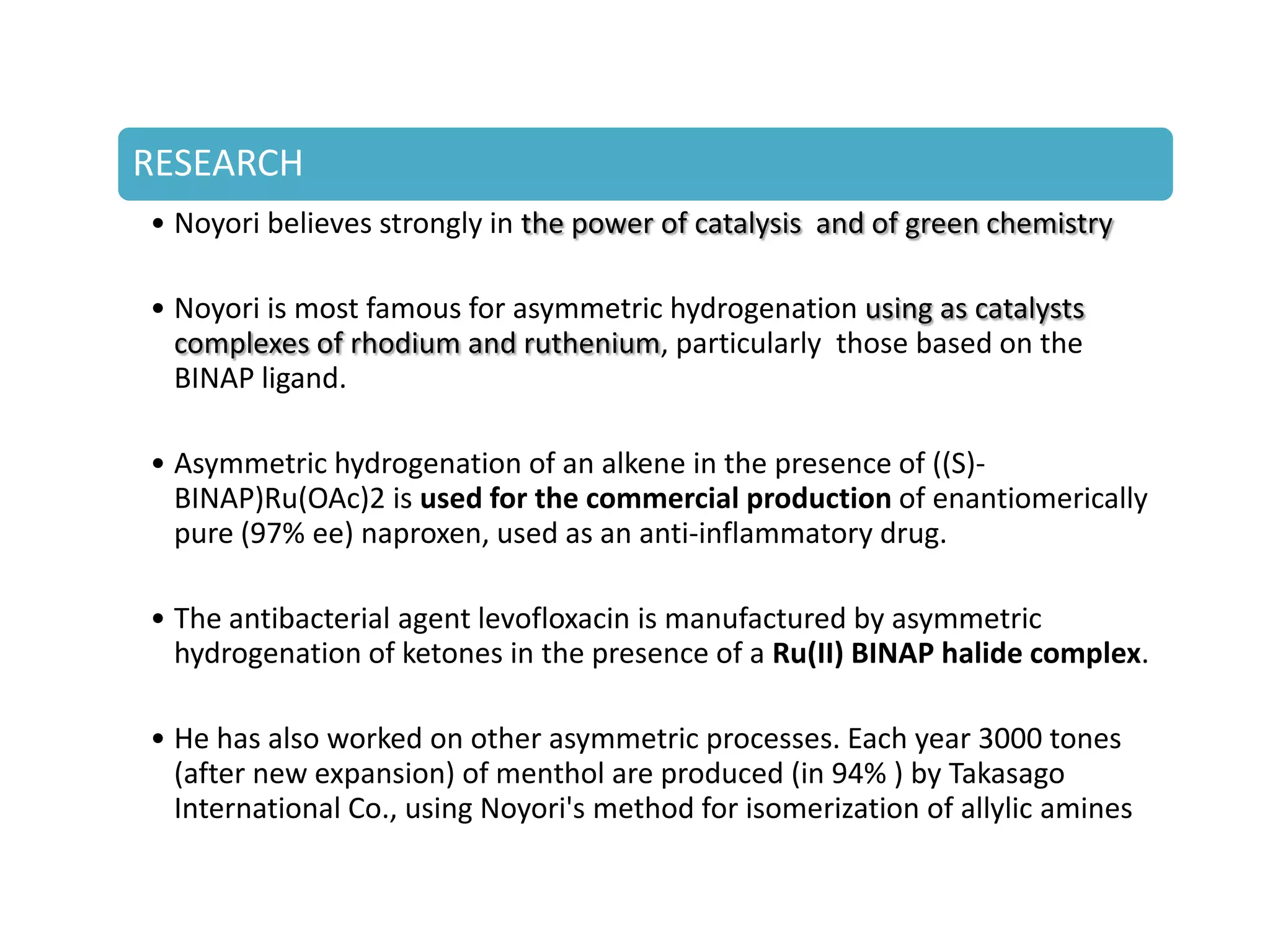
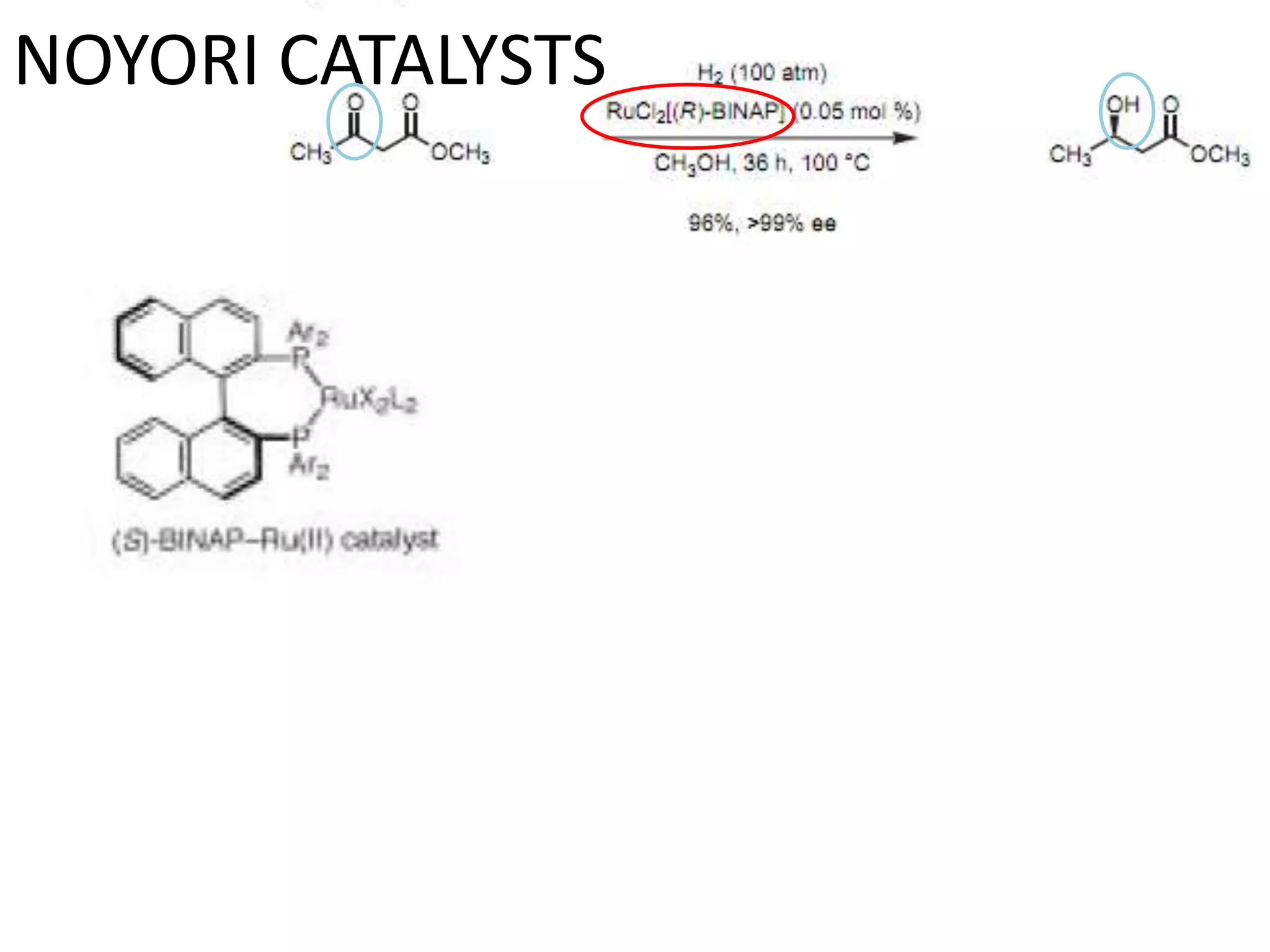
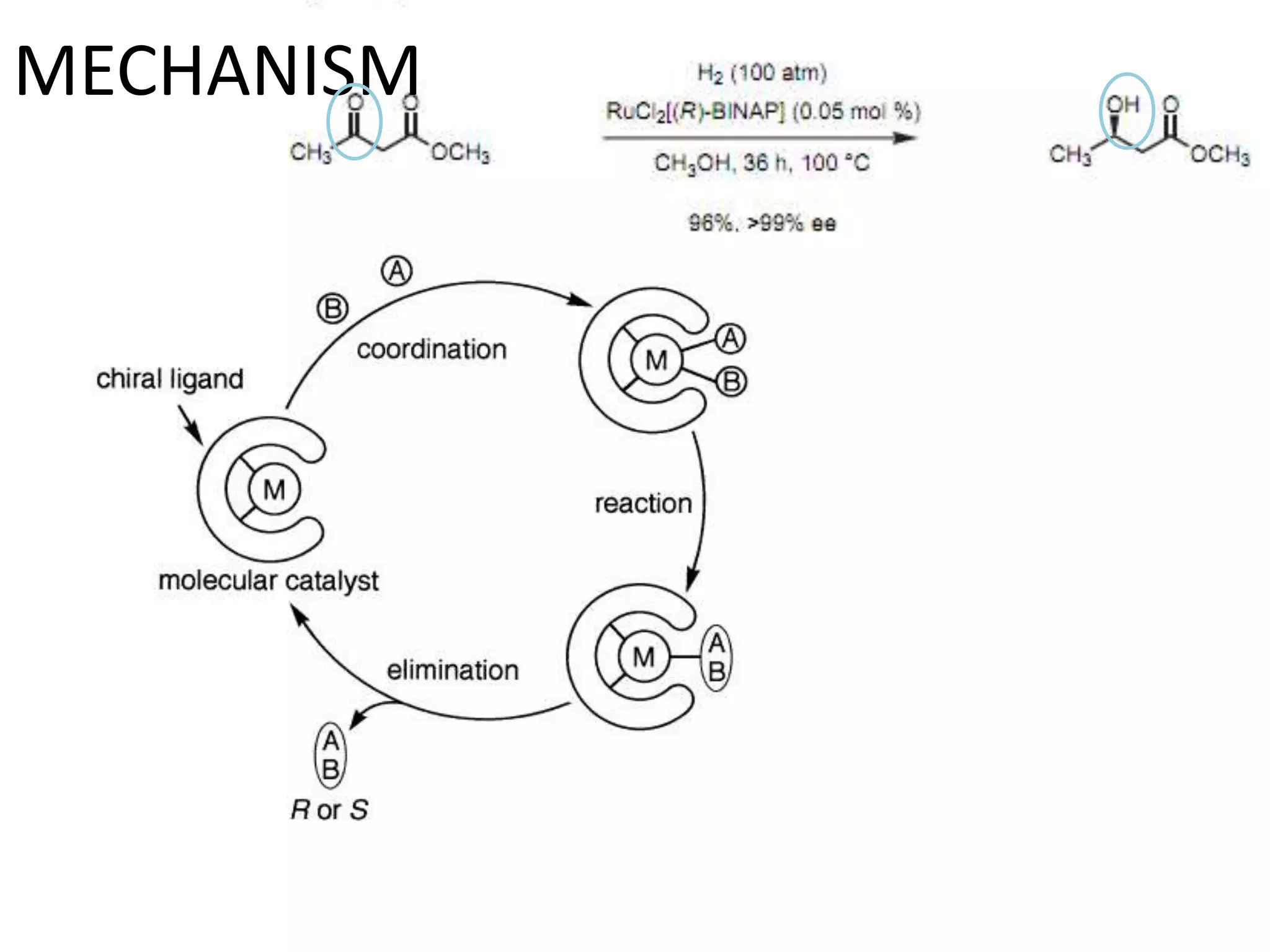
