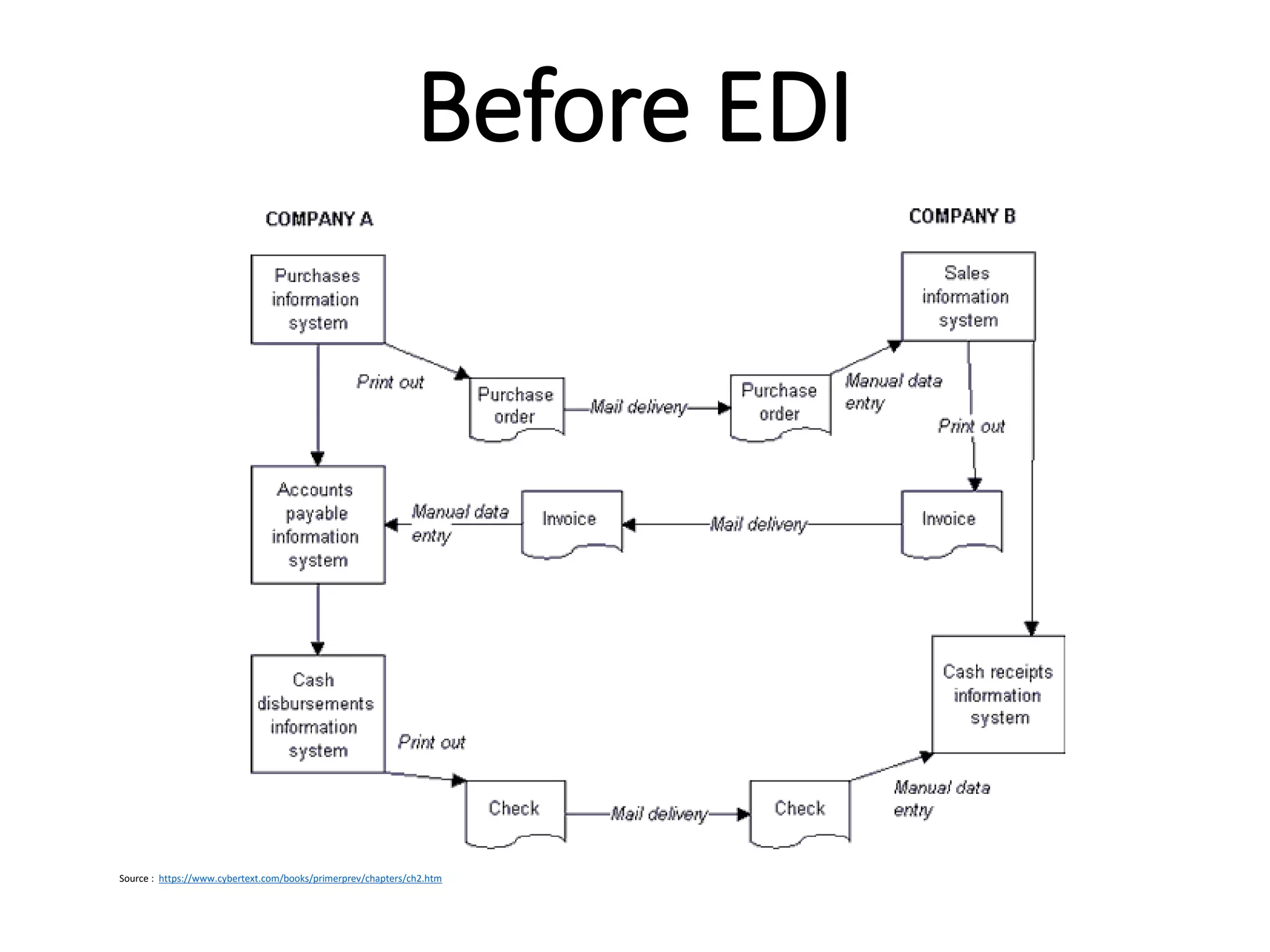
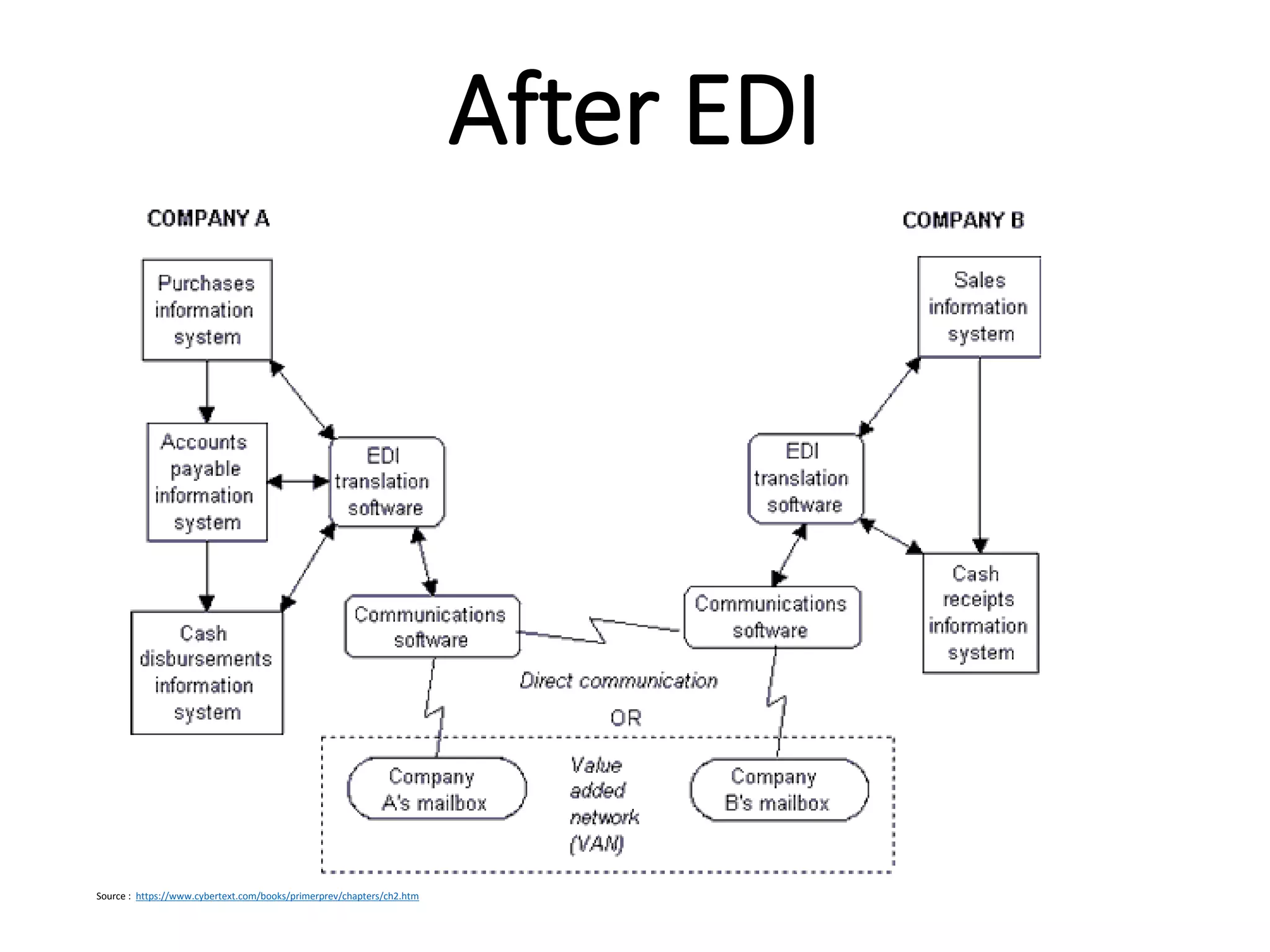
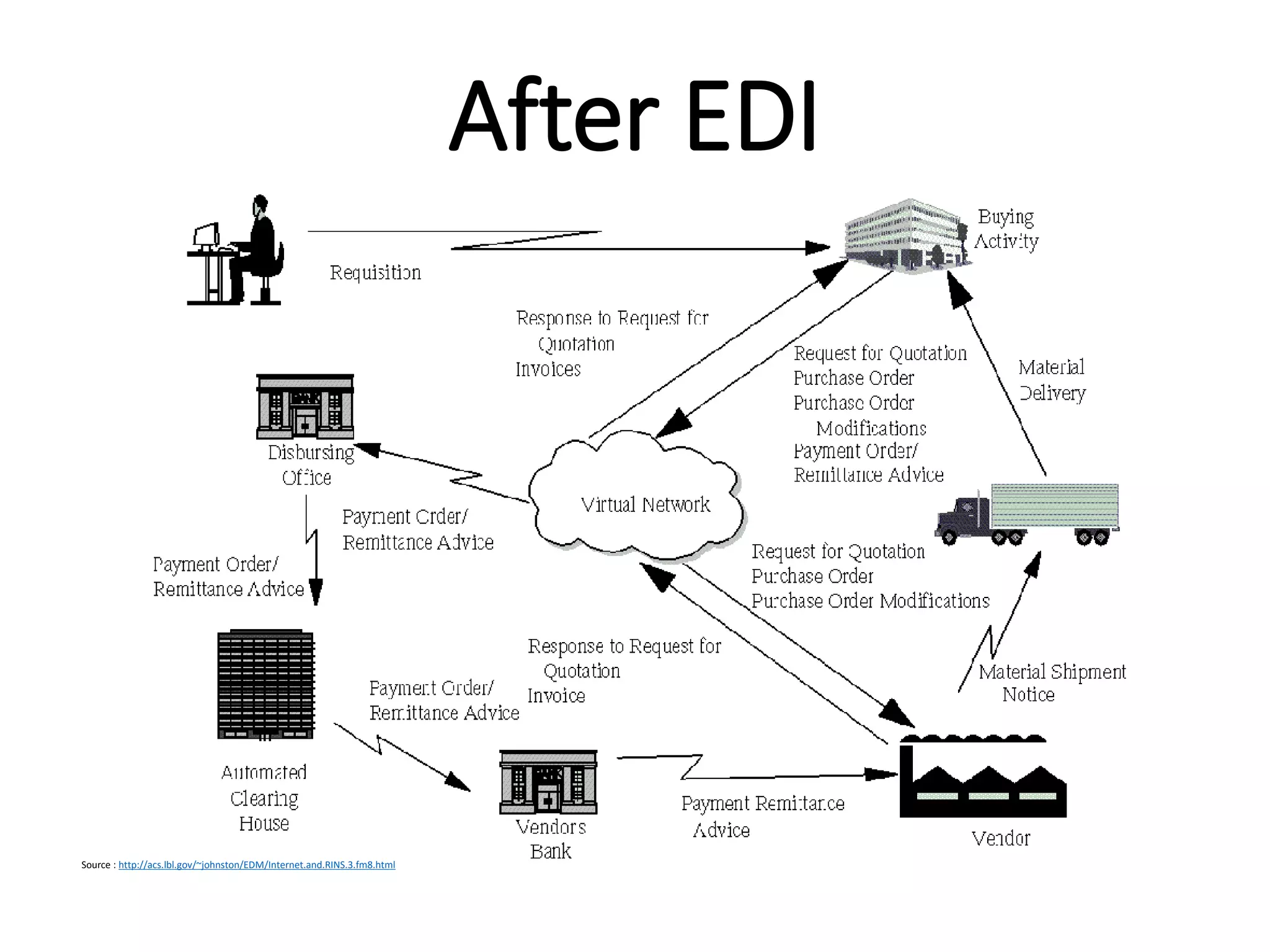
