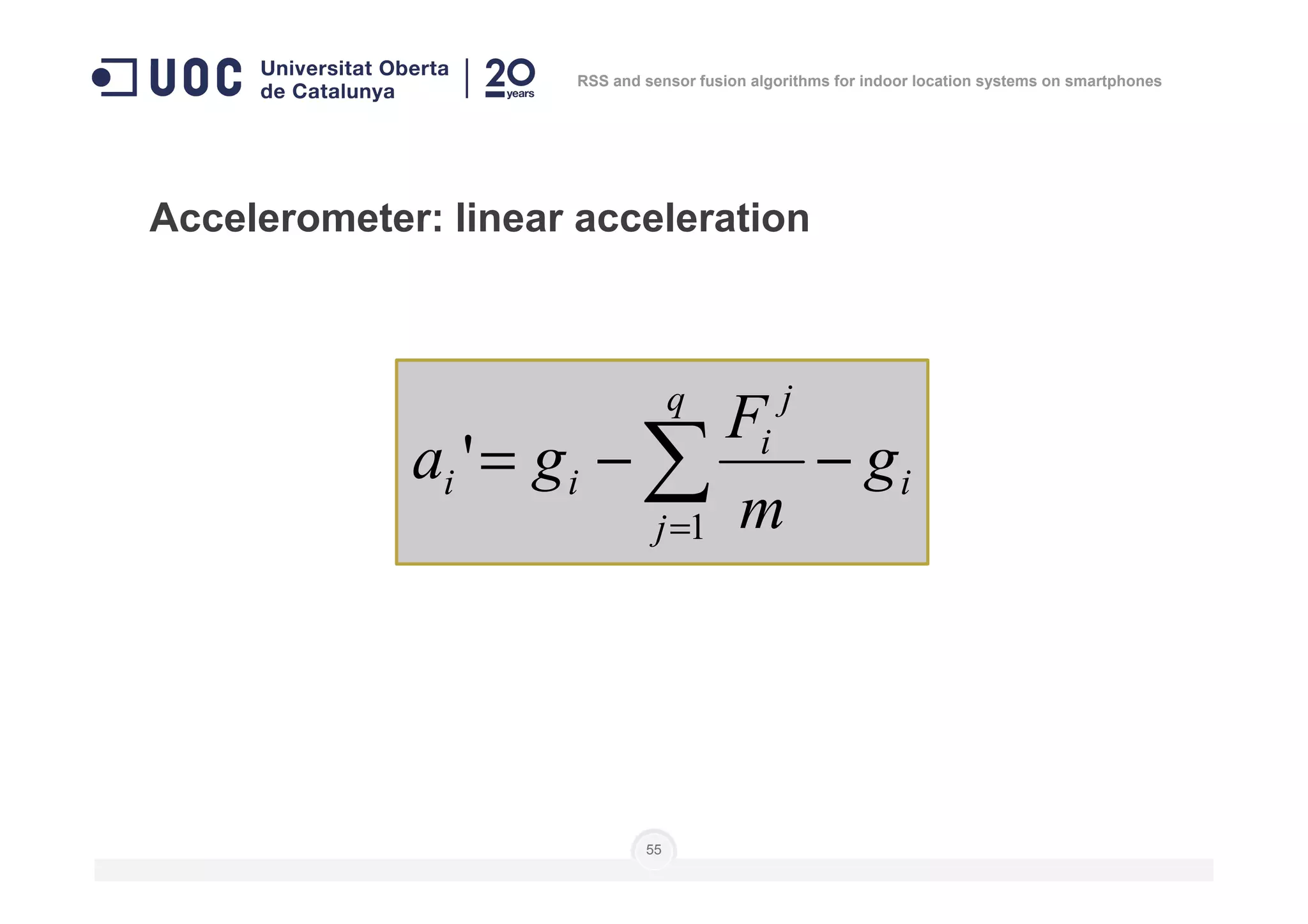
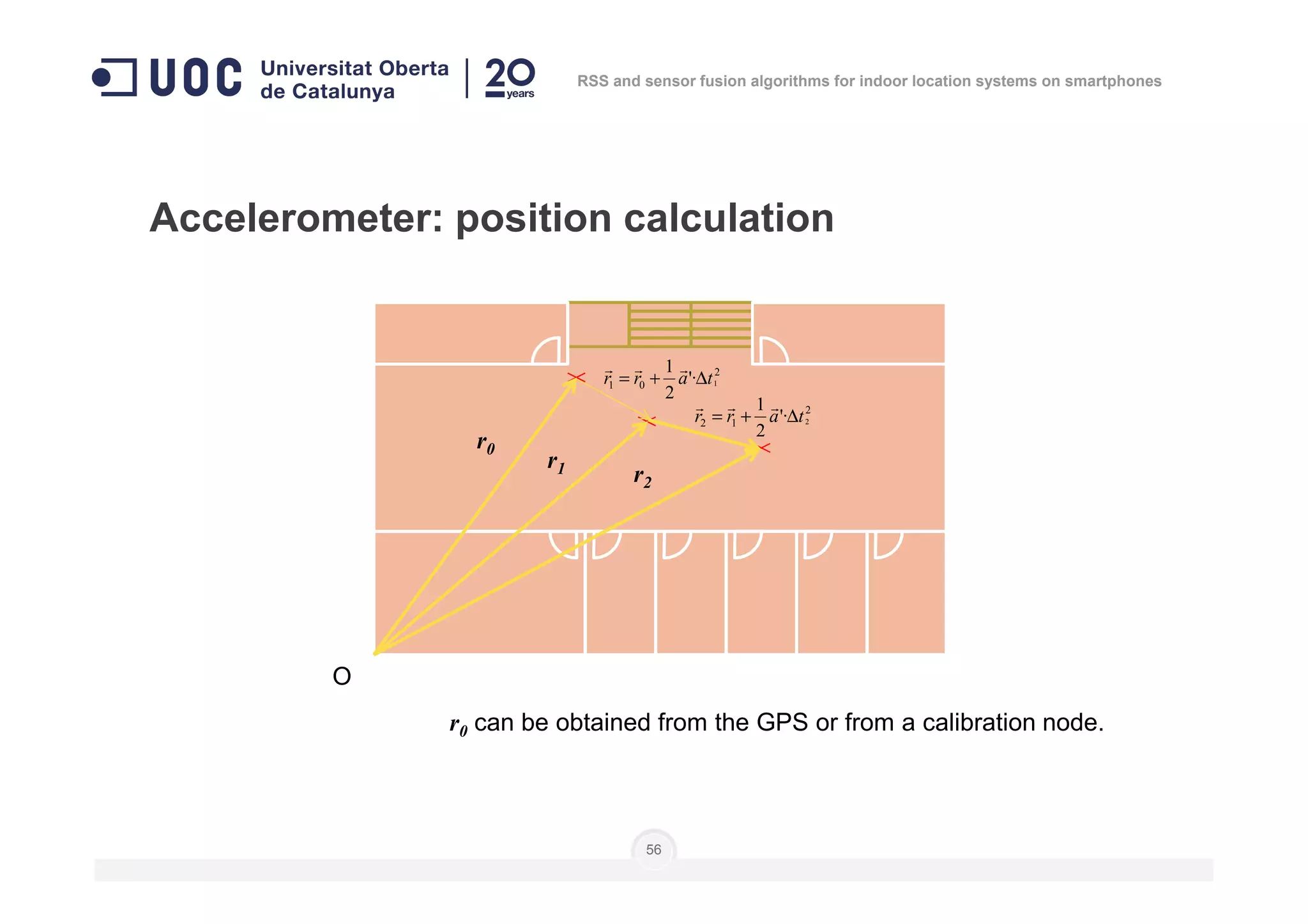
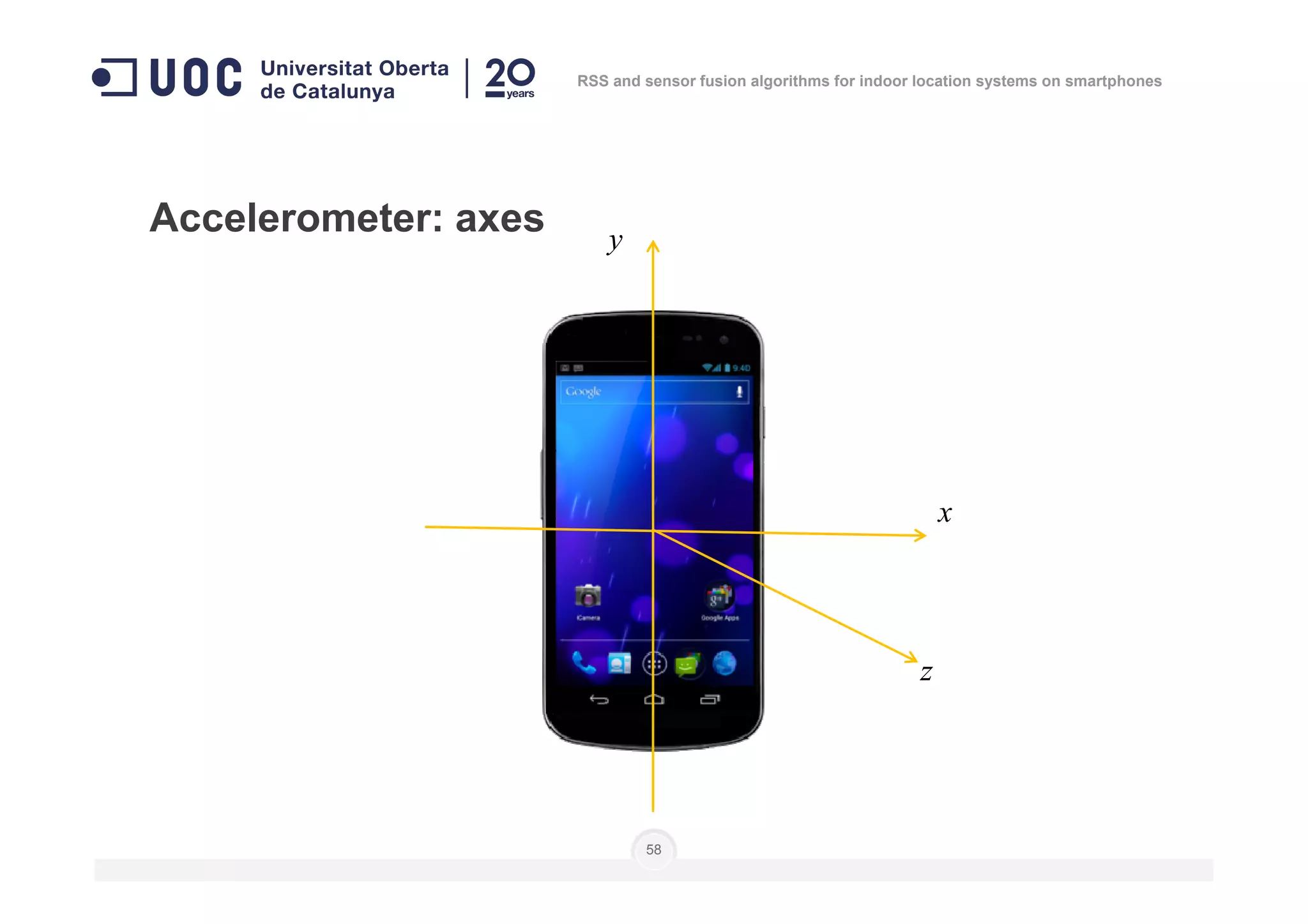
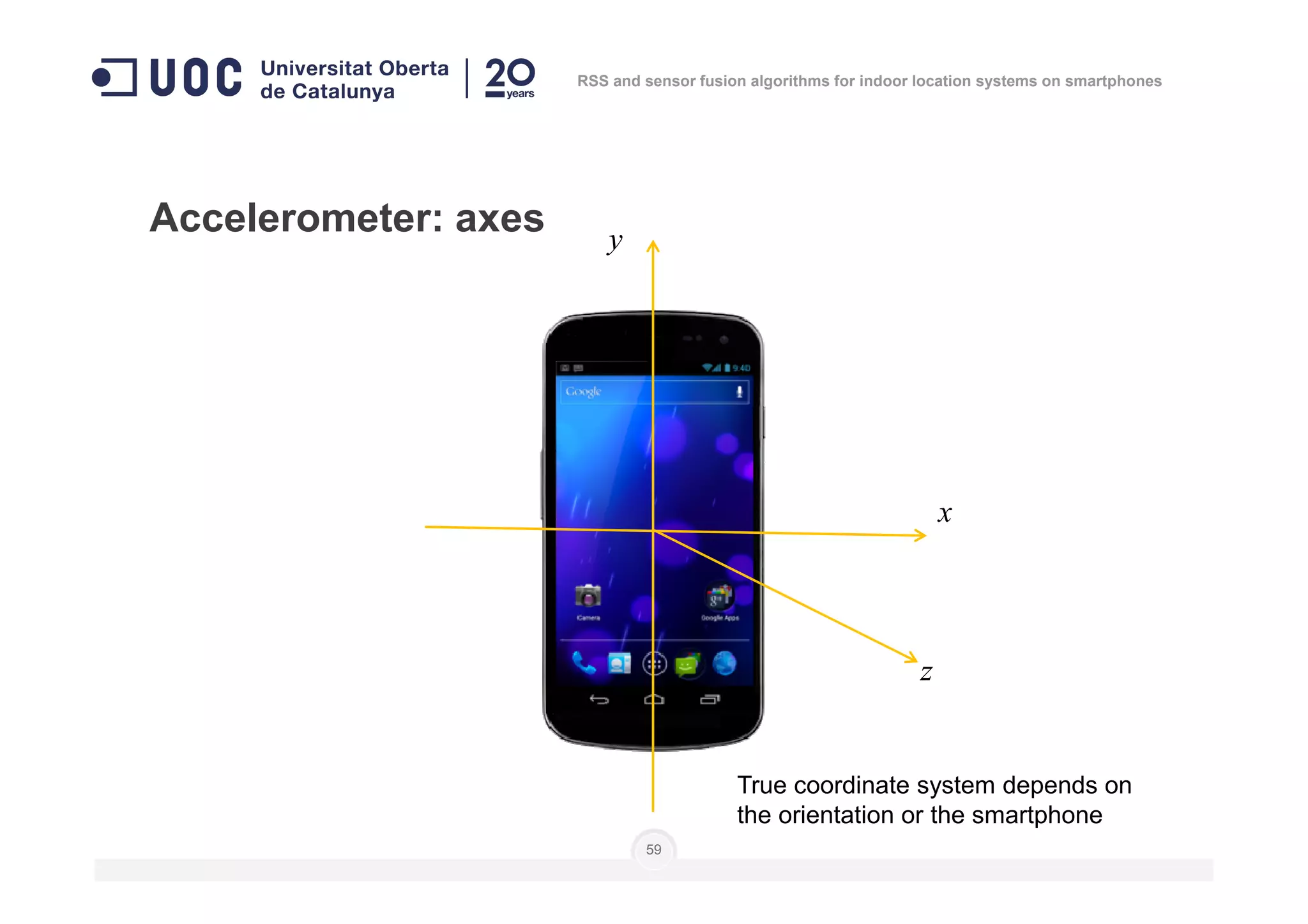
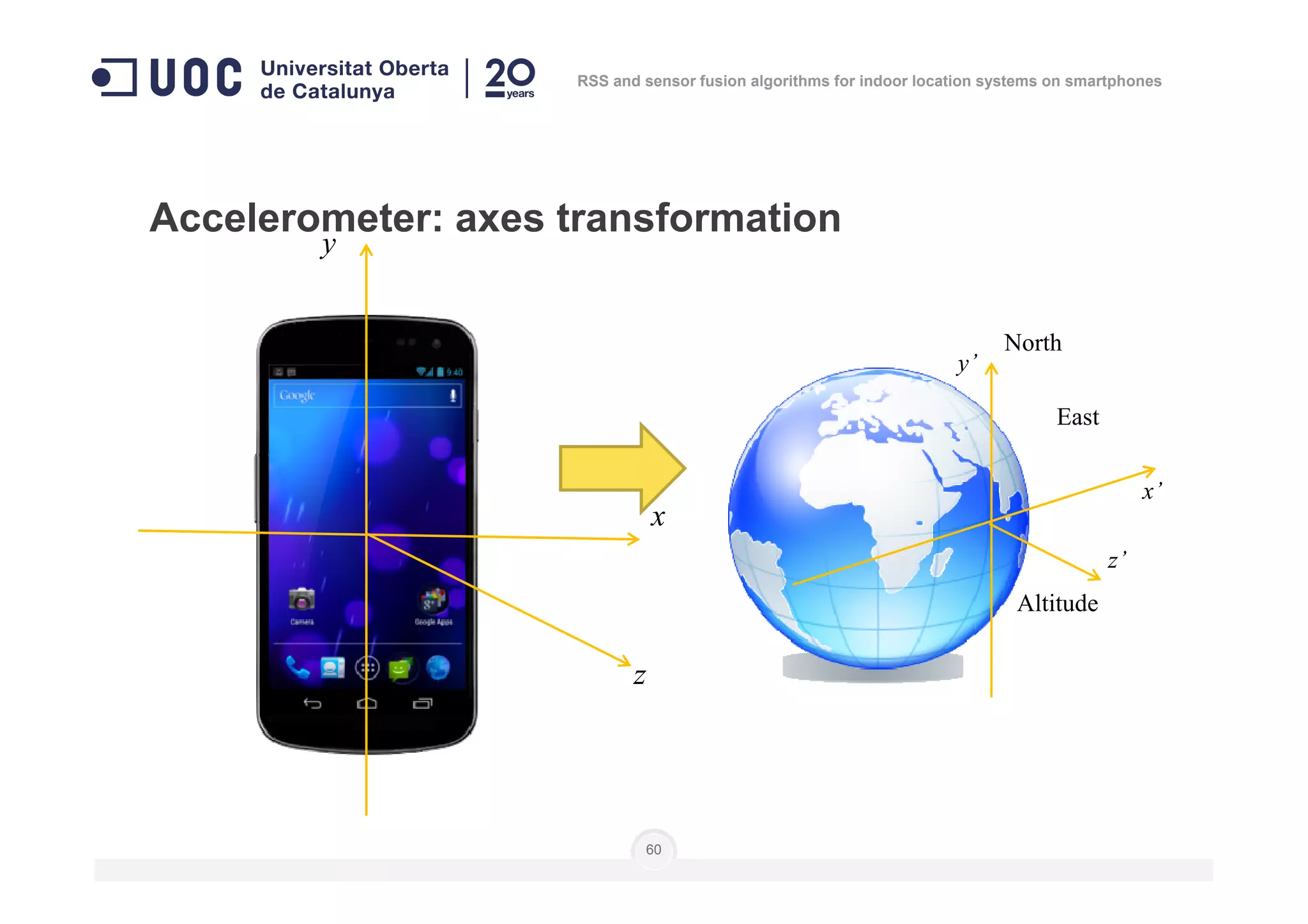
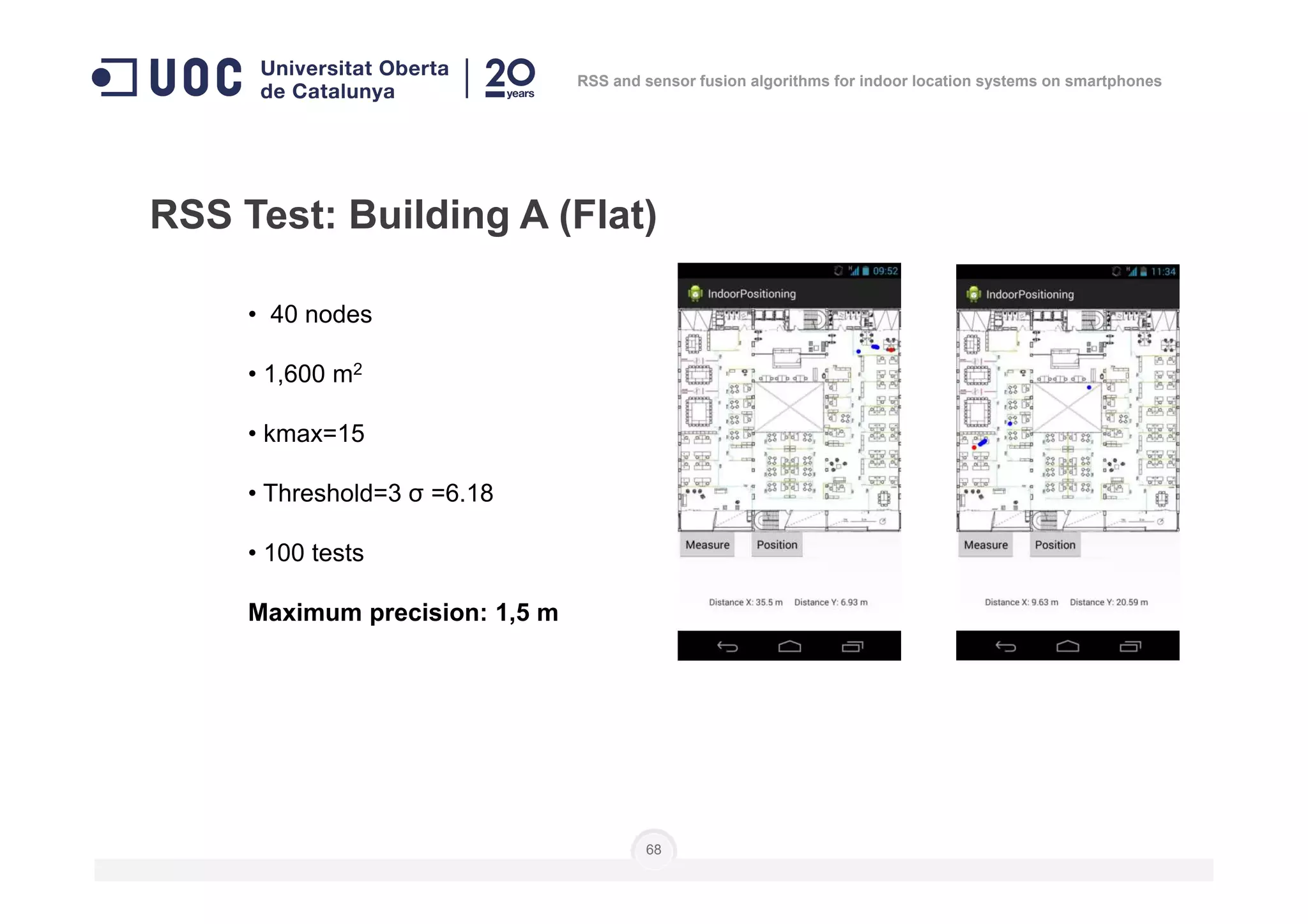
The document discusses the use of RSS and sensor fusion algorithms for indoor location systems on smartphones, highlighting