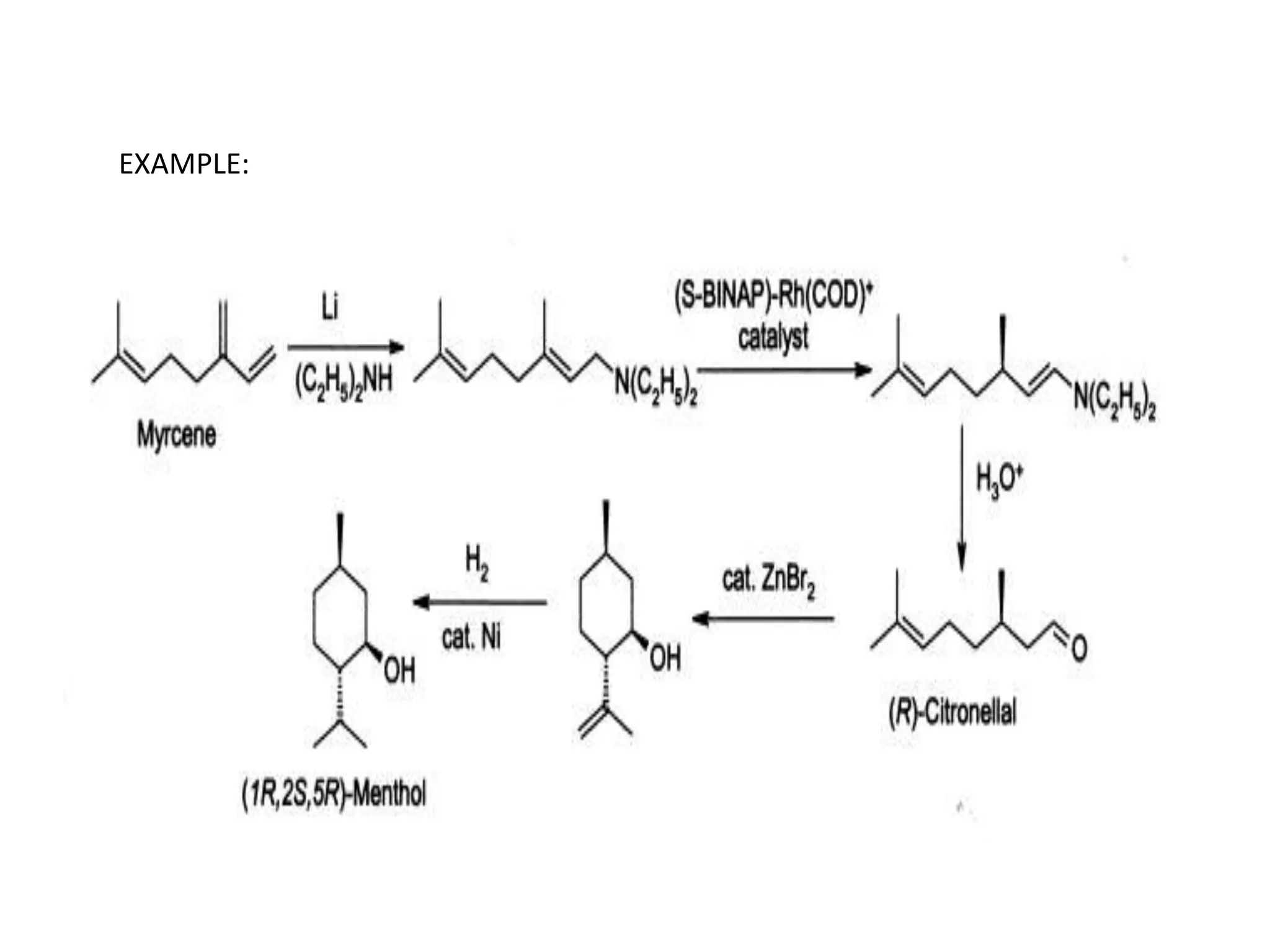
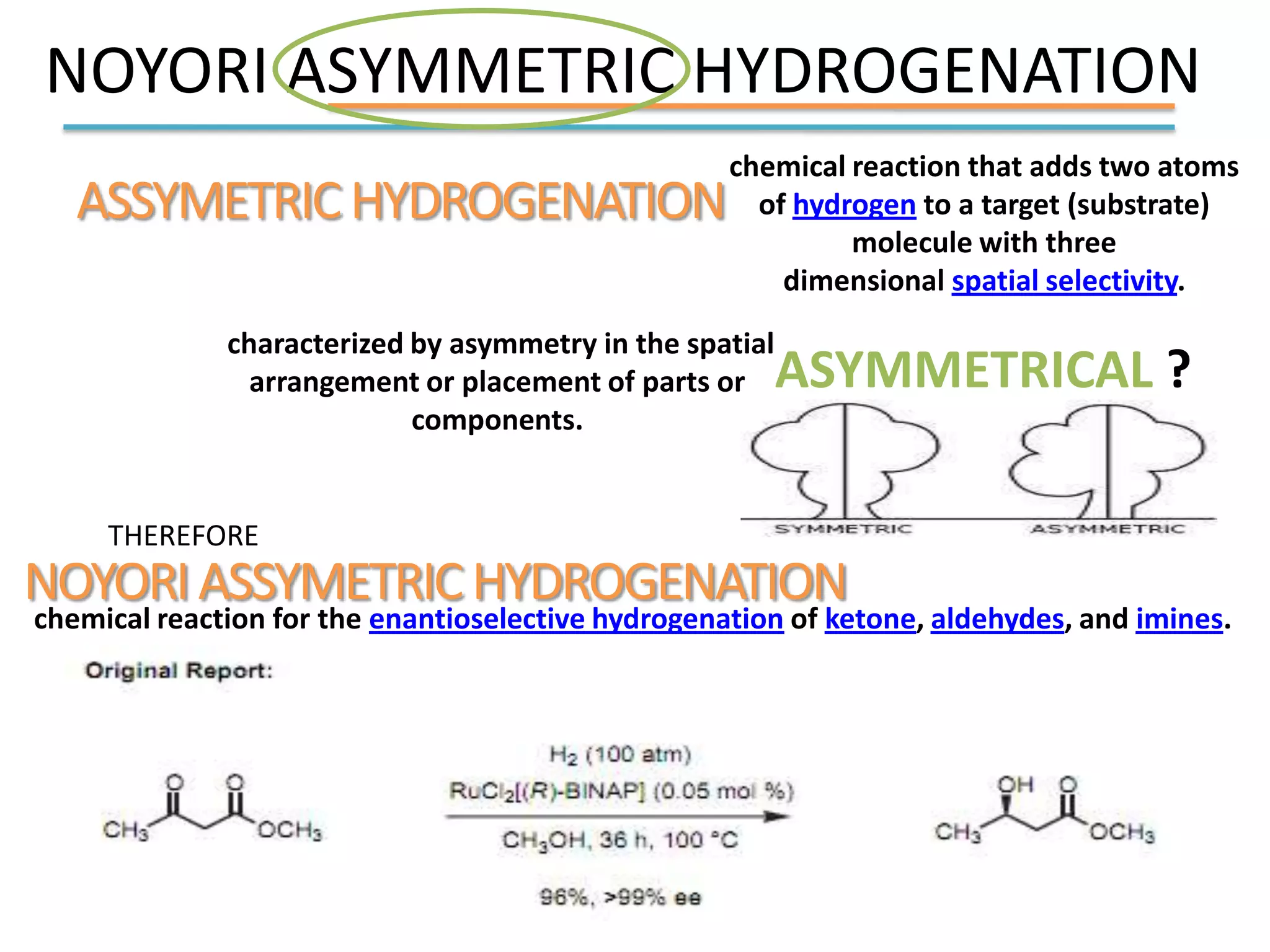
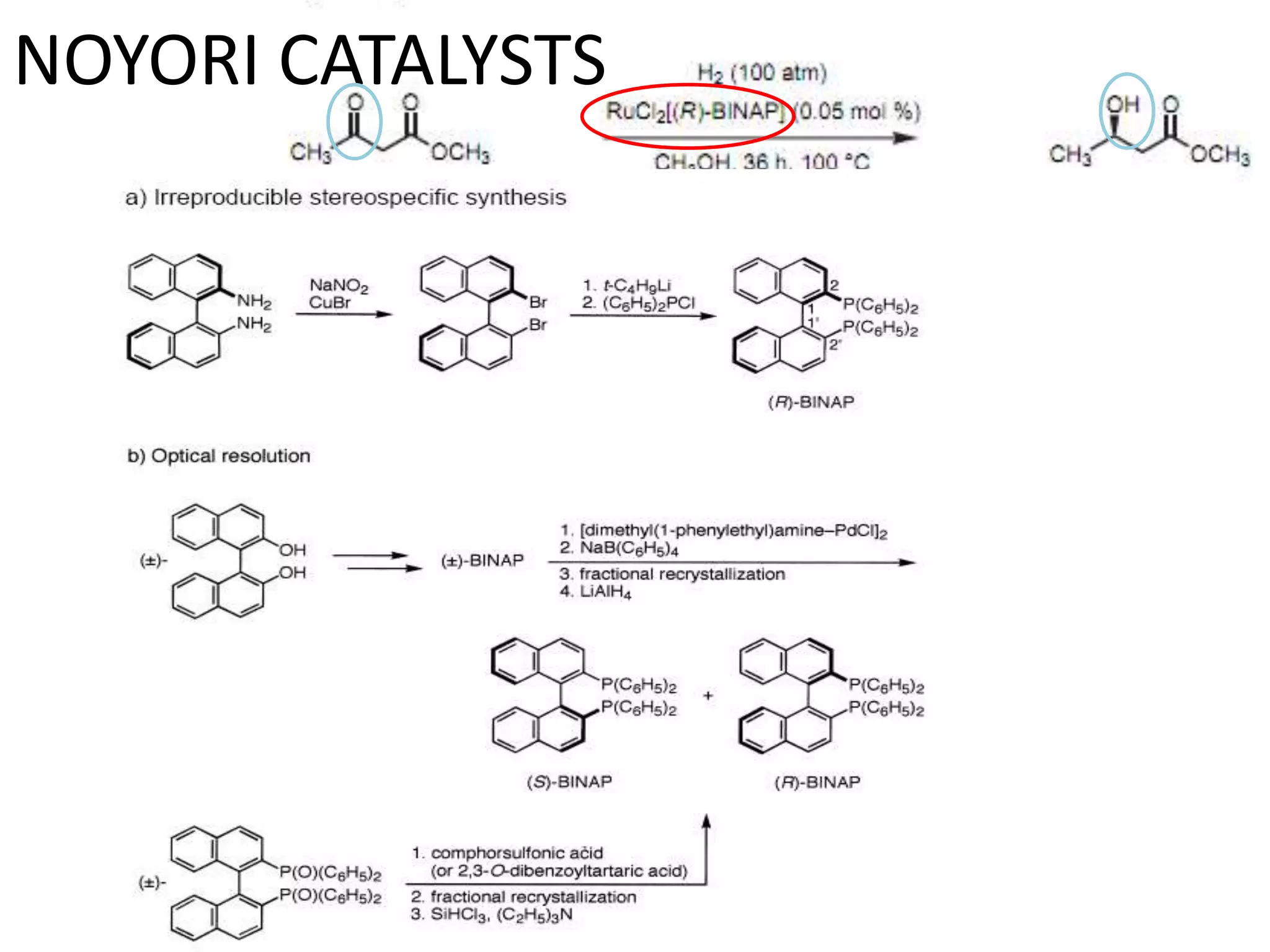
