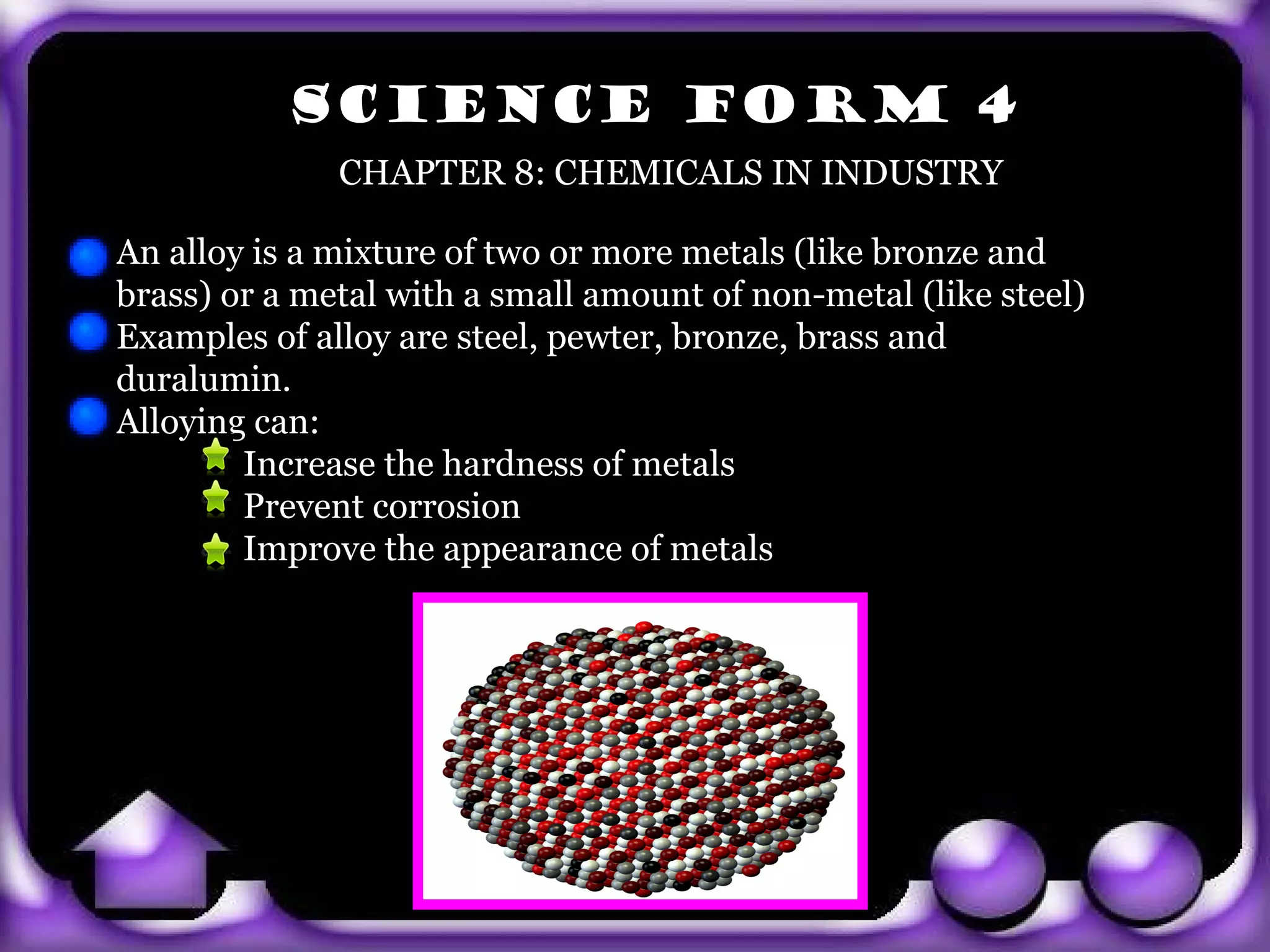
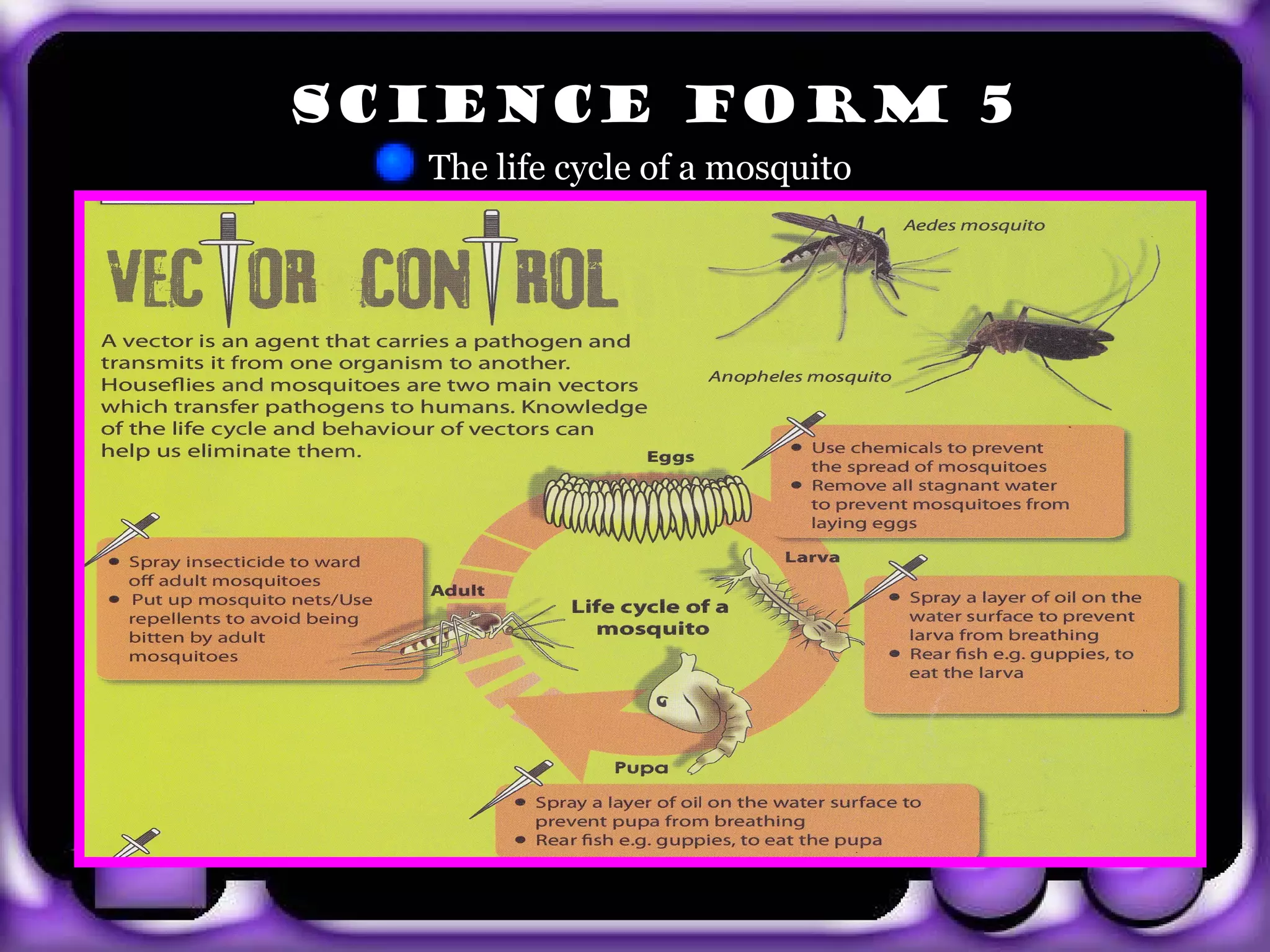
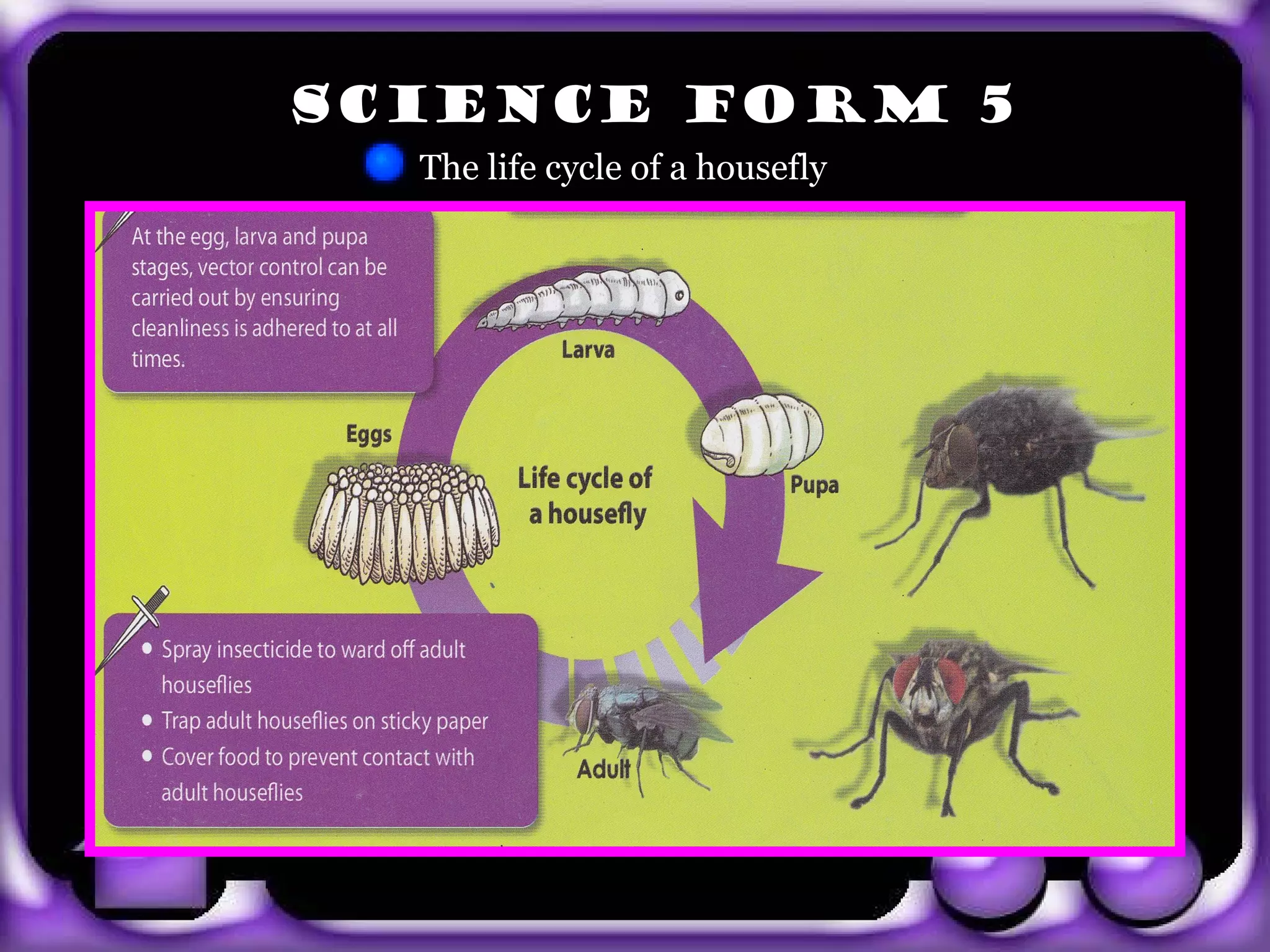