the need for effective positioning methods when GNSS fails indoors. It explores various approaches, including Wi-Fi fingerprinting and inertial systems, as well as the processes of calibration and positioning using existing infrastructure. Key aspects include achieving high precision and a user-friendly experience without requiring an internet connection.

























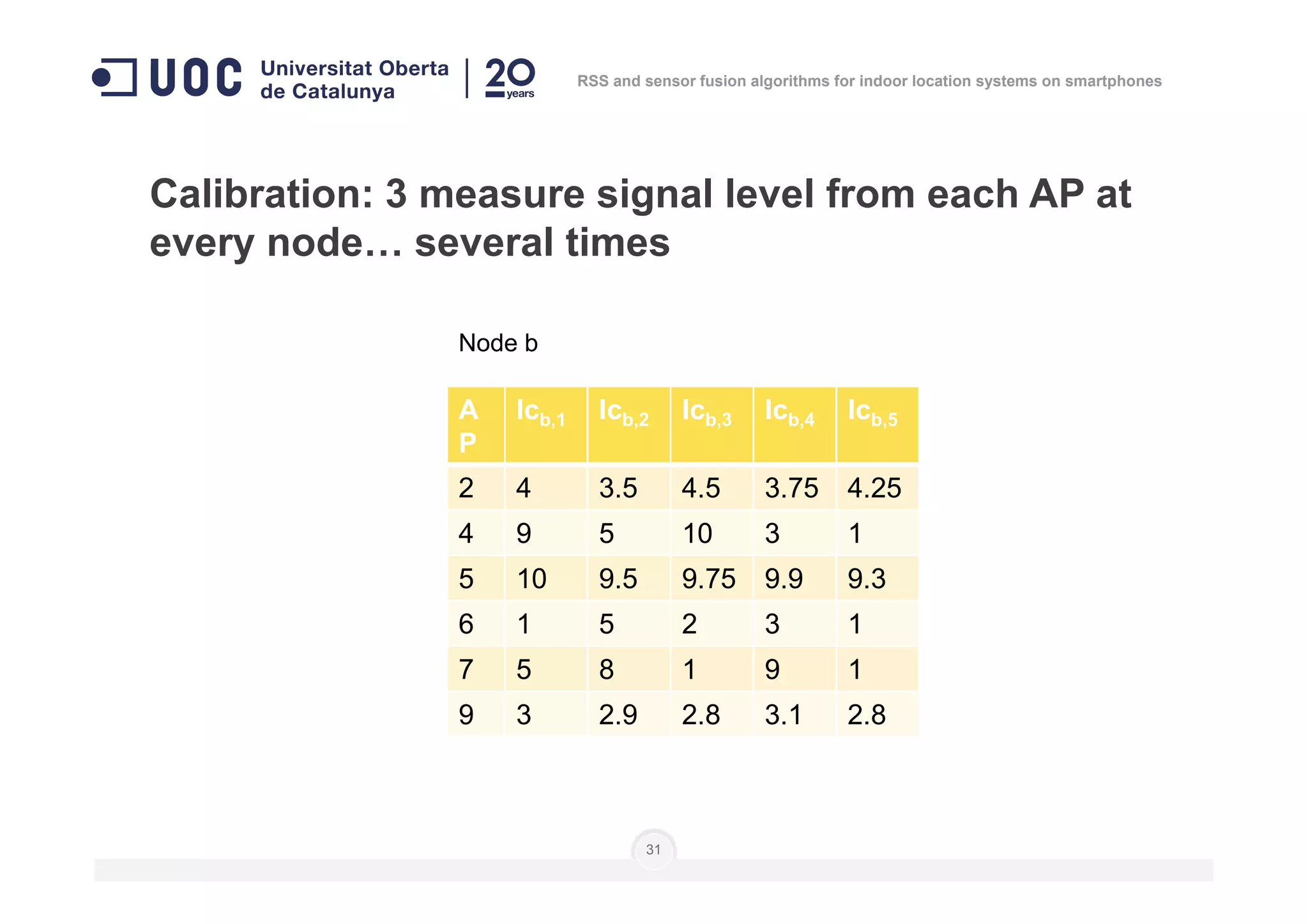
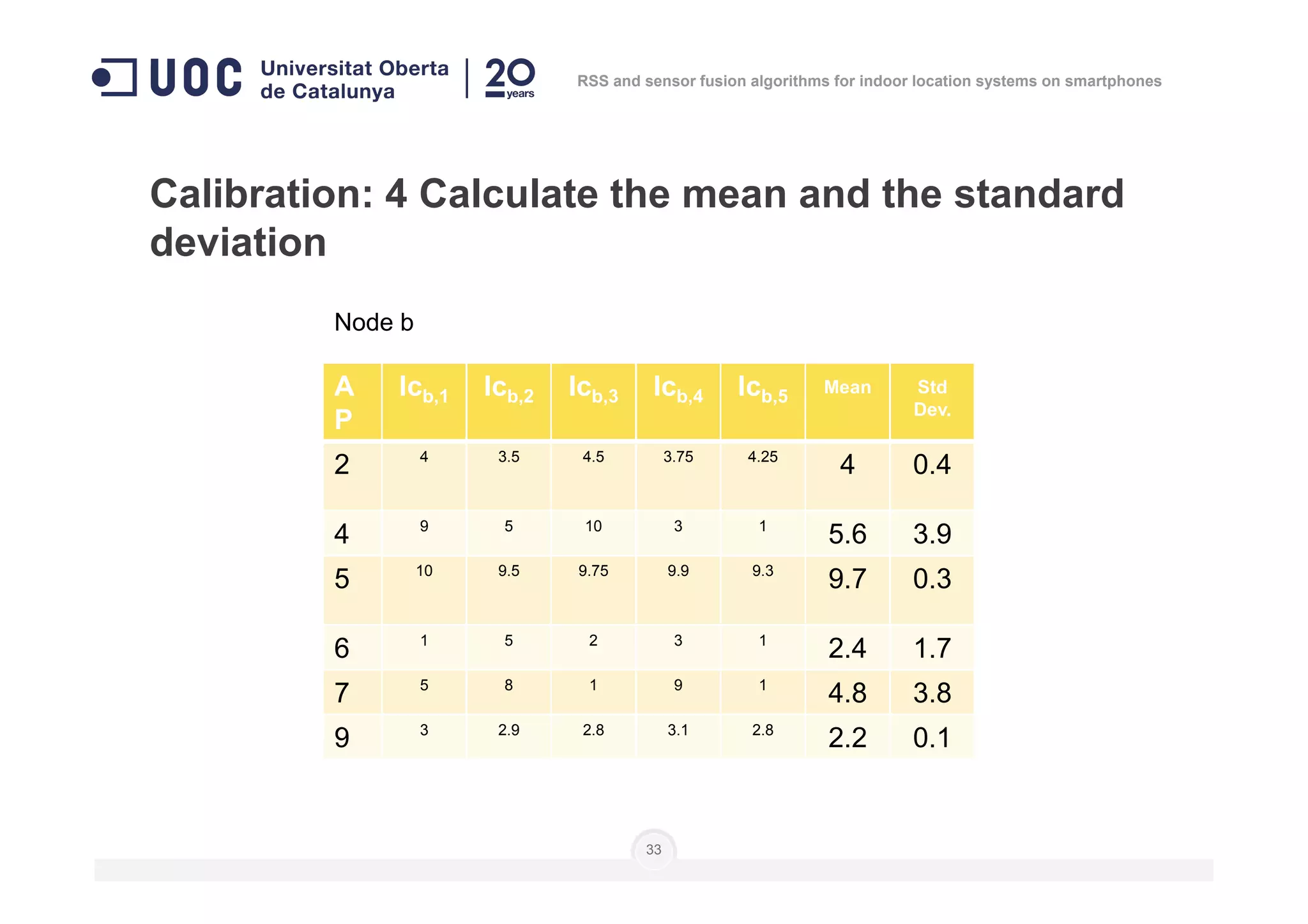
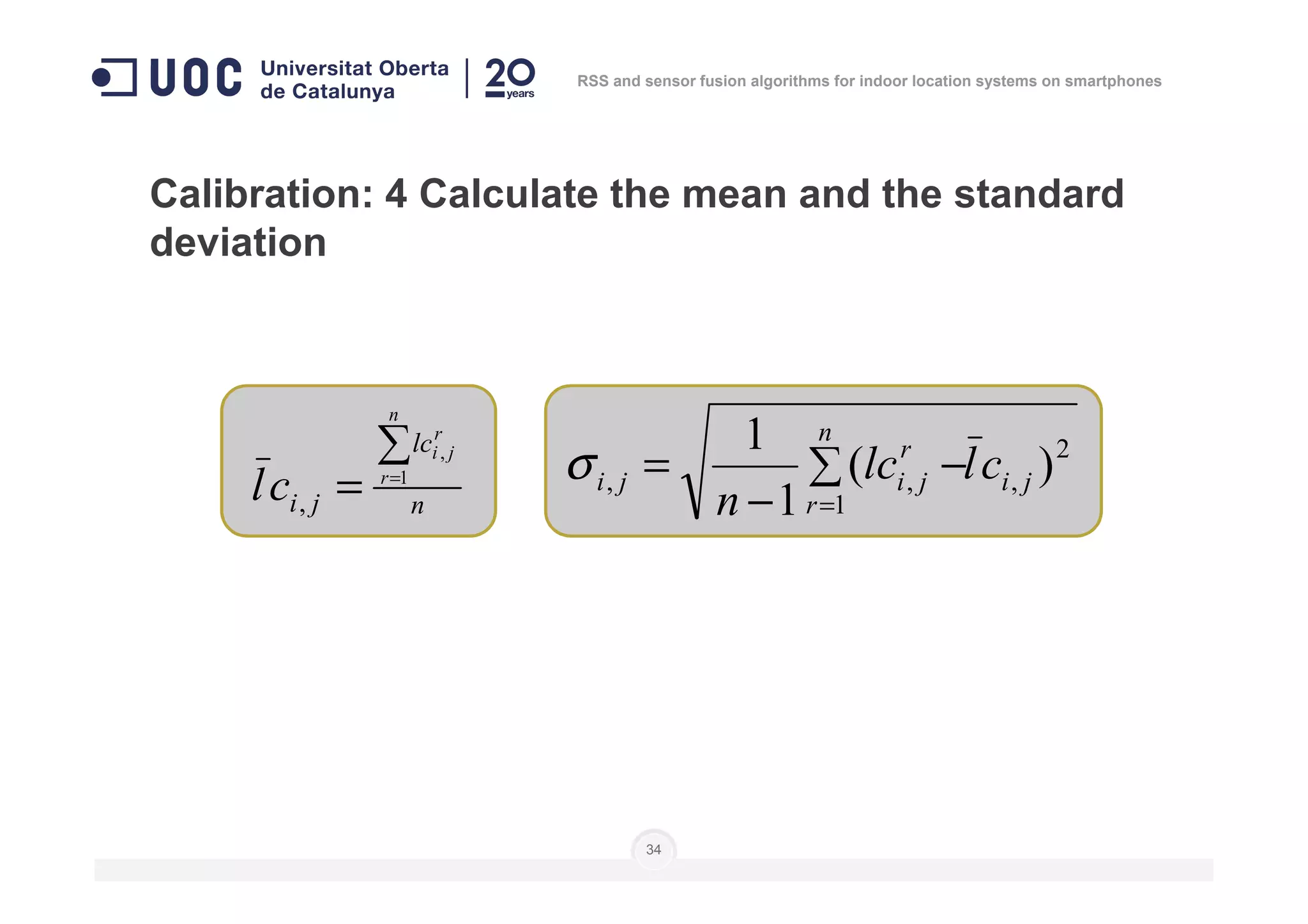
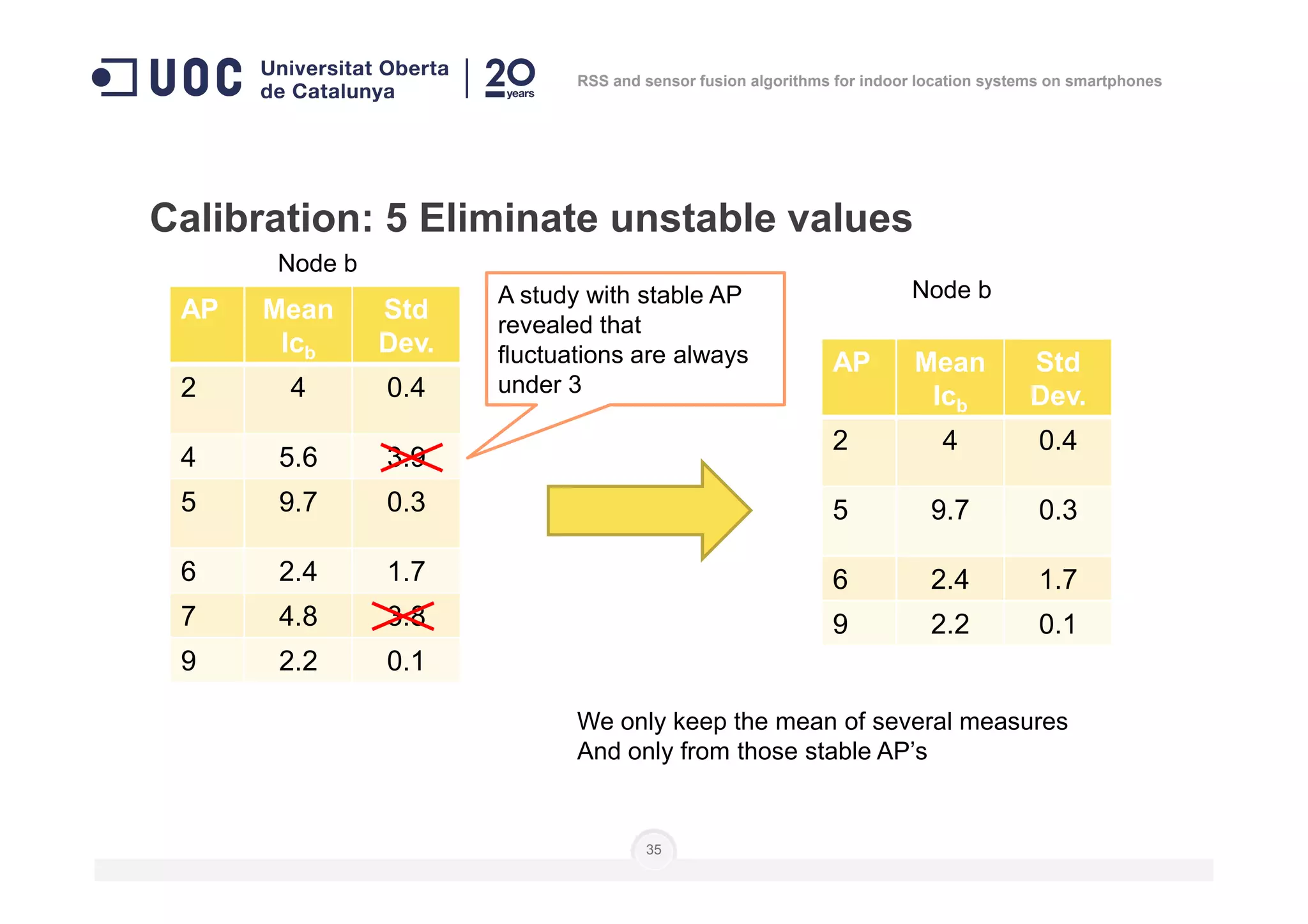
![Calibration: 3 measure signal level from each AP at
every node… several times
]],...,[],...,,...,[],...,,...,[[)( 111 nnn
i lclclclclclcnN =
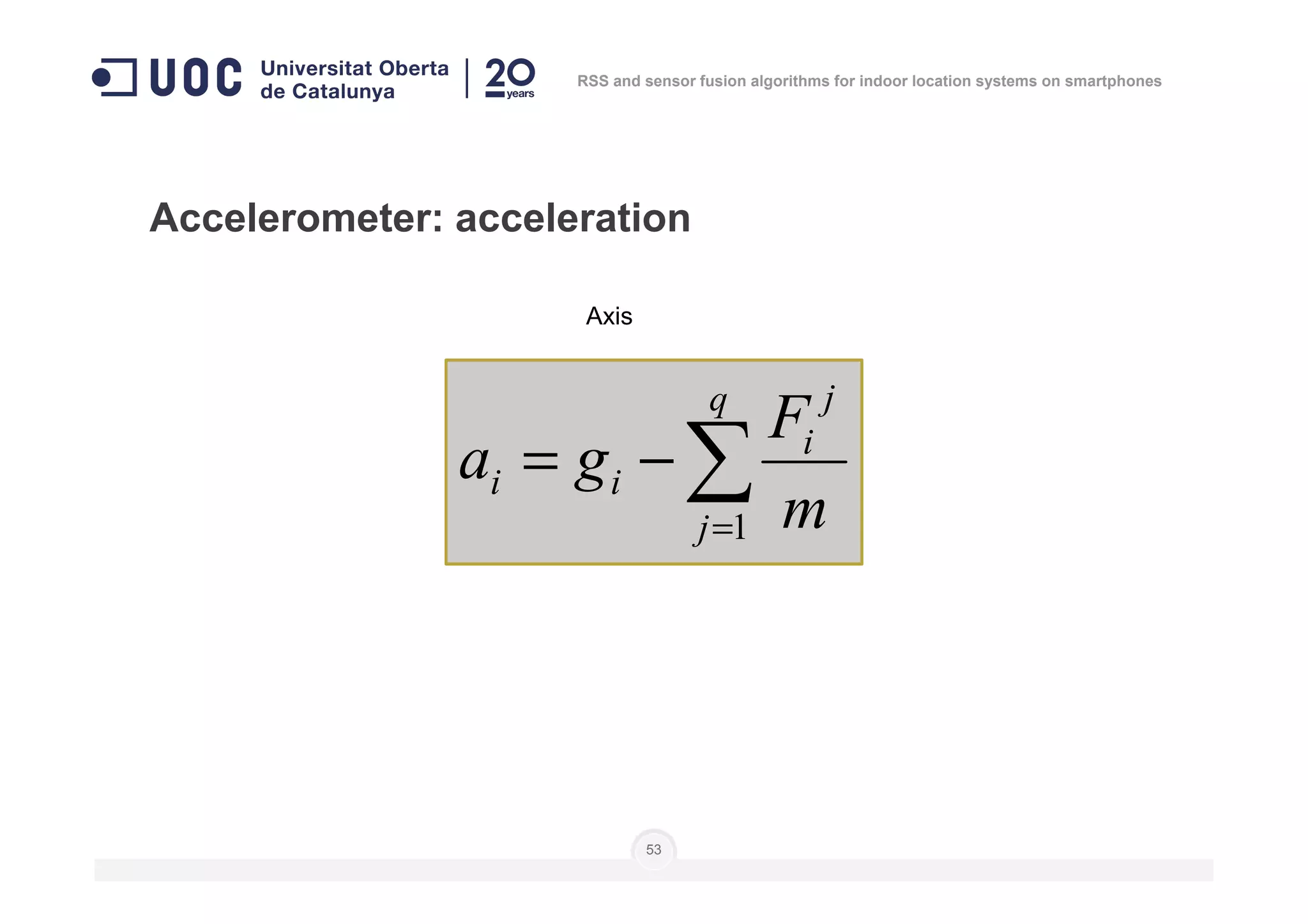
