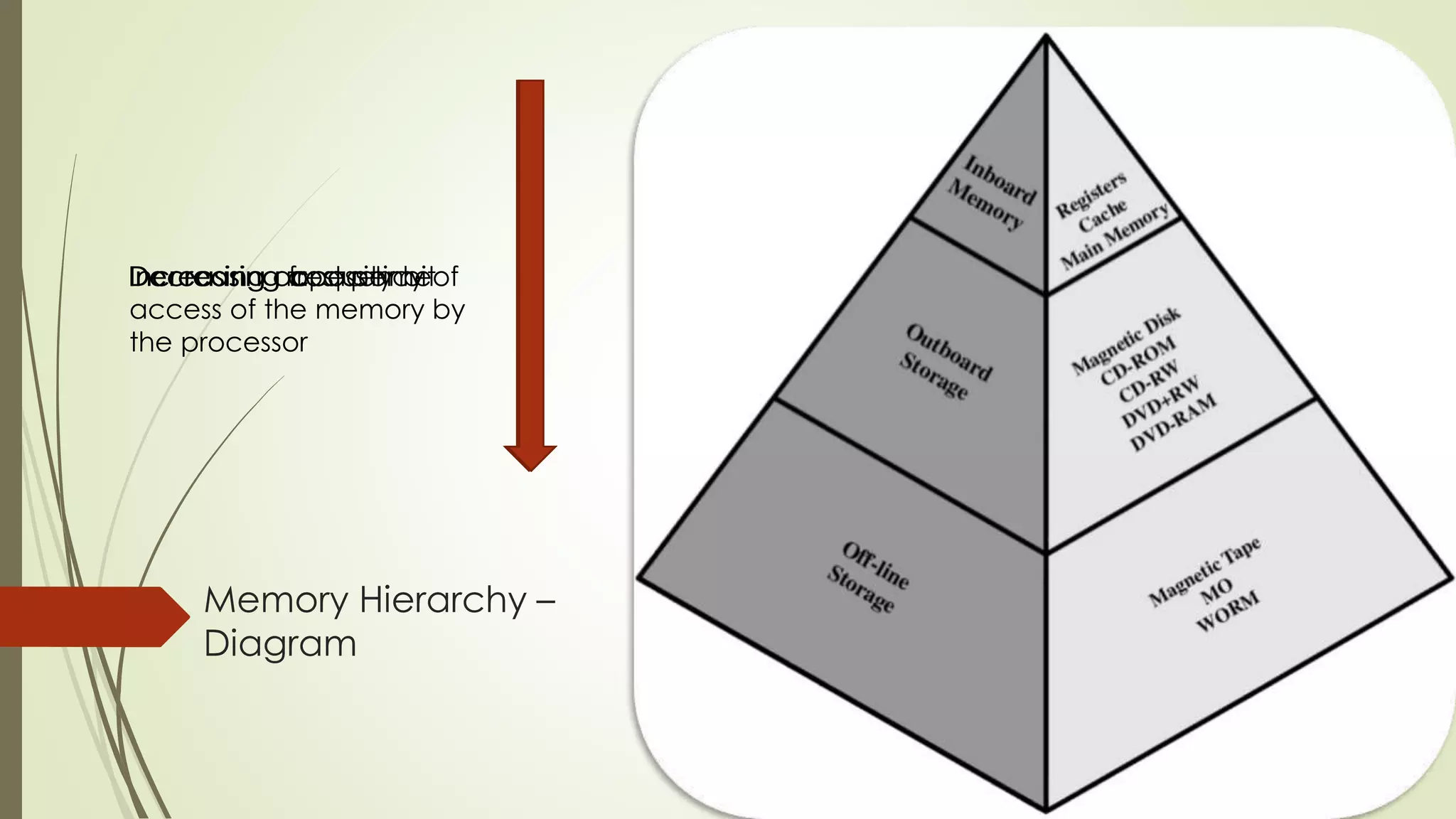
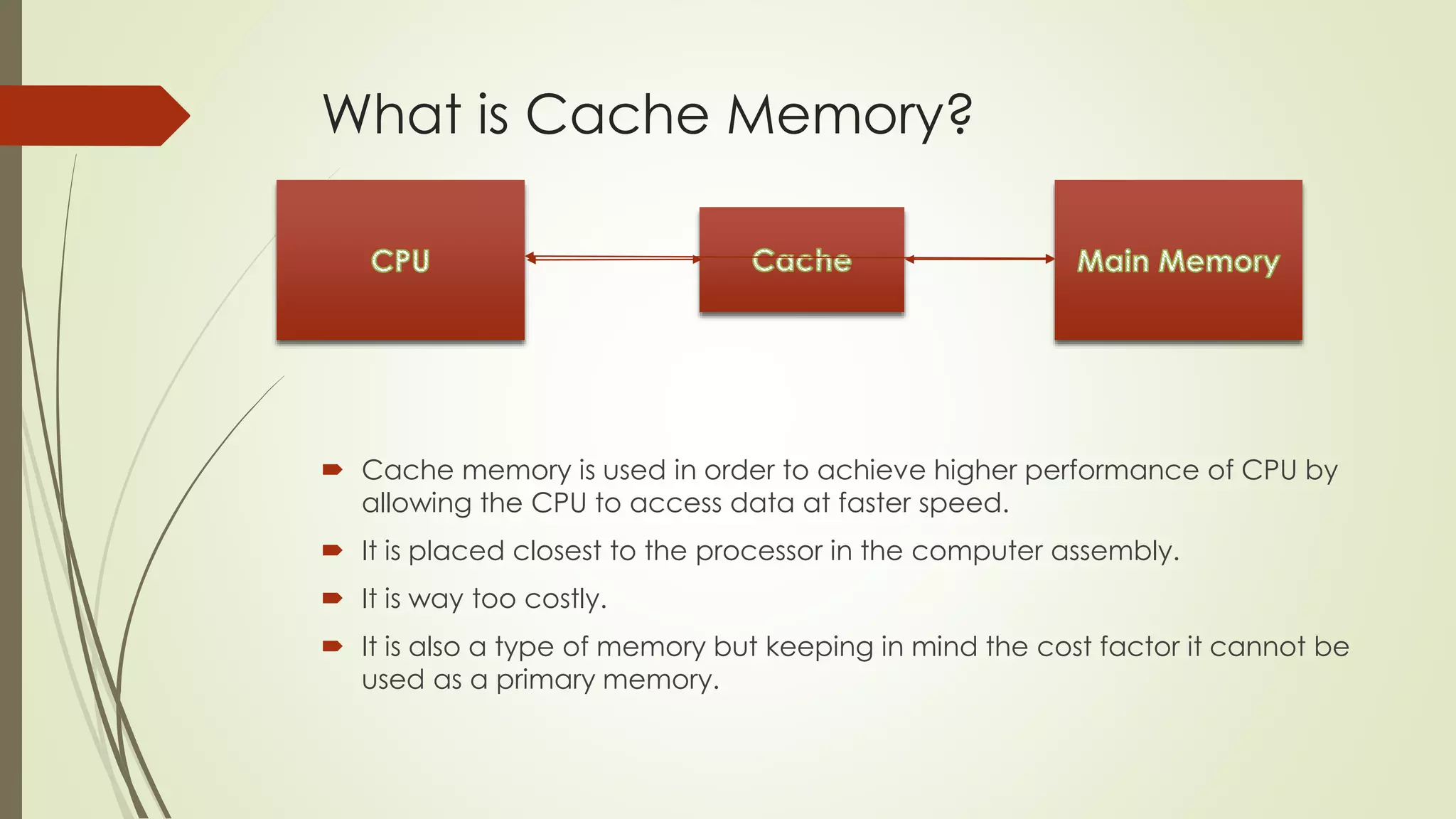
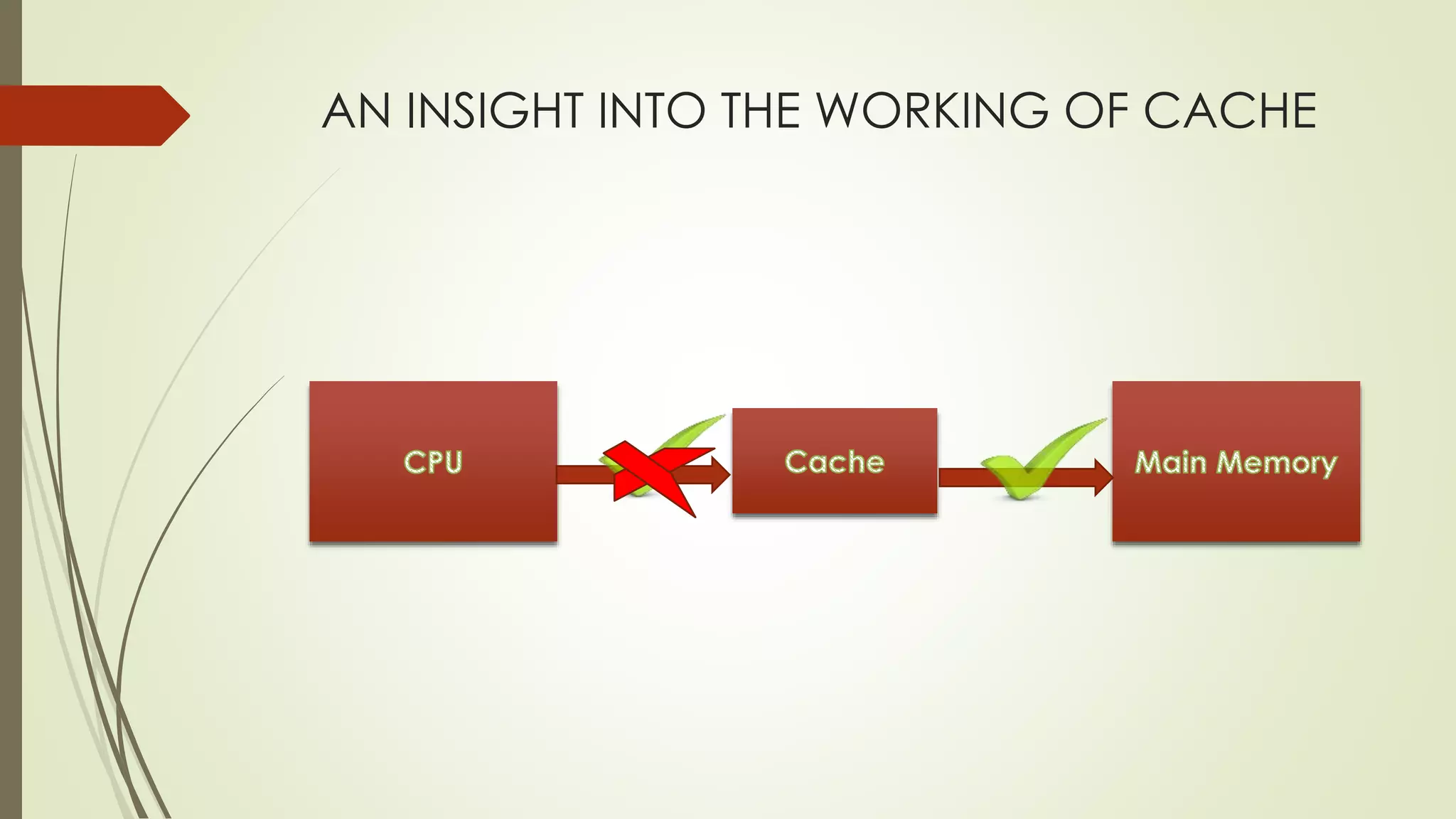
