Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX





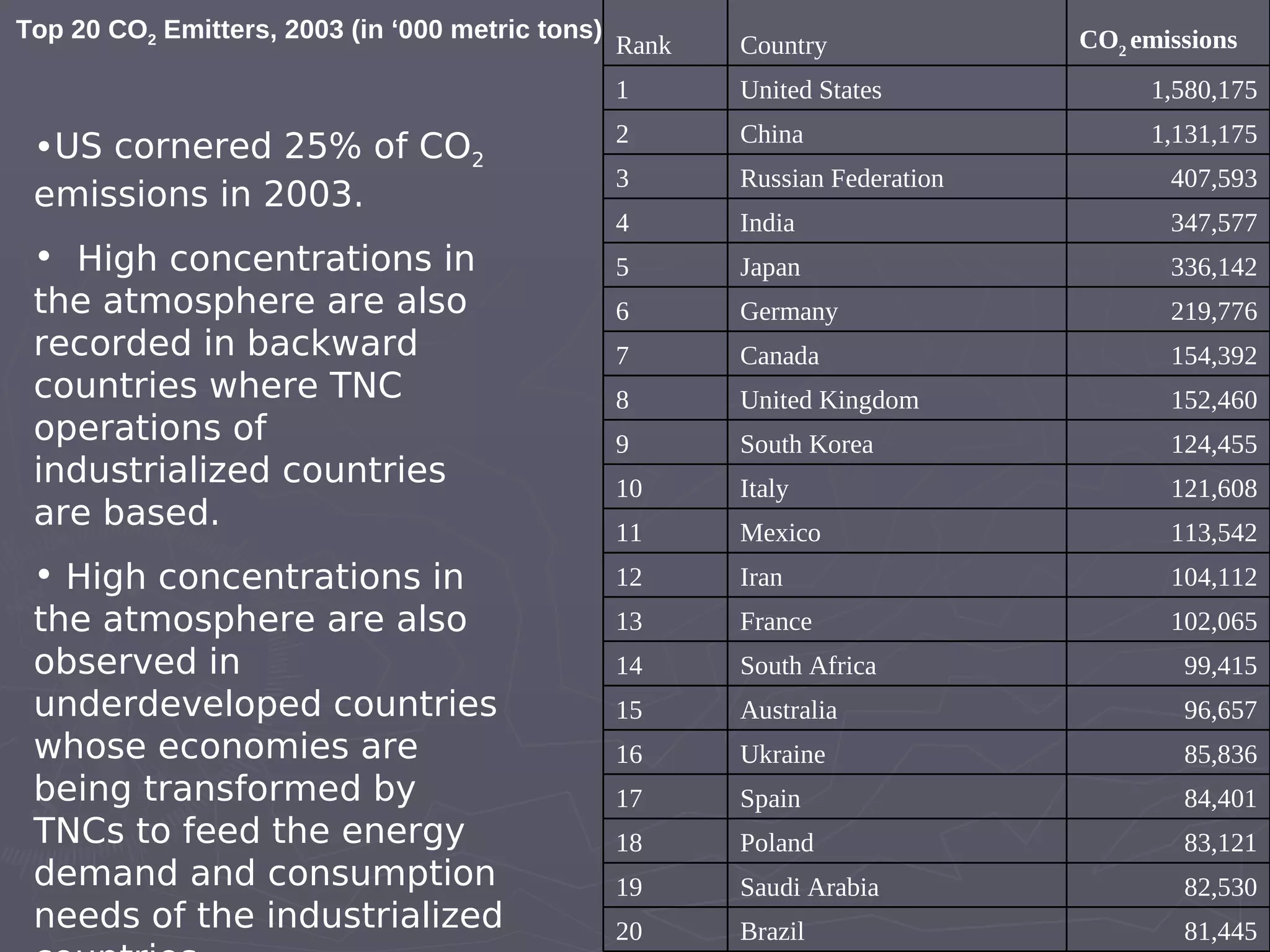