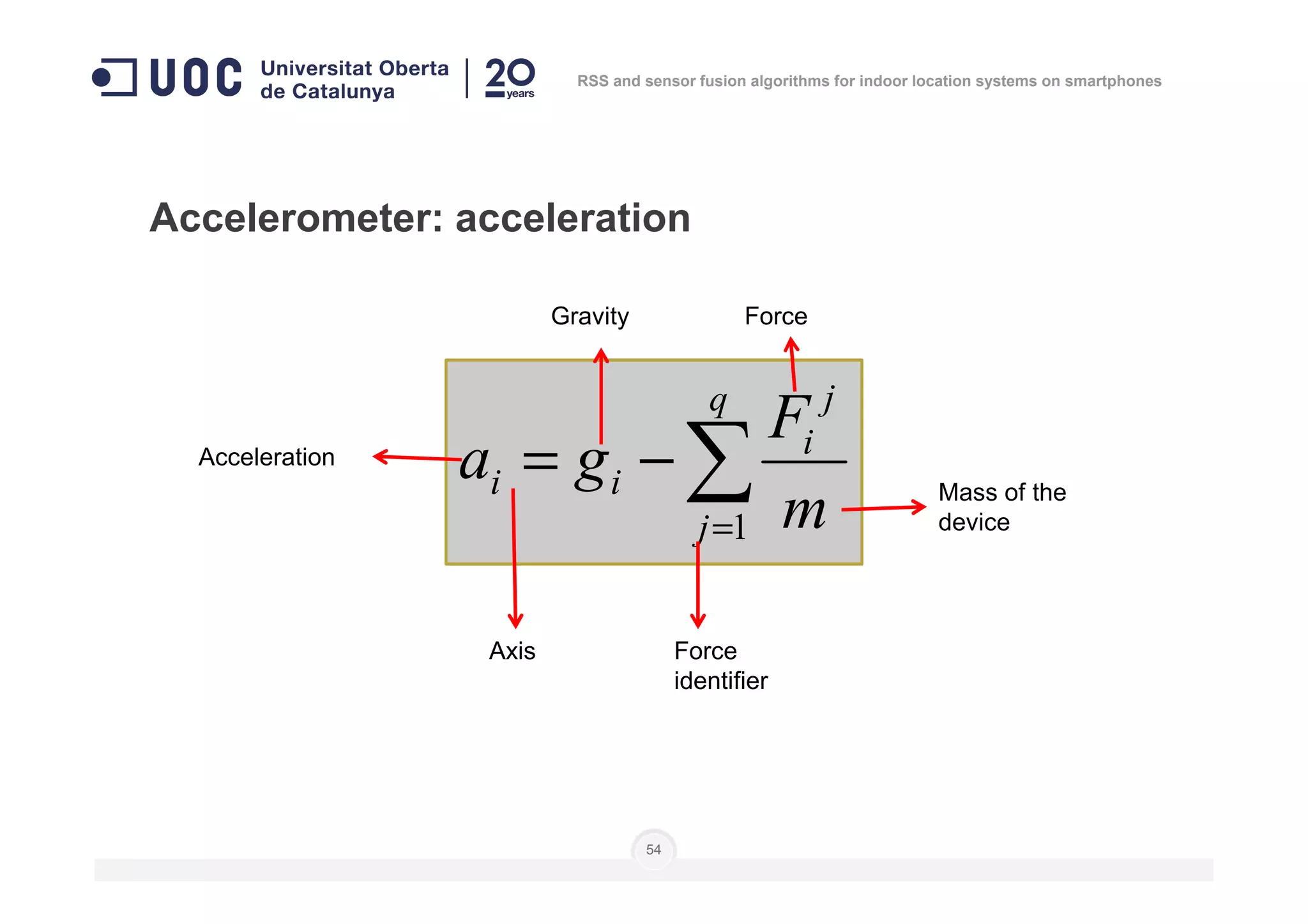
Number of
measures
Level of
calibration
RSS and sensor fusion algorithms for indoor location systems on smartphones
32
]],...,[],...,,...,[],...,,...,[[)( ,,,,1,1,i kikijijiii
lclclclclclcnN =
Node
identifier
AP
identifier
AP
measured](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/showcase2015rss-sensor-algorithms-geolocation