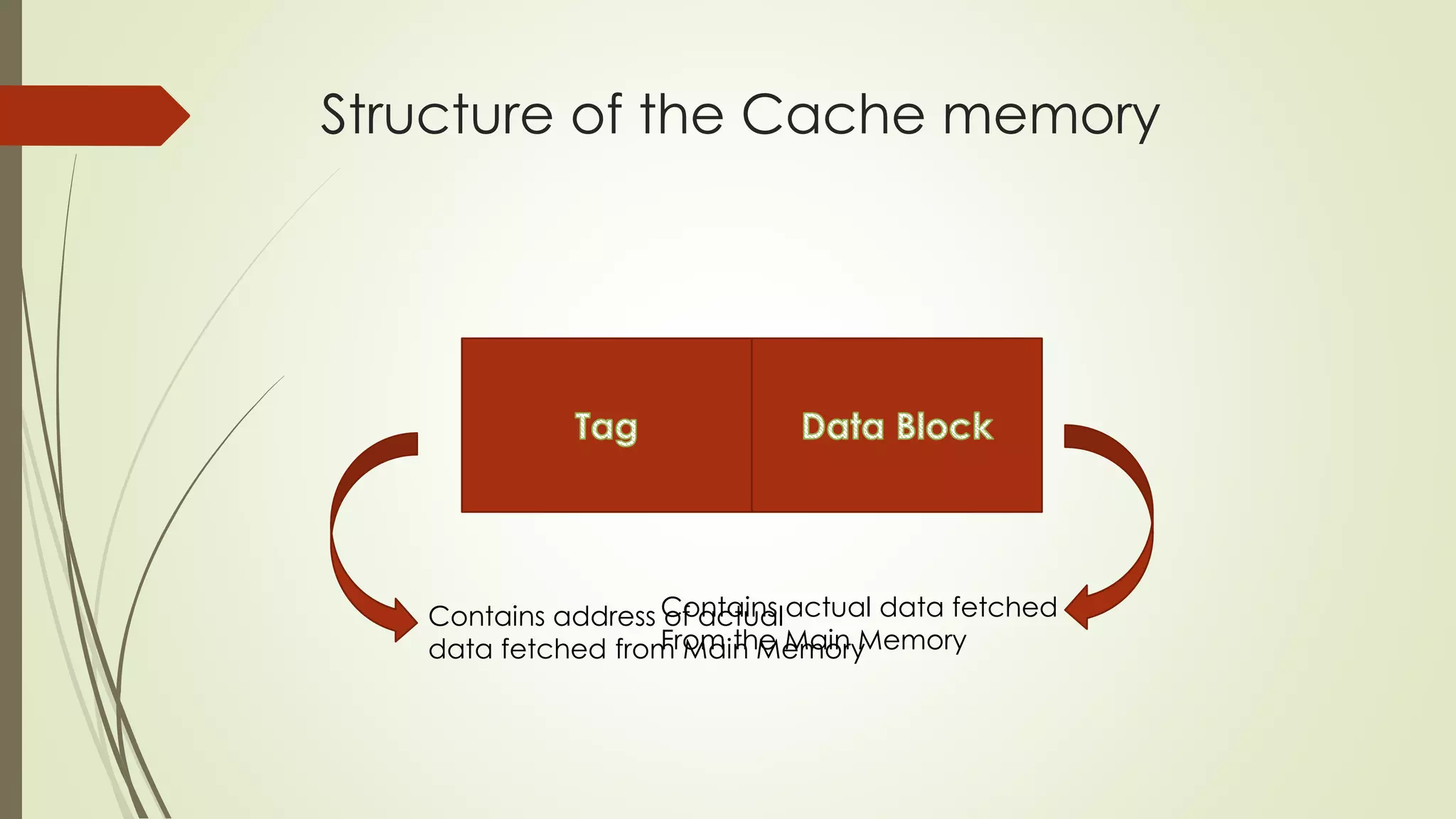
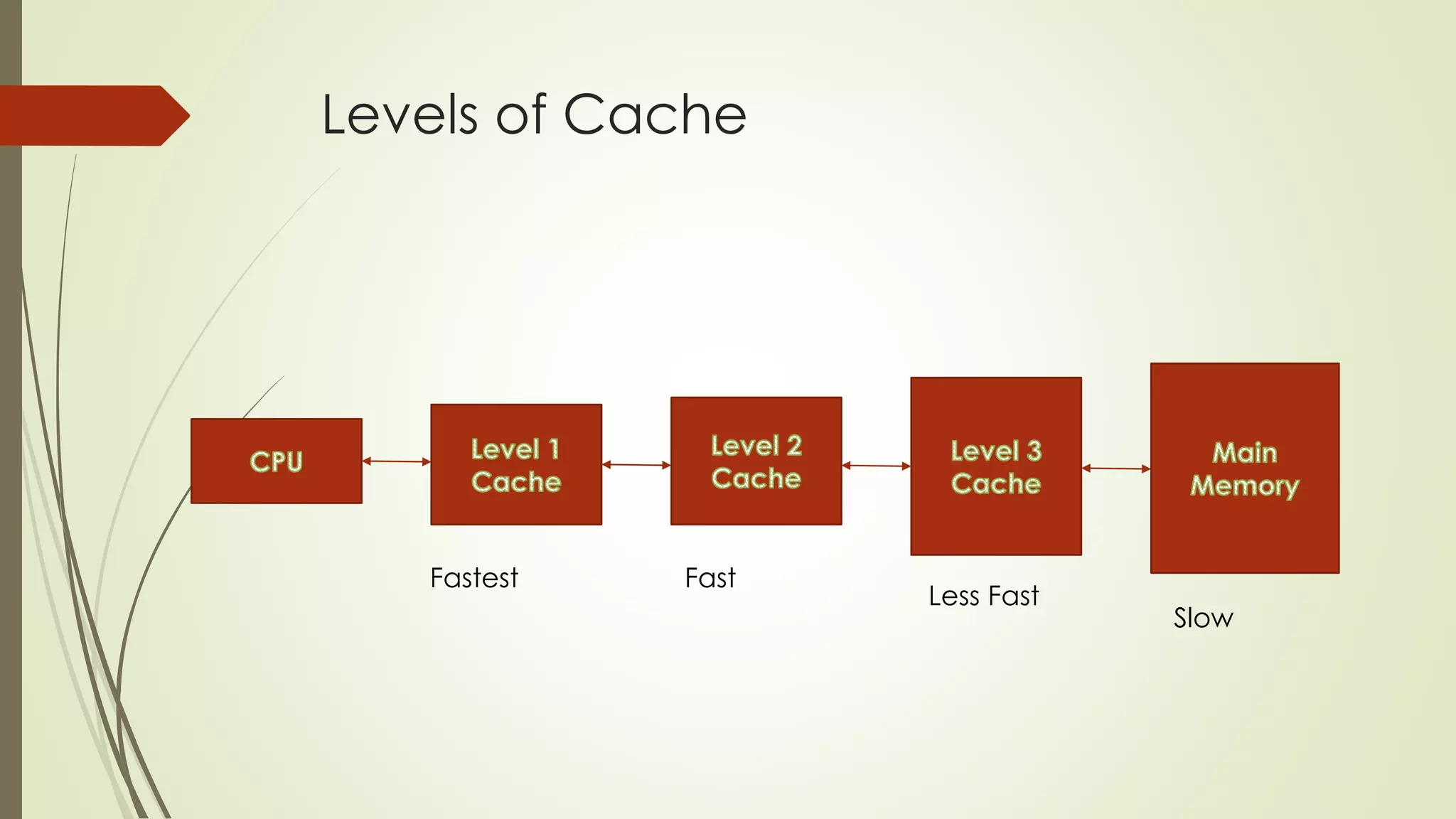
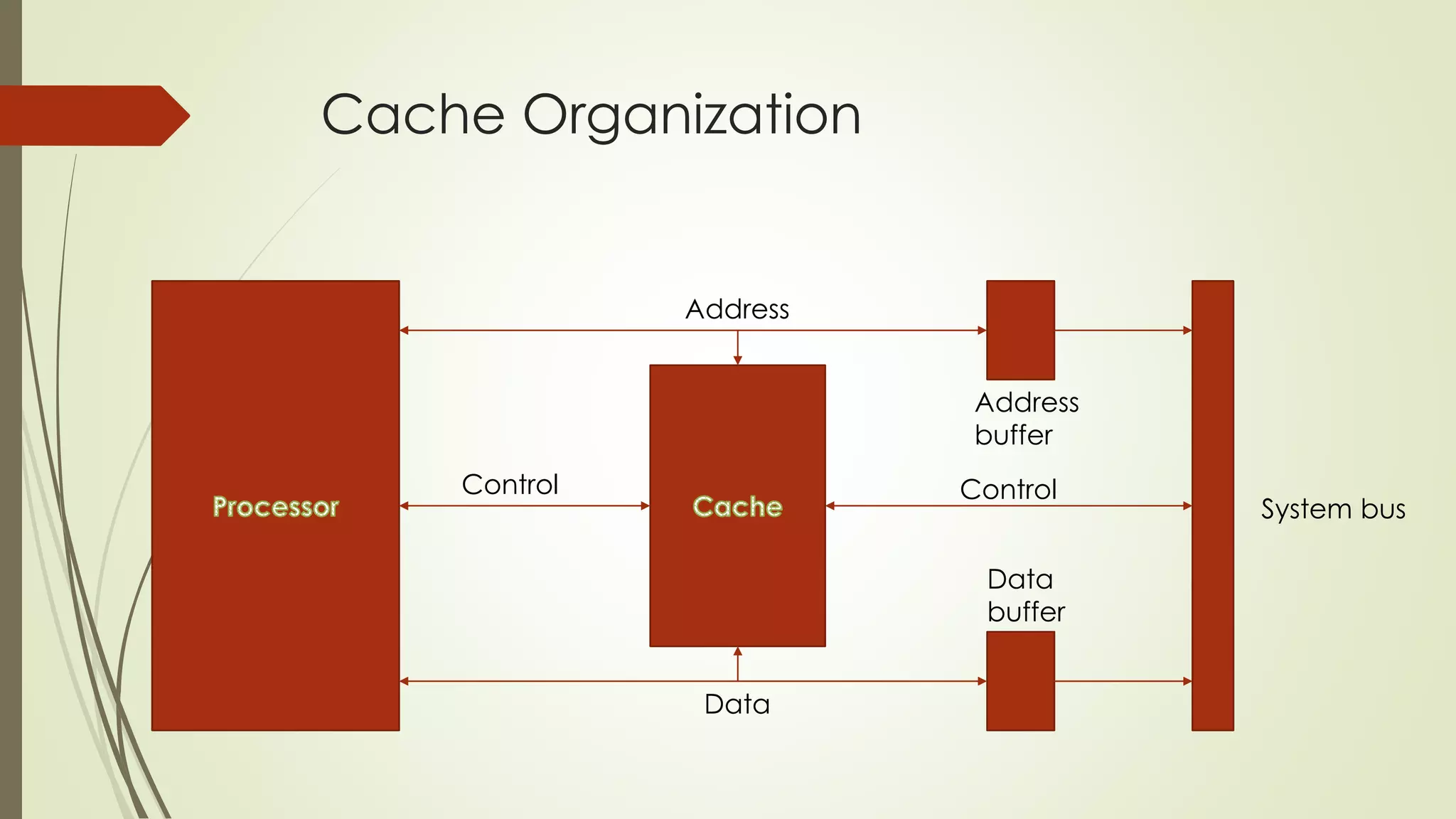