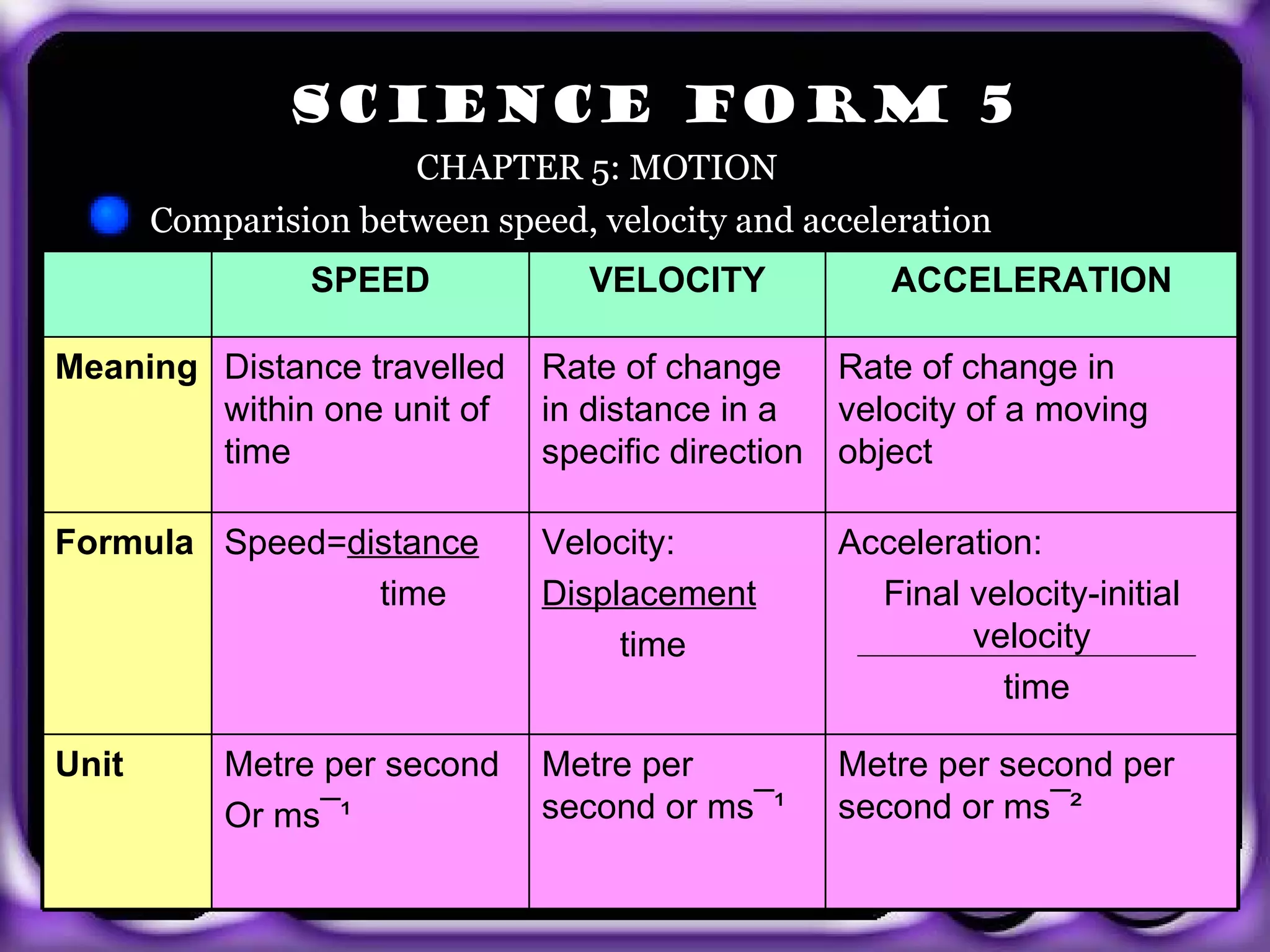
The document provides information about body