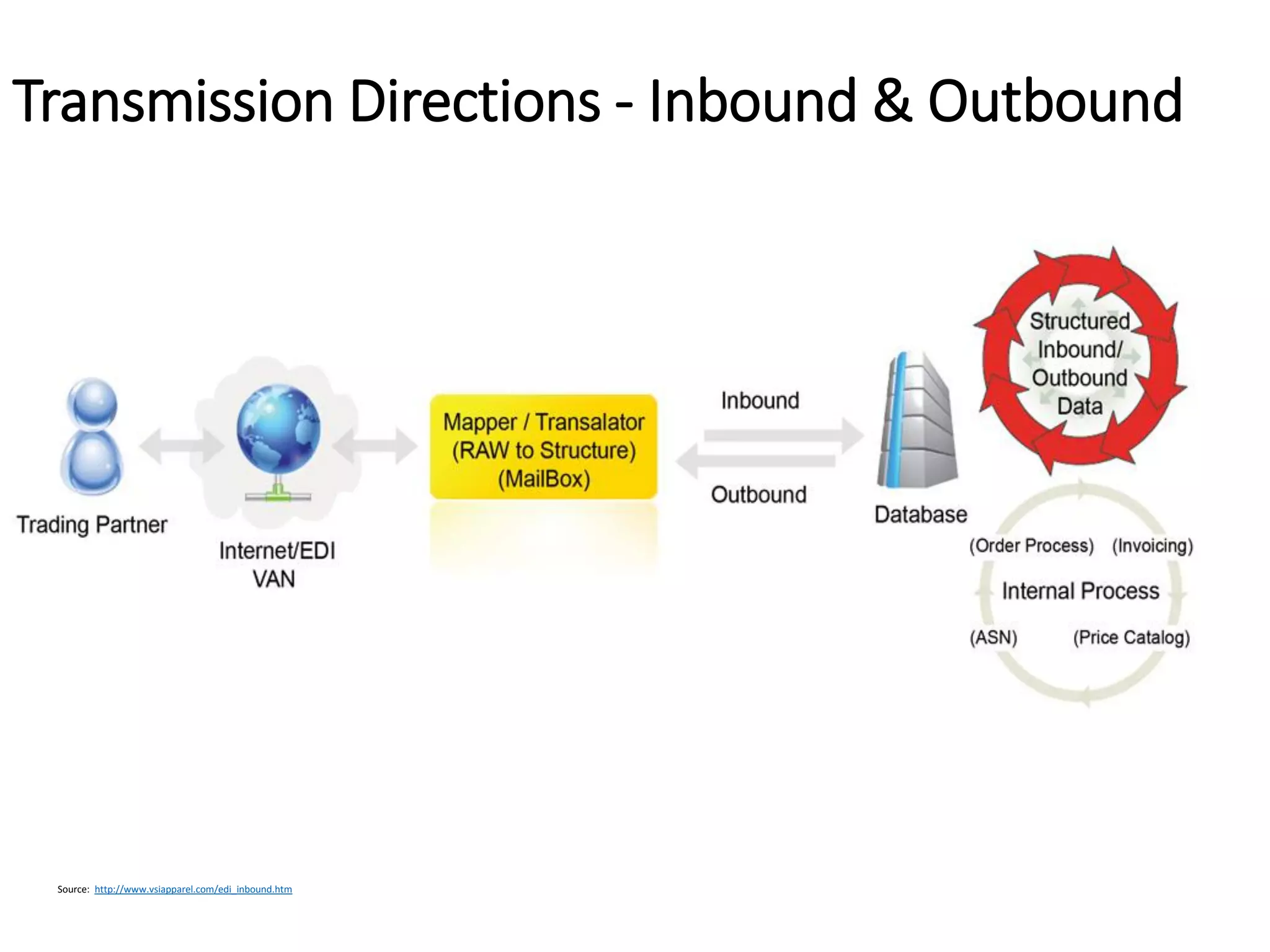
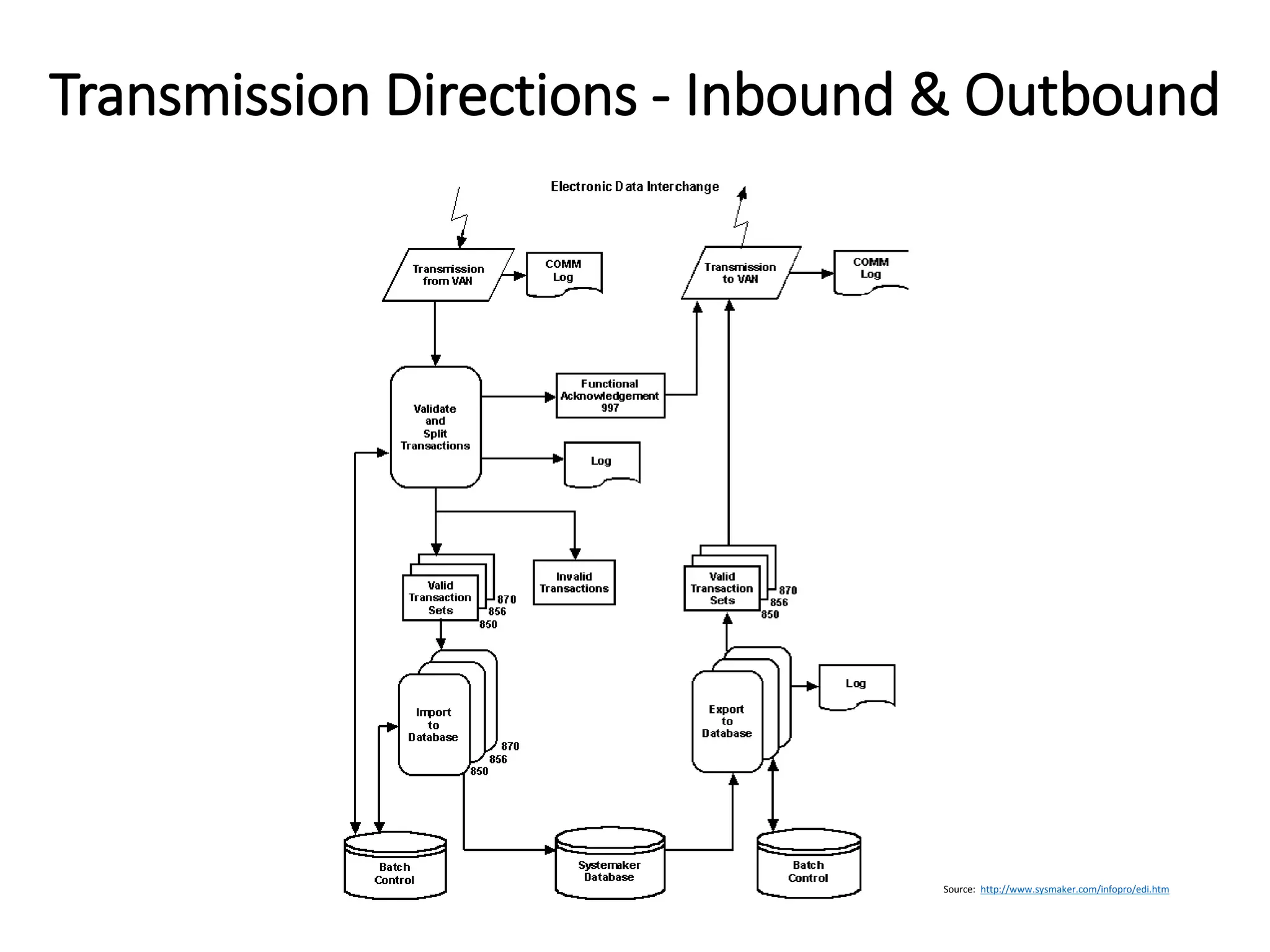
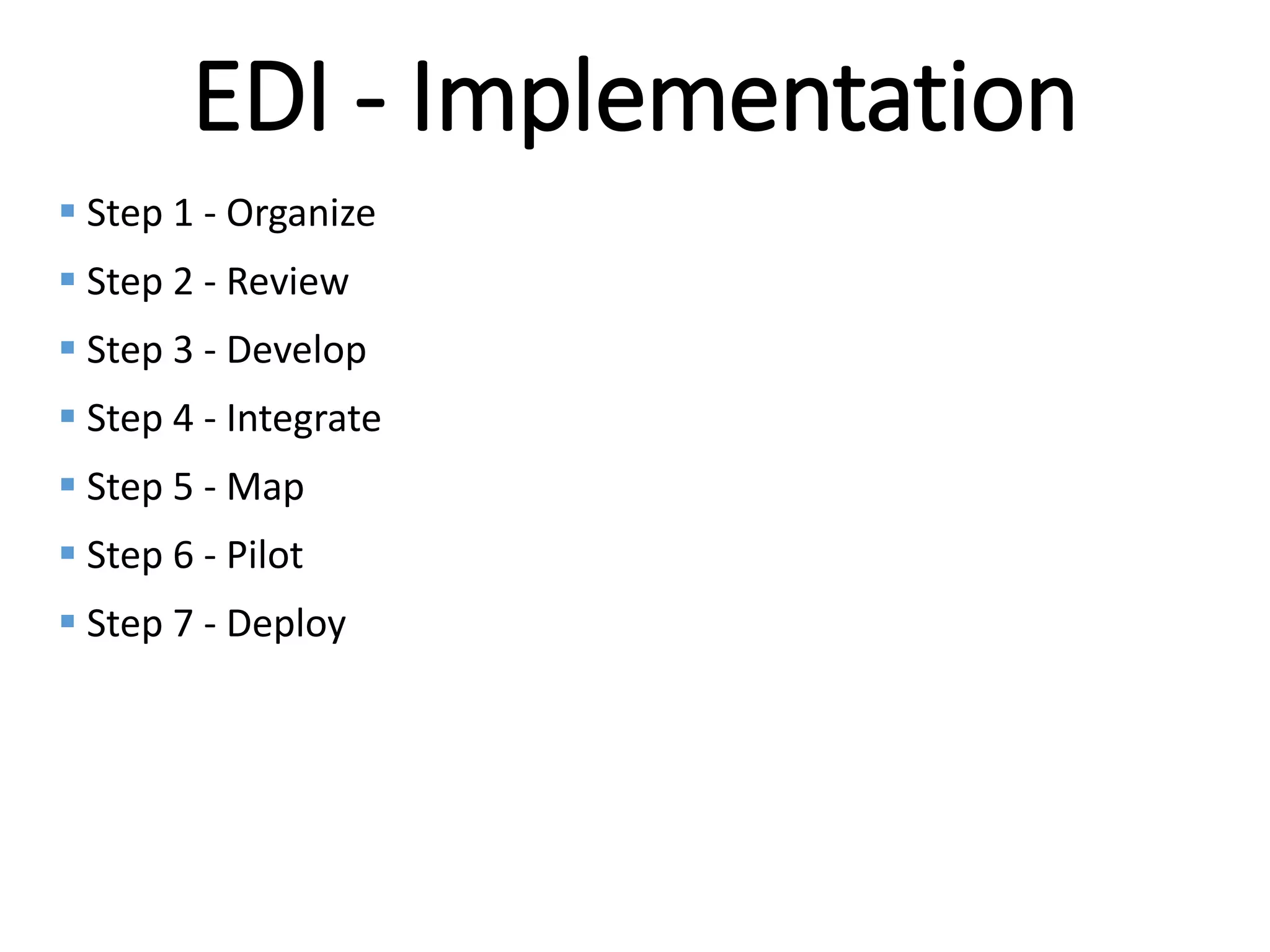
