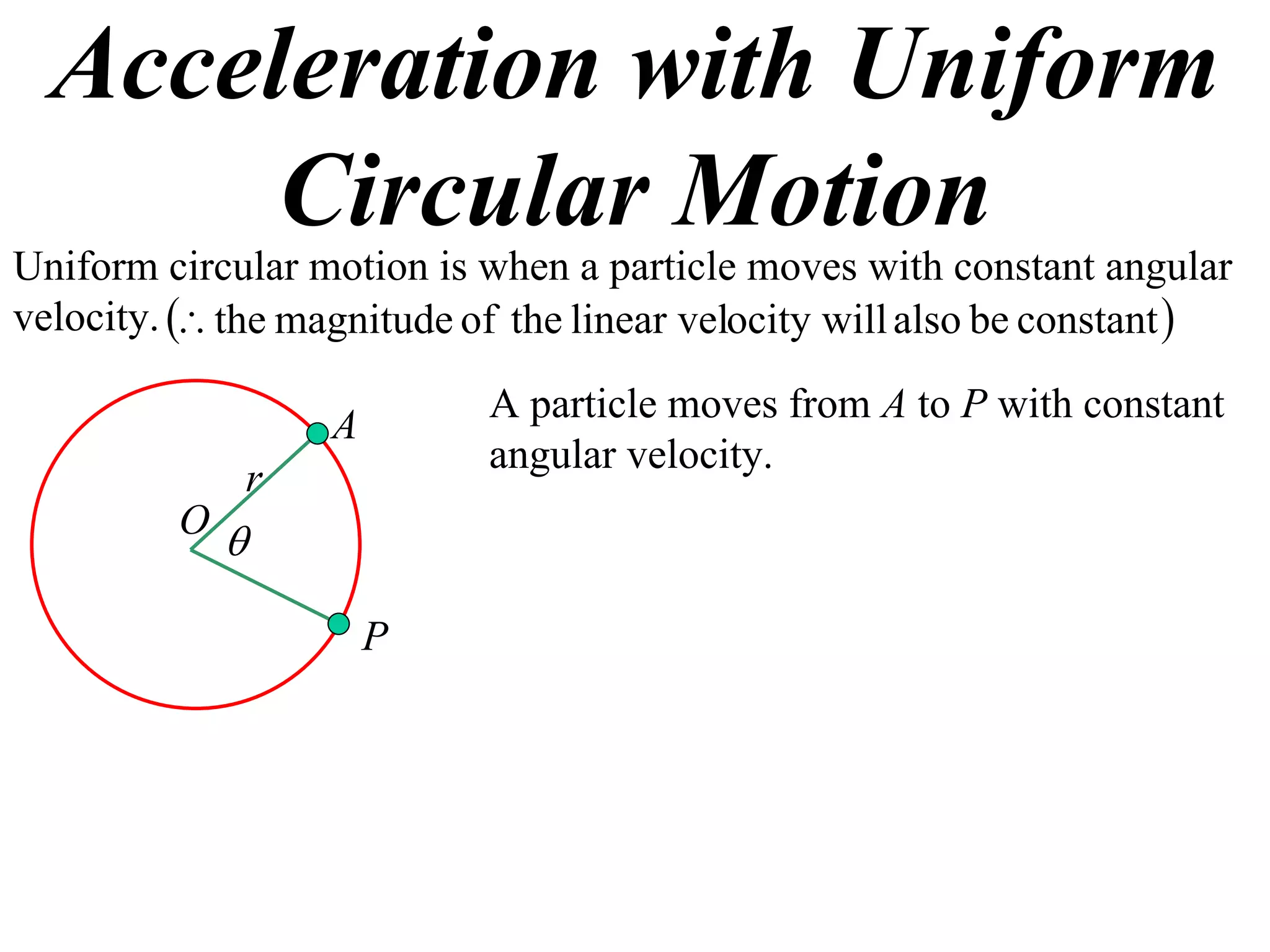
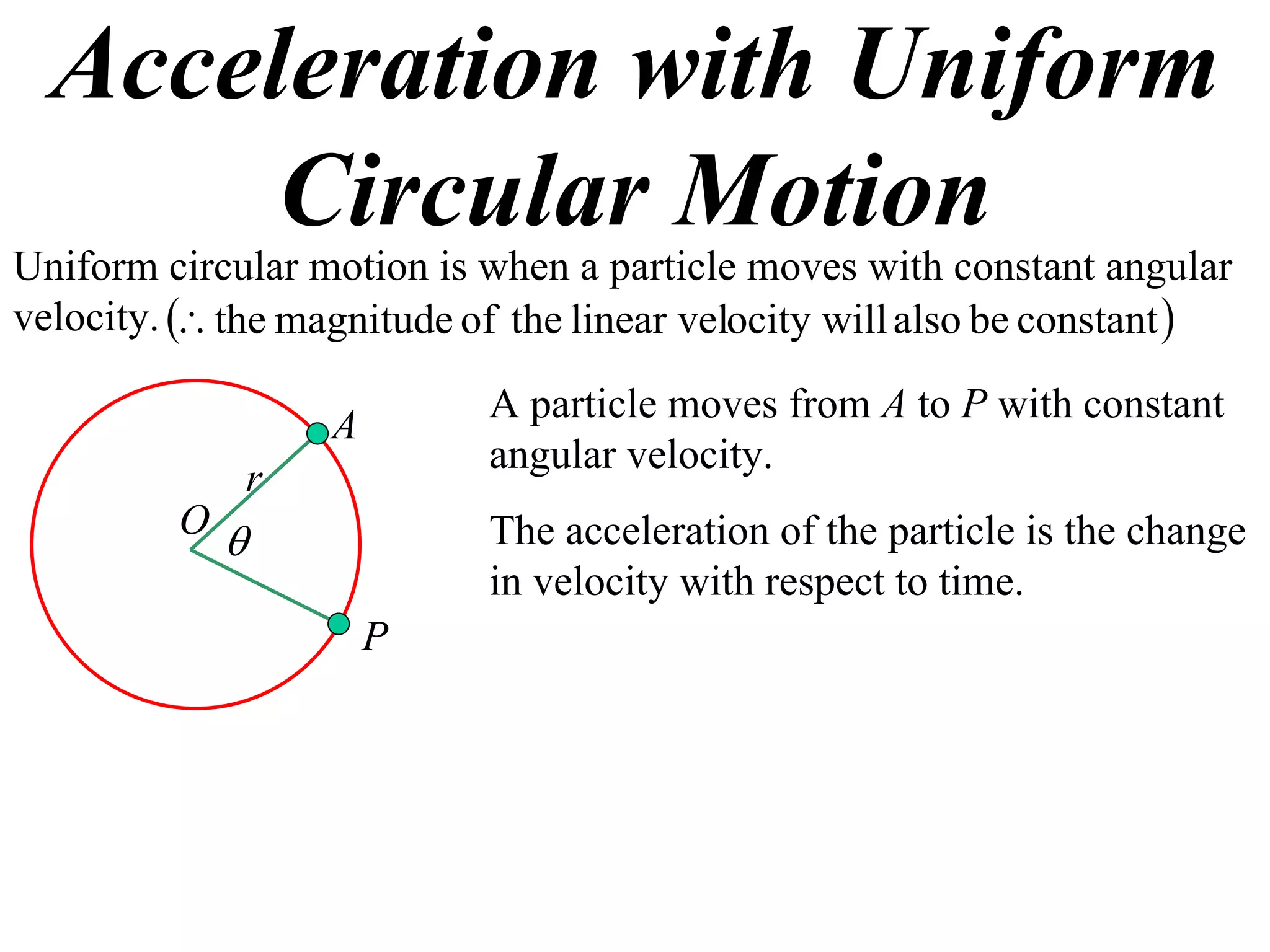
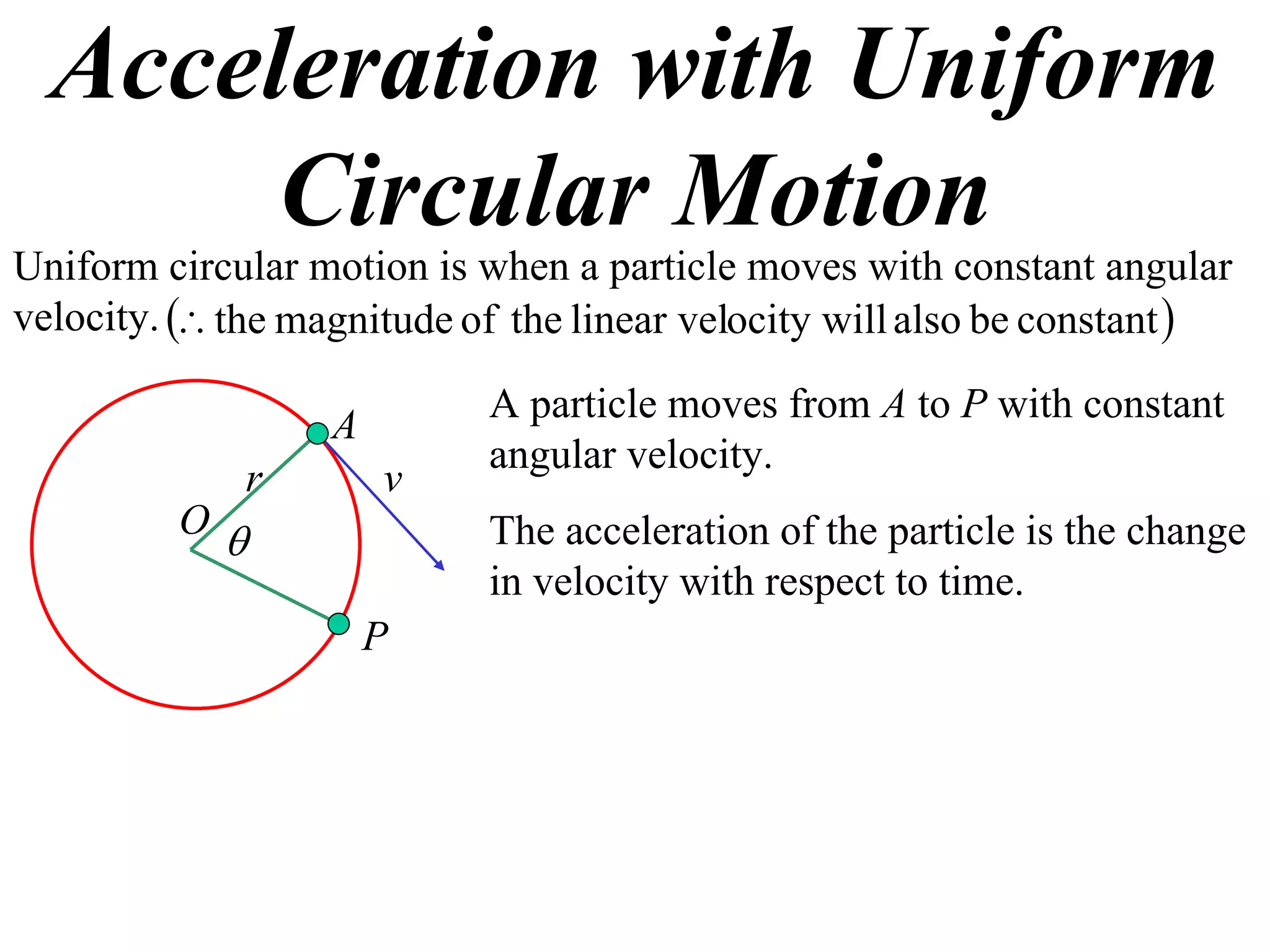
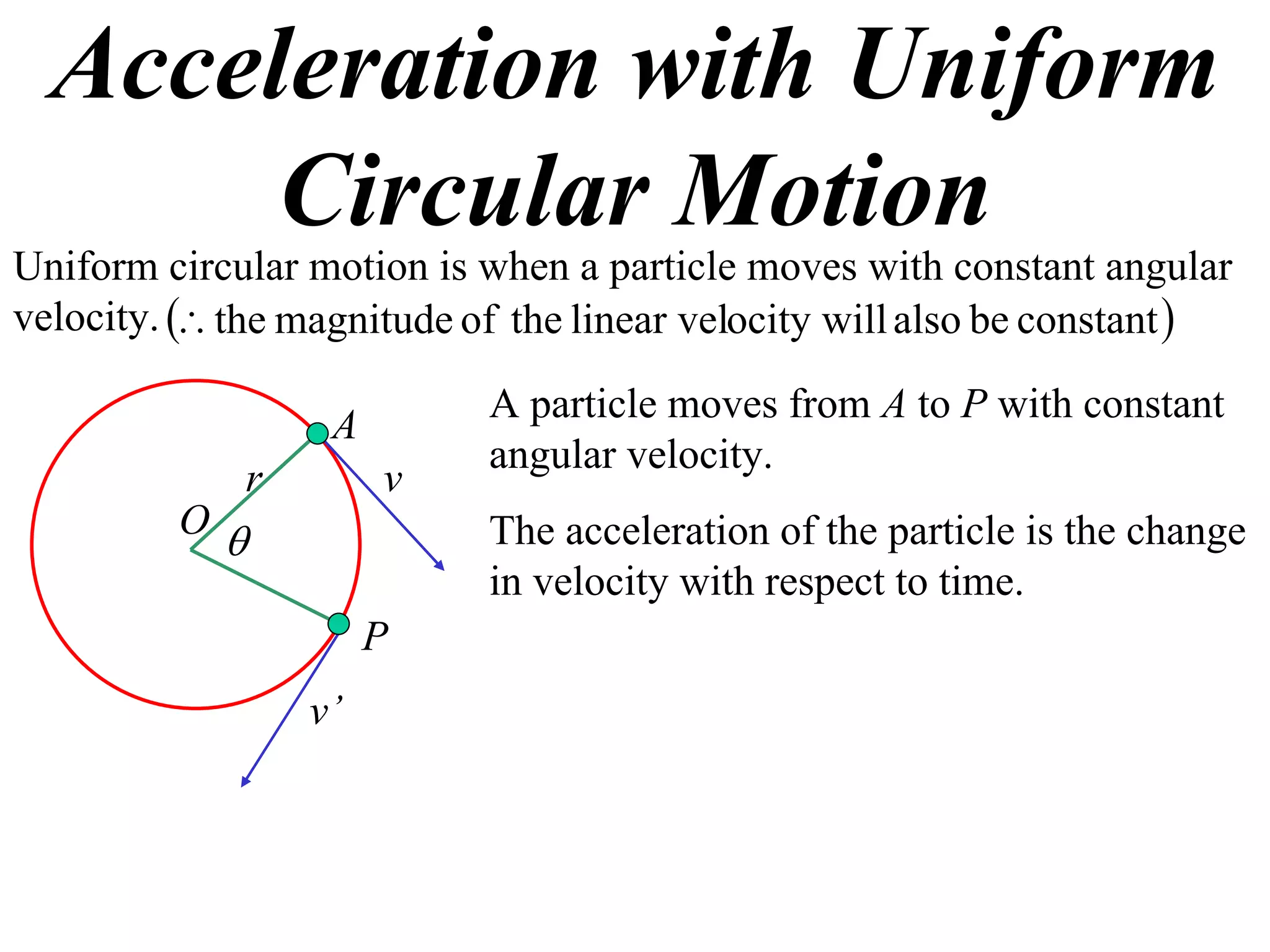
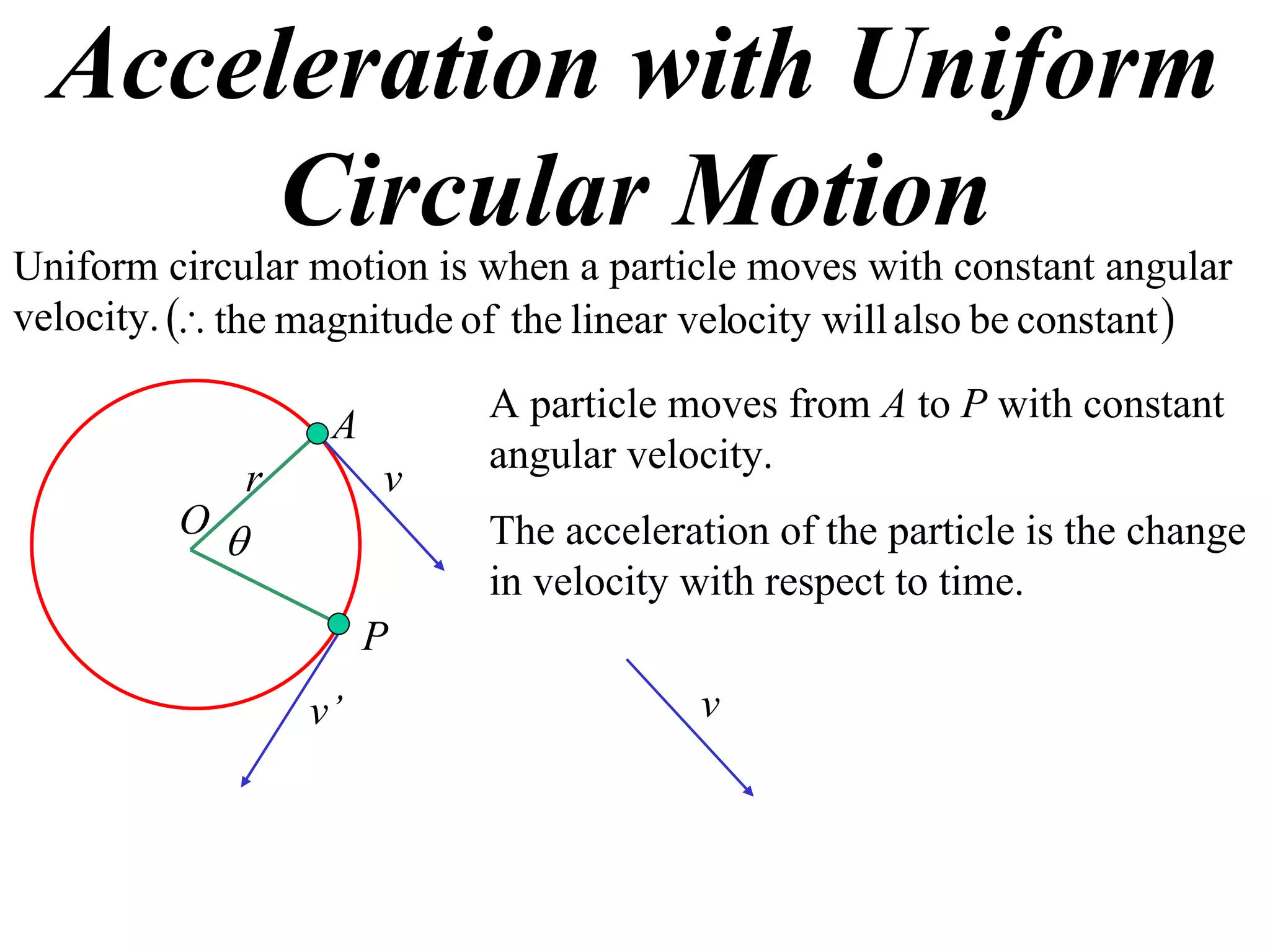
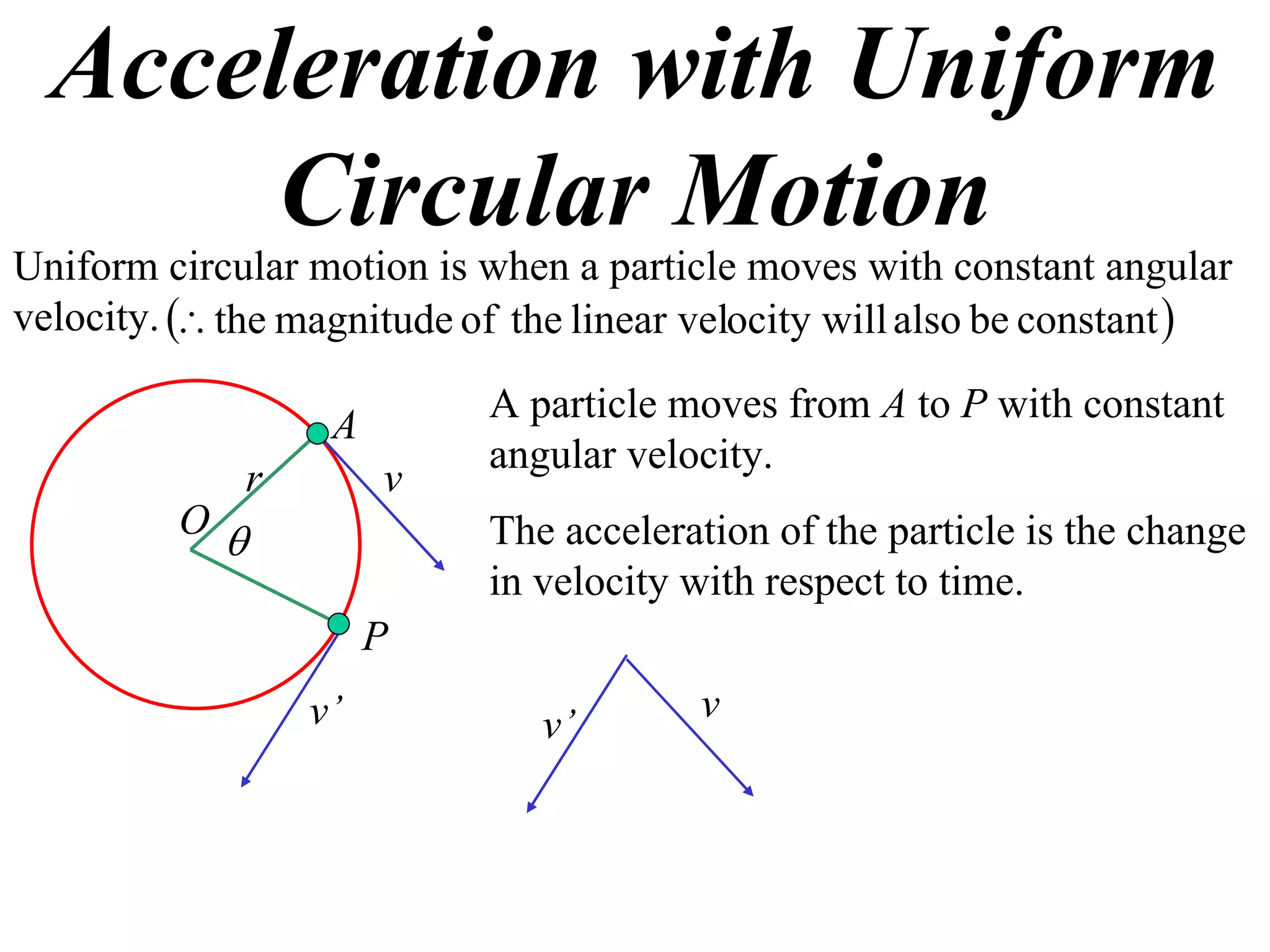