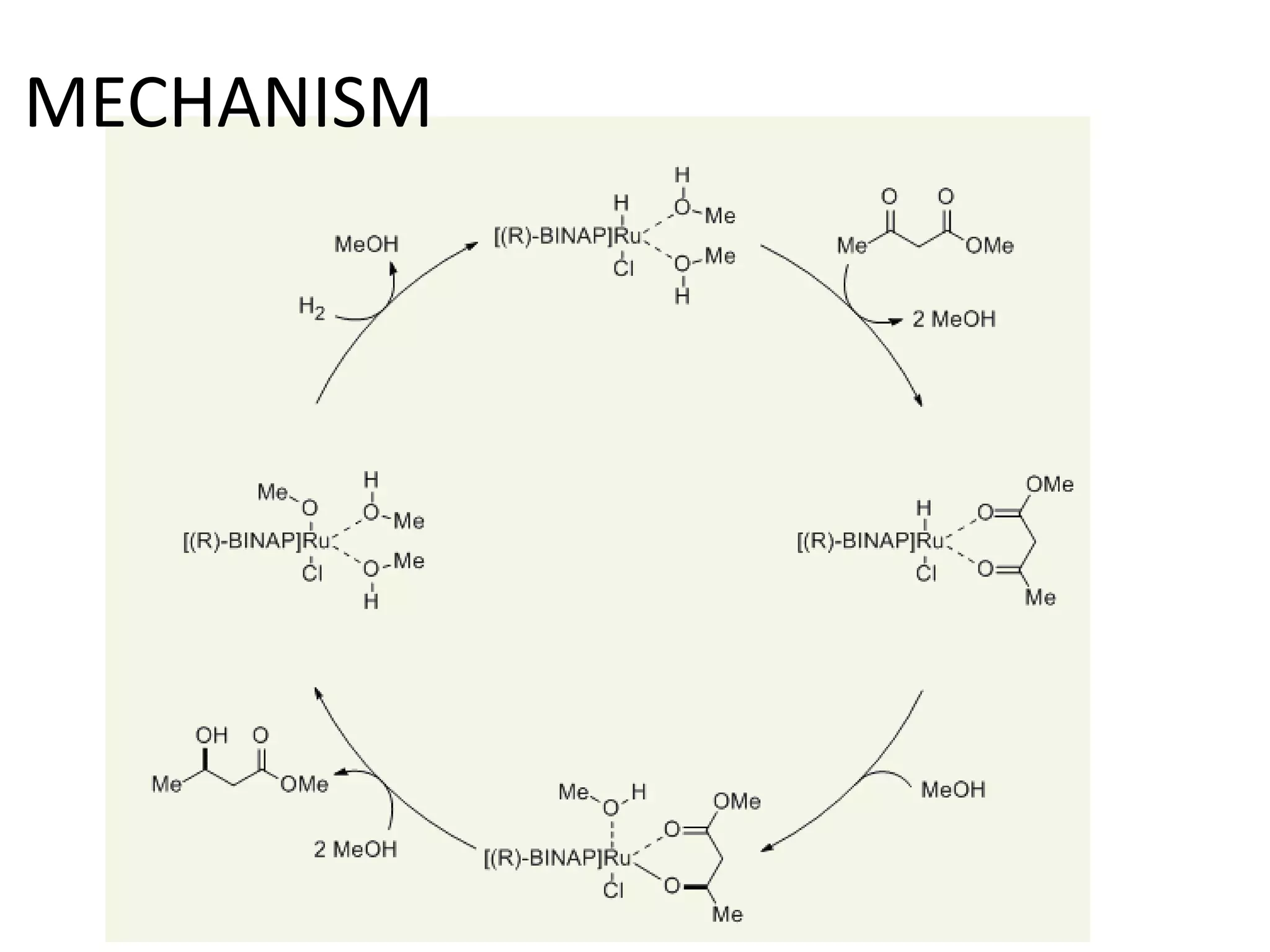
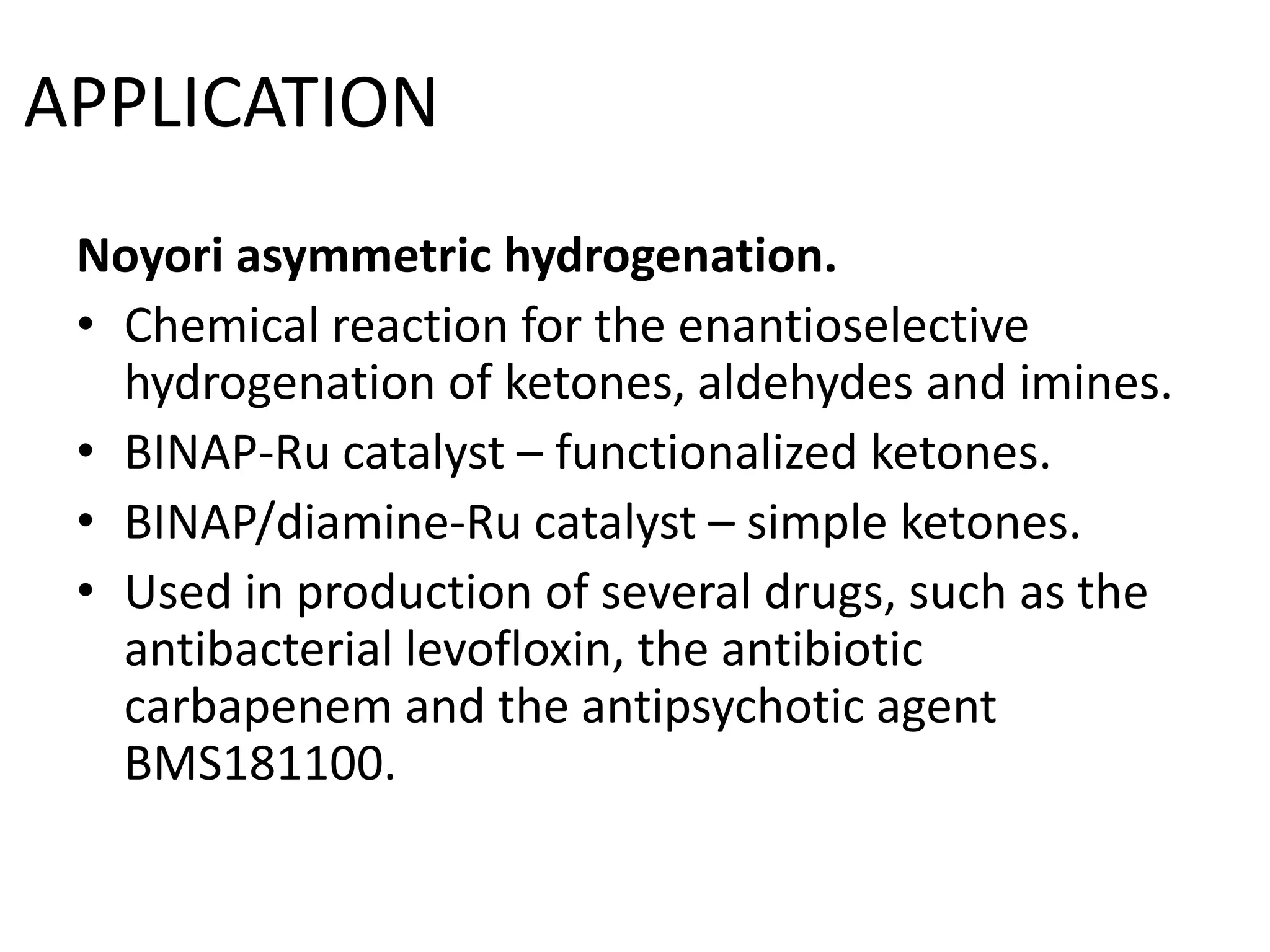
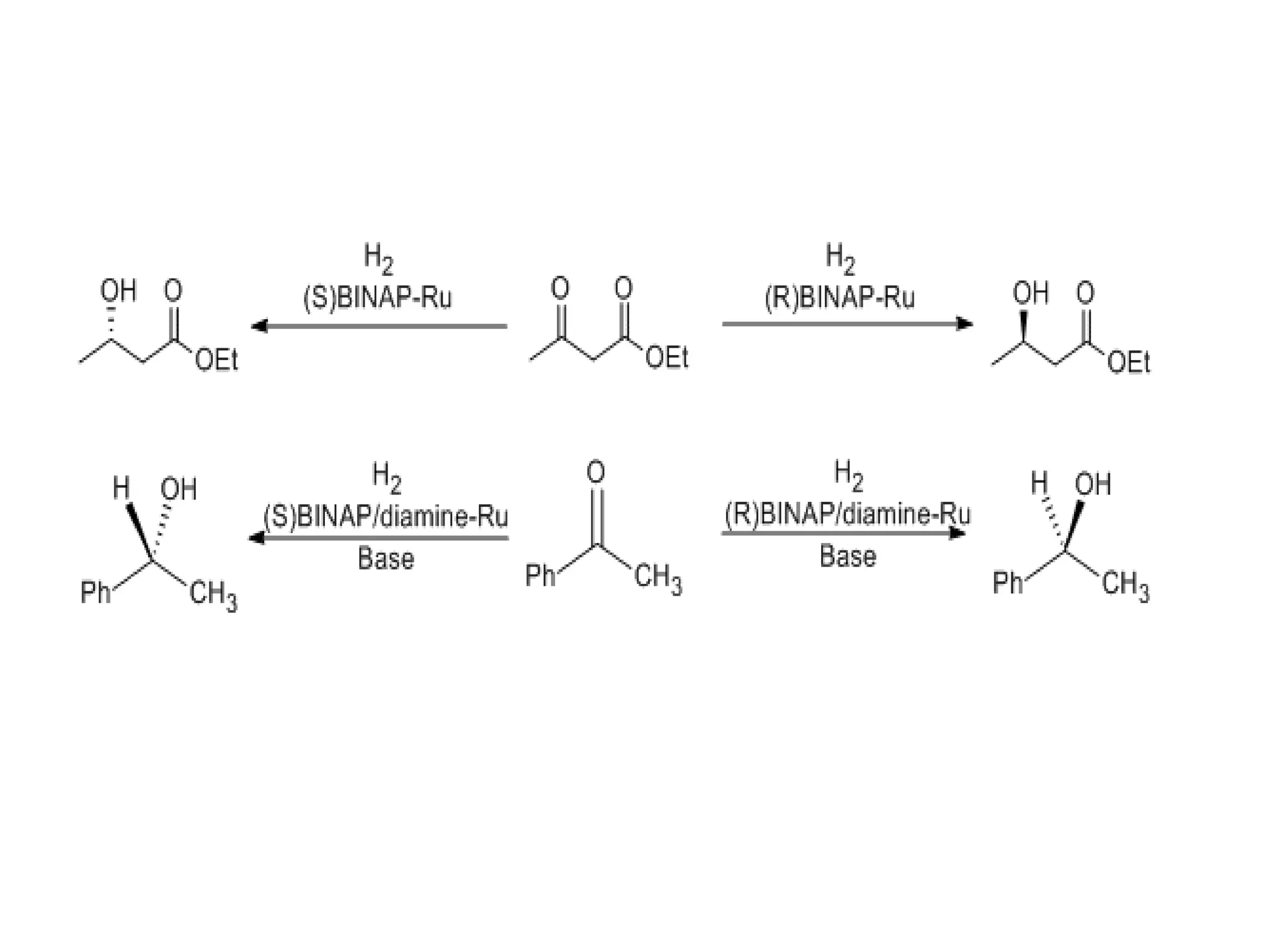
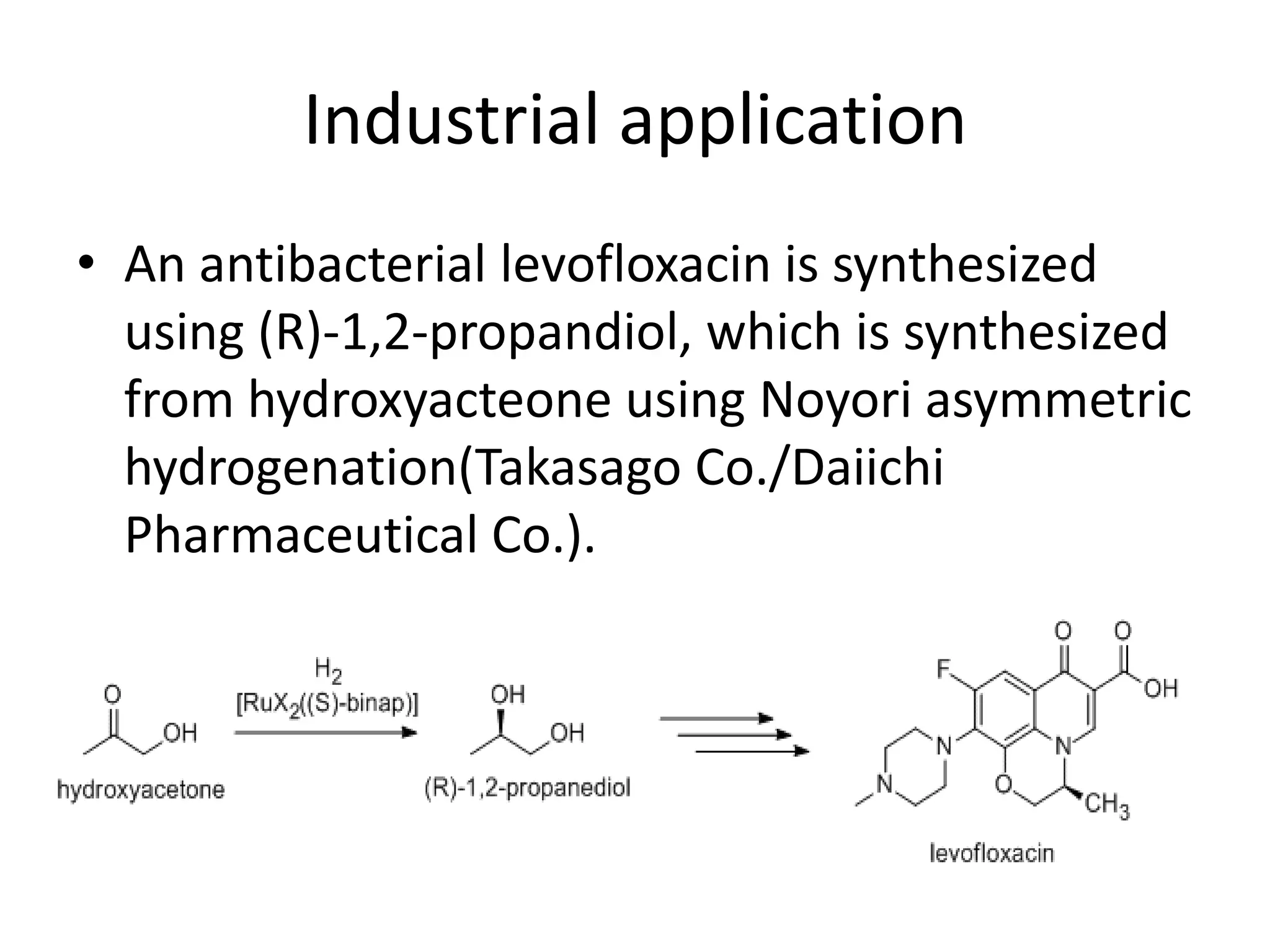