coordination and the nervous system. It discusses the following key points:
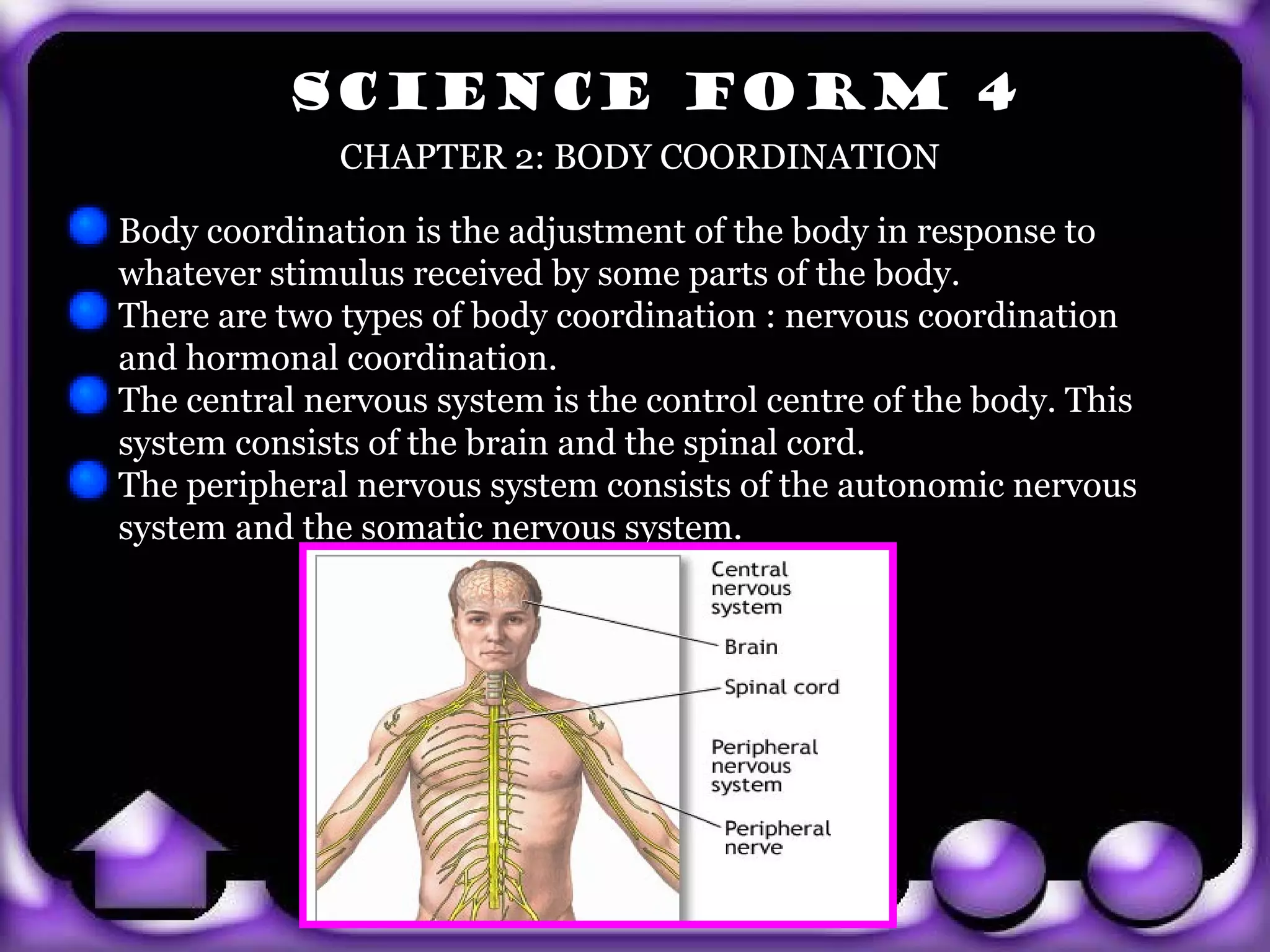
- The central nervous system, made up of the brain and spinal cord, acts as the control center of the body.
- The peripheral nervous system consists of the autonomic and somatic nervous systems.
