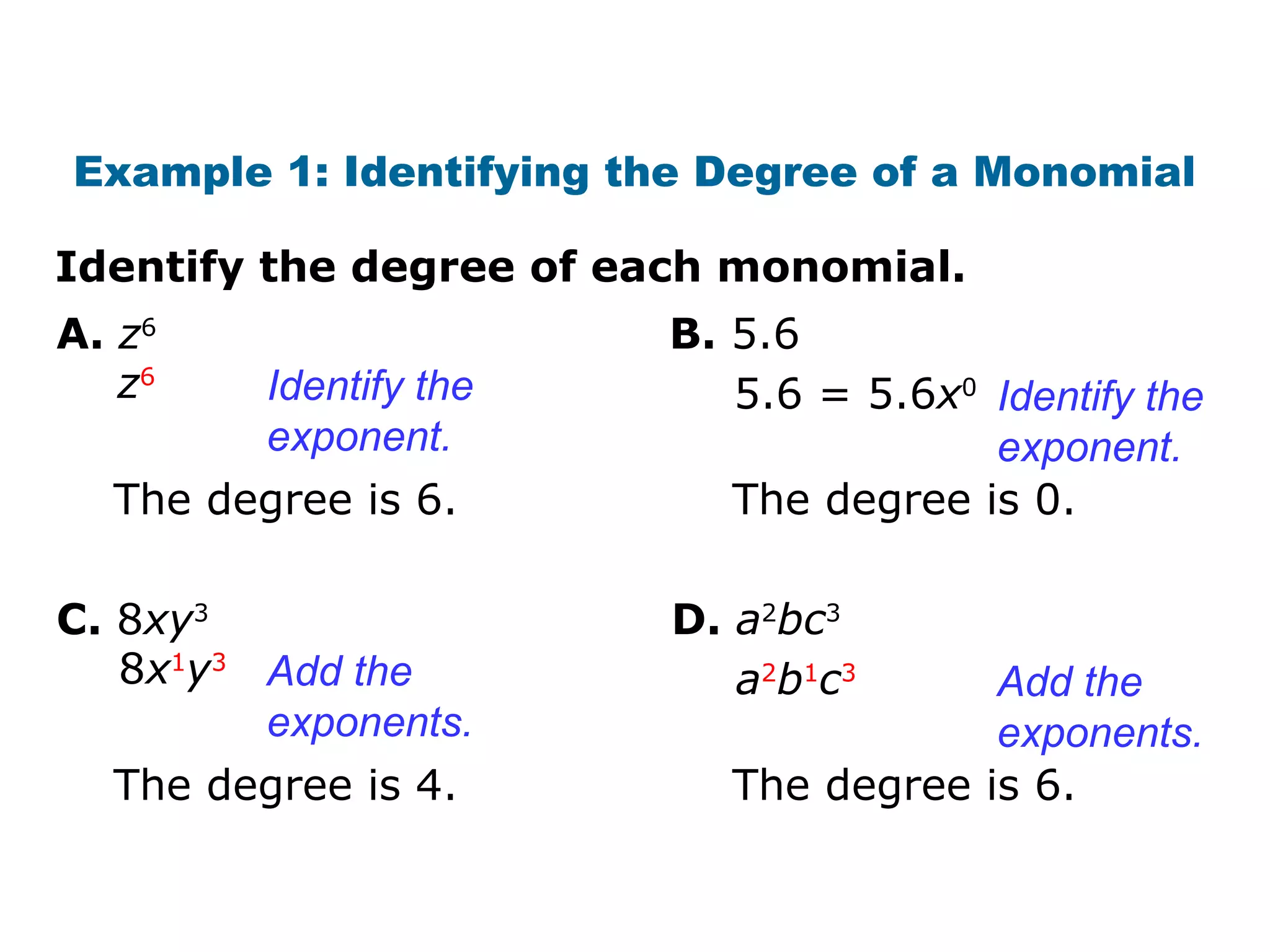
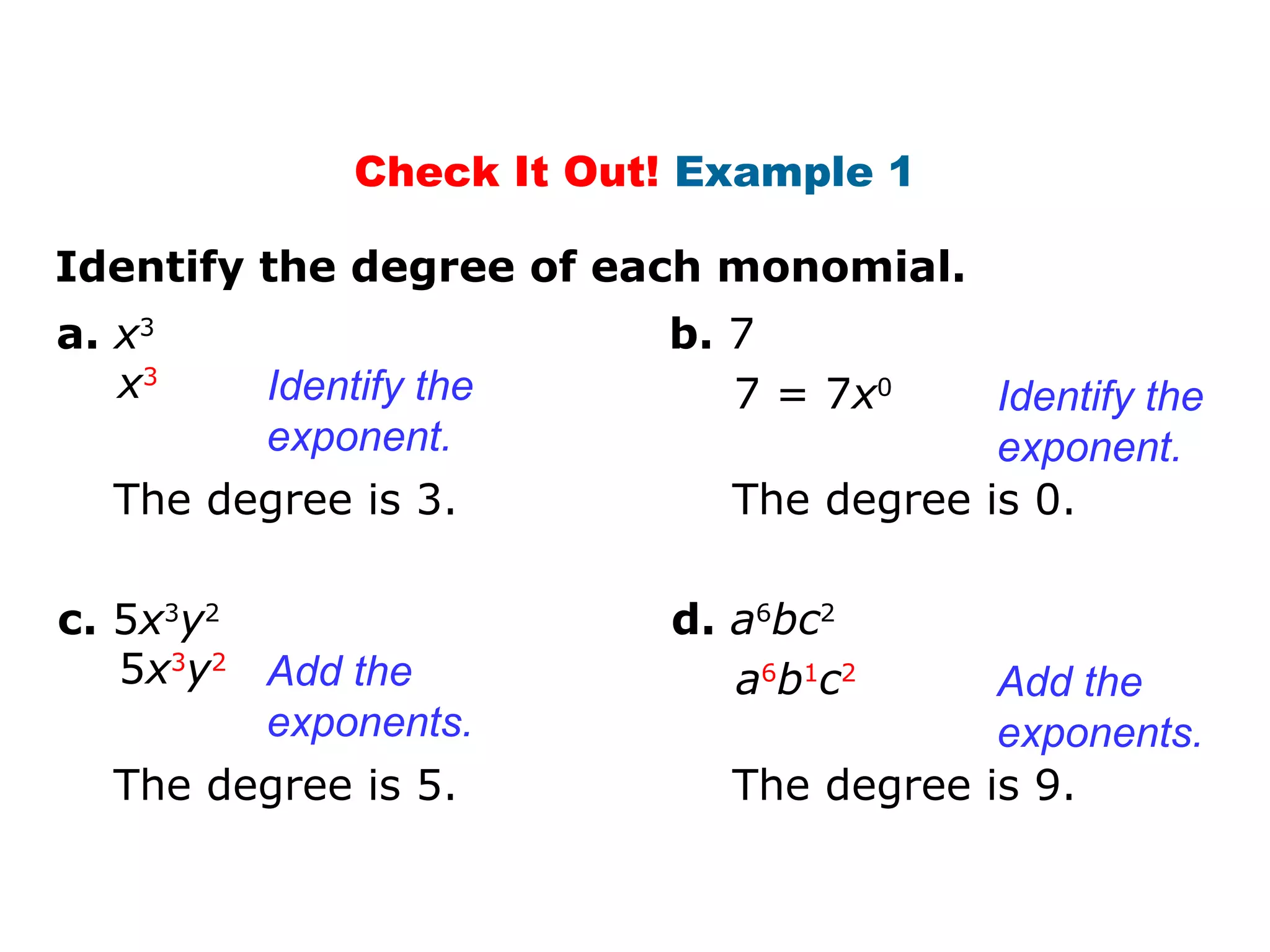
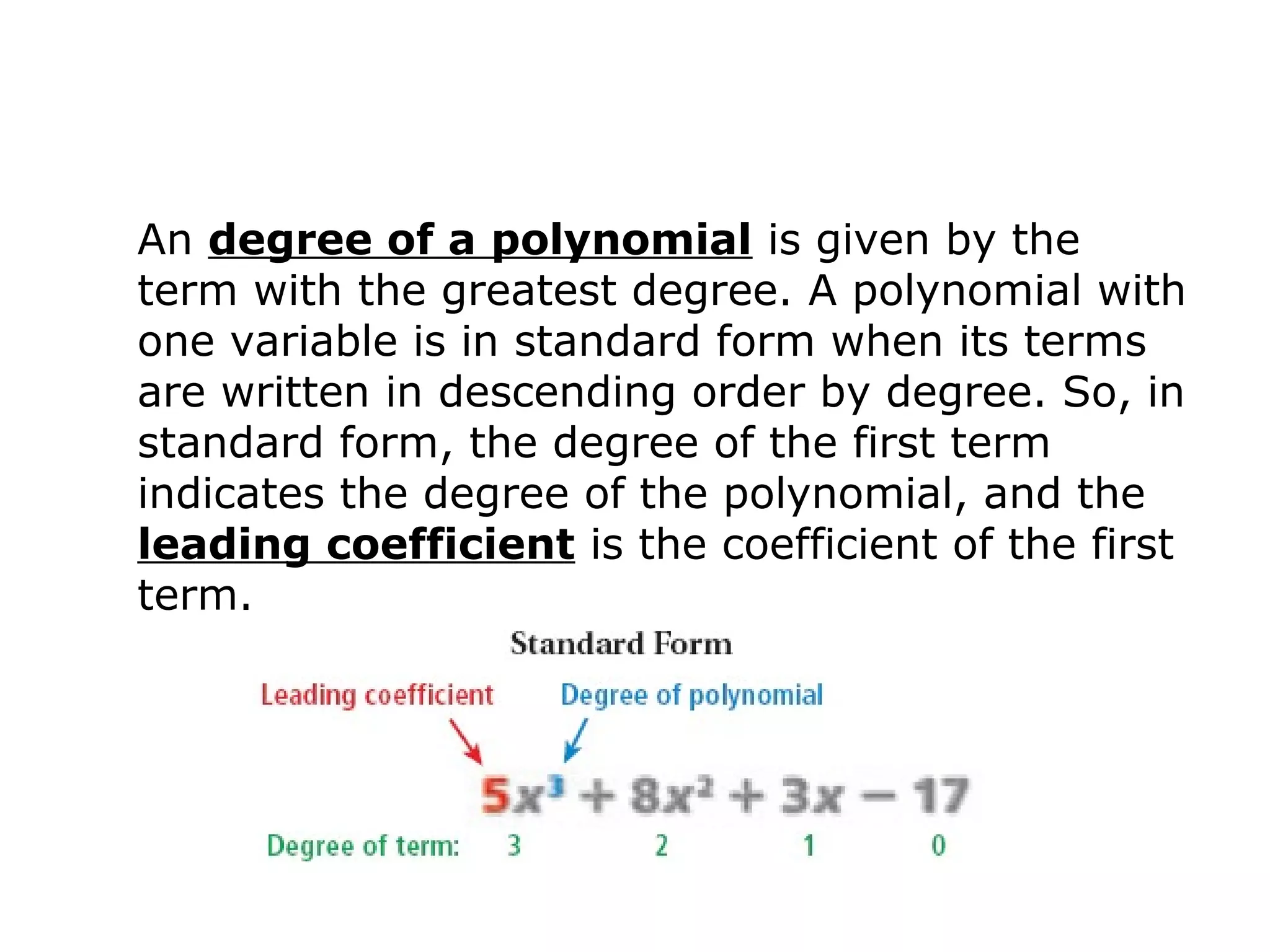