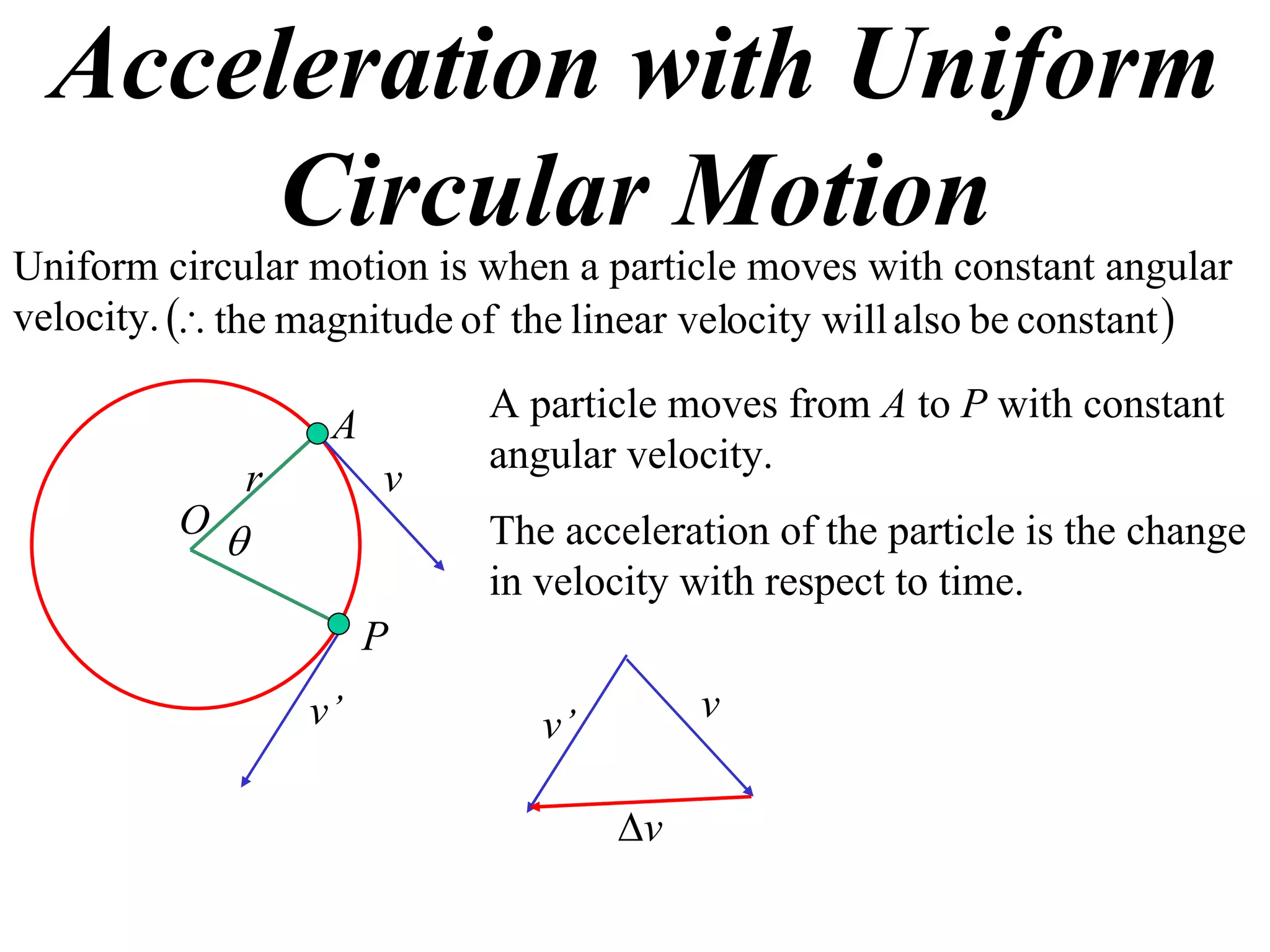
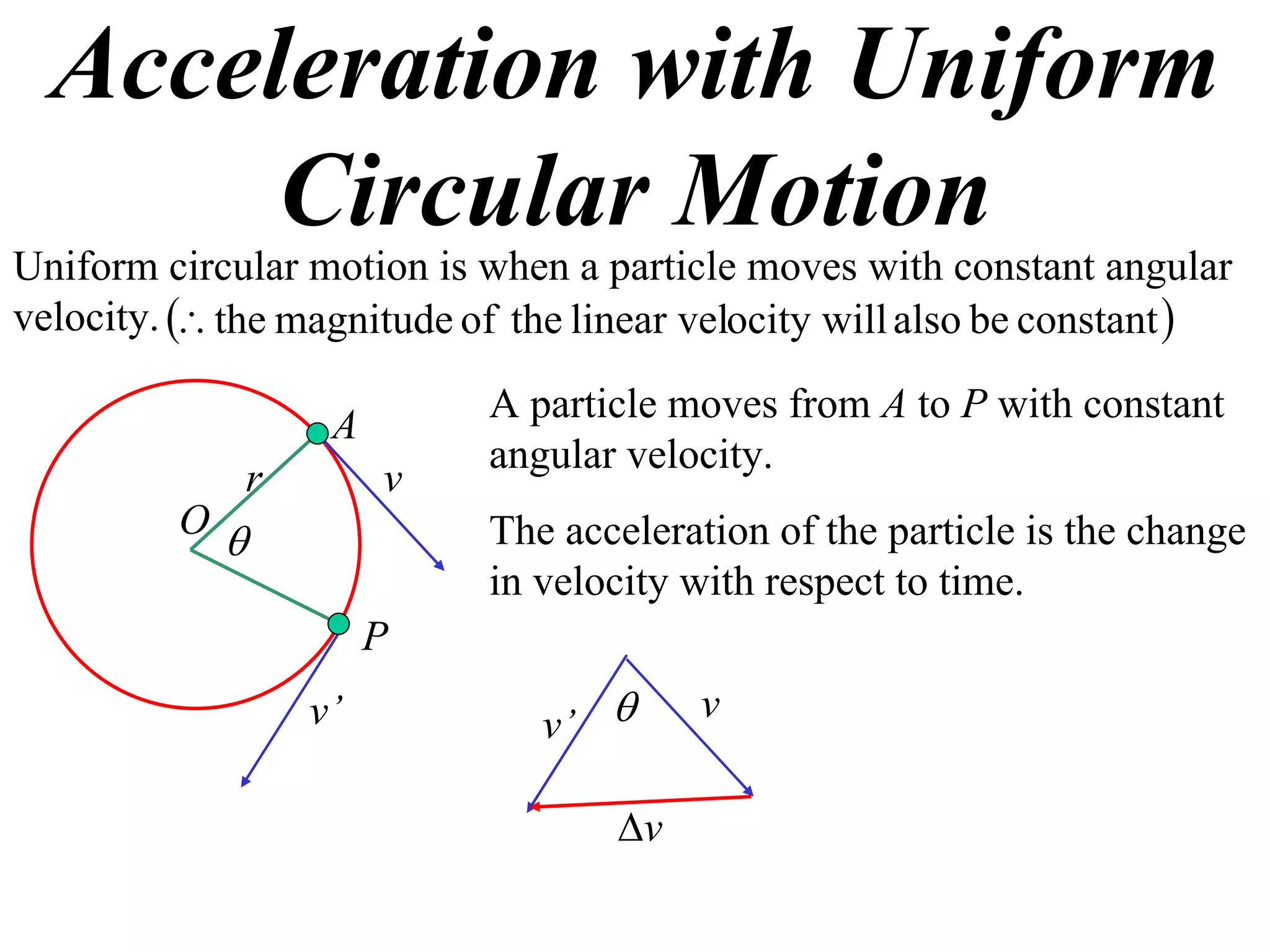
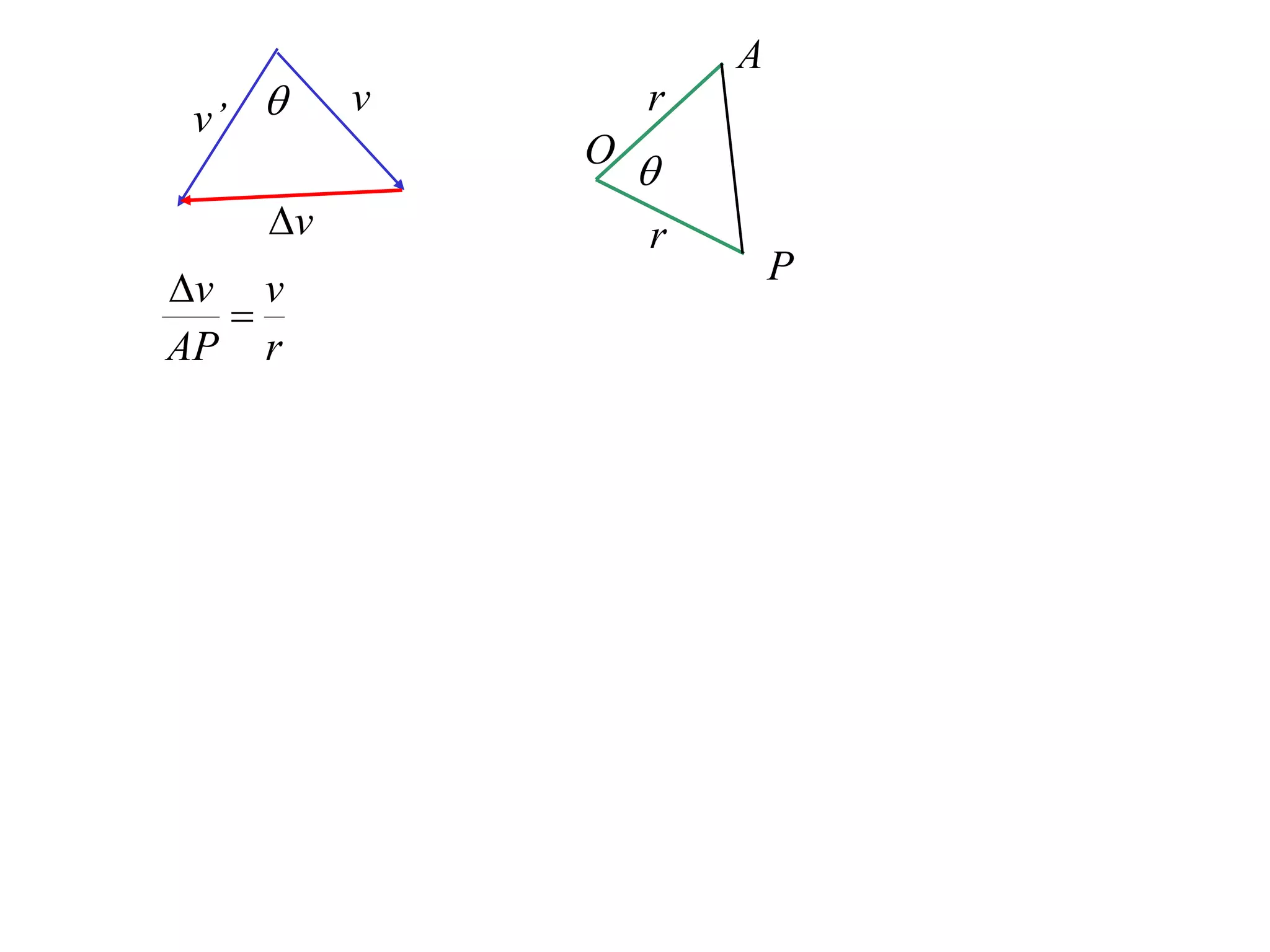
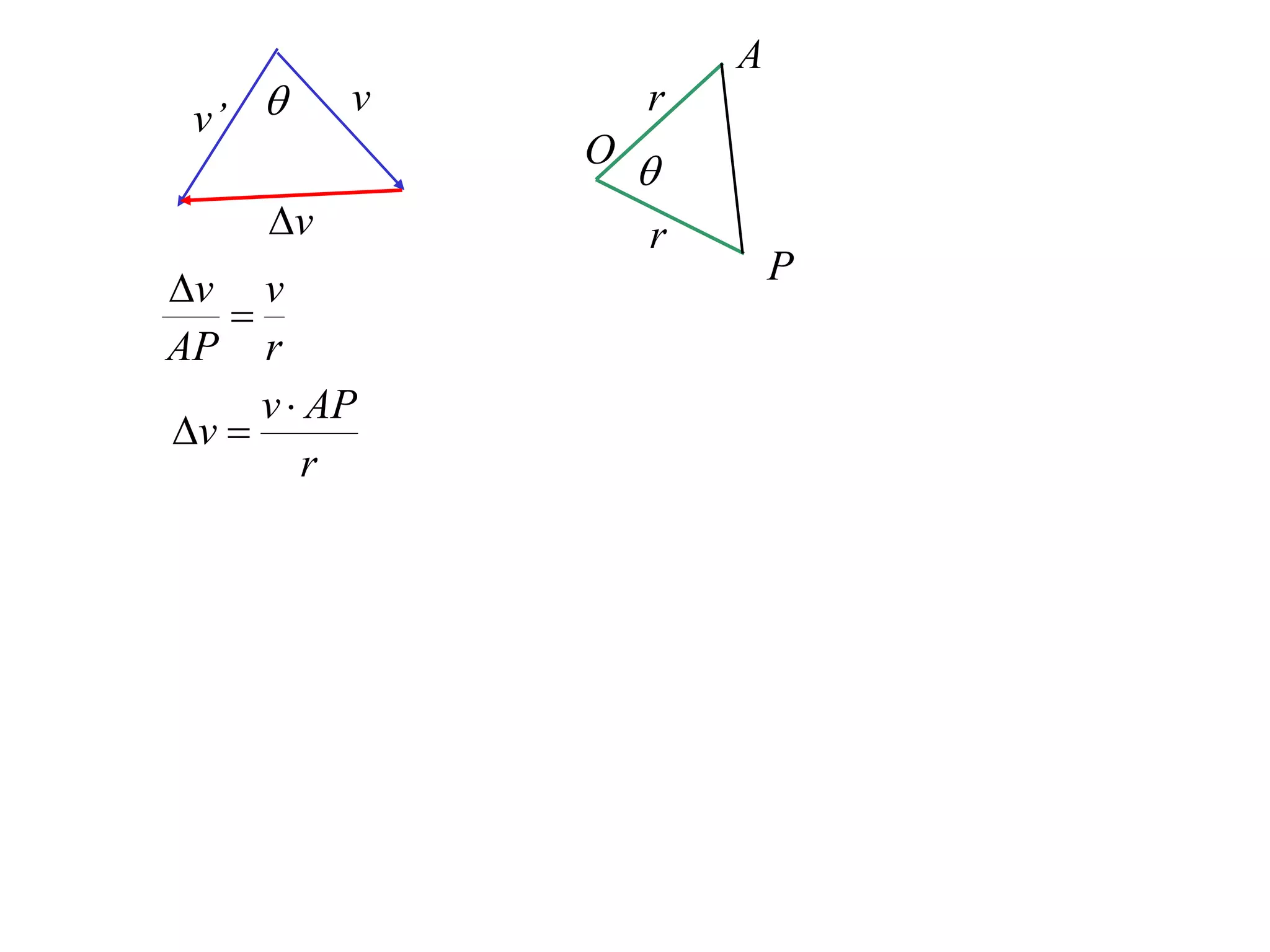
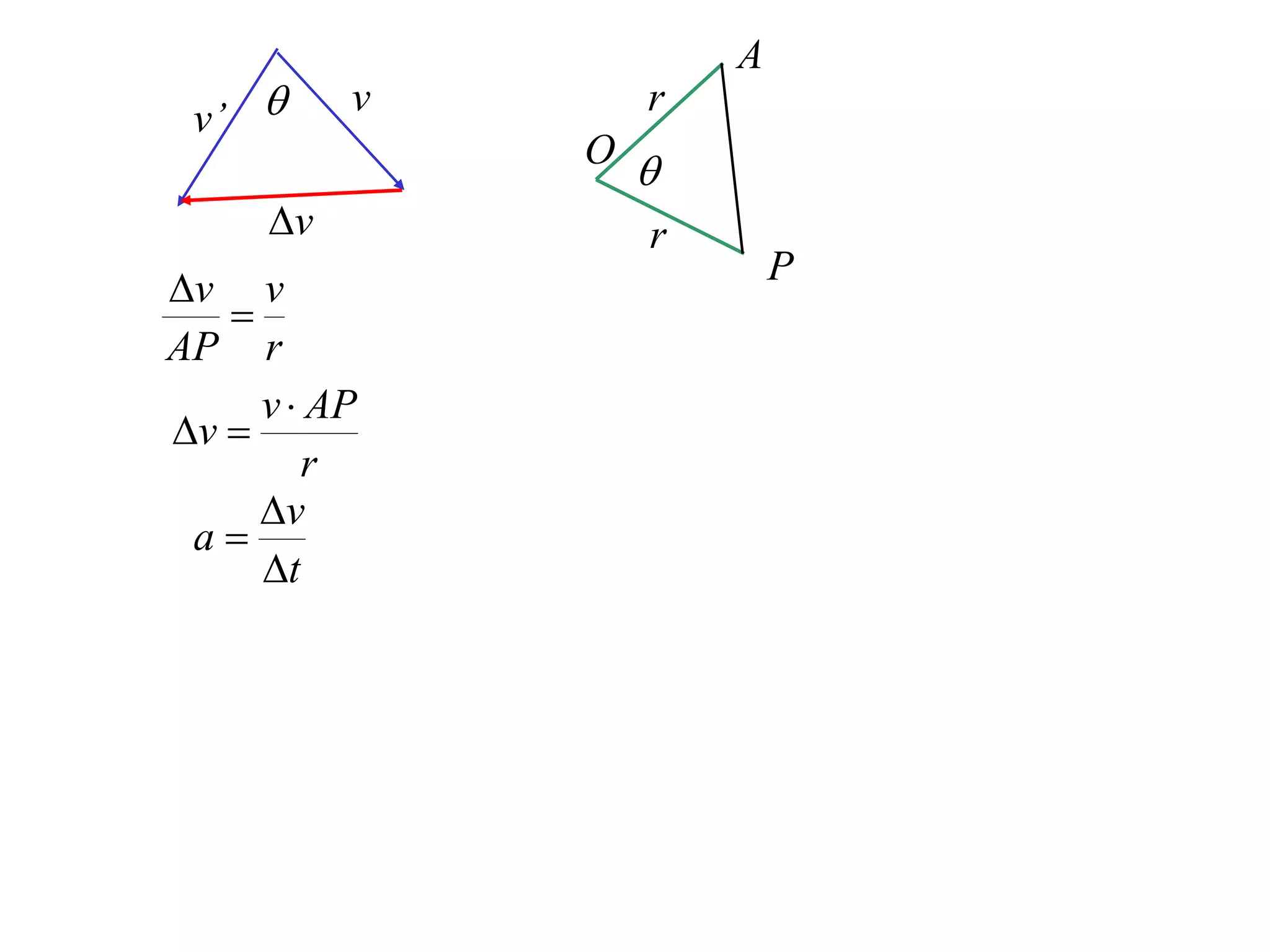
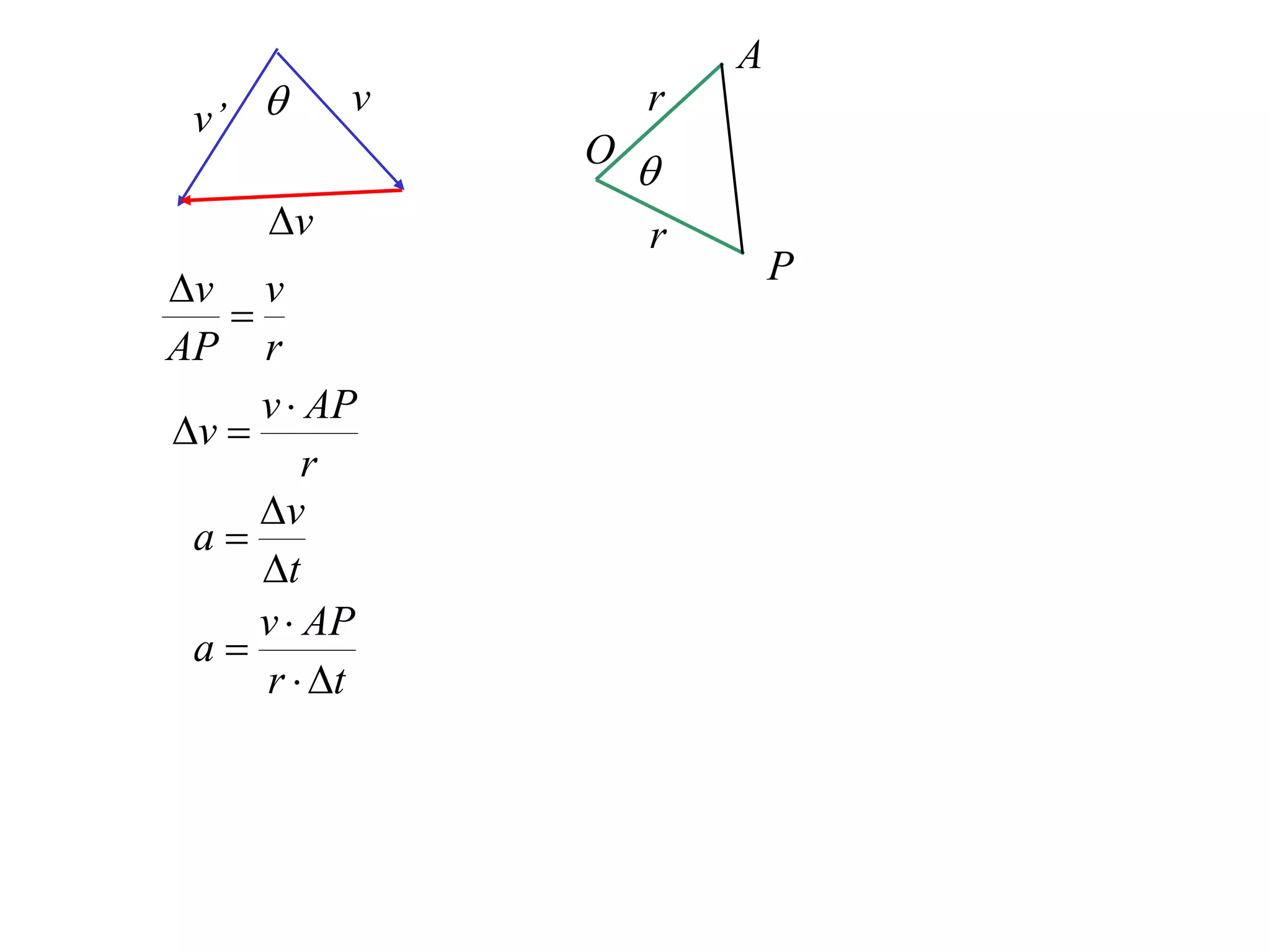