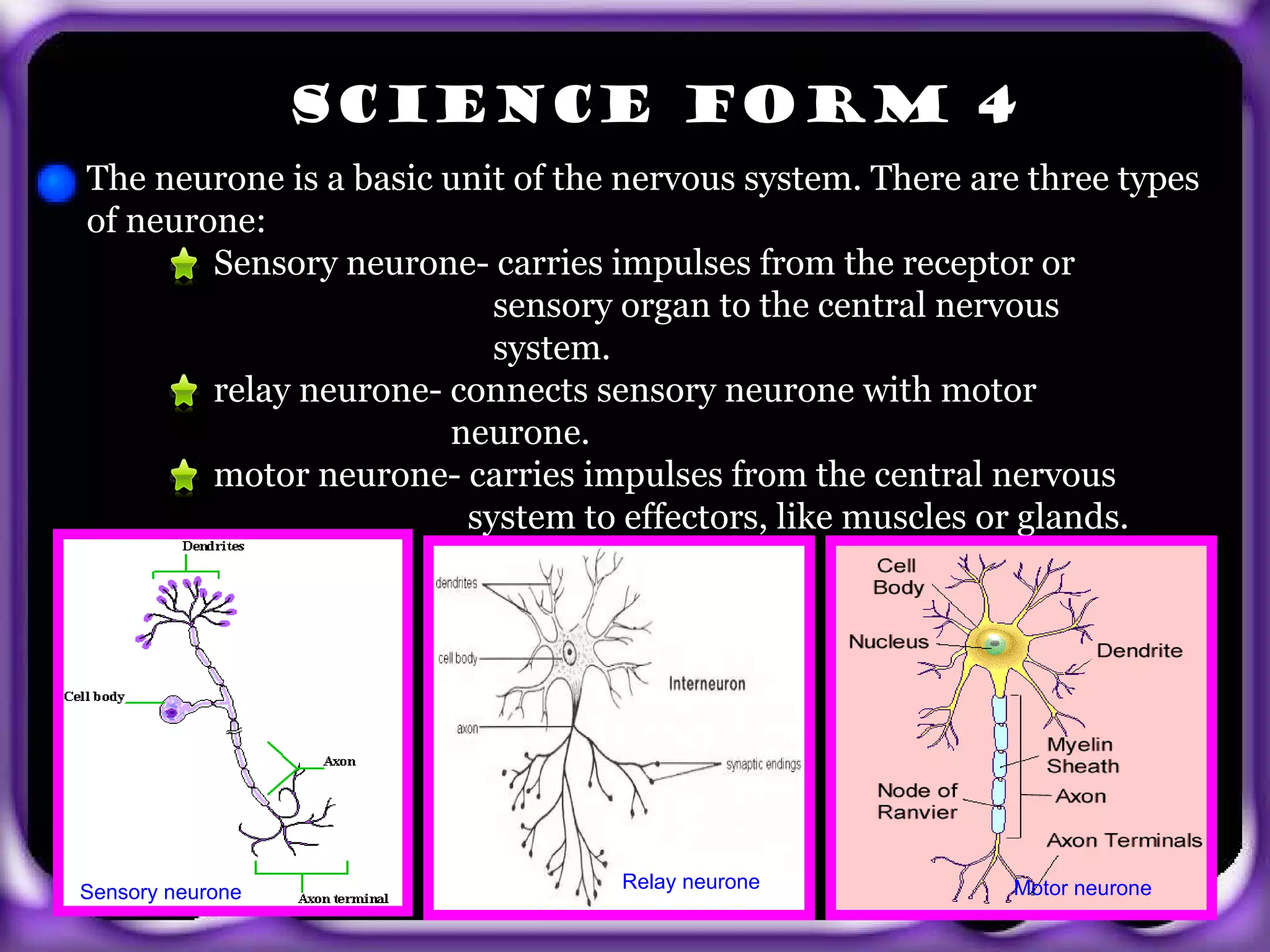
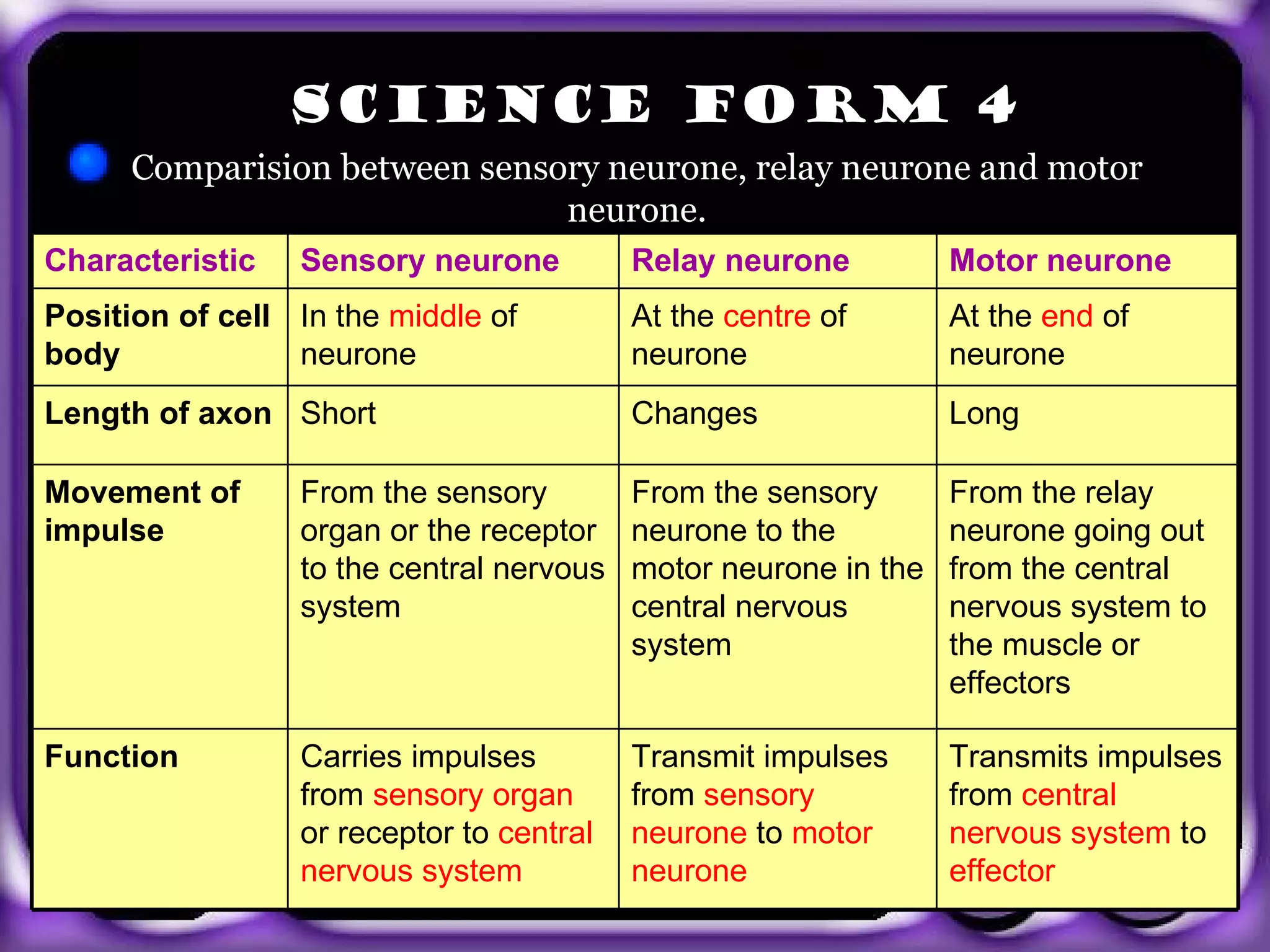
- There are three types of neurons: sensory neurons that carry signals to the CNS, relay neurons that connect sensory and motor neurons, and motor neurons that carry signals from the CNS to effectors like muscles.