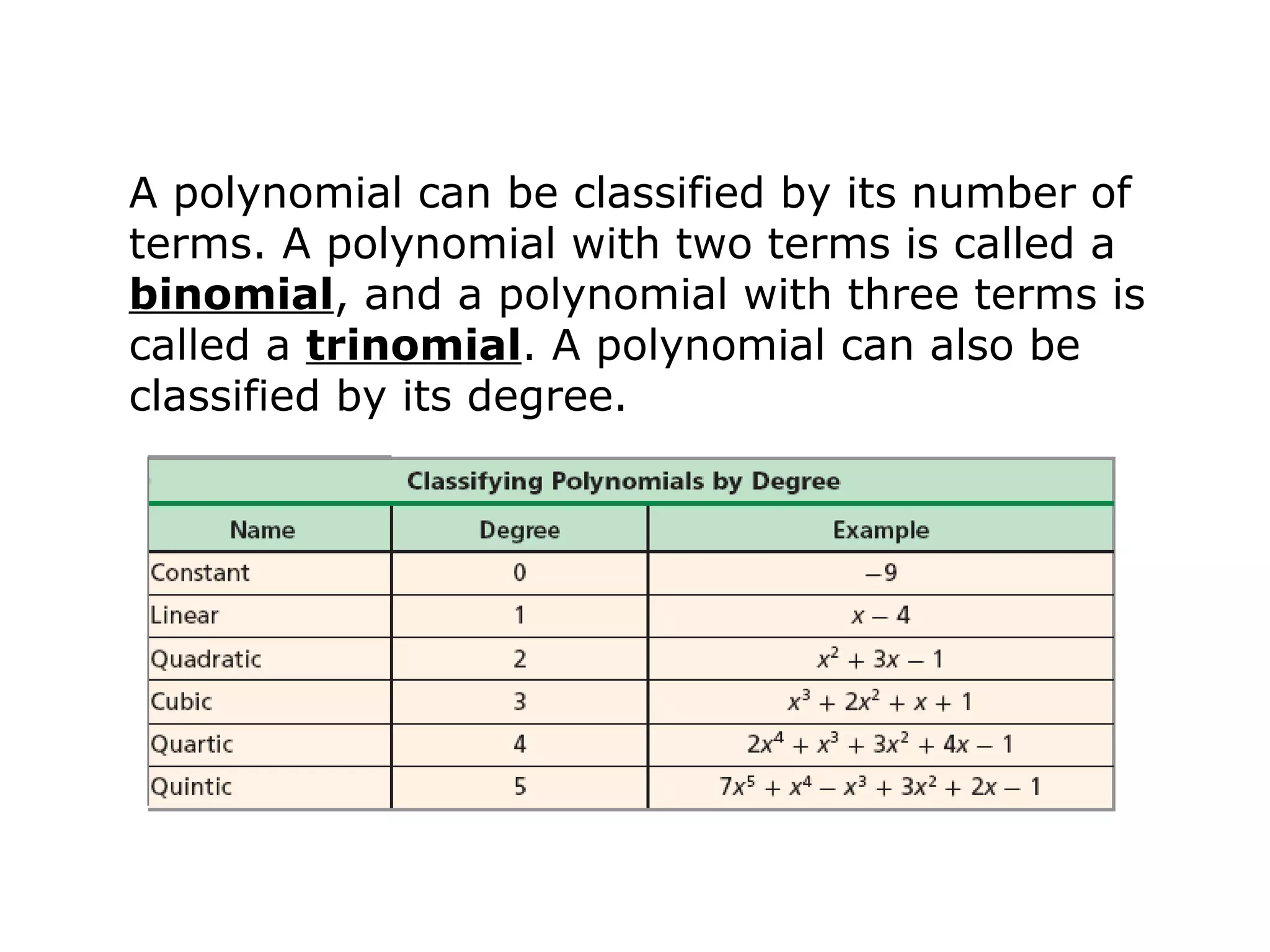
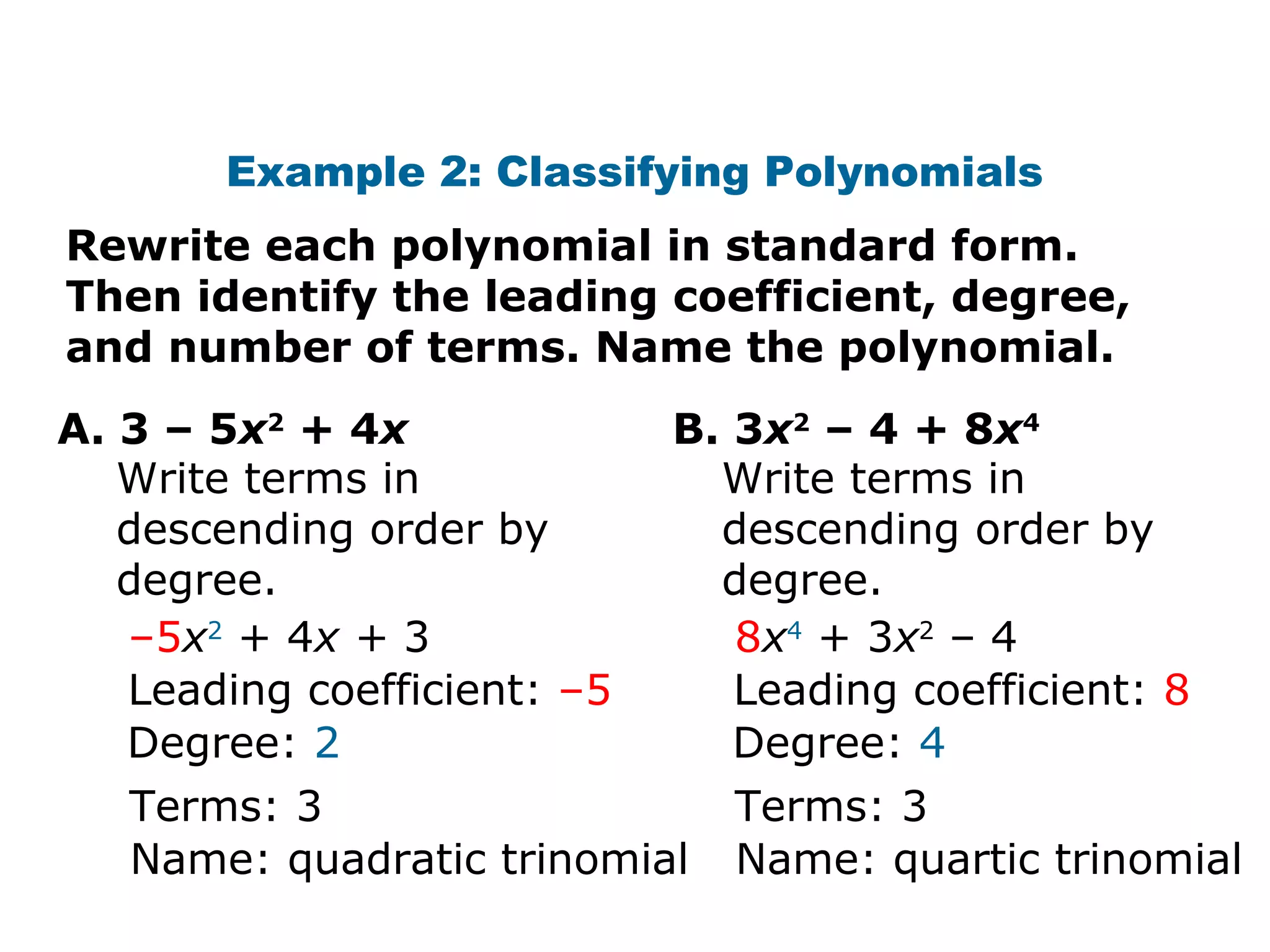