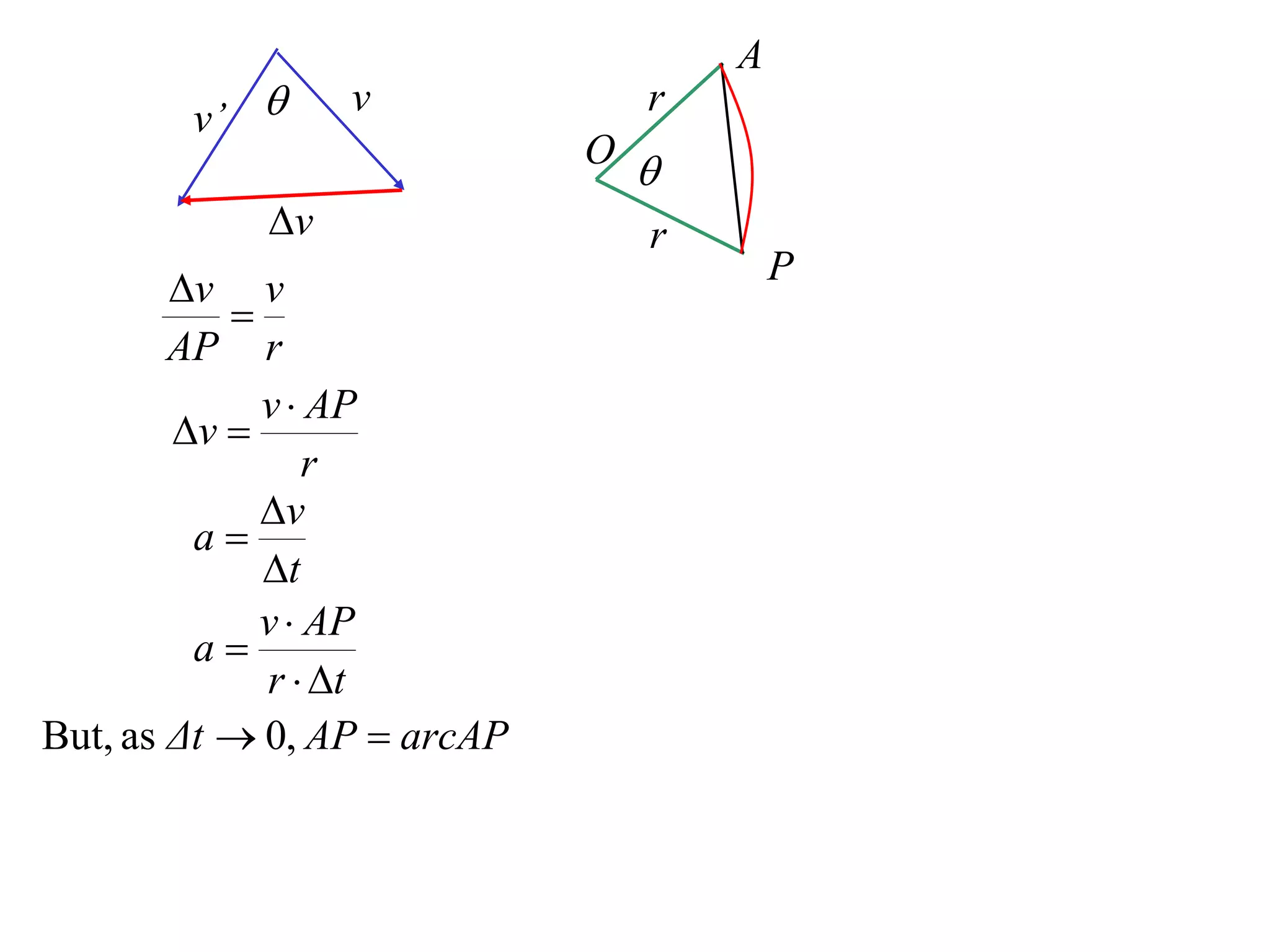
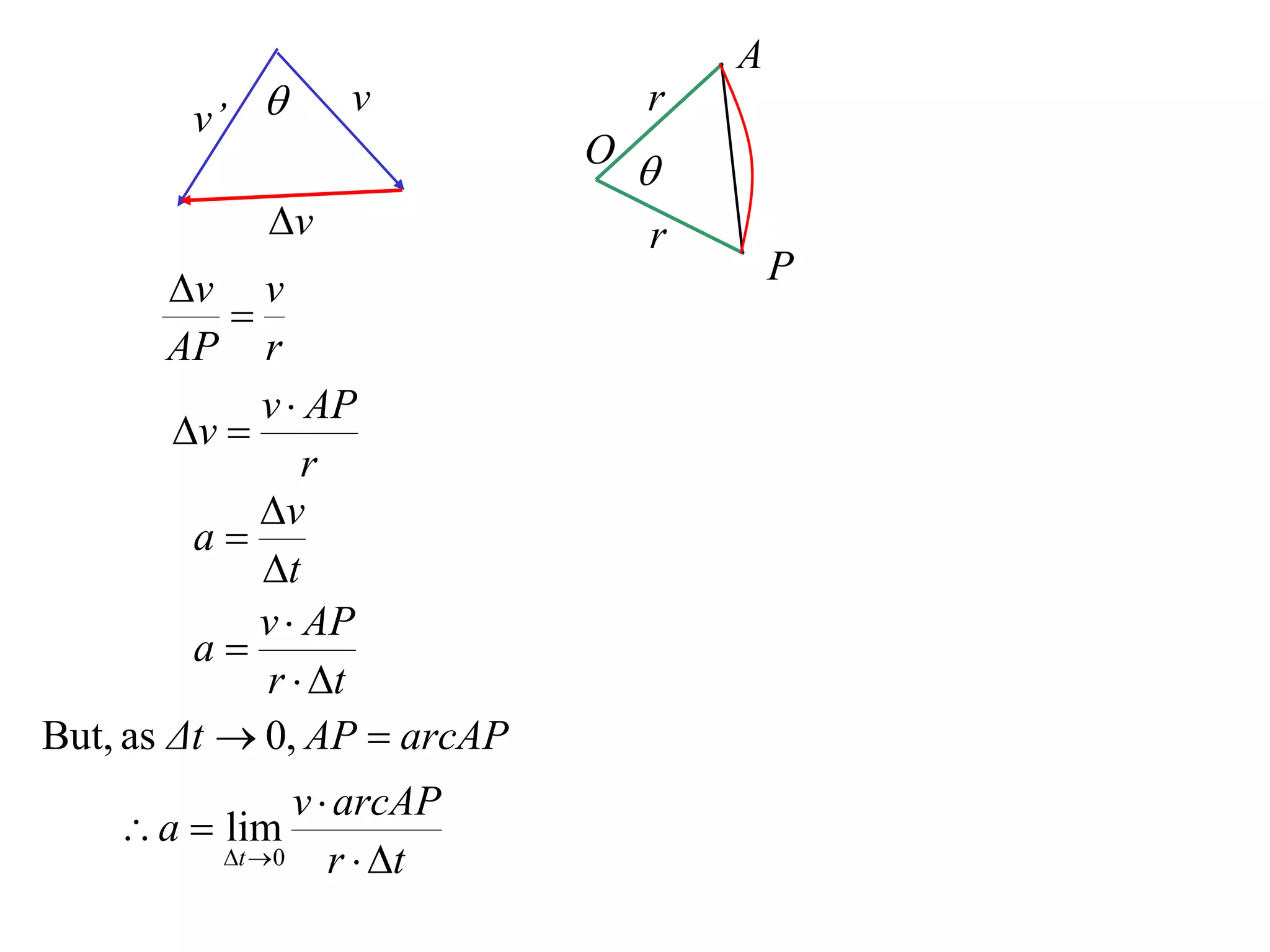
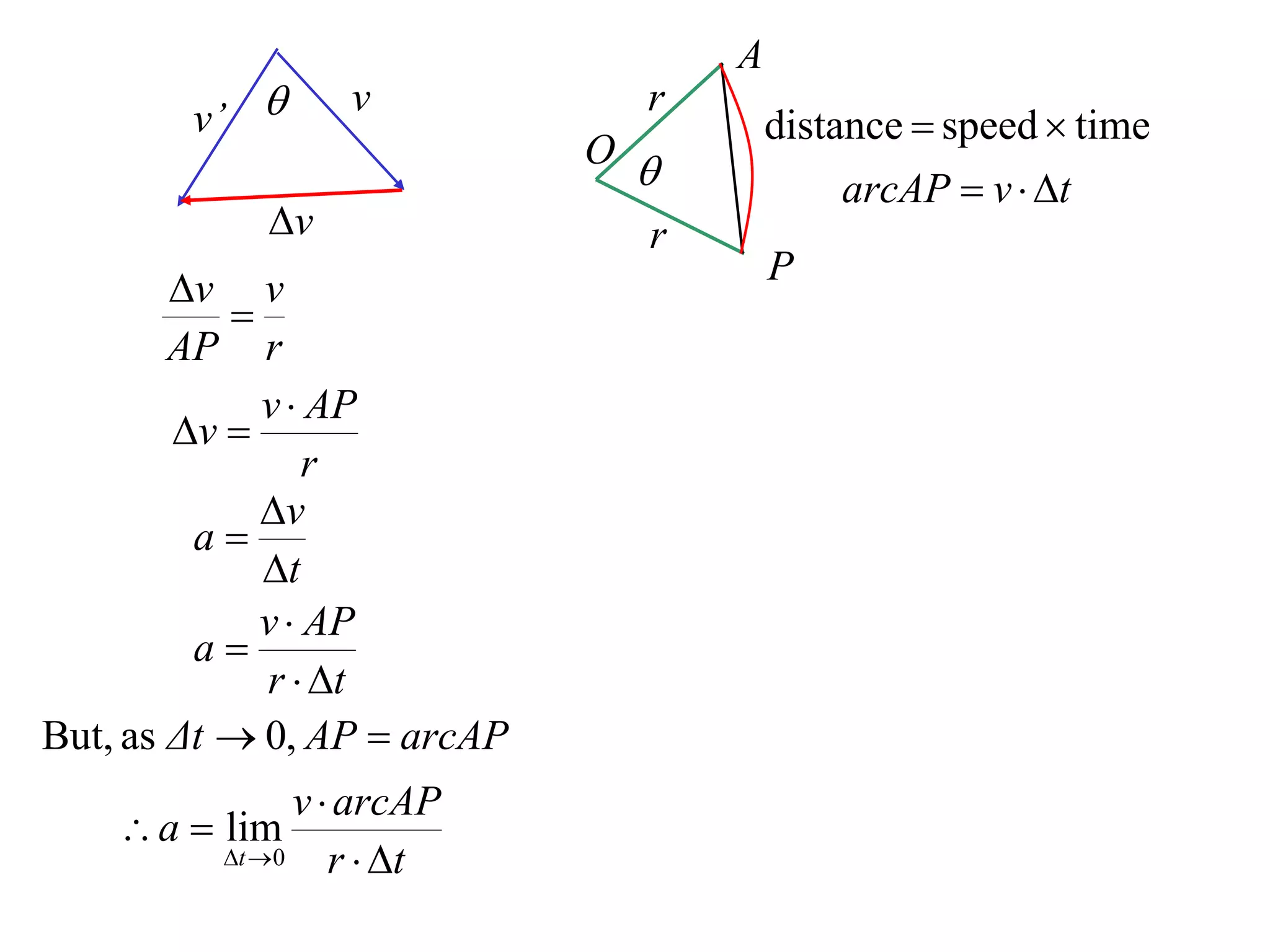
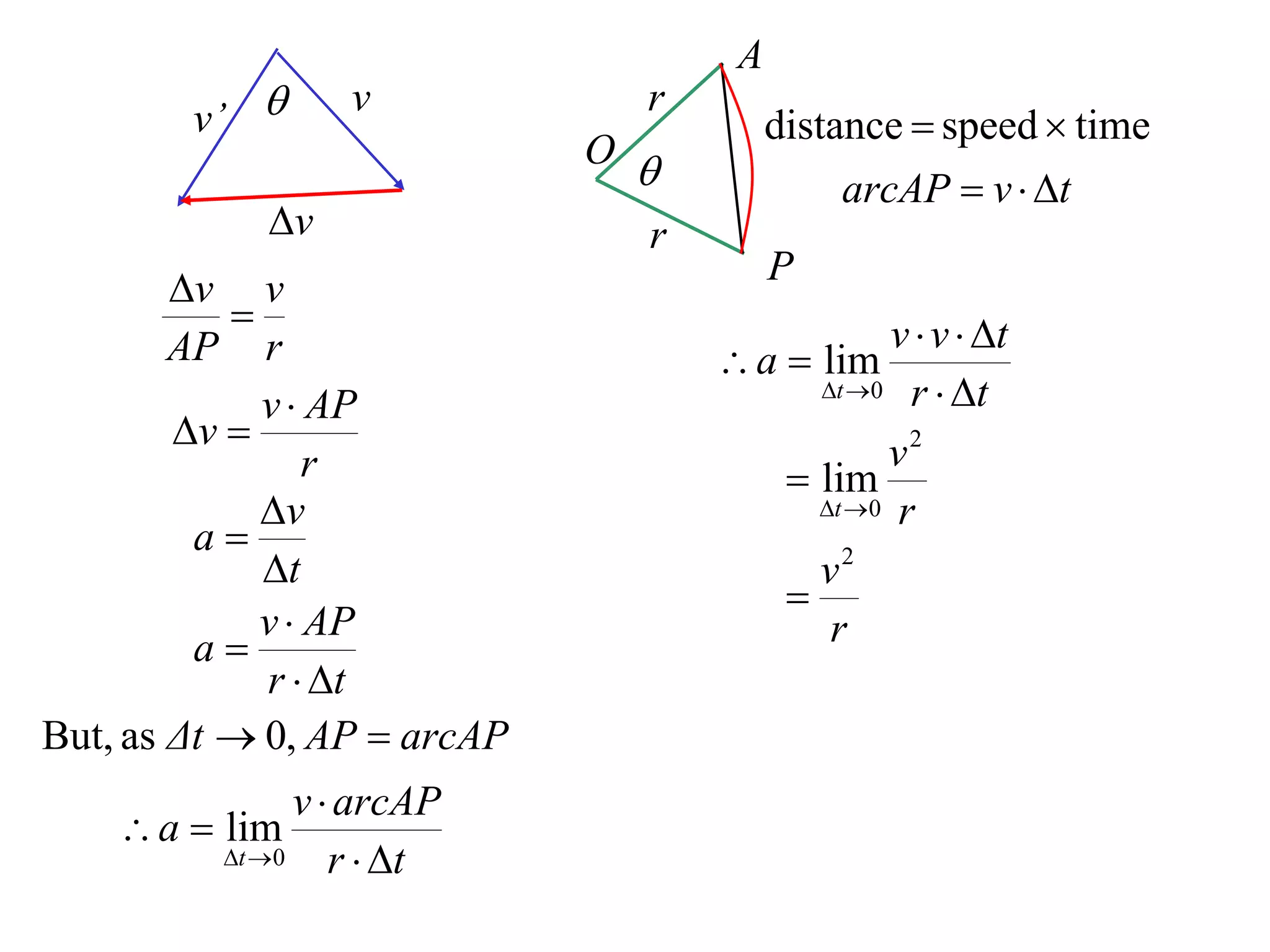
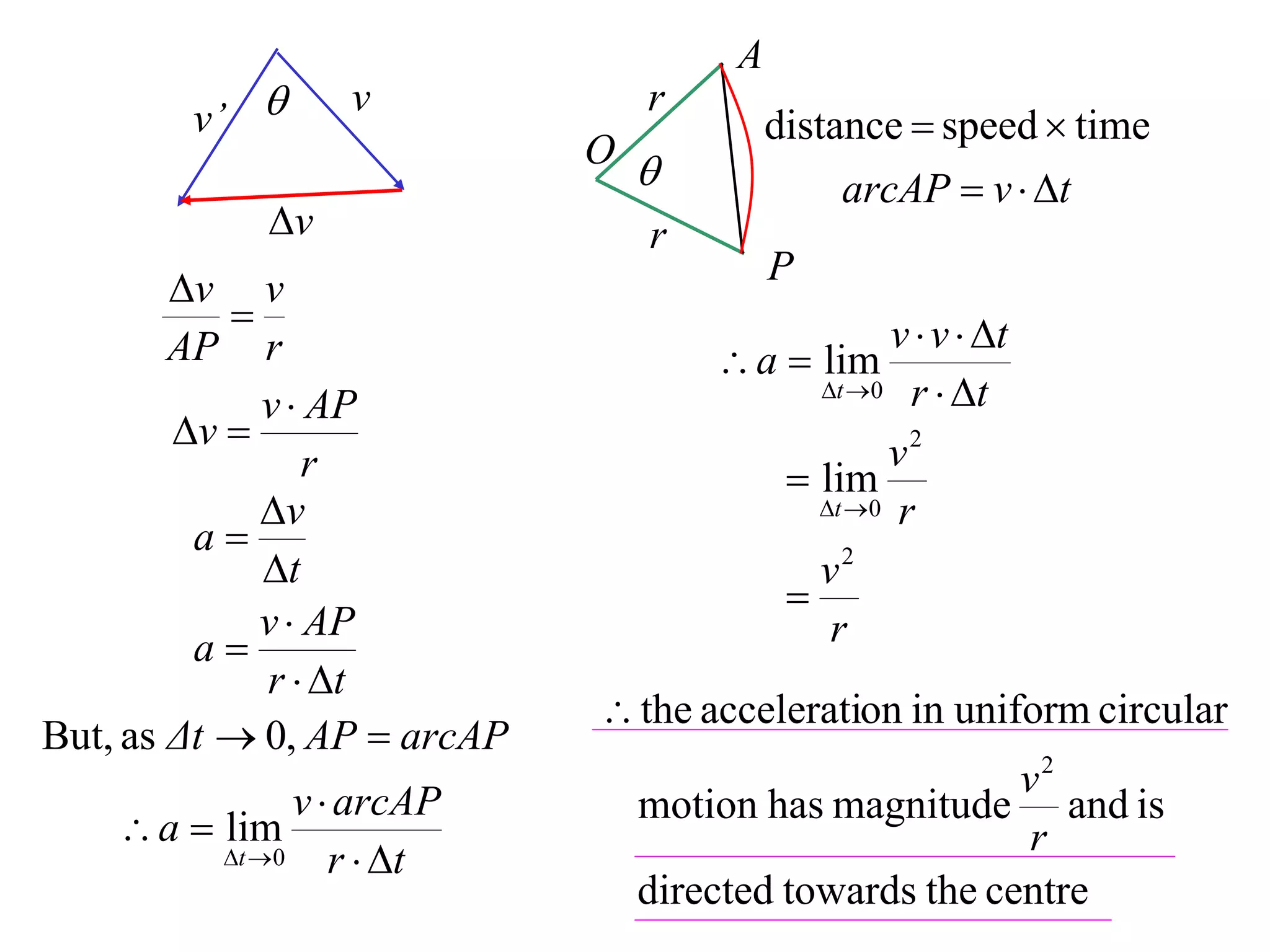
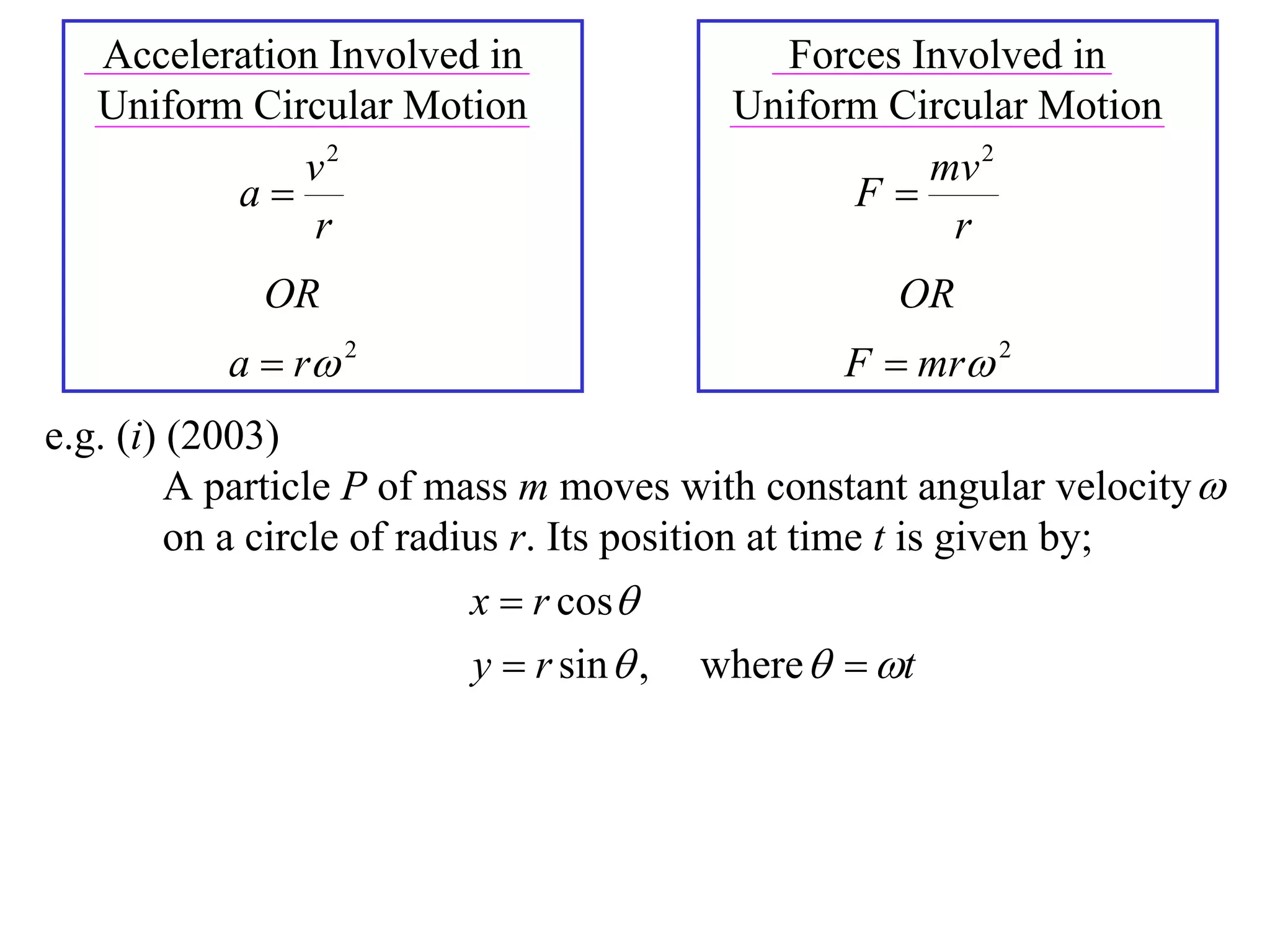
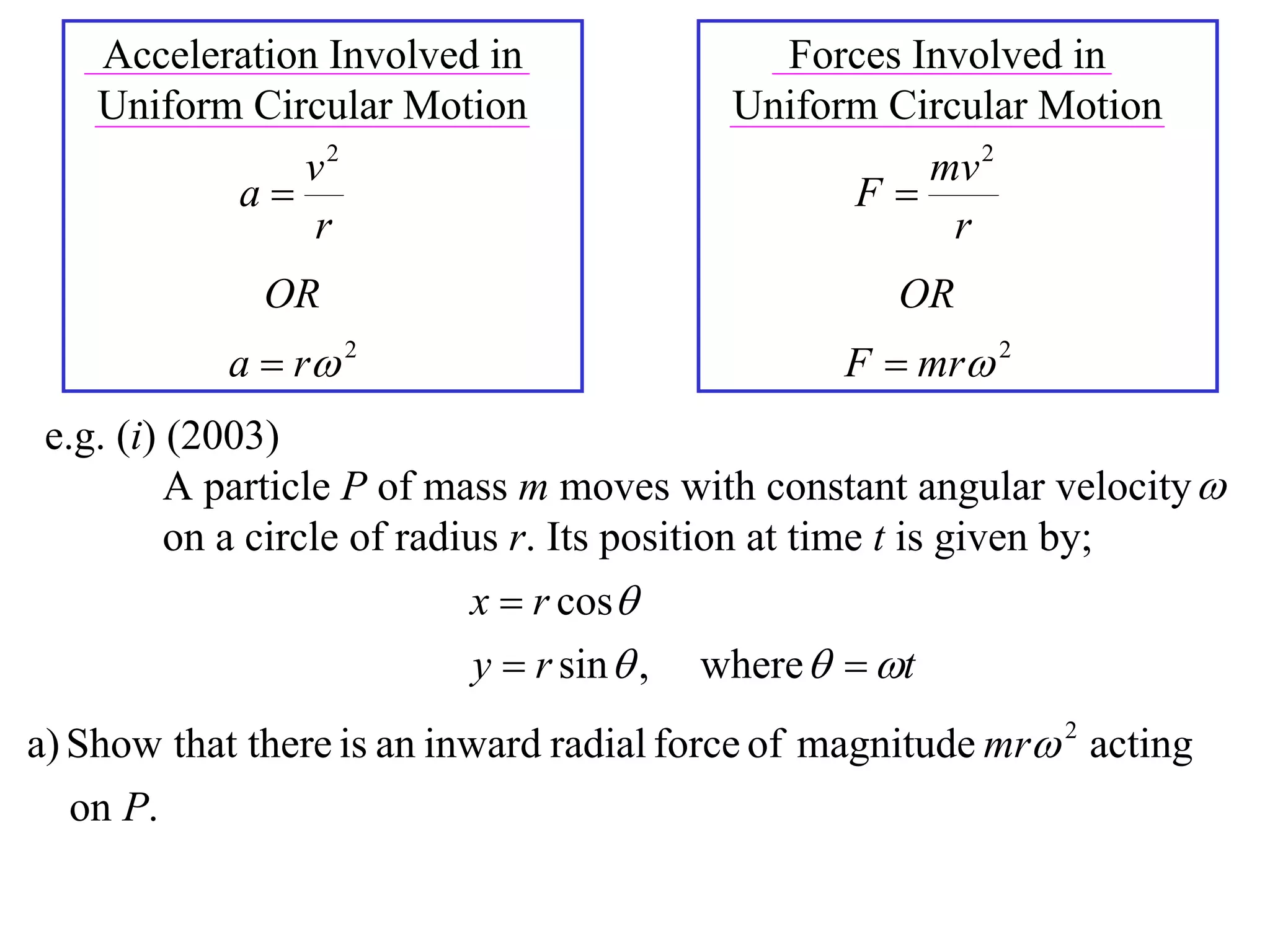
