Teaching phonetics
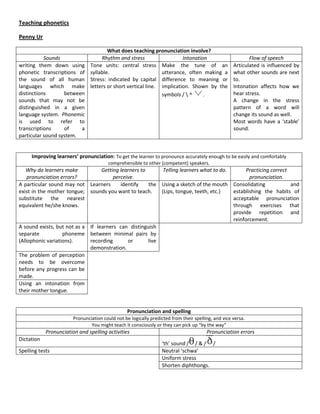
- 1. Teaching phonetics Penny Ur What does teaching pronunciation involve? Sounds Rhythm and stress Intonation Flow of speech writing them down using Tone units: central stress Make the tune of an Articulated is influenced by phonetic transcriptions of syllable. utterance, often making a what other sounds are next the sound of all human Stress: indicated by capital difference to meaning or to. languages which make letters or short vertical line. implication. Shown by the Intonation affects how we distinctions between symbols / ^ . hear stress. sounds that may not be A change in the stress distinguished in a given pattern of a word will language system. Phonemic change its sound as well. is used to refer to Most words have a ‘stable’ transcriptions of a sound. particular sound system. Improving learners’ pronunciation: To get the learner to pronounce accurately enough to be easily and comfortably comprehensible to other (competent) speakers. Why do learners make Getting learners to Telling learners what to do. Practicing correct pronunciation errors? perceive. pronunciation. A particular sound may not Learners identify the Using a sketch of the mouth Consolidating and exist in the mother tongue; sounds you want to teach. (Lips, tongue, teeth, etc.) establishing the habits of substitute the nearest acceptable pronunciation equivalent he/she knows. through exercises that provide repetition and reinforcement. A sound exists, but not as a If learners can distinguish separate phoneme between minimal pairs by (Allophonic variations). recording or live demonstration. The problem of perception needs to be overcome before any progress can be made. Using an intonation from their mother tongue. Pronunciation and spelling Pronunciation could not be logically predicted from their spelling, and vice versa. You might teach it consciously or they can pick up “by the way” Pronunciation and spelling activities Pronunciation errors Dictation ‘th’ sound / / & / / Spelling tests Neutral ‘schwa’ Uniform stress Shorten diphthongs.
- 2. Paul Lyndsay 1. What are the three main areas of pronunciation? The three main areas of pronunciation are sound, stress & rhythm and intonation. 2. In what ways is the written alphabet in English an imperfect guide to the sounds of the language? Give two or three examples. In a way that the alphabet has 26 letters and English has 44 different sounds. e.g. The word rhythm has no vowels in it, but it does has vowel sounds. /ˈrɪð.əm/ 3. What’s the main difference in sound between a simple vowel and a diphthong? A vowel is one sound and a diphthong is a glide from one vowel sound to another. 4. Why should language teachers get to know the IPA? What are the most useful phonemic symbols to know? It is useful to manage the IPA chart because; it helps students to focus on sounds that do not exist in their native language. A visual representation helps learners with errors and students can use more effectively their dictionary. The phonemic symbols that are most useful to know are the ones which are not in the mother tongue. 5. Why use minimal pairs in teaching pronunciation? Using minimal pairs help students to be understood and for them to understand the meaningful differences between words. 6. Which words in a sentence usually carry greater stress than others? The lexical words carry greater stress than the structural words. 7. How can a change of syllable stress change the meaning of a word? It change the category of a word and by that reason the ‘meaning’ and use of it. e.g. Pre’sent verb ‘Present noun 8. What is intonation? Catenation? Intonation is a change in the pitch used to express surprise, pleasure, disappointment, irony, and other feelings. It also makes the difference between questions and statements & marks new information. Jeremy Harmer 1. Pronunciation issues -Perhaps teachers feel they have too much to do already and pronunciation teaching will only make things worse. -Without specific pronunciation reaching many students seem to acquire serviceable pronunciation in the course of their studies. -Makes students aware of different sounds and sound features improve their speaking immeasurably. - Help them achieve the goal of improve comprehension and intelligibility.
- 3. -Being made aware of pronunciation issues will be of immense benefit not only to their own production, but also to their own understanding of spoken English. 1.1 Perfection versus intelligibility -We should be happy if they can at least make themselves understood. -Perfect pronunciation will depend on their attitude to how they speak and how well they hear. -Retain their own accent is part of their identity. -Consider intelligibility as the prime goal of pronunciation teaching. -Some sounds have to be right if the speaker is to get their message across. -Stressing words and phrases correctly is vital if emphasis is to be given to the important parts of messages. 1.2 Problems -What students can hear: /b/ and /v/ for Spanish speakers is the same sound. How sounds are made through demonstration. Draw the sound to their attention every time they appear on a tape. When they can hear correctly they are on the way to being able to speak correctly. -The intonation problem: Most of us can hear when someone I being enthusiastic or bored. Give the students the opportunity to recognize such moods. -Have them to listen and notice how English is spoken. 1.3 The phonemic alphabet: to use or not to use? -Without every using any phonemic symbols. -By saying the words enough times. -Describe how the sounds are made. -It may make sense for them to be aware of the different phonemes. -Dictionaries usually give the pronunciation of their words in phonemic symbols. The students can know how a word is said even without having to hear it. -Easy to explain what mistakes has occurred. -Introduced to the various symbols gradually rather than all at once. 1.4 When to teach pronunciation -Whole lesson: To work on connected speech concentrating on stress and intonation over some forty-five minutes; Rehearsing and performing of a short play extract; Working on listening skills before moving to the pronunciation part of the sequence; Vocabulary before going on to work on words stress, sounds, and spelling. -Discrete slots: Either separately or in contrasting pairs. -Integrated phases: Draw their attention to pronunciation features on the tape or get them to imitate intonation patterns for questions. -Opportunistic teaching: Because it has ‘come up’. 2. Examples of pronunciation teaching 2.1 Working with sound -Words in a list to demonstrate the position of the lips. -Contrasting to very similar sounds. -Practicing each sound separately. -Diagram the mouth to help students see where the sounds are made. -Can be done whether or not the teacher and students work with phonemic symbols. -Play a sound bingo with the phonemic spelt of words instead of ordinary orthographic words.
- 4. -Noughts and crosses. -Stick the phonemic sounds on the wall and when a learner says something and produces an incorrect sound, the teacher can point to the sound they should have made. -Tongue twisters -Rhymes and poems written in phonemic sounds instead of ordinary orthographic words. 2.2 Working with stress -Underline words that are specially stressed in a sentence and ask them what it would mean if different words took the main stress. -Cuisenaire rods as a graphic illustration of how words and phrases are stressed. 2.3 Working with intonation -To show how many different meanings can be squeezed out of just one word such as ‘yes’. - To raise the students’ awareness of the power of intonation and to encourage them to vary their own speech. -Make dialogs without words -Use a variety of devices such as arrows on the board and arm movements which ‘draw’ patterns in the air to demonstrate intonation. 2.4 Sounds and spelling -Sound-Spelling correspondence for particular spellings. -Letter ‘x’ can be pronounced in two ways. 2.5 Connected speech and fluency -The sounds of words change when they come into contact with each other. -Three-stage procedure for teaching students about features such as elision and assimilation a. Stage 1. Comparing: Showing students sentences and phrases. Then someone says a sentence which includes those words or phrases. b. Stage 2. Identifying: We could say a sentence in phonemic sounds and then expect the students to write it down. c. Stage 3. Production: Get them to say phrases and sentences. Getting students to perform dialogues and play extracts improve their overall fuency.