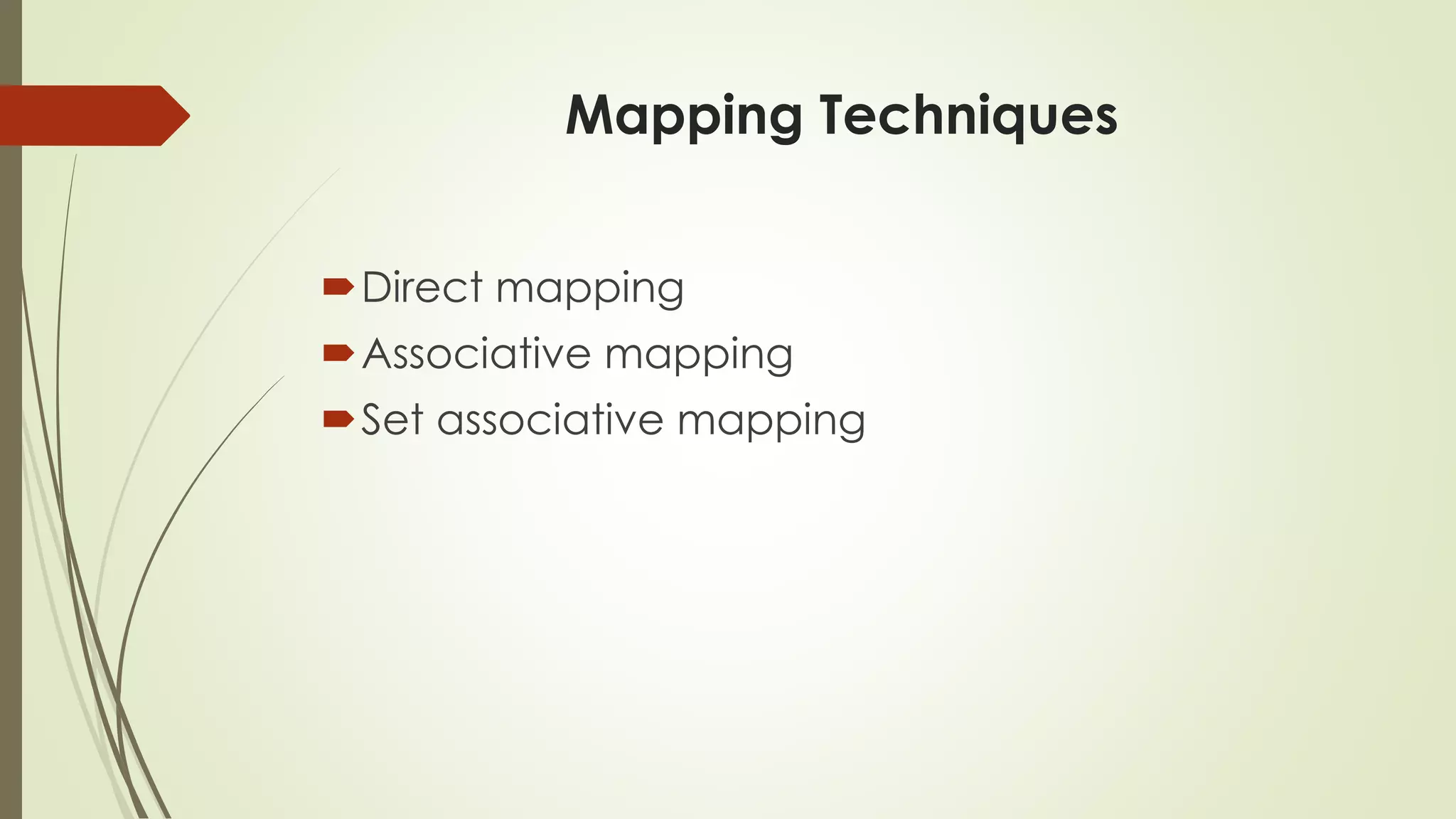
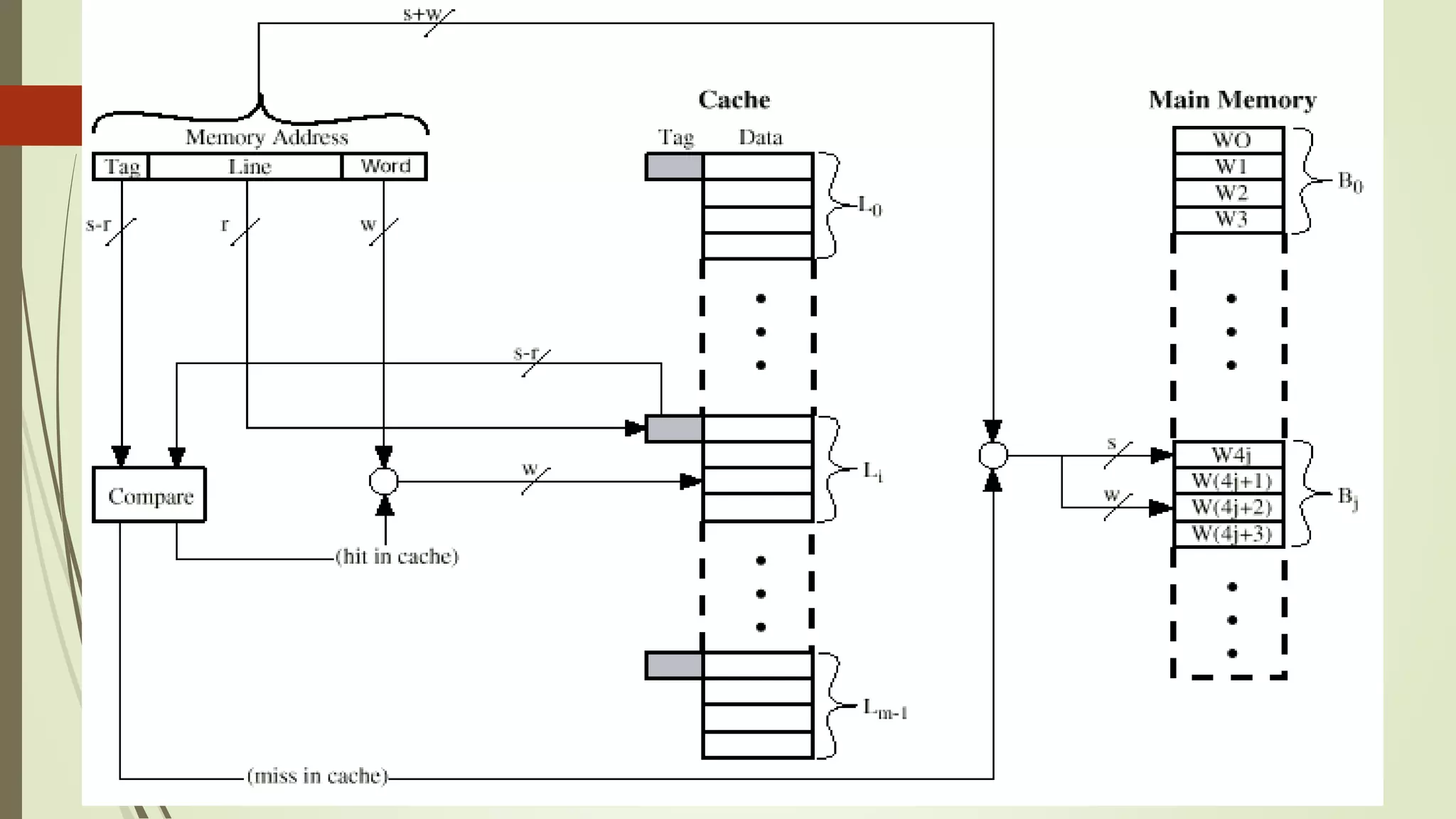
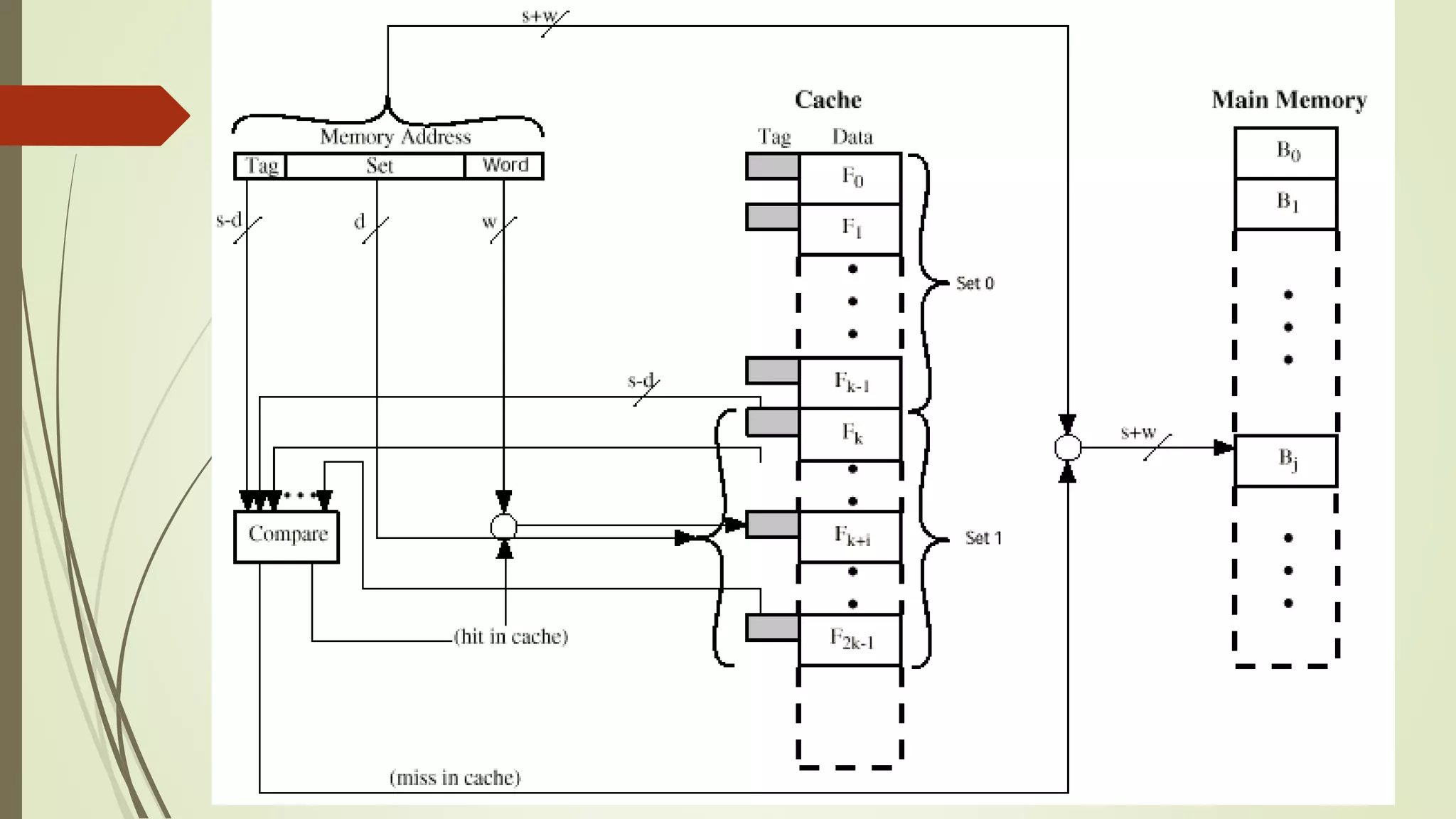
Cache memory is a small, fast memory located close to the CPU that stores frequently accessed instructions and data. It aims to bridge the gap between the fast CPU and slower main memory. Cache memory is organized into blocks that each contain a tag field identifying the memory address, a data field containing the cached data, and status bits. There are different mapping techniques like direct mapping, associative mapping, and set associative mapping to determine how blocks are stored in cache. When cache is full, replacement algorithms like LRU, FIFO, LFU, and random are used to determine which existing block to replace with the new block.