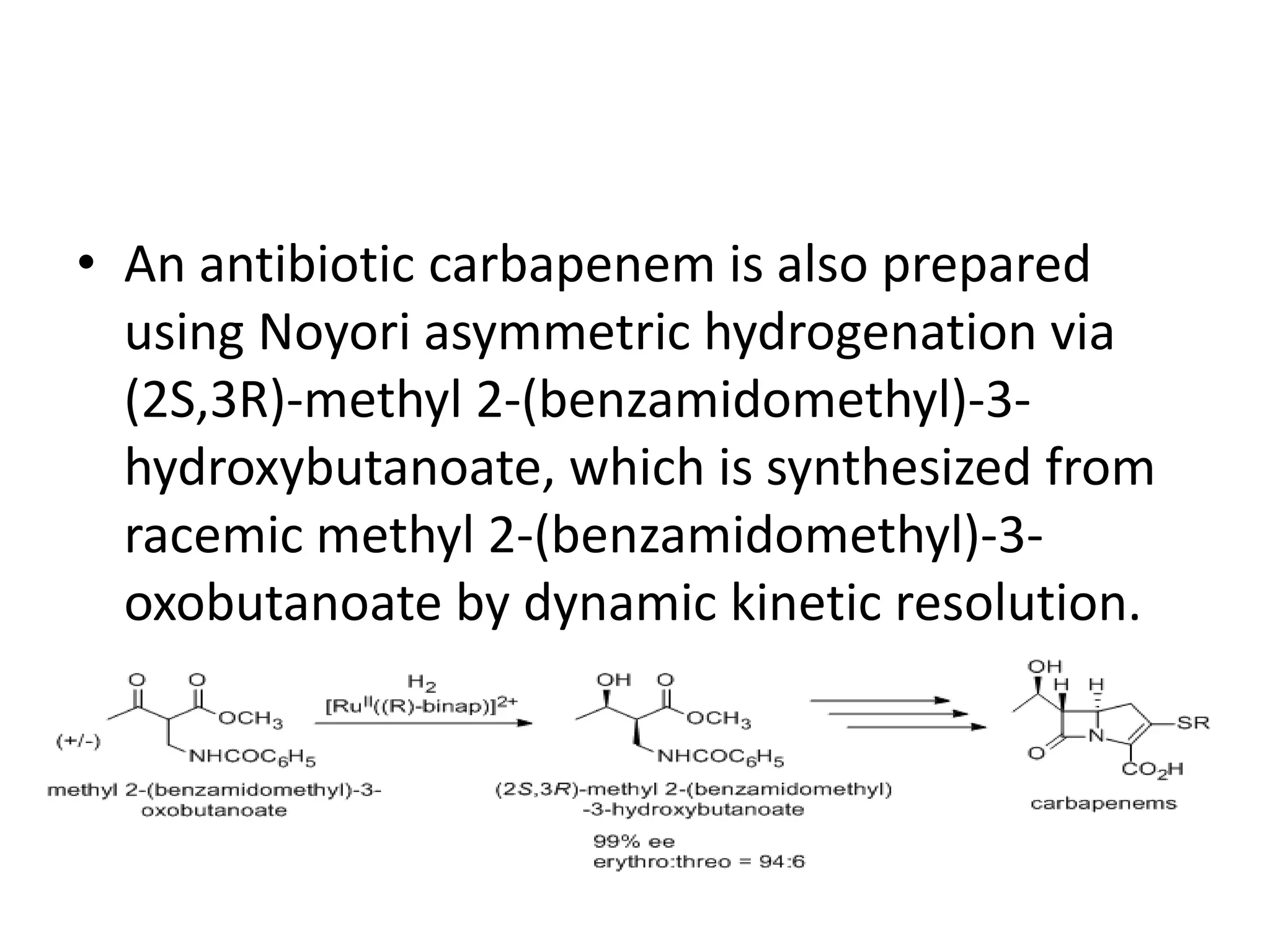
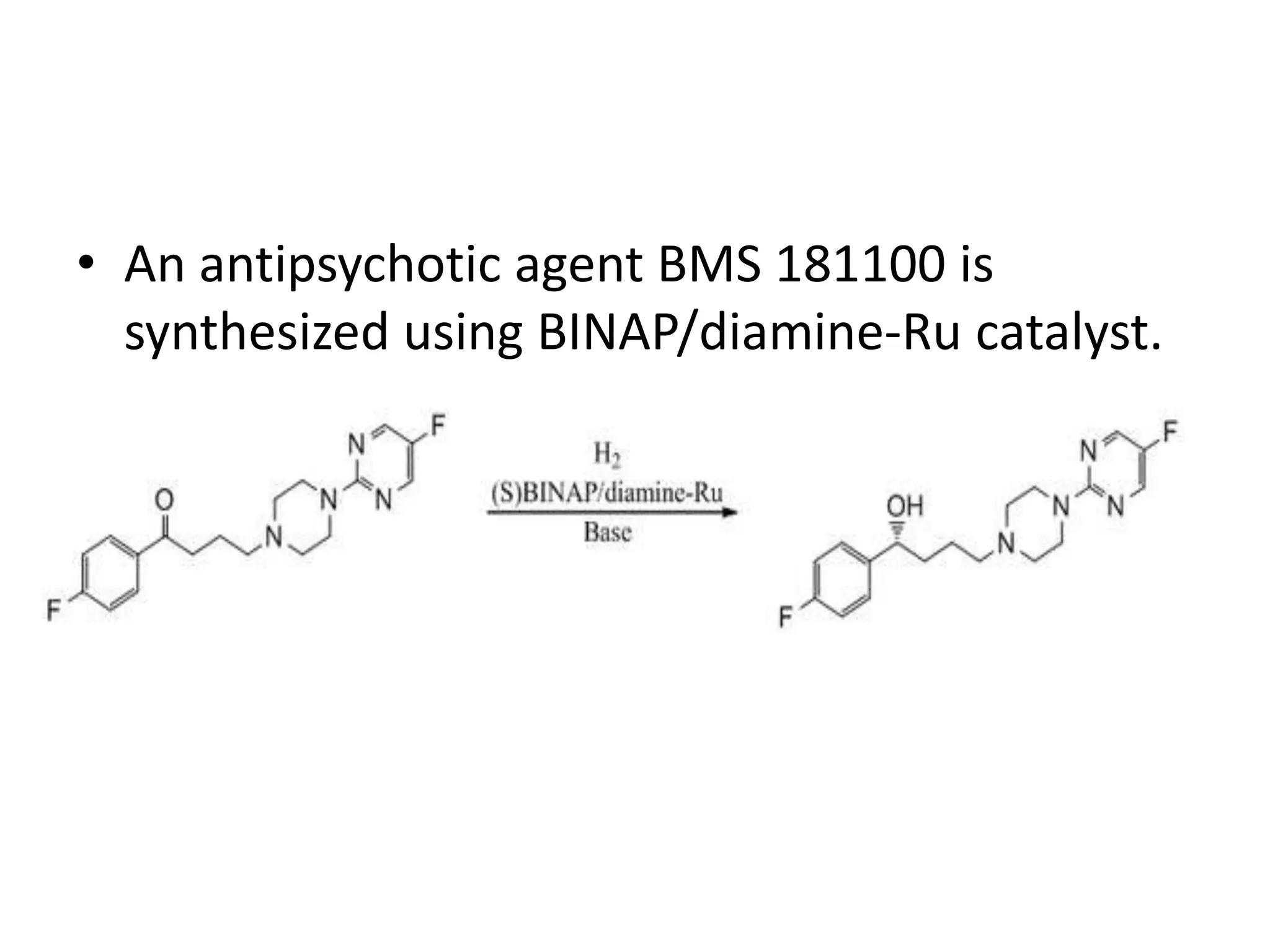
Ryoji Noyori was born in 1938 in Japan and won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2001 for his work developing chiral catalysts for asymmetric hydrogenation reactions. Some of his key accomplishments include developing ruthenium and rhodium complexes with BINAP ligands that allow for the asymmetric hydrogenation of alkenes. This has enabled the commercial production of drugs like naproxen. He has also developed catalyst systems for other asymmetric reactions and his methods are used industrially, such as for the production of menthol.