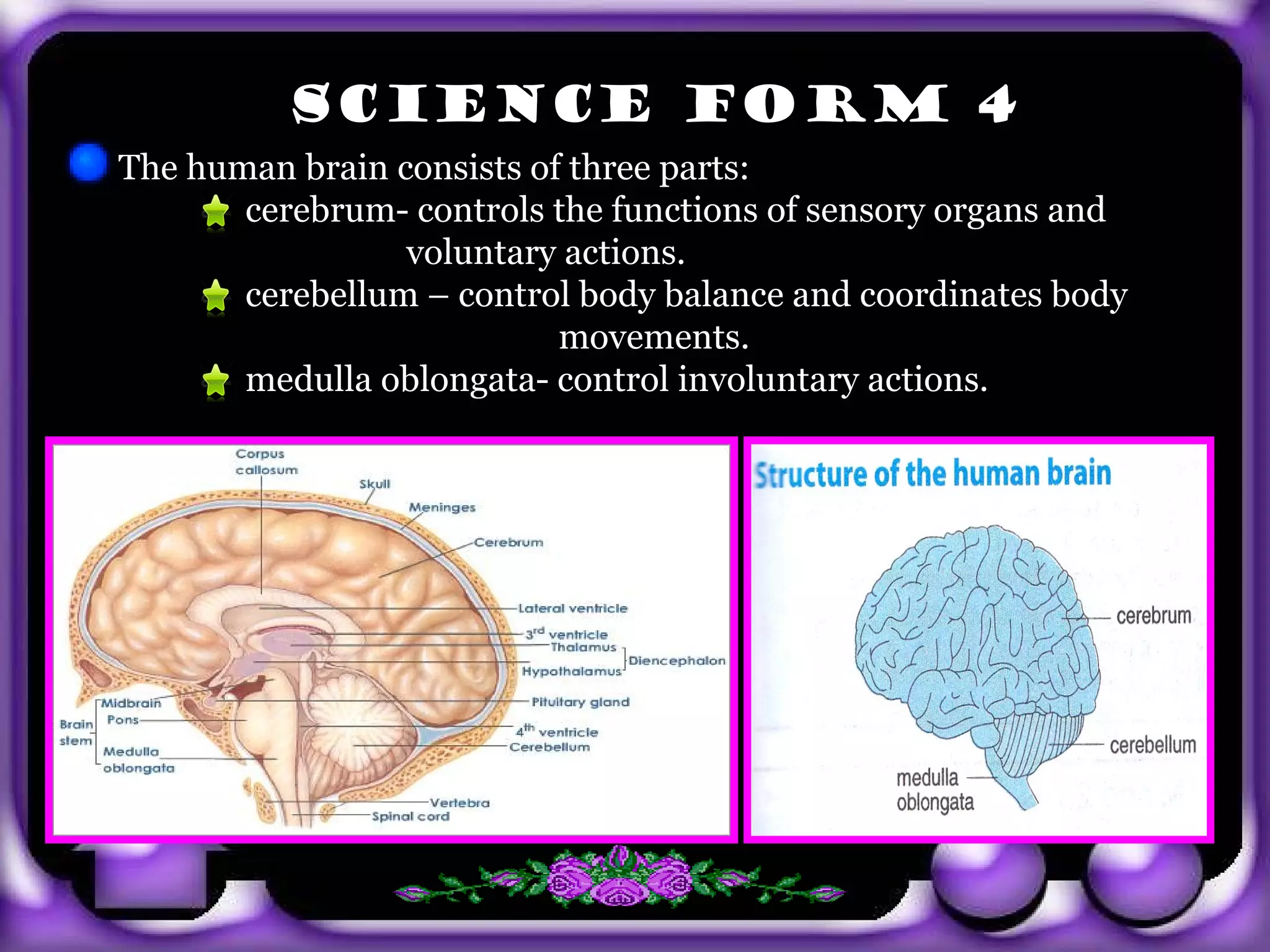
- The brain contains the cerebrum, cerebellum and medulla oblongata, which control various voluntary and involuntary functions.