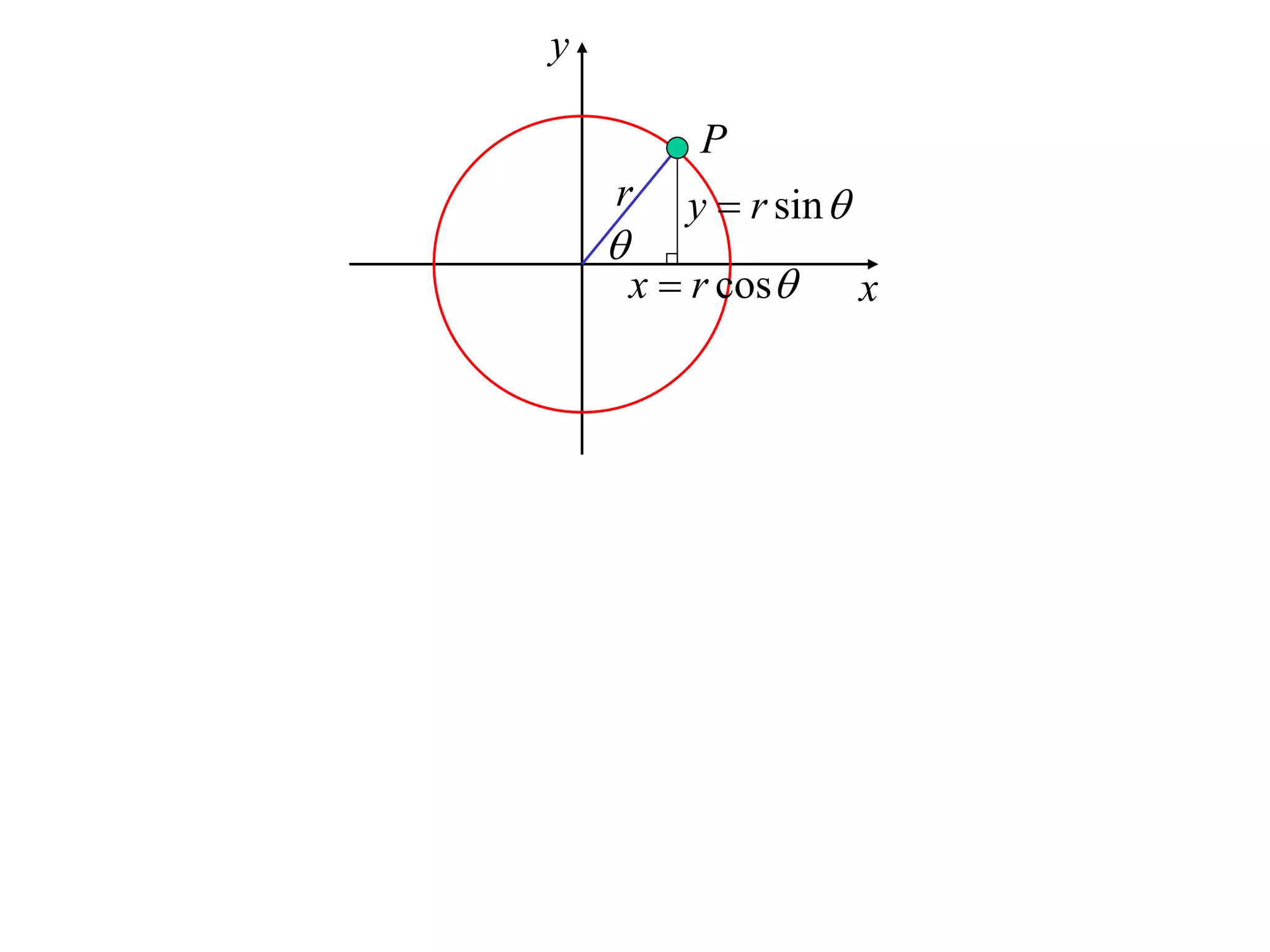
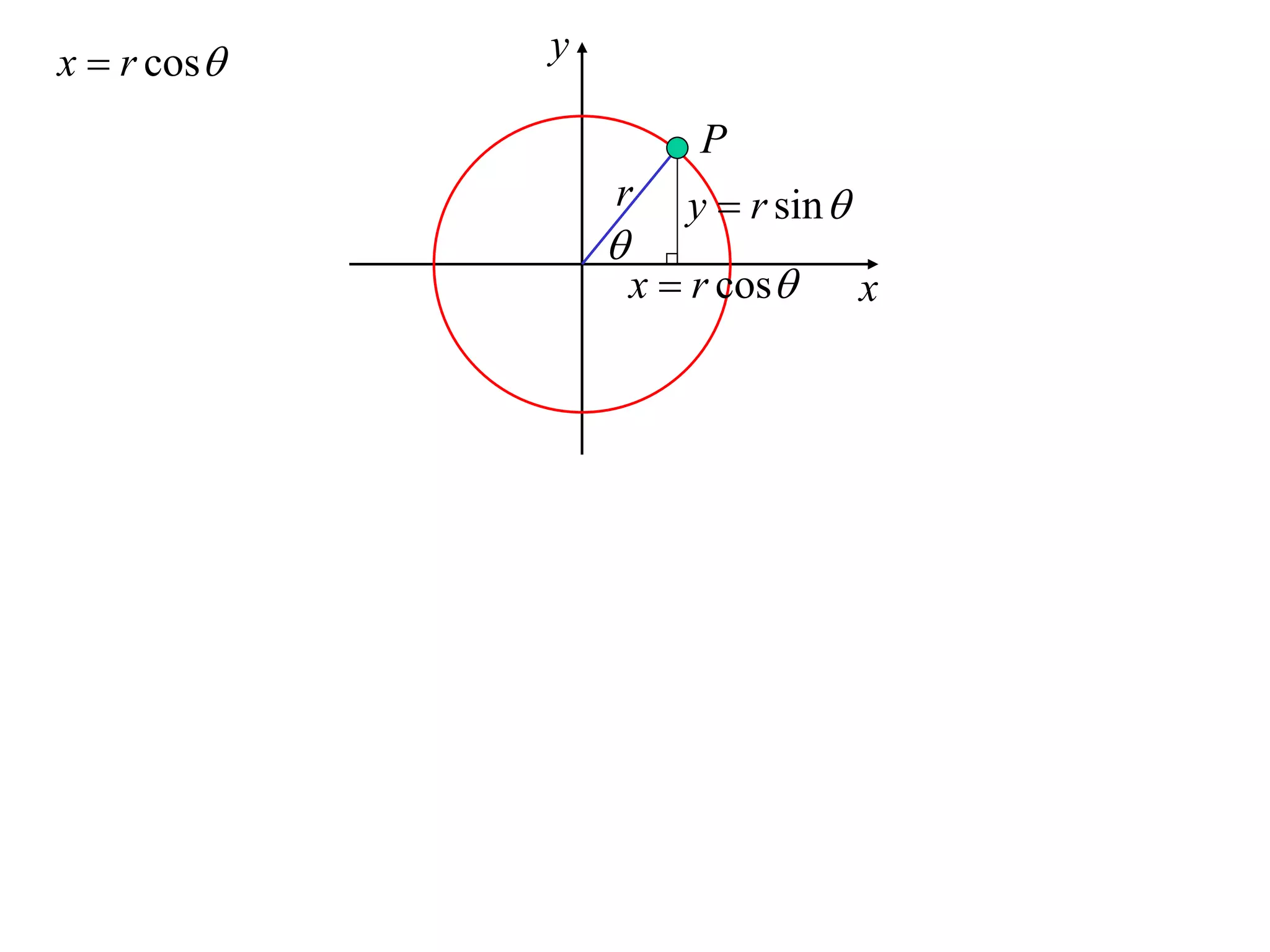
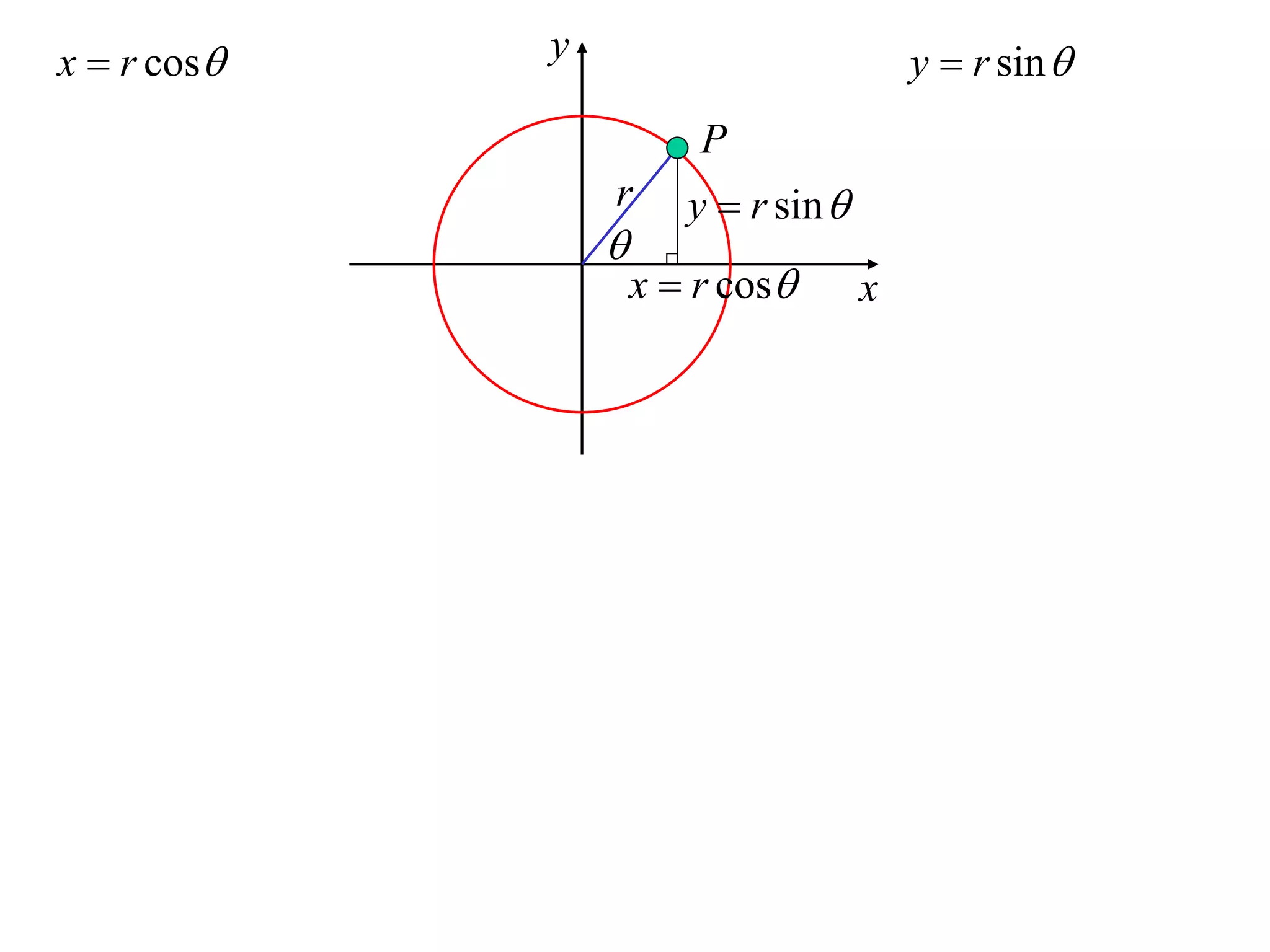
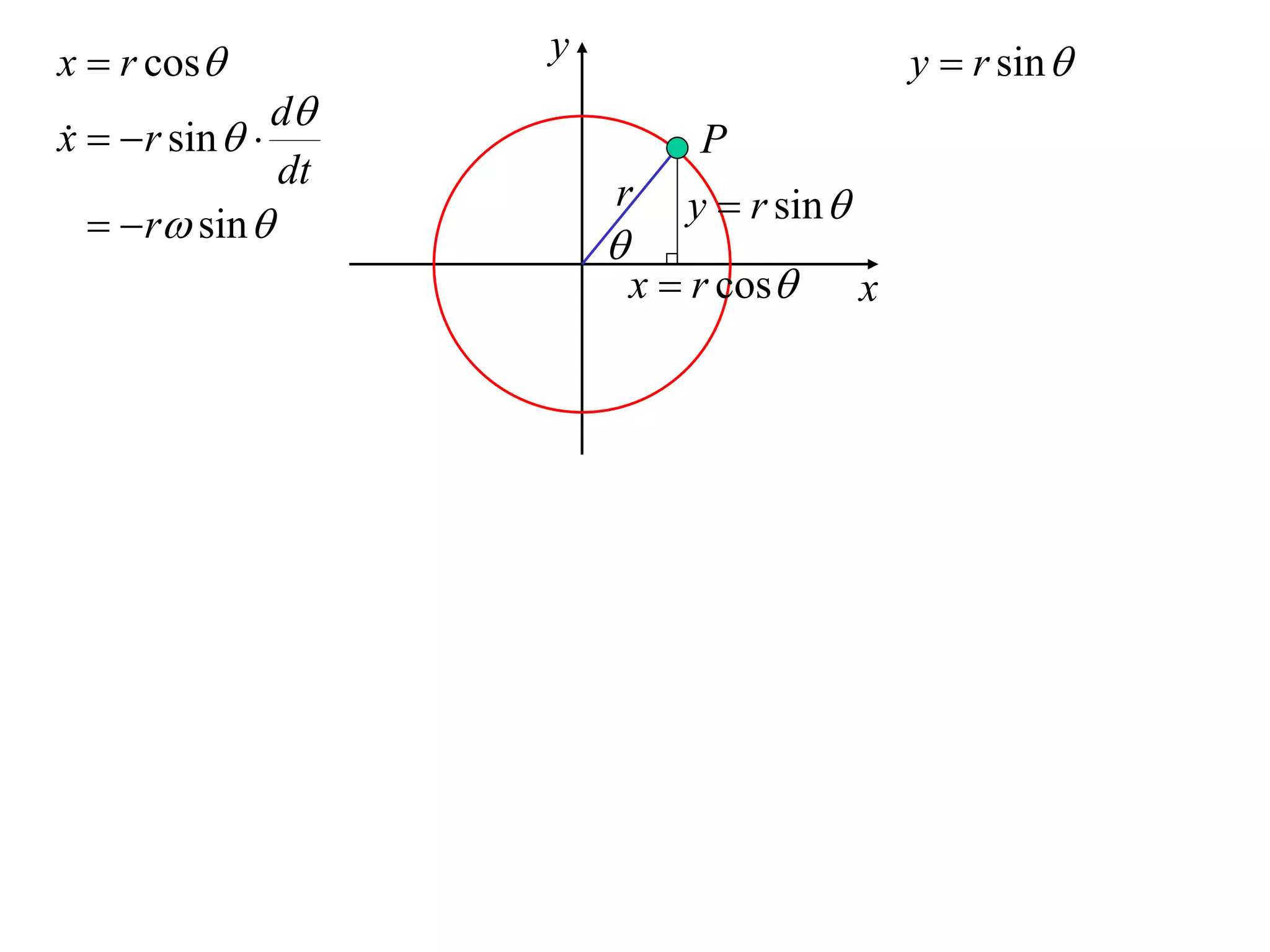
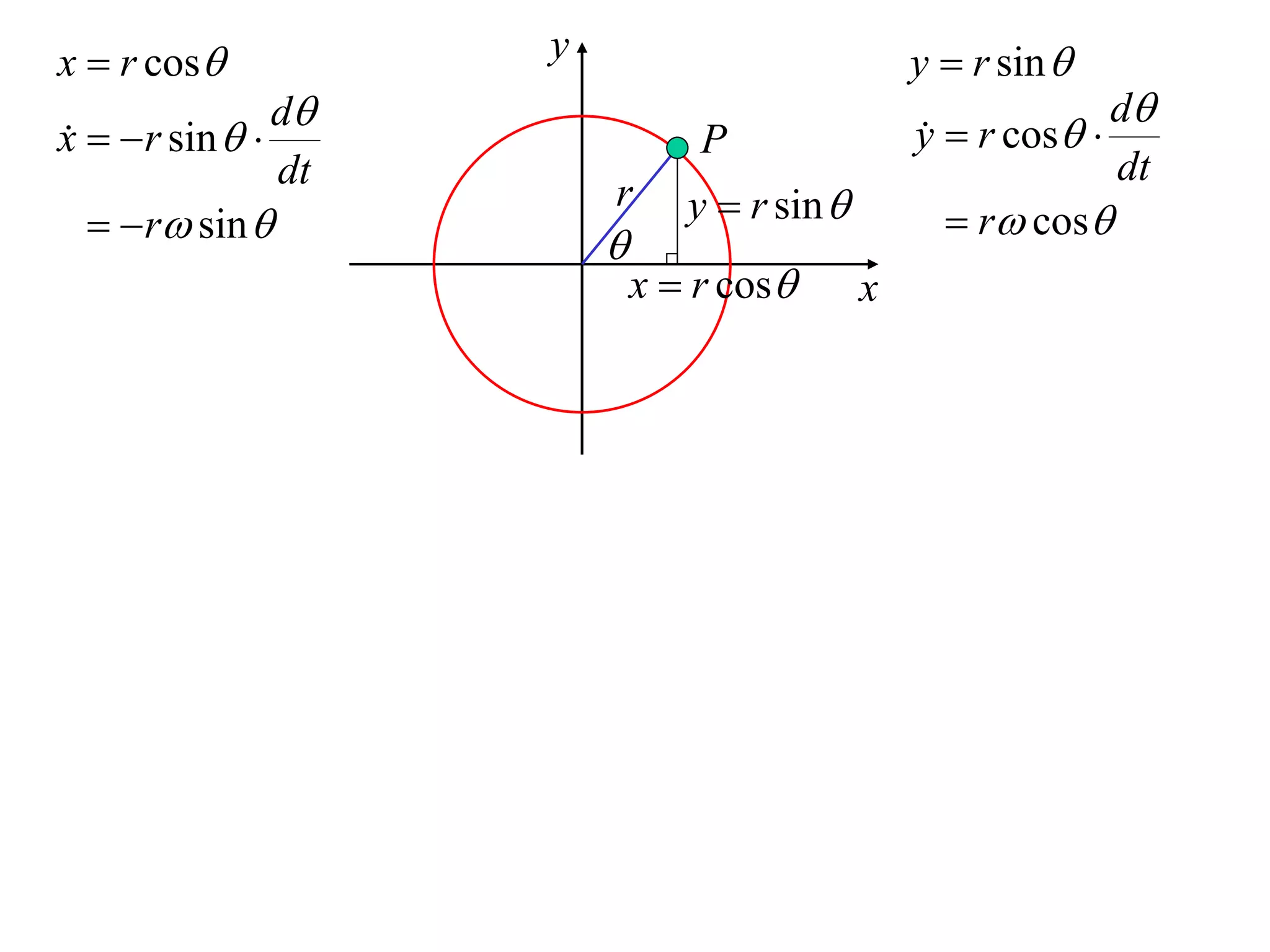
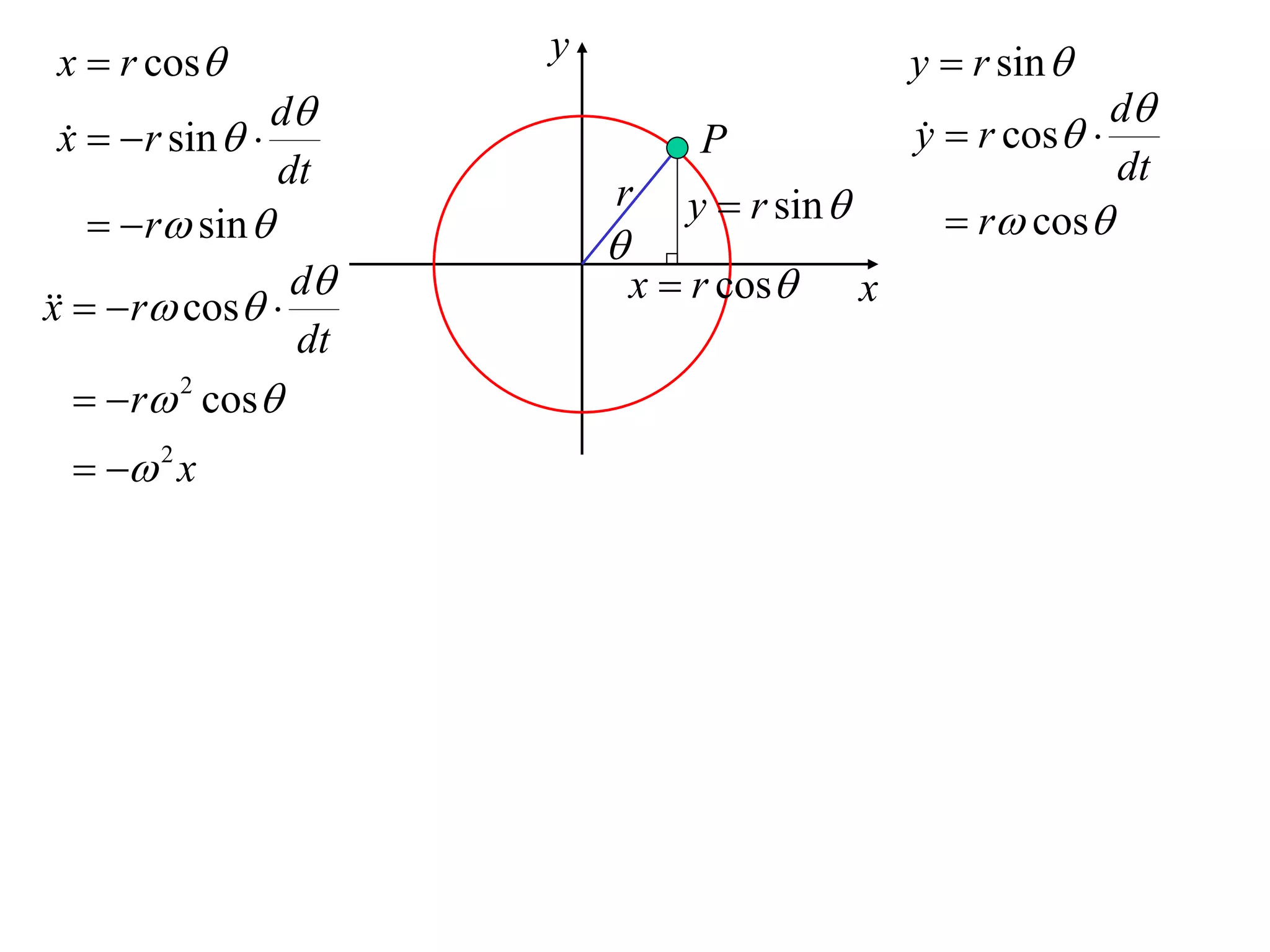