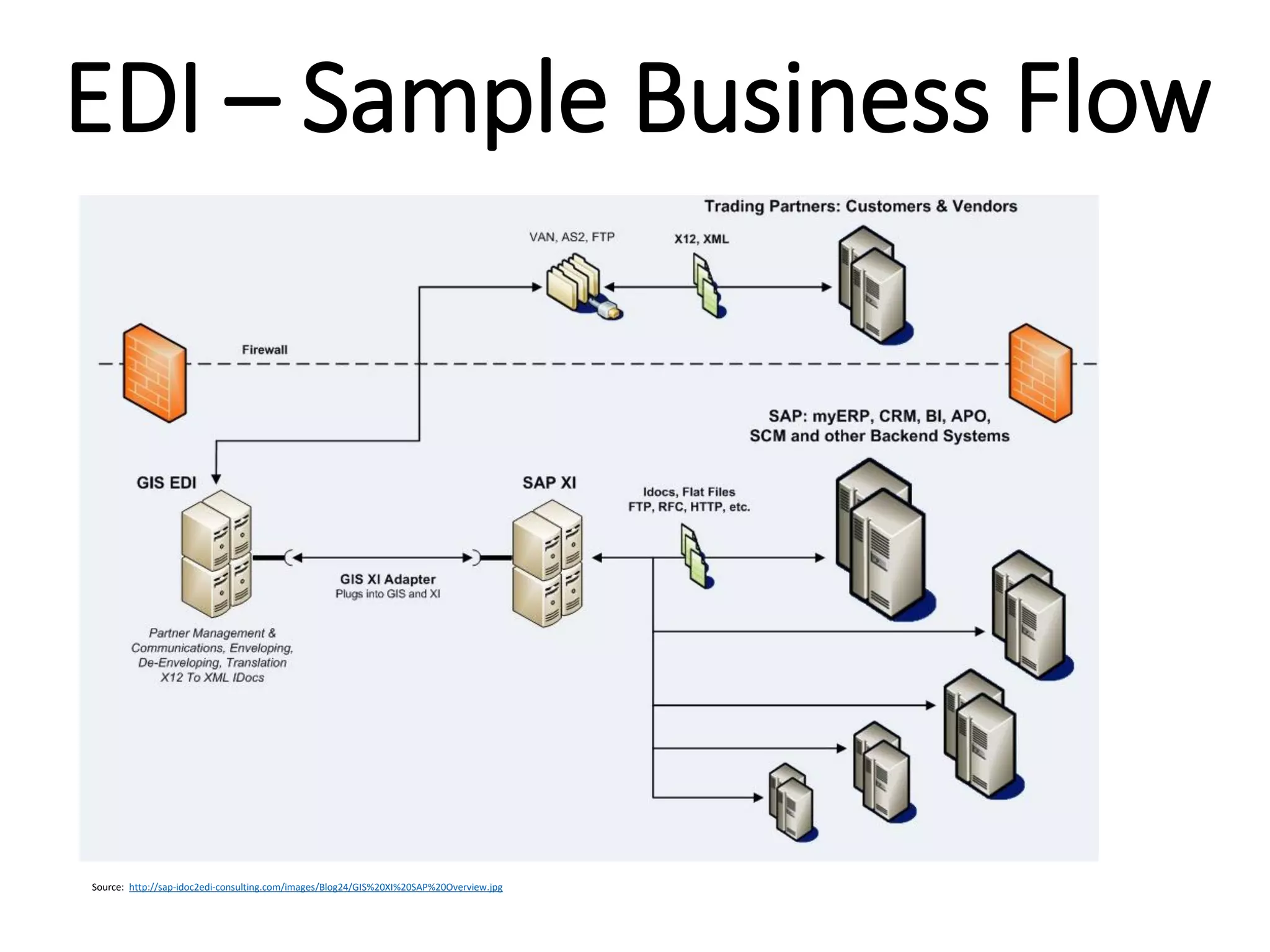
The document provides an introduction to electronic data interchange (EDI), including definitions, history, benefits, transmission methods, and common standards. EDI allows structured business documents like purchase orders to be electronically transmitted between trading partners in a standardized format, streamlining processes. It originated in the 1960s and saw growing adoption through the 1980s as industry standards like ANSI X12 emerged. Key benefits of EDI include reduced costs, improved speed, accuracy and inventory management.