-smartphones-aperezn-150212104600-conversion-gate01/75/RSS-and-Sensor-Fusion-Algorithms-for-Indoor-Location-Systems-on-Smartphones-32-2048.jpg)
![Calibration Matrix
],0(;],0(_ kjsiclmatrixCal ∈∈=
RSS and sensor fusion algorithms for indoor location systems on smartphones
37
],0(;],0(_ , kjsiclmatrixCal ji ∈∈=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/showcase2015rss-sensor-algorithms-geolocation-smartphones-aperezn-150212104600-conversion-gate01/75/RSS-and-Sensor-Fusion-Algorithms-for-Indoor-Location-Systems-on-Smartphones-37-2048.jpg)

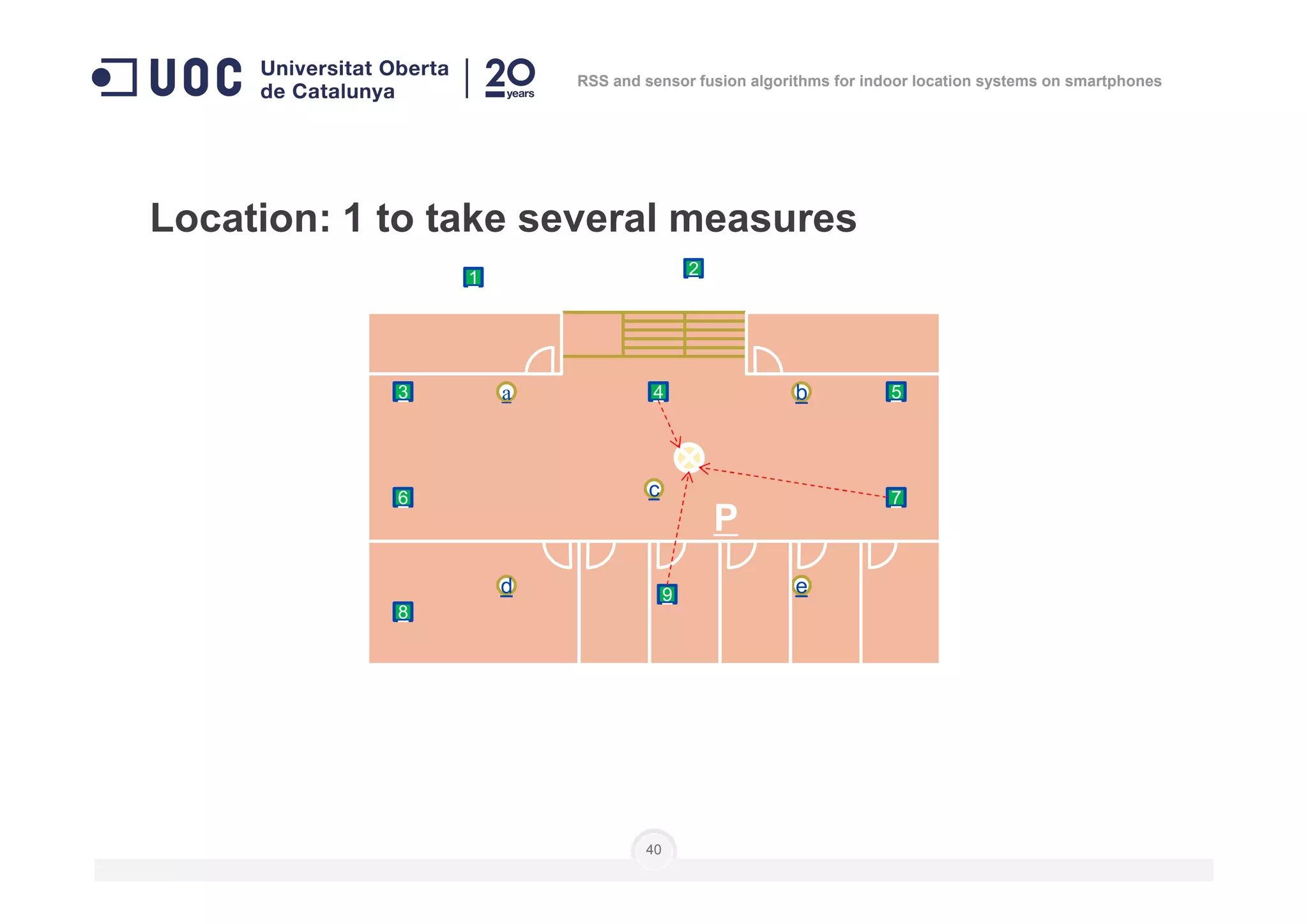

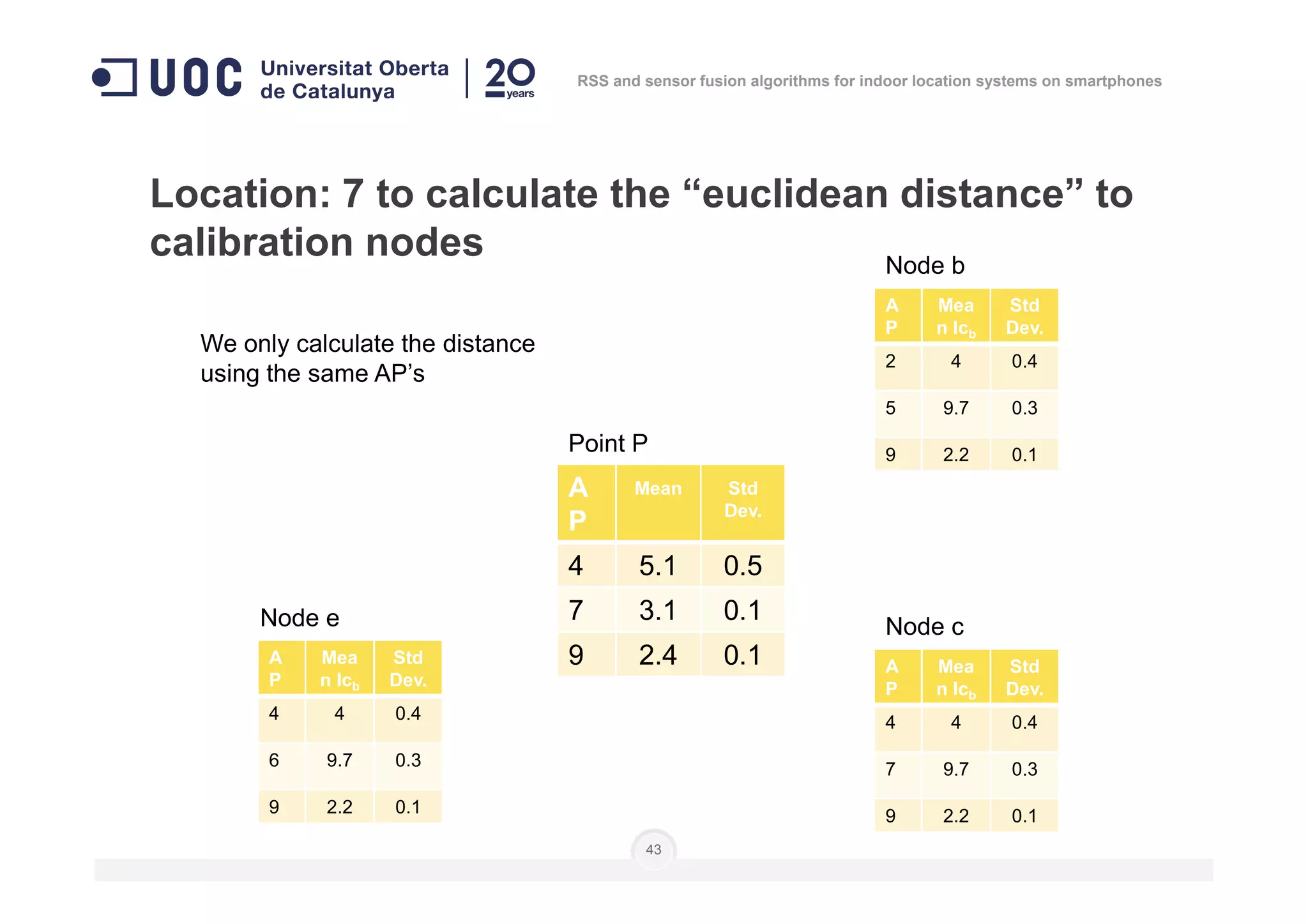
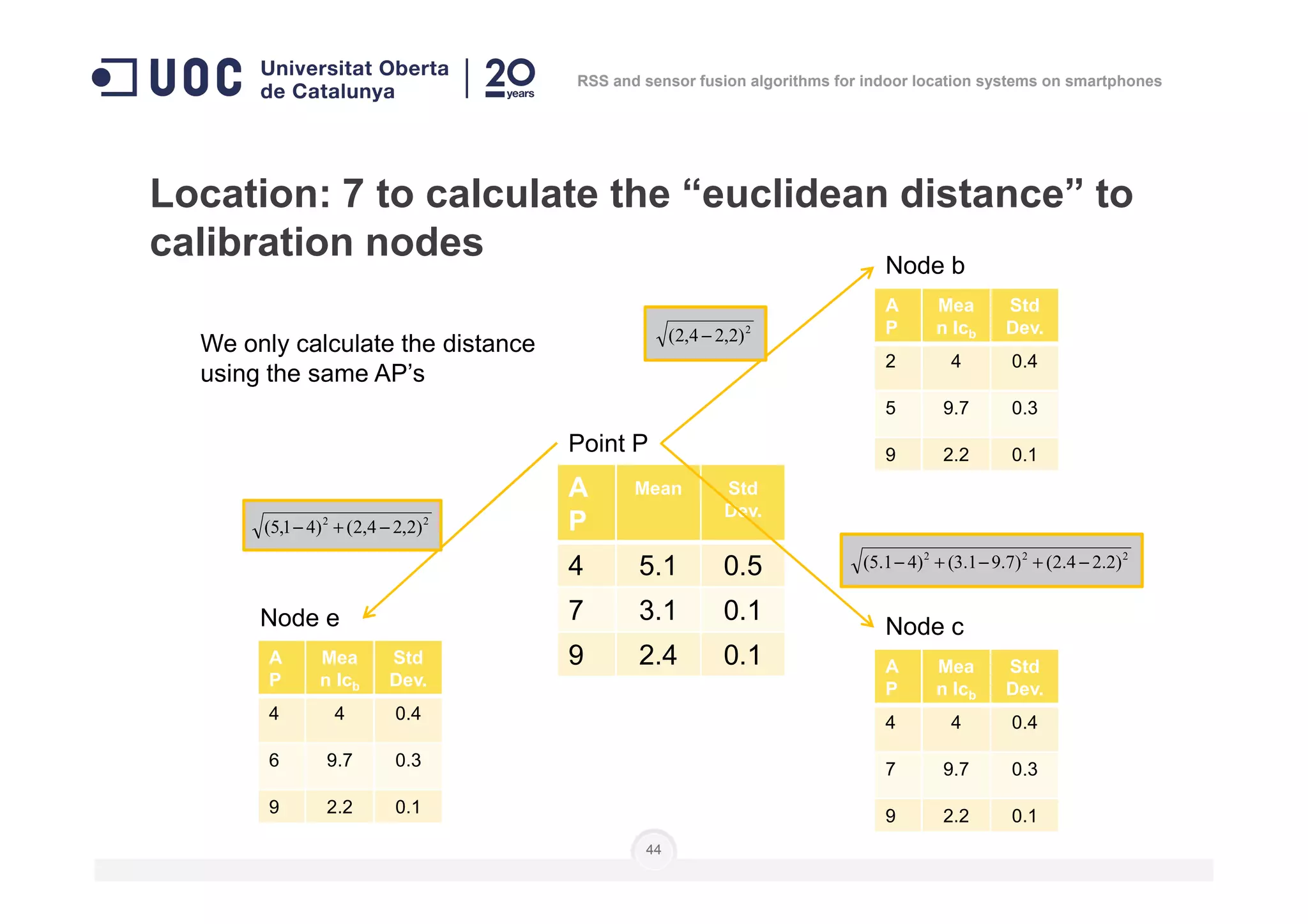
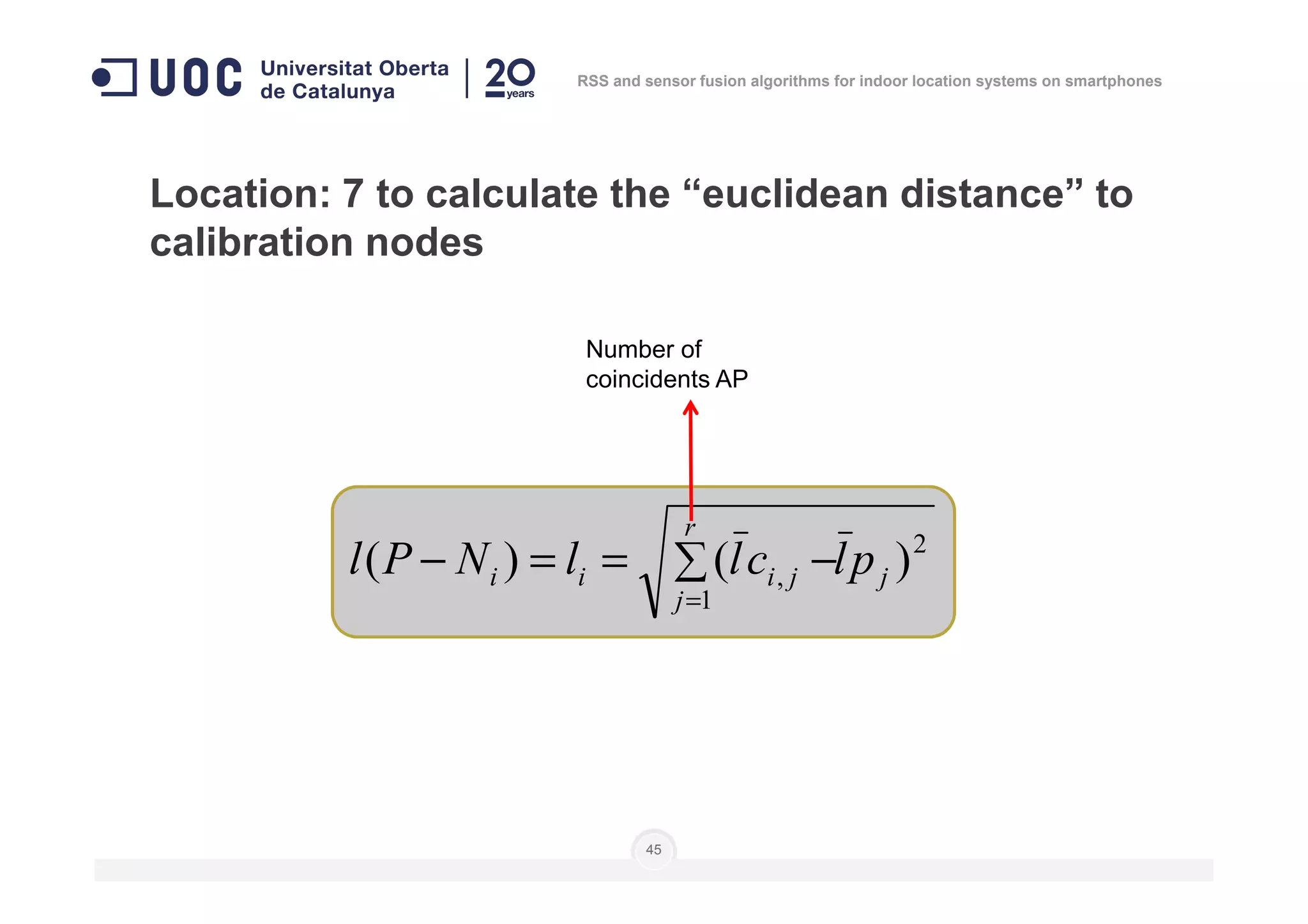