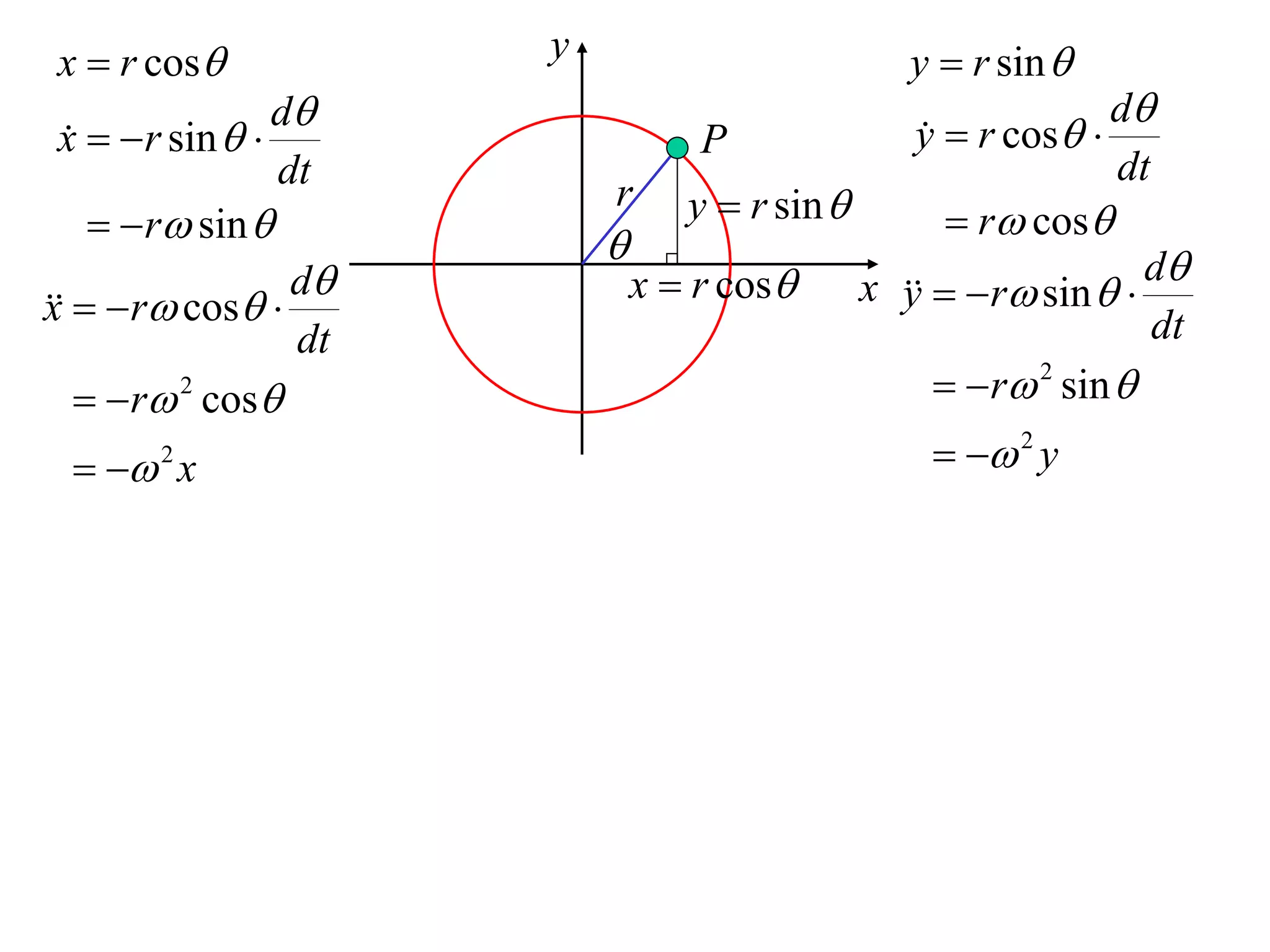
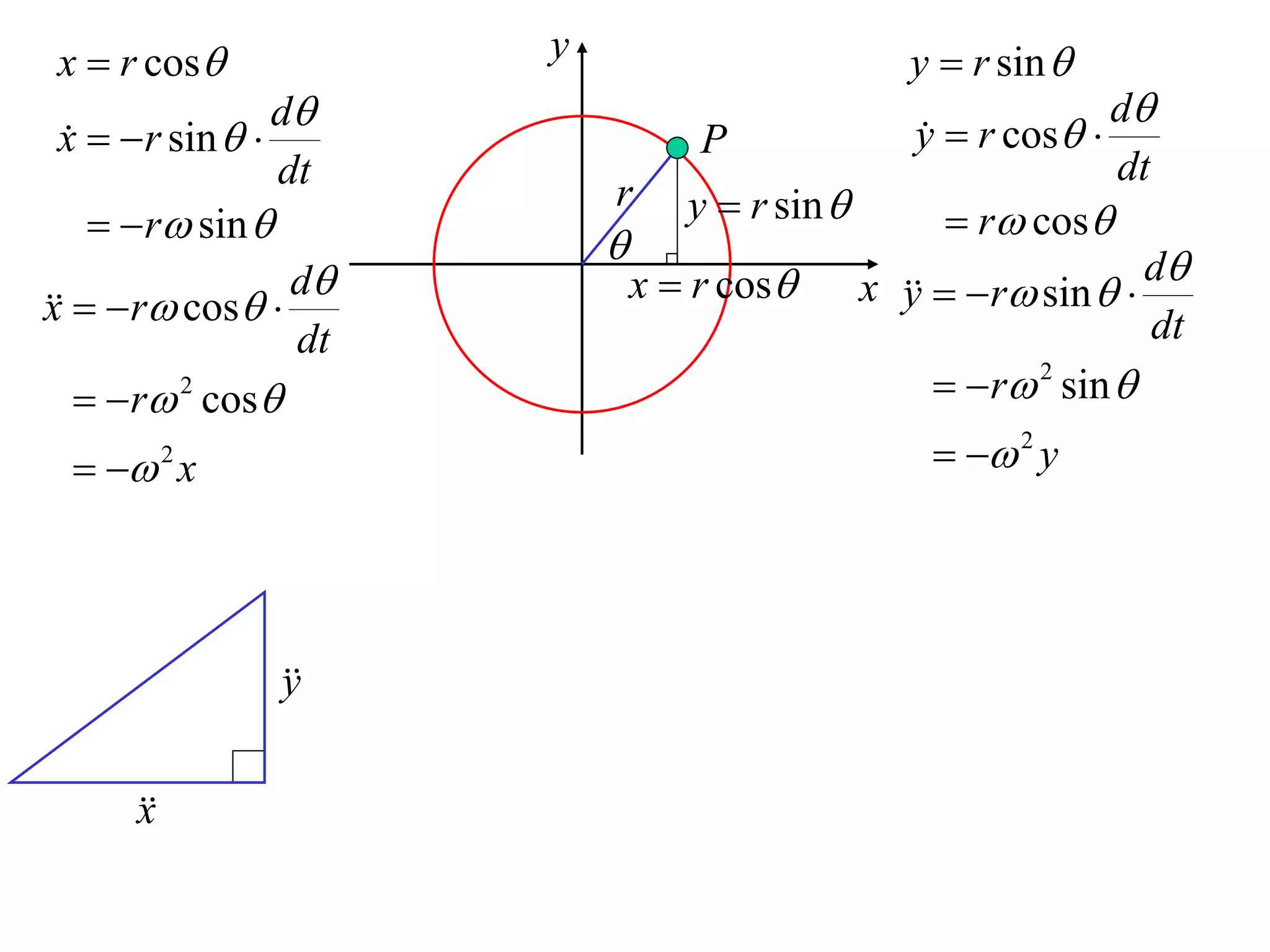
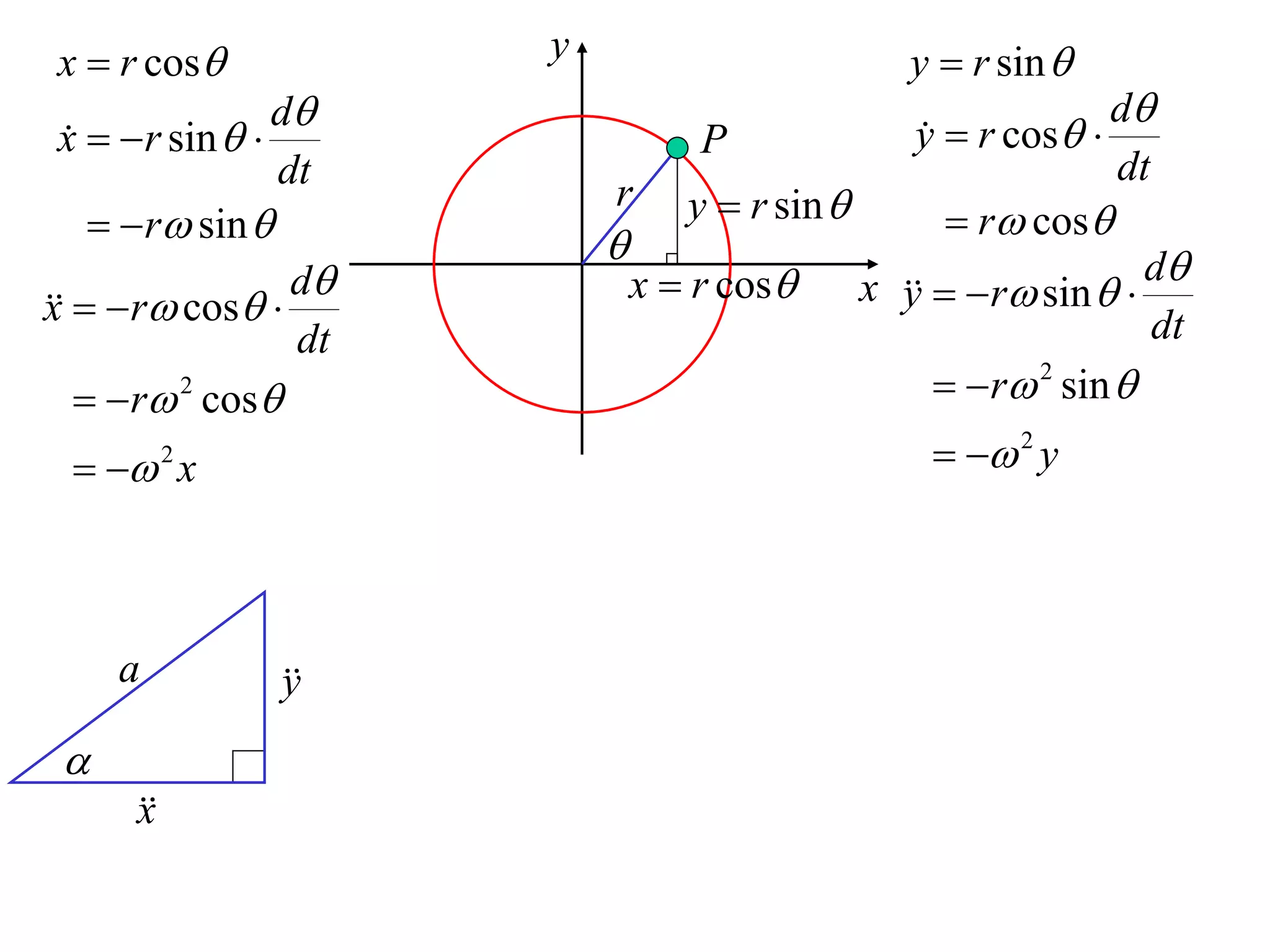
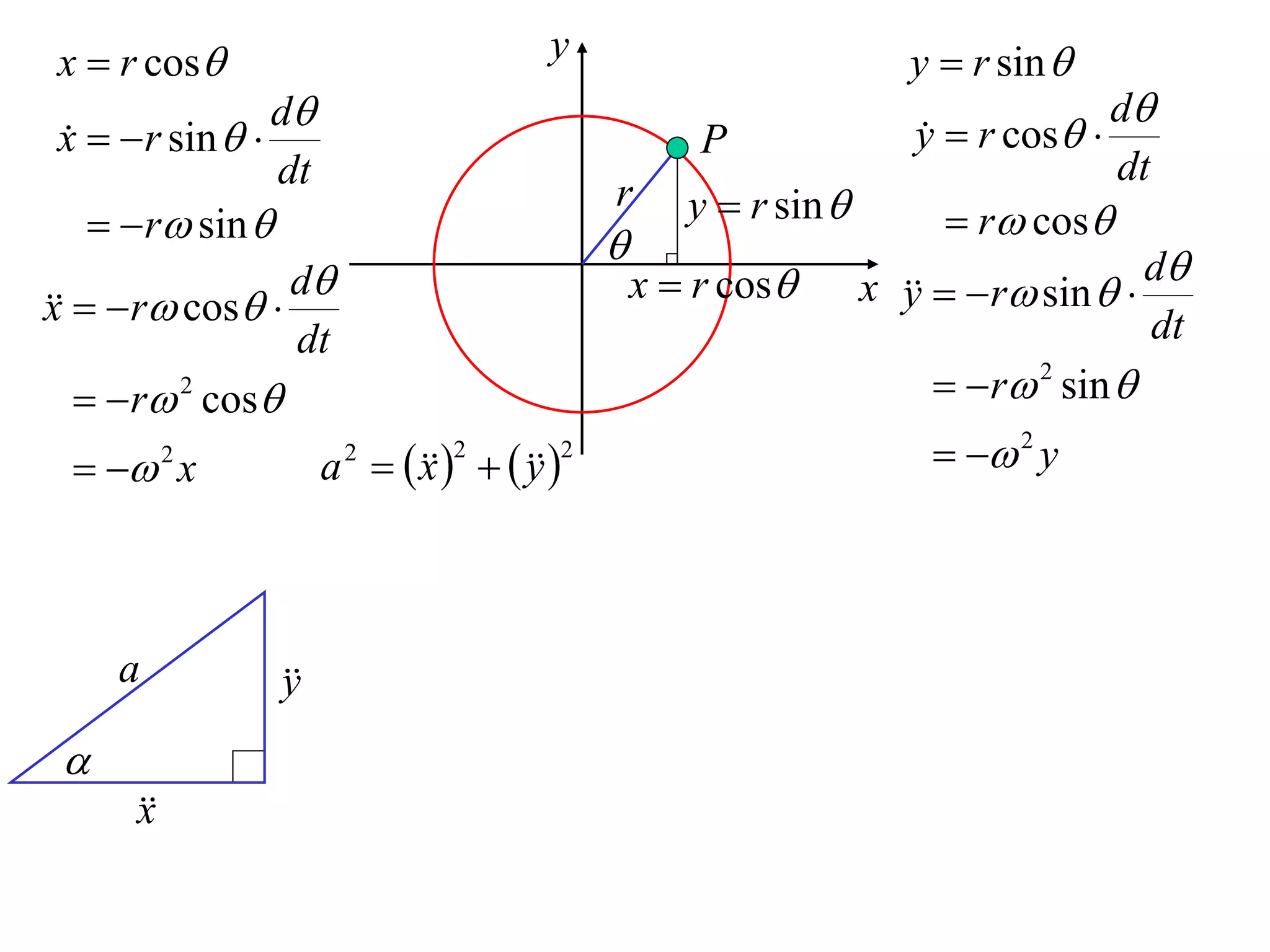
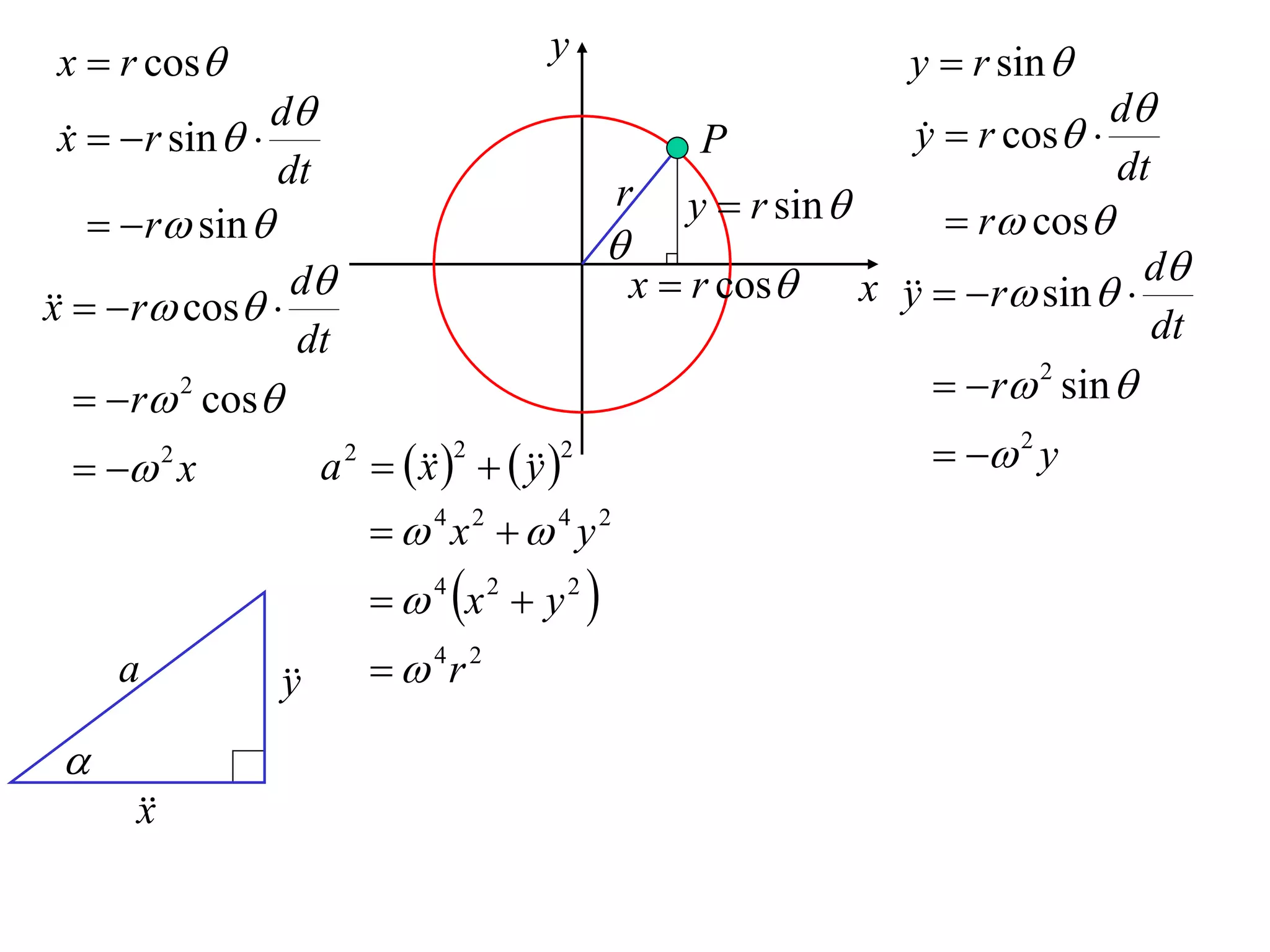
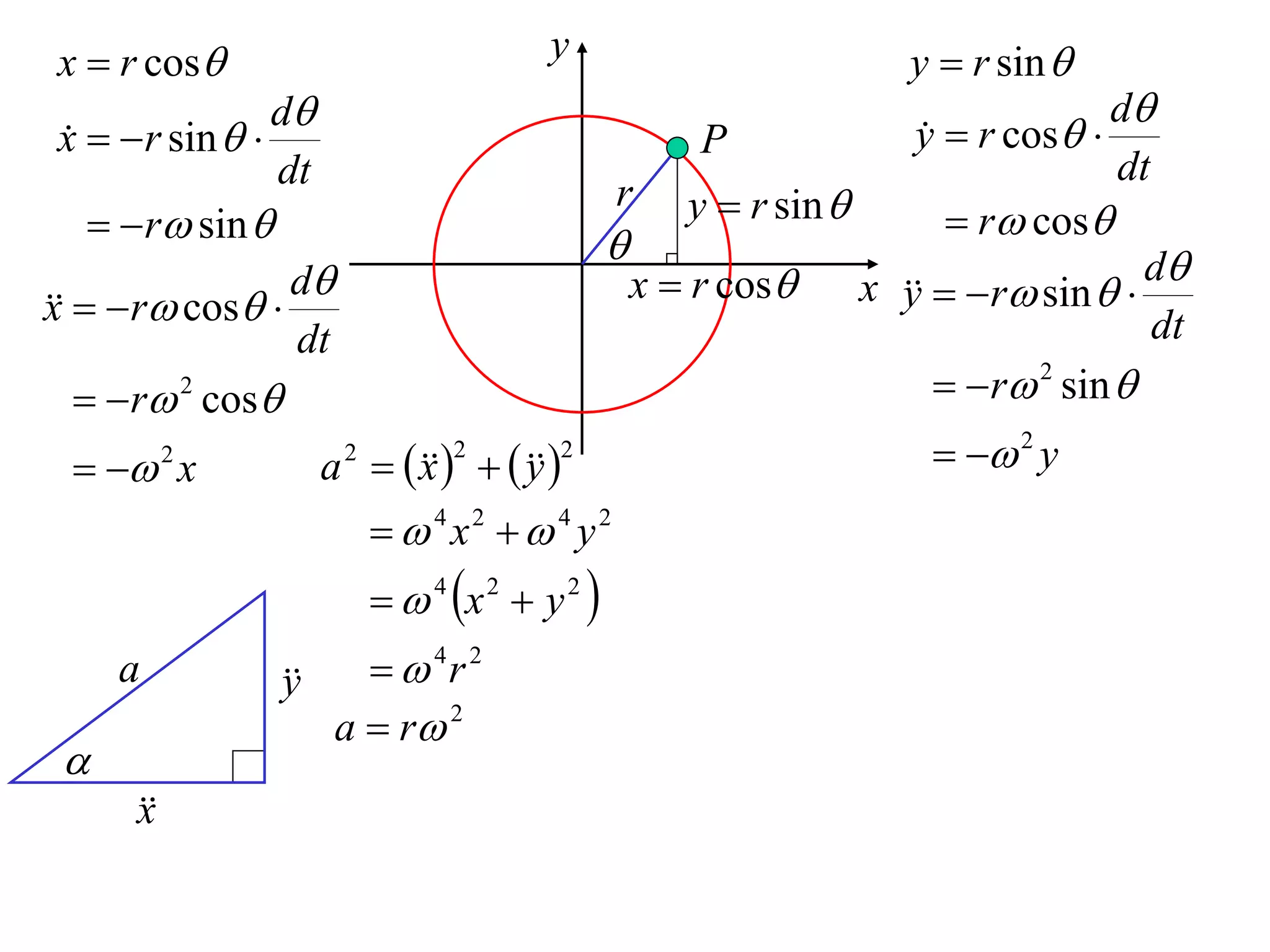
