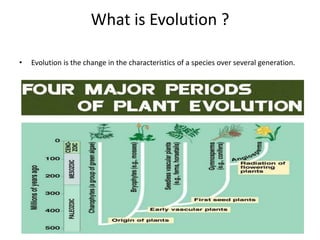
This document contains questions submitted by a student for their PhD dissertation discussion. It includes questions about evolution, genome evolution, gene migration, DNA mutation, intron evolution, genome size variation, gene duplication, and references related to these topics. Experimental evidence is discussed for endosymbiotic theory, chloroplast and mitochondria DNA originating from bacteria, and gene migration between organelle and nuclear genomes.