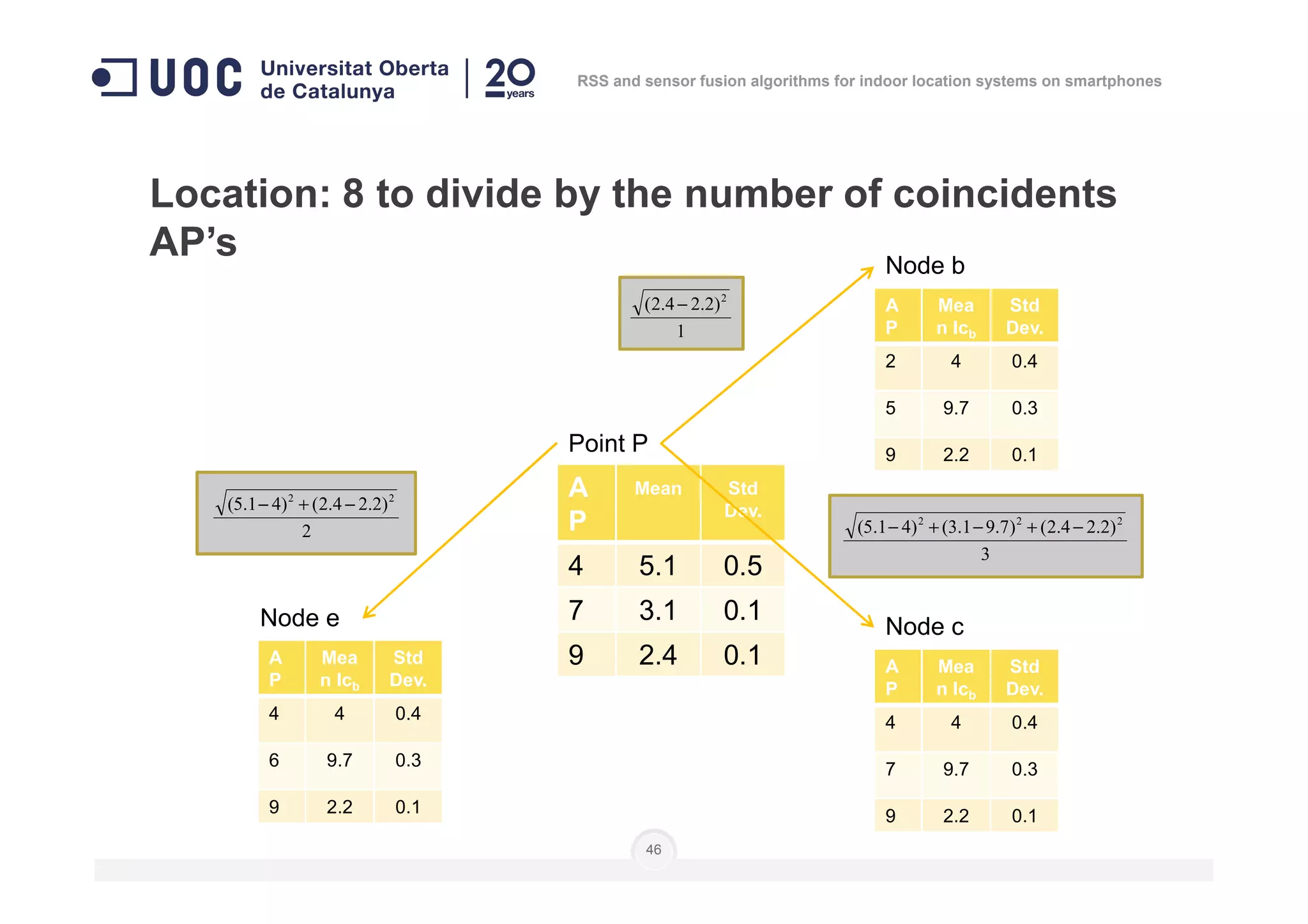
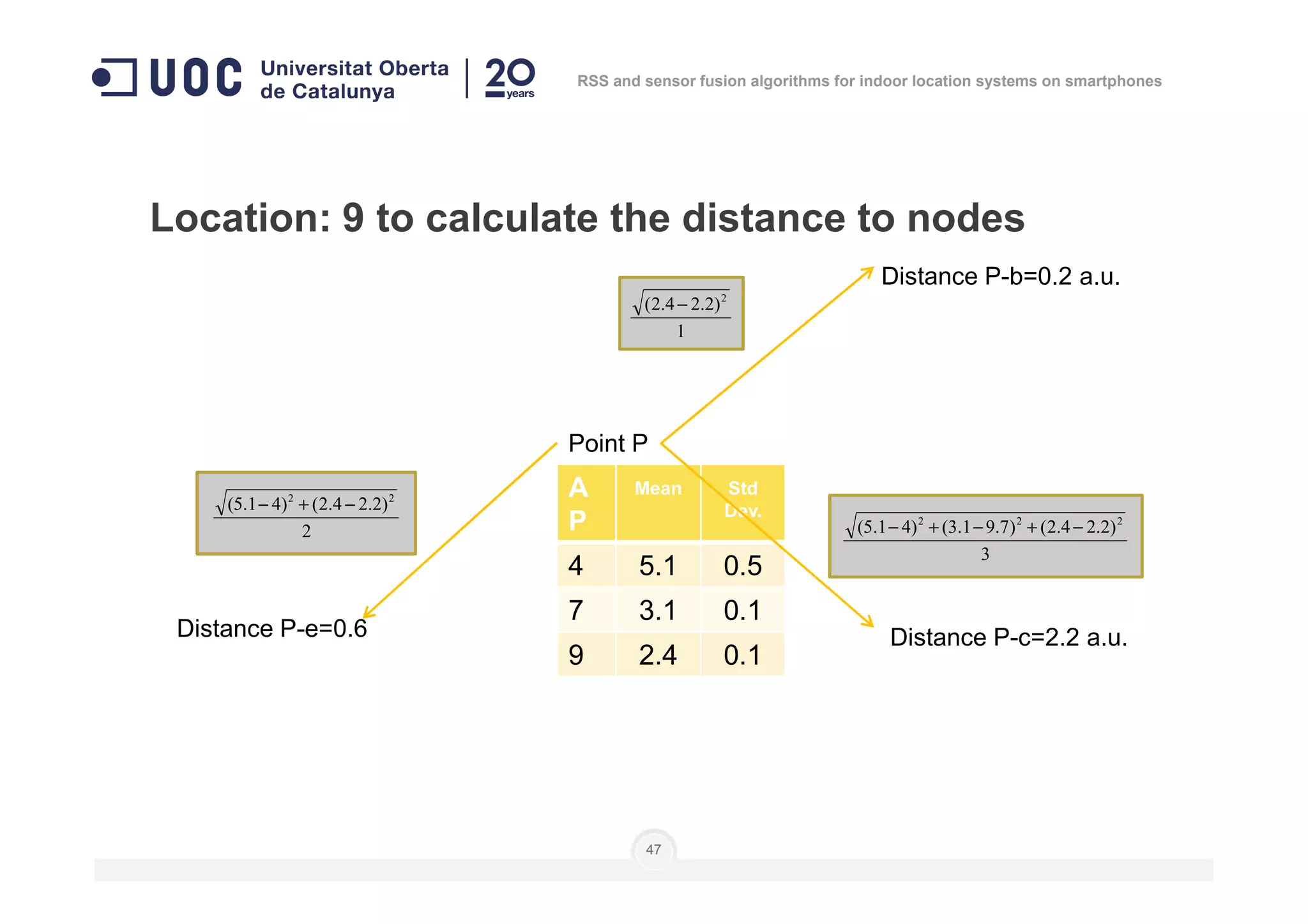
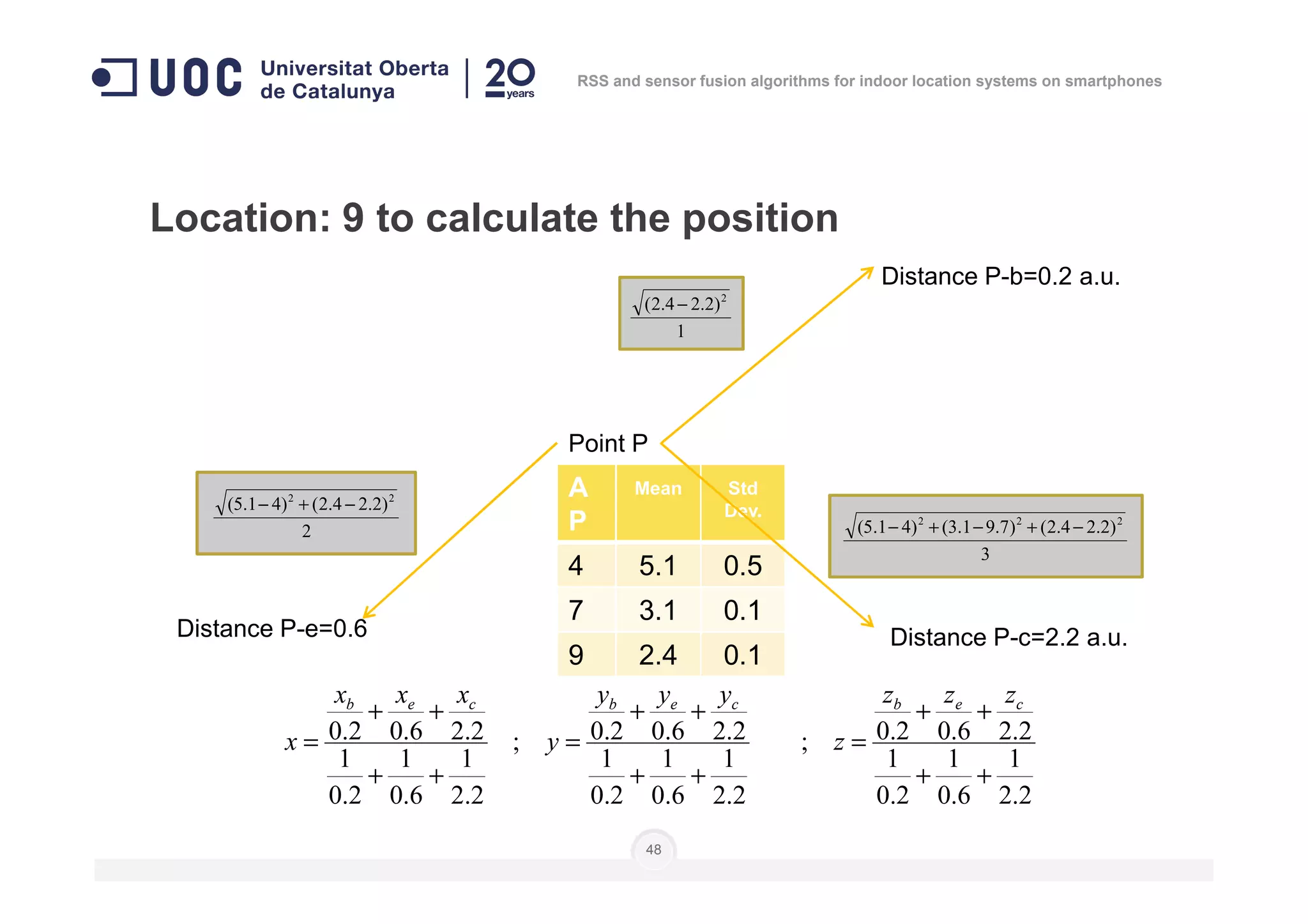
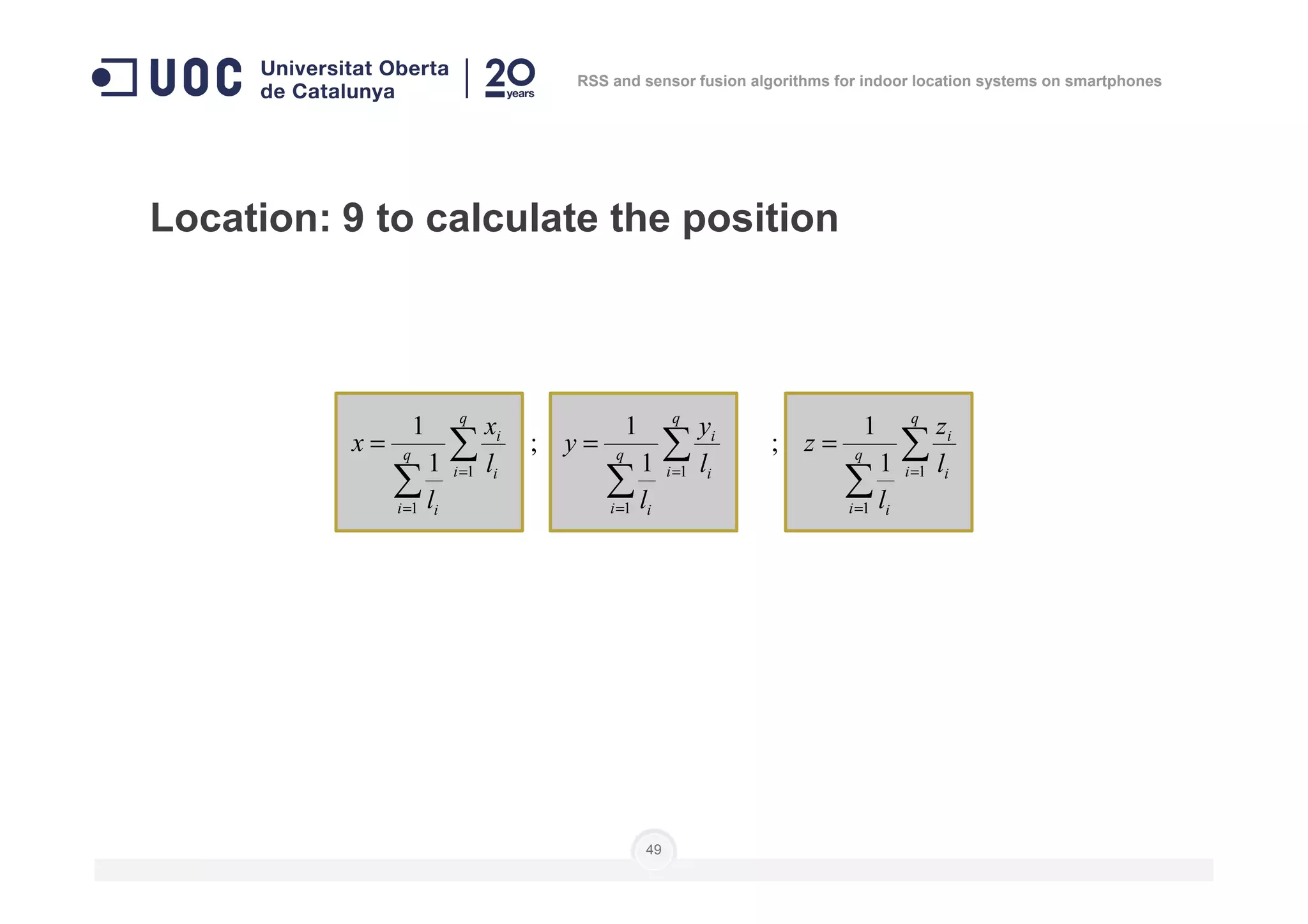
![Location: to do as in calibration steps 3 to 6
]],...,[],...,,...,[],...,,...,[[)( 111 nnn
lplplplplplpnP =
Number of
measures
Level of
position
RSS and sensor fusion algorithms for indoor location systems on smartphones
42
]],...,[],...,,...,[],...,,...,[[)( ,,,,1,1, mimijijiii
lplplplplplpnP =
Node
identifier
AP
identifier
AP
measured
(≠ k)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/showcase2015rss-sensor-algorithms-geolocation-smartphones-aperezn-150212104600-conversion-gate01/75/RSS-and-Sensor-Fusion-Algorithms-for-Indoor-Location-Systems-on-Smartphones-42-2048.jpg)