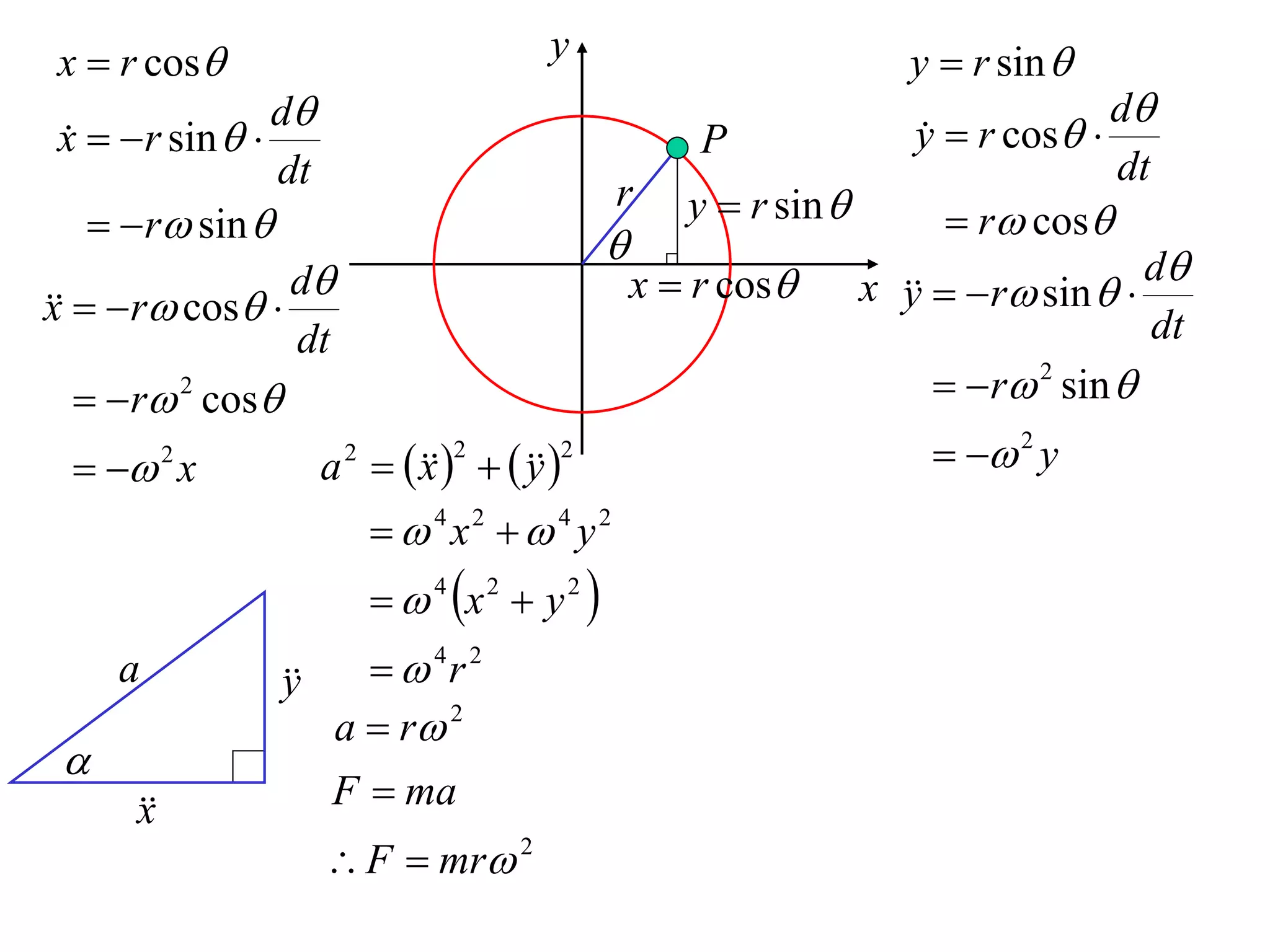
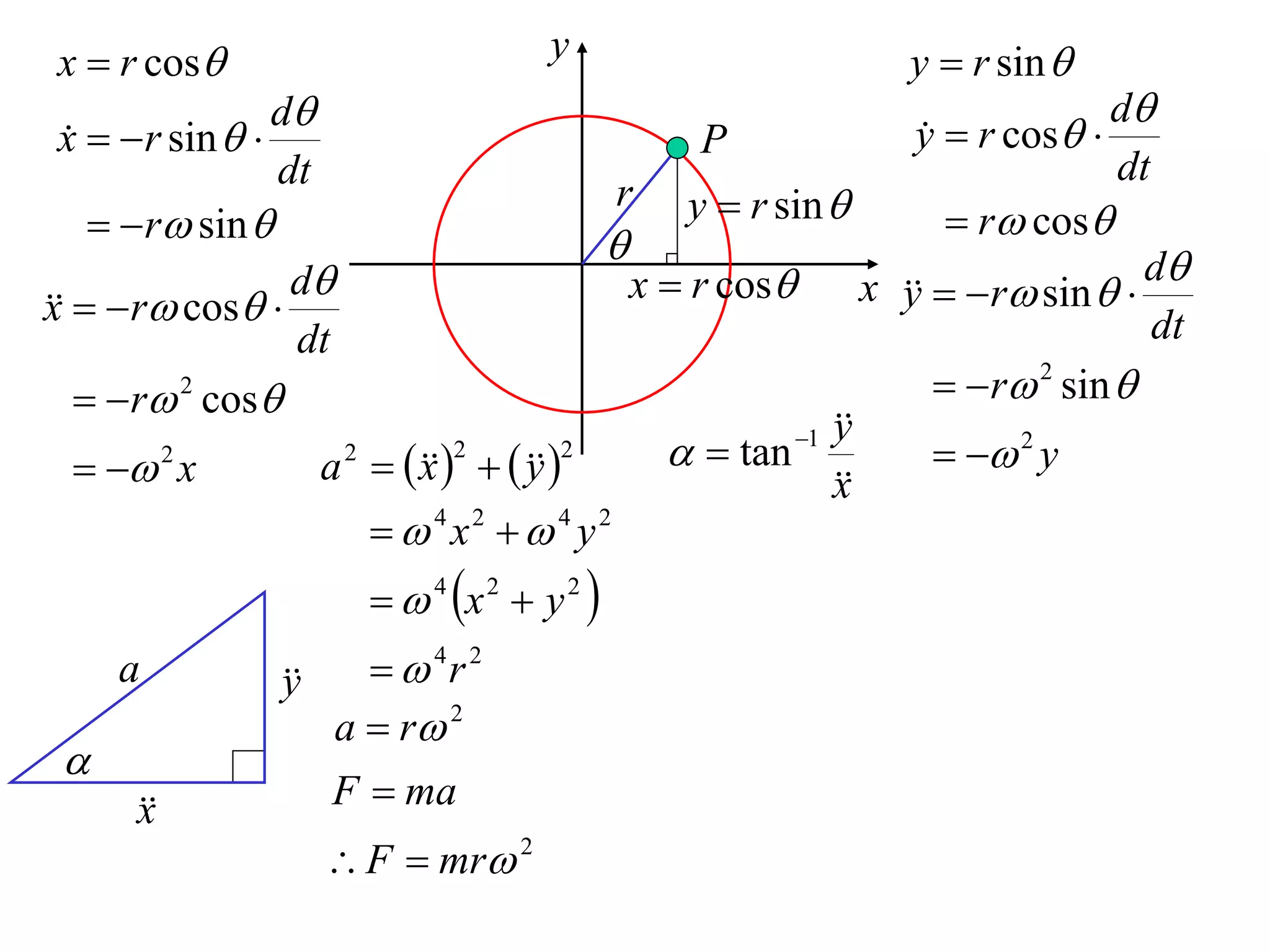
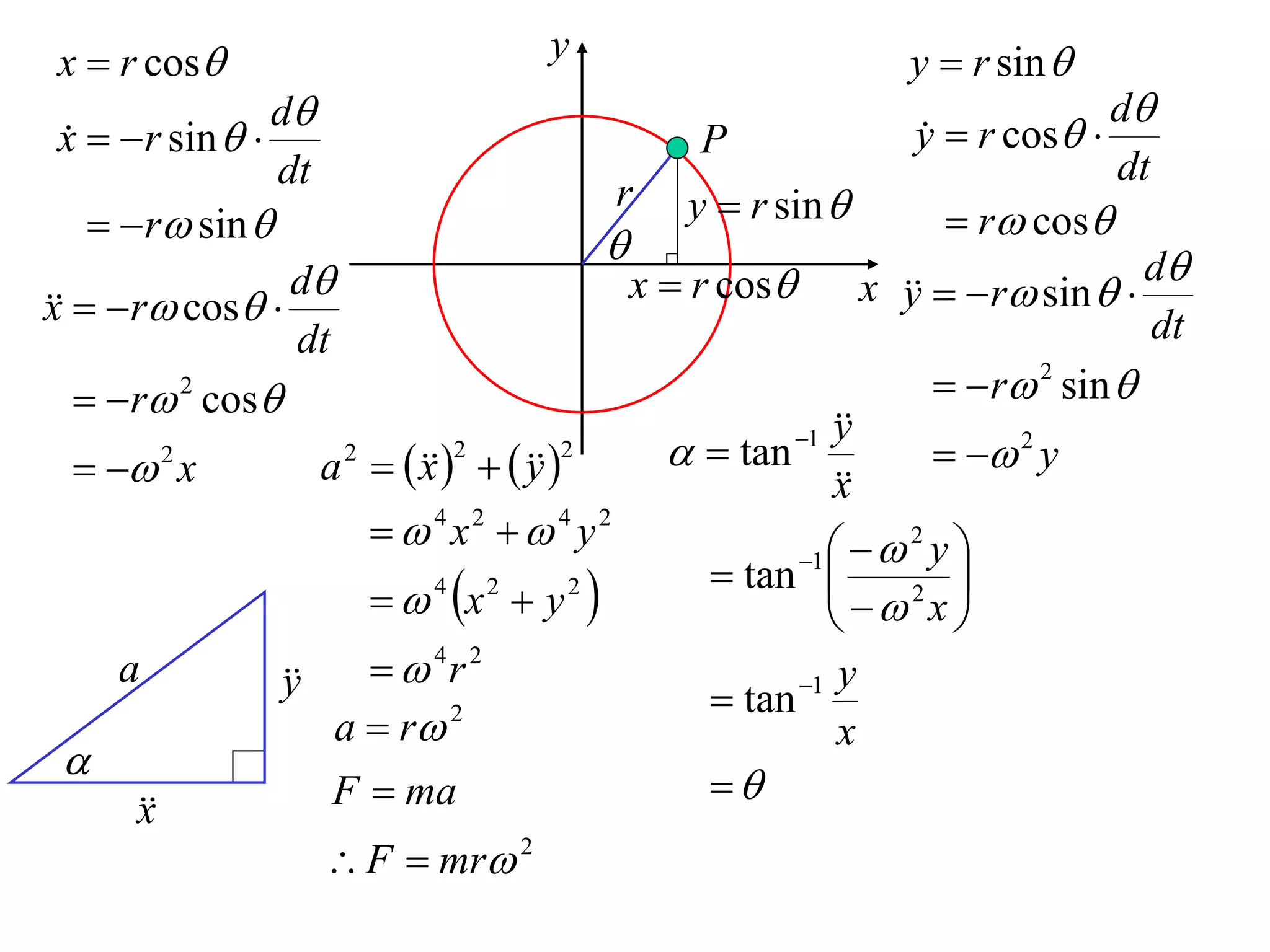
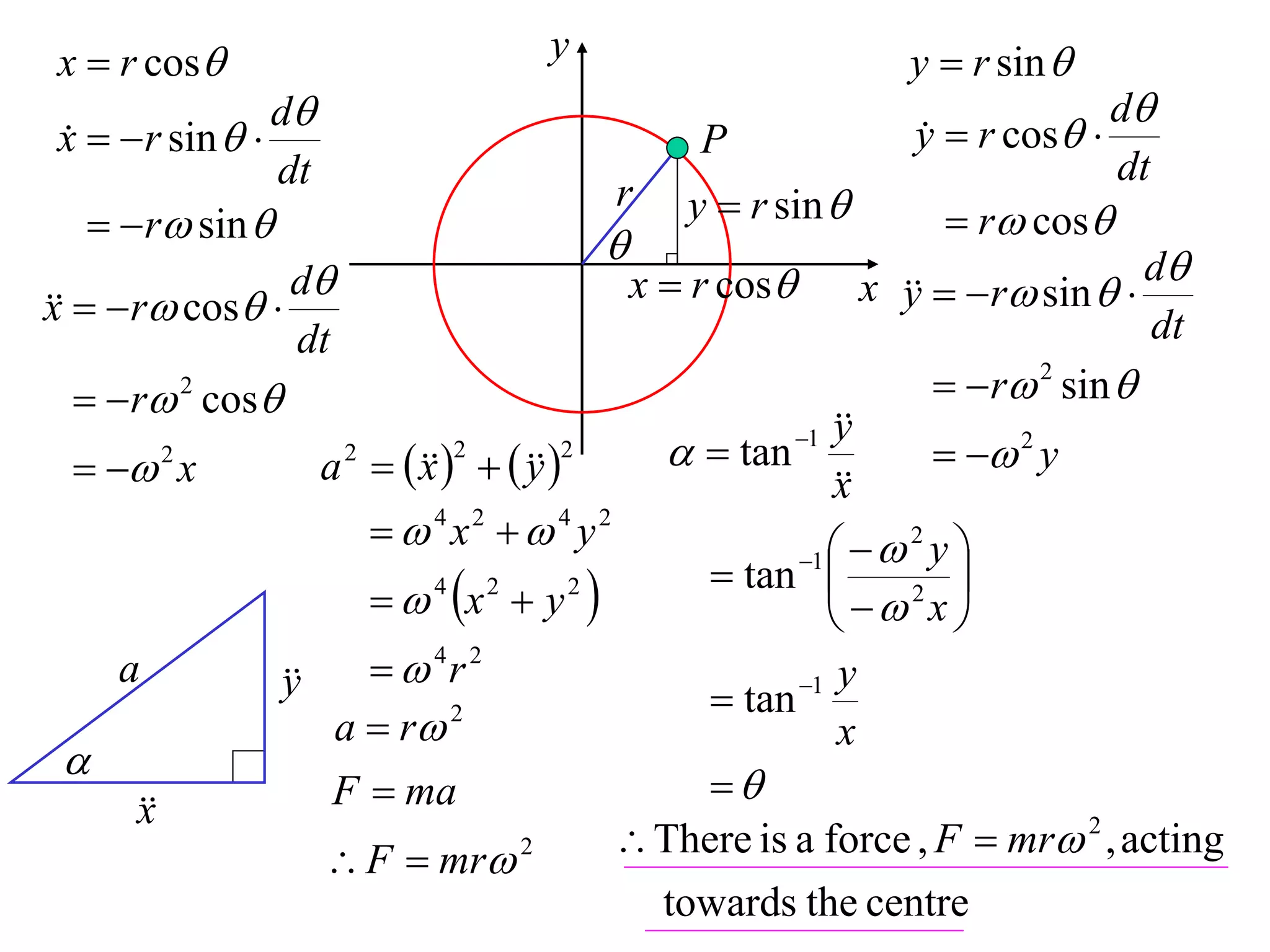
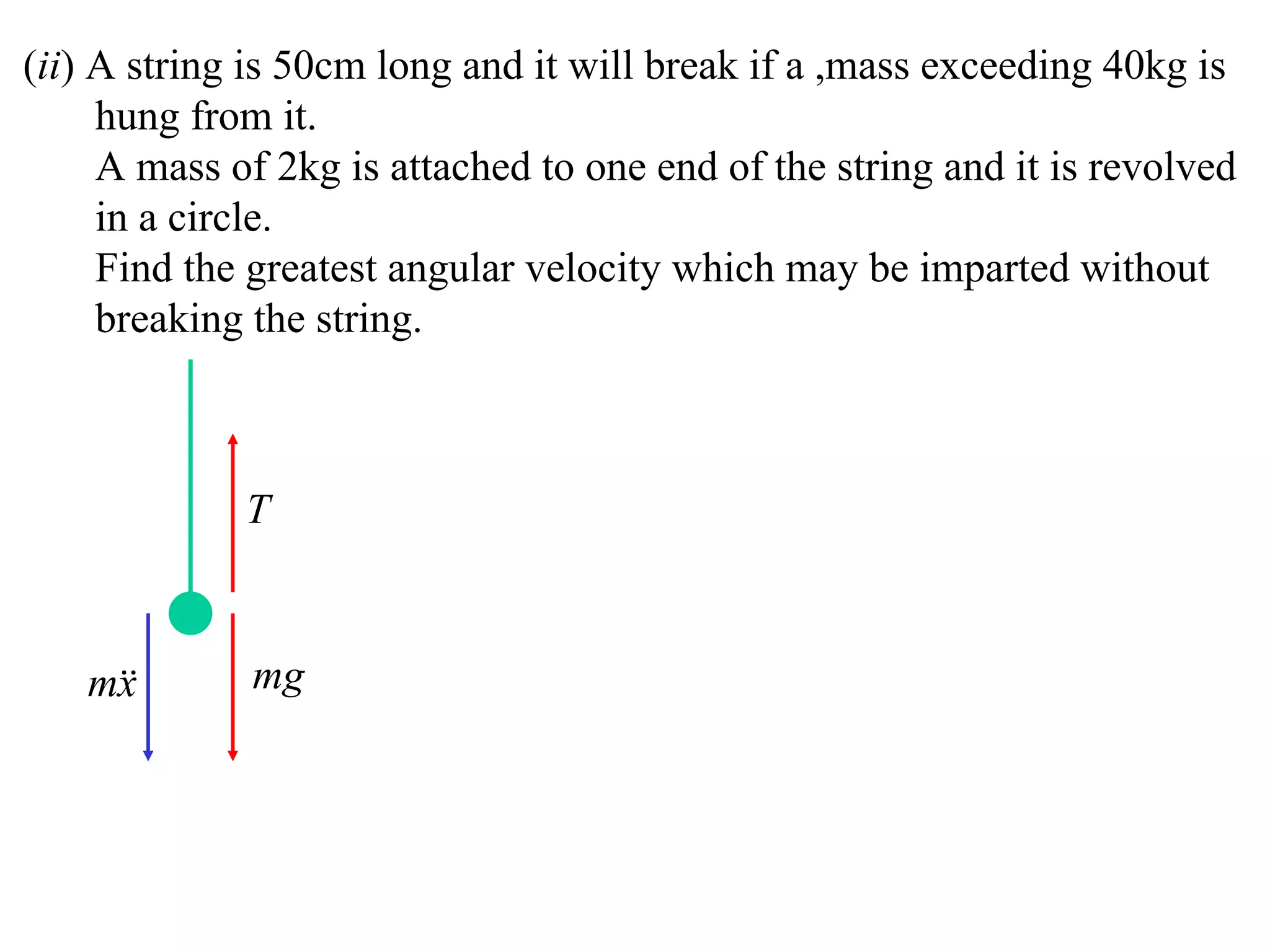
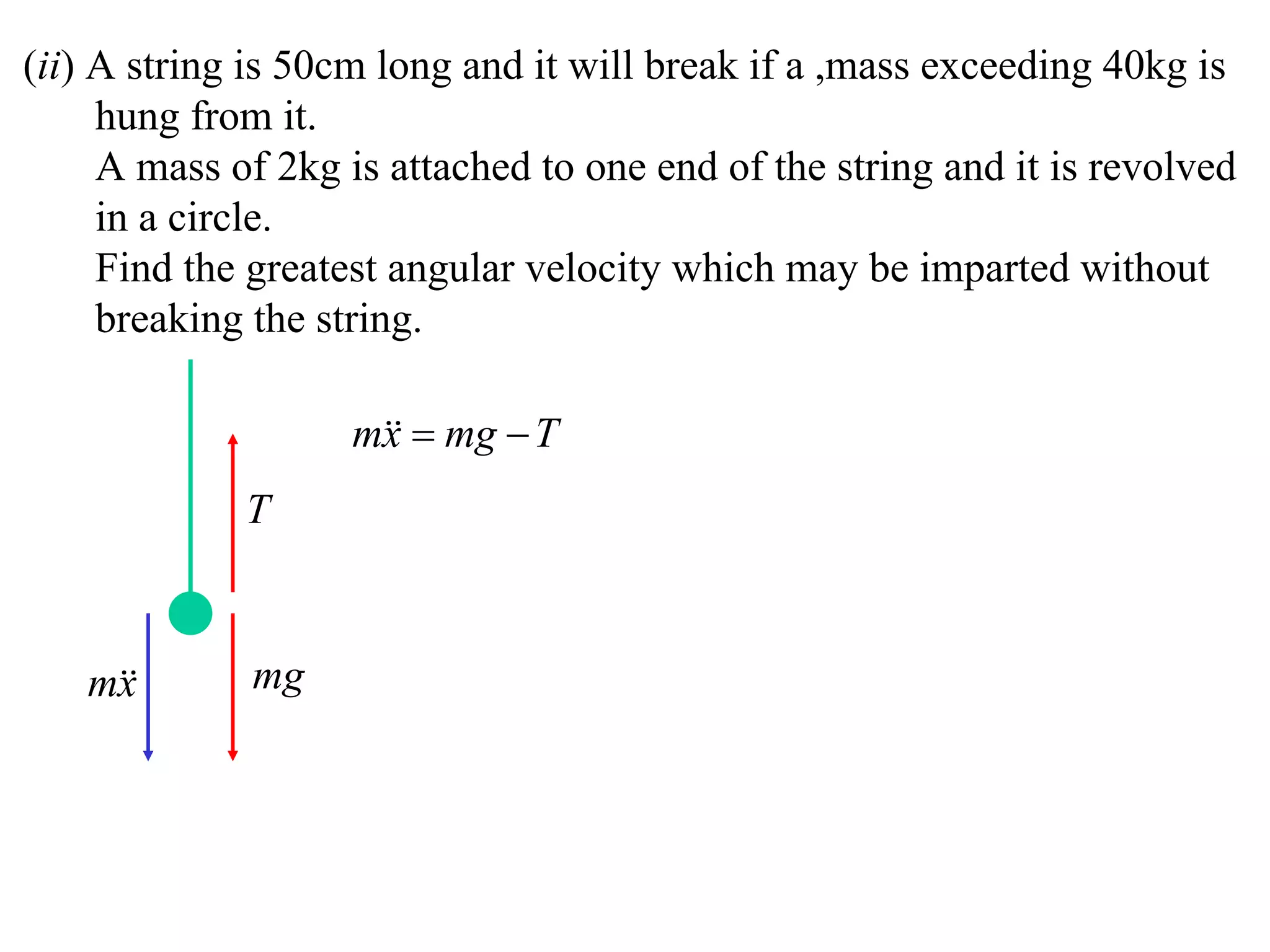