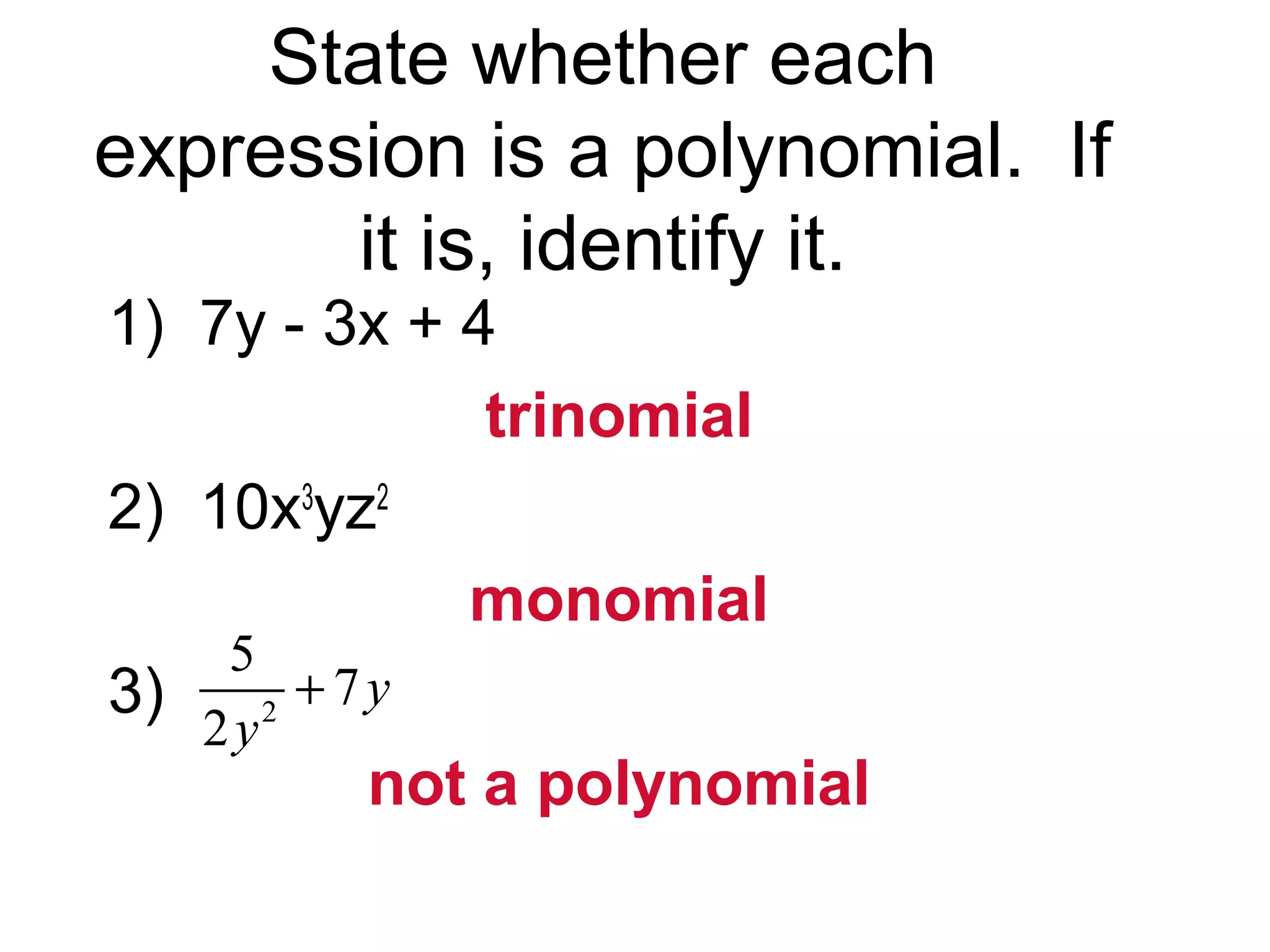
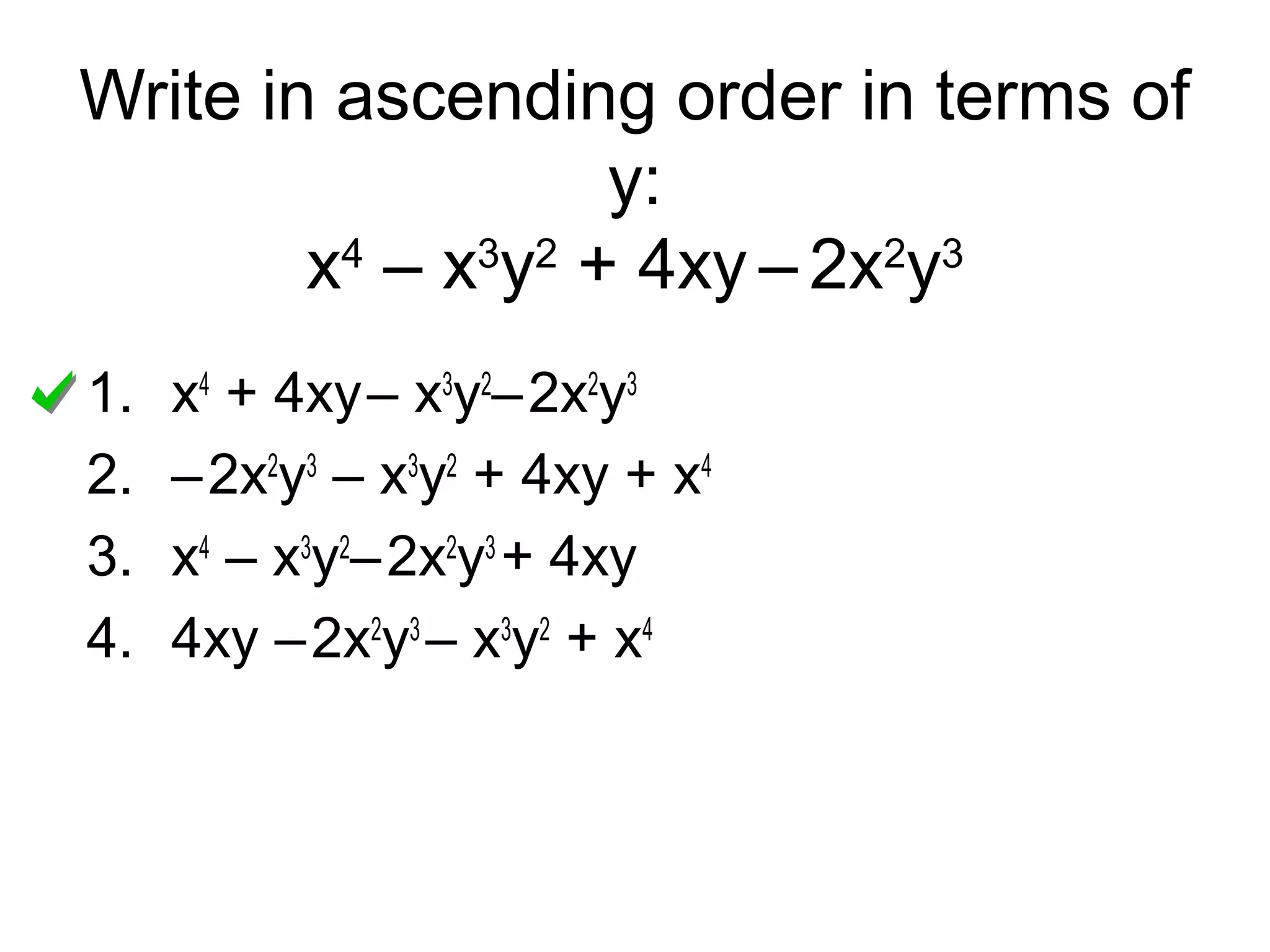
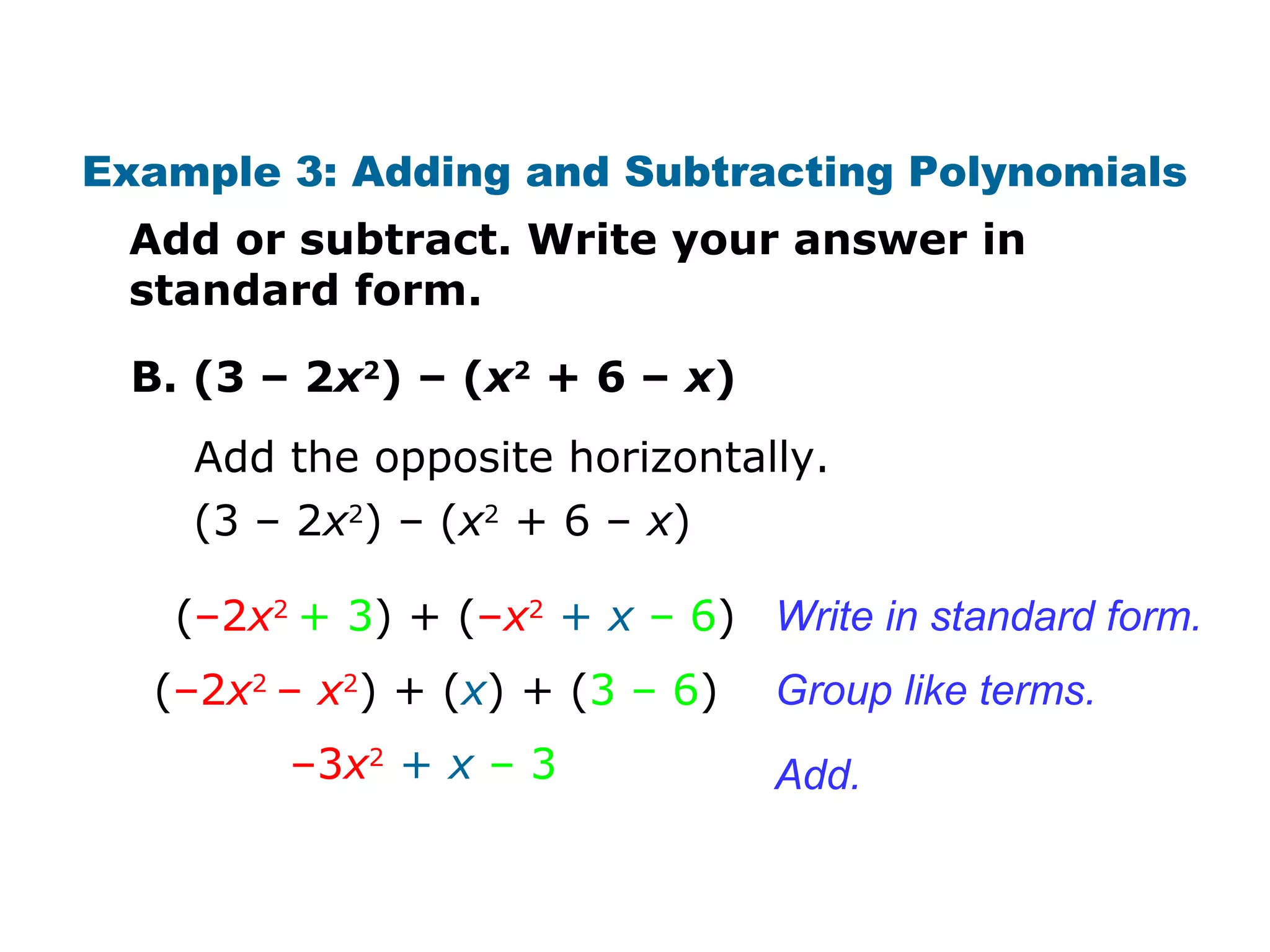
The document discusses polynomials. It defines a monomial as a number or product of numbers and variables with whole number exponents, and a polynomial as a sum or difference of monomials. It explains that the degree of a monomial or polynomial is determined by summing the exponents of its variables. The document provides examples of identifying the degree of monomials, classifying polynomials by their leading coefficient, degree, and number of terms, and adding or subtracting polynomials.