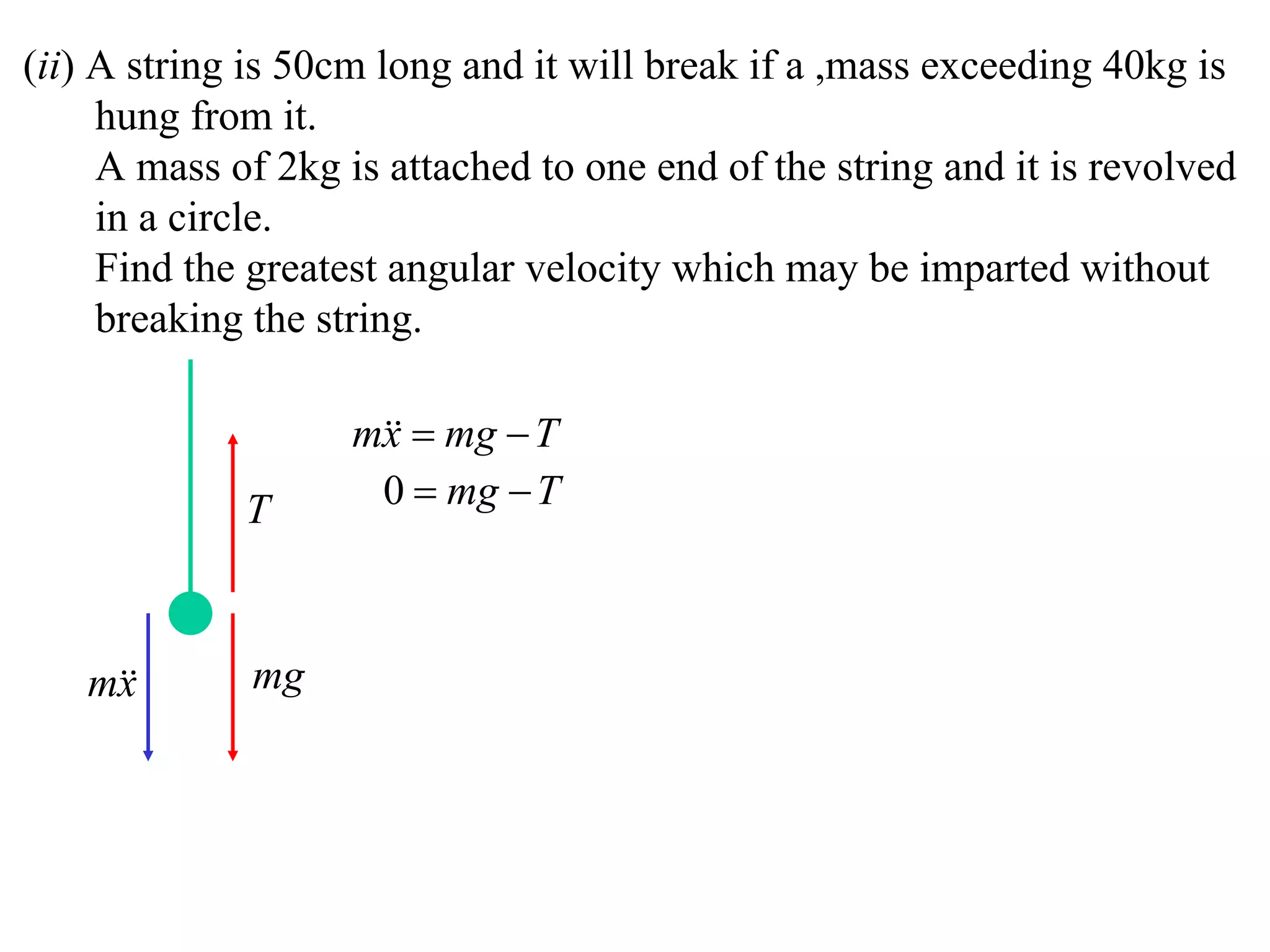
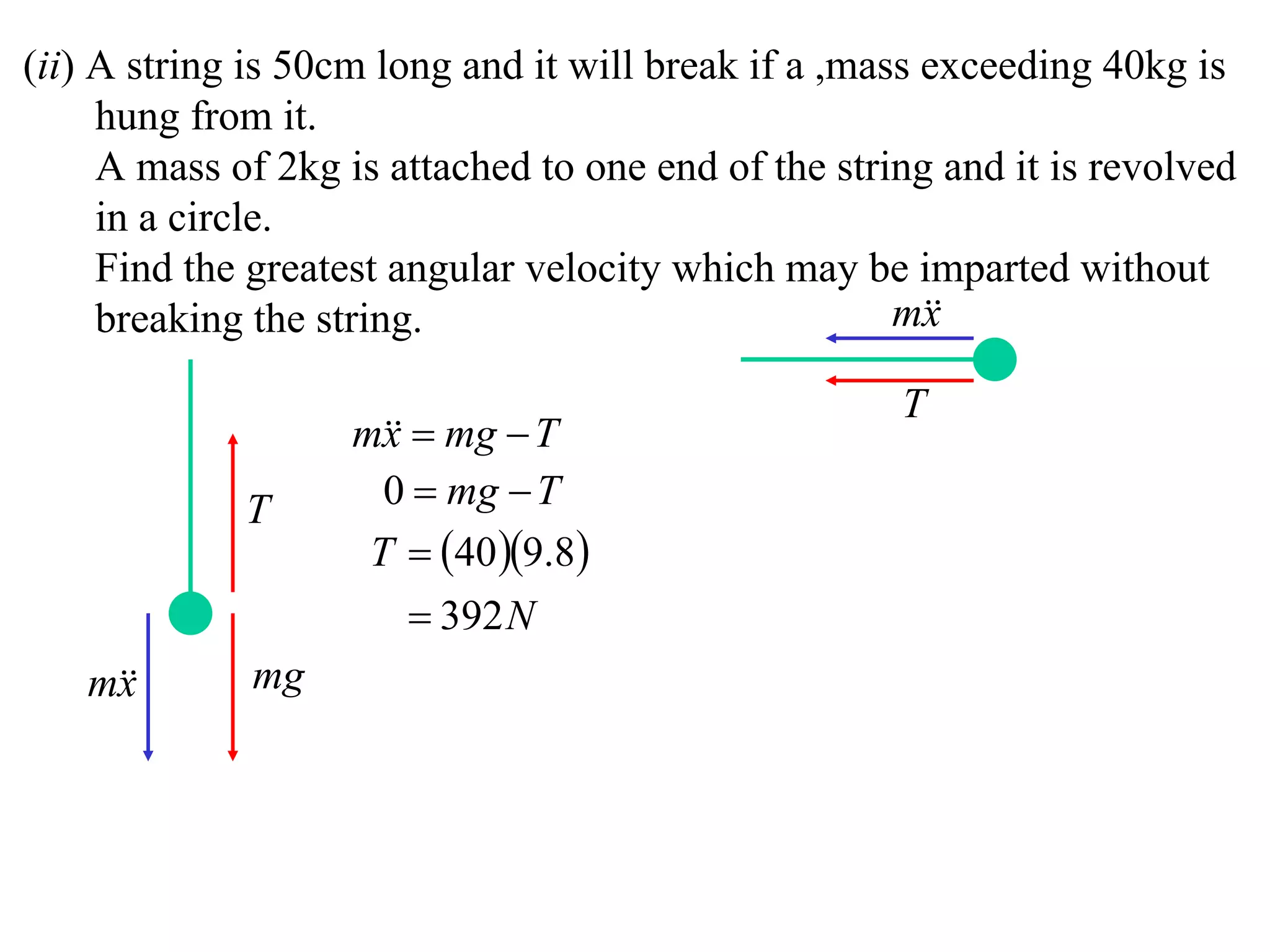
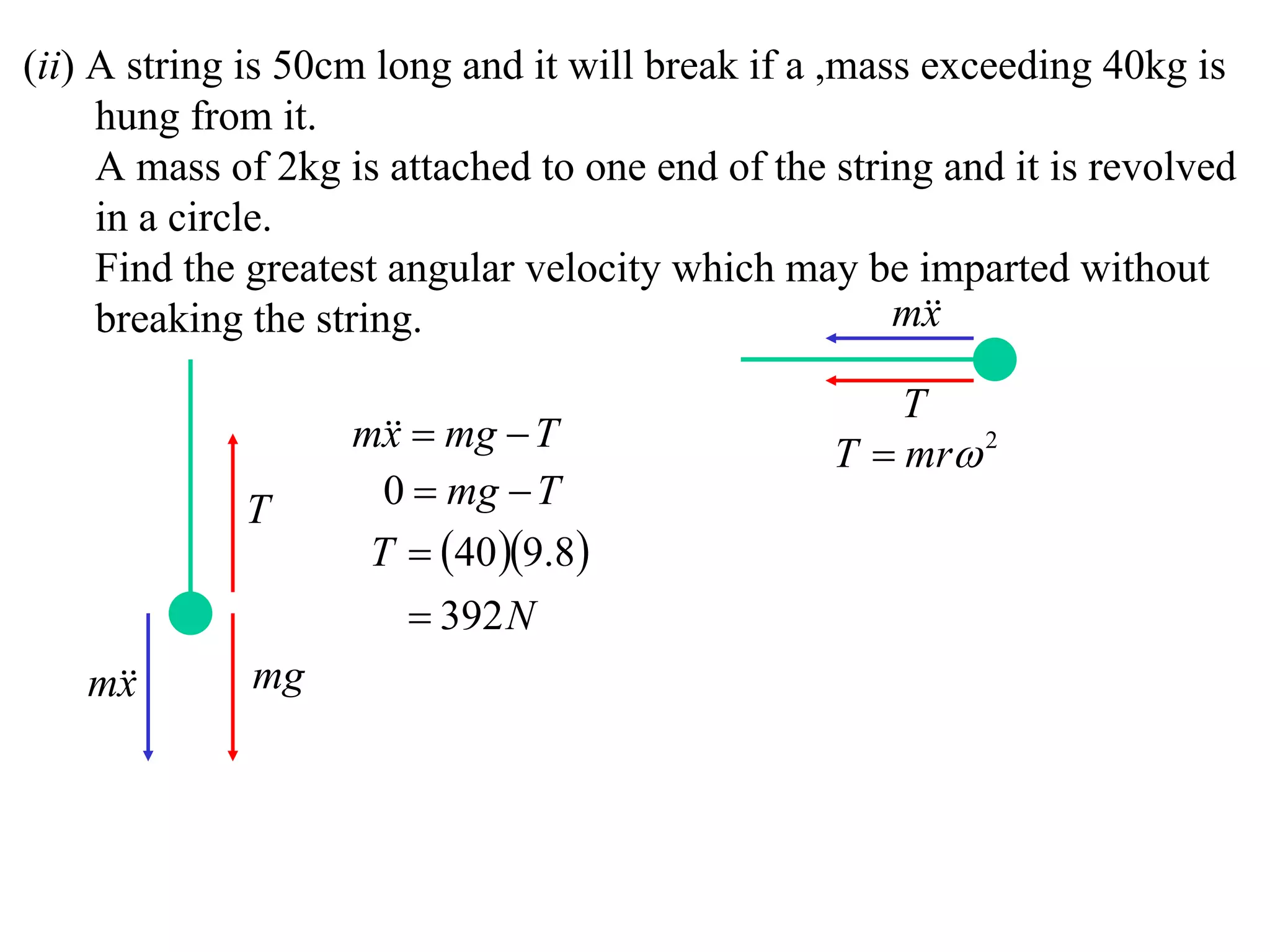
1) Uniform circular motion occurs when a particle moves with a constant angular velocity, meaning its linear velocity also remains constant.
2) For an object moving in uniform circular motion, its acceleration is calculated as the change in velocity over time.
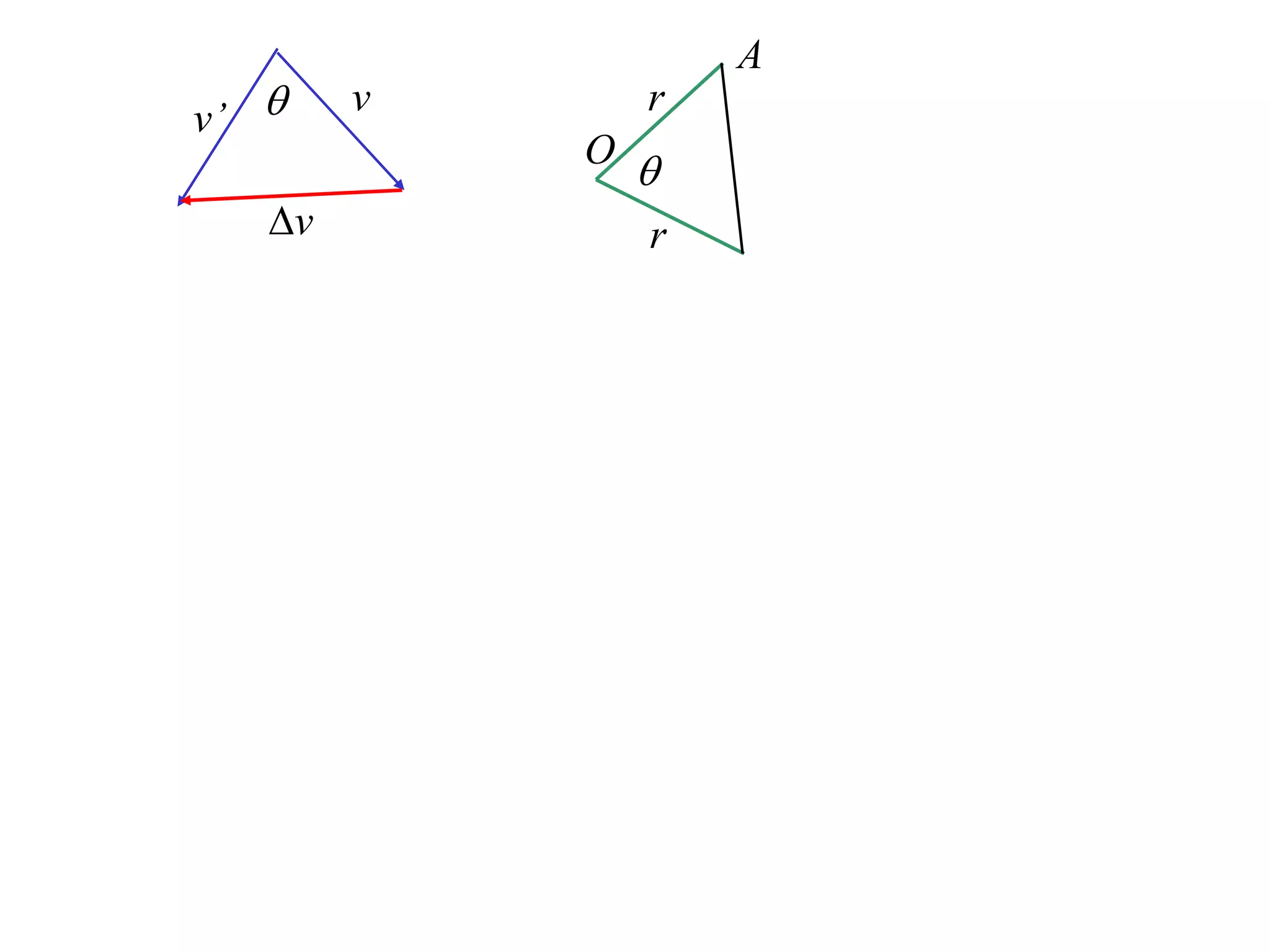
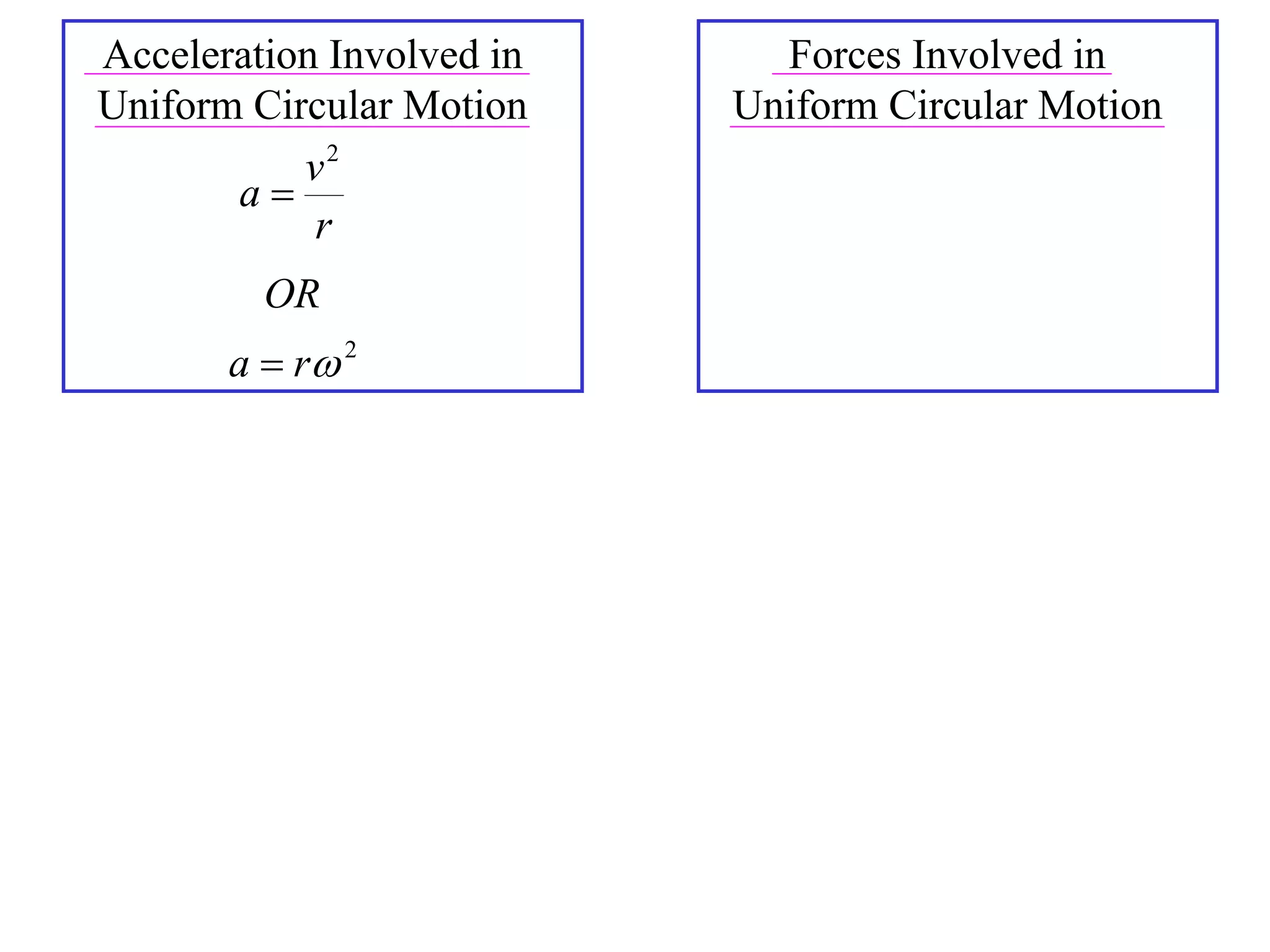
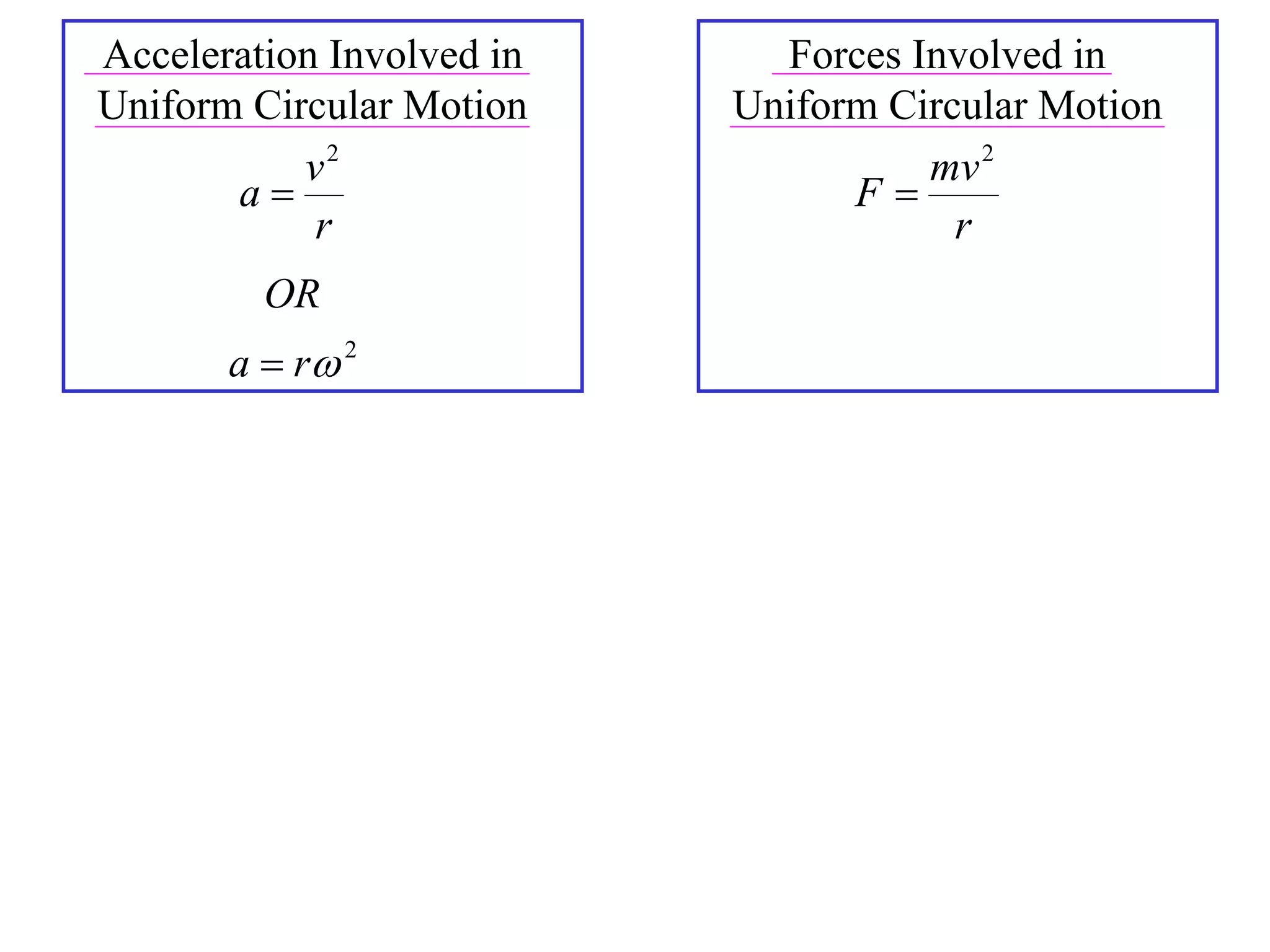
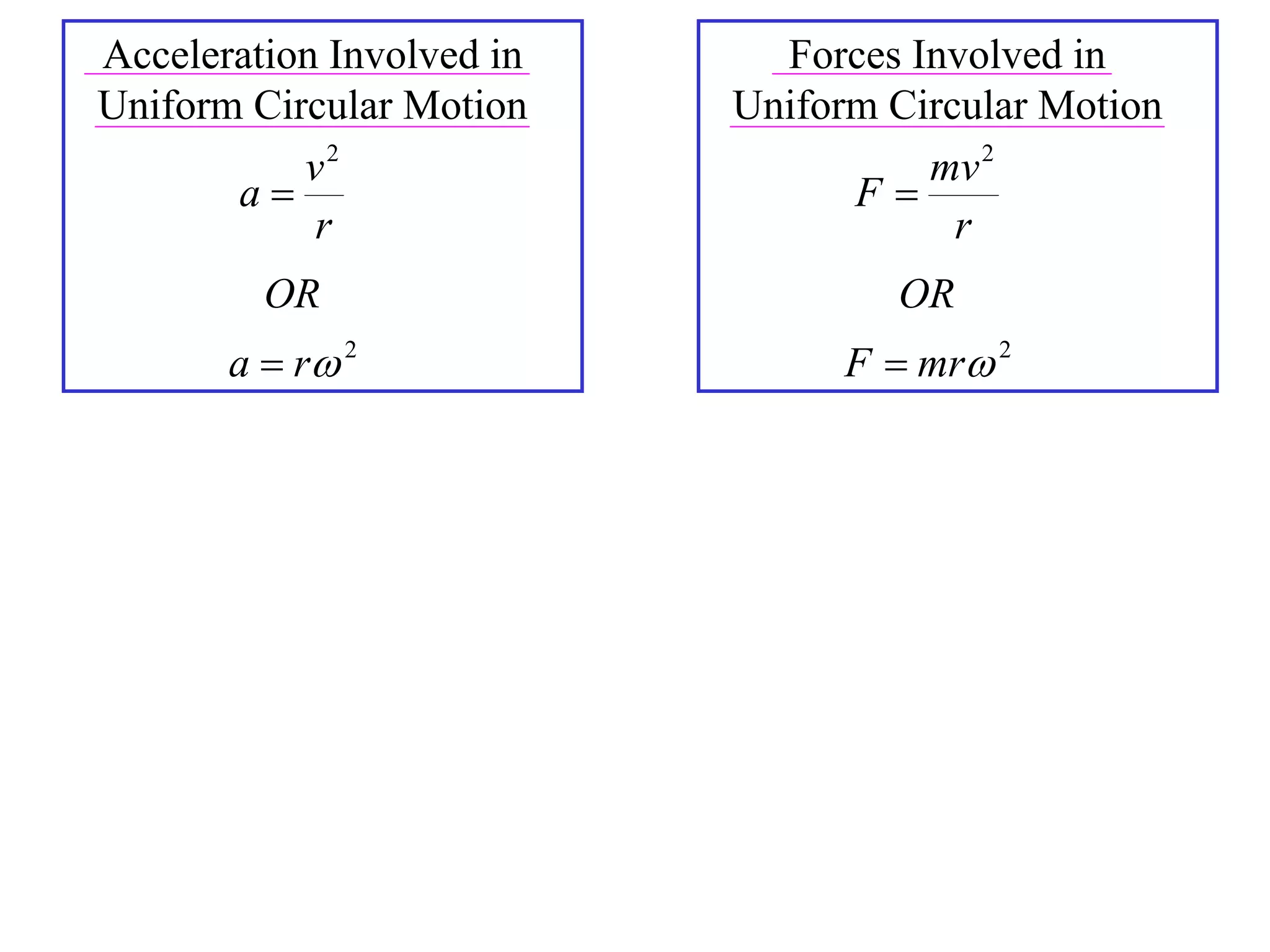
3) This acceleration can be shown to equal v^2/r, where v is the object's linear velocity and r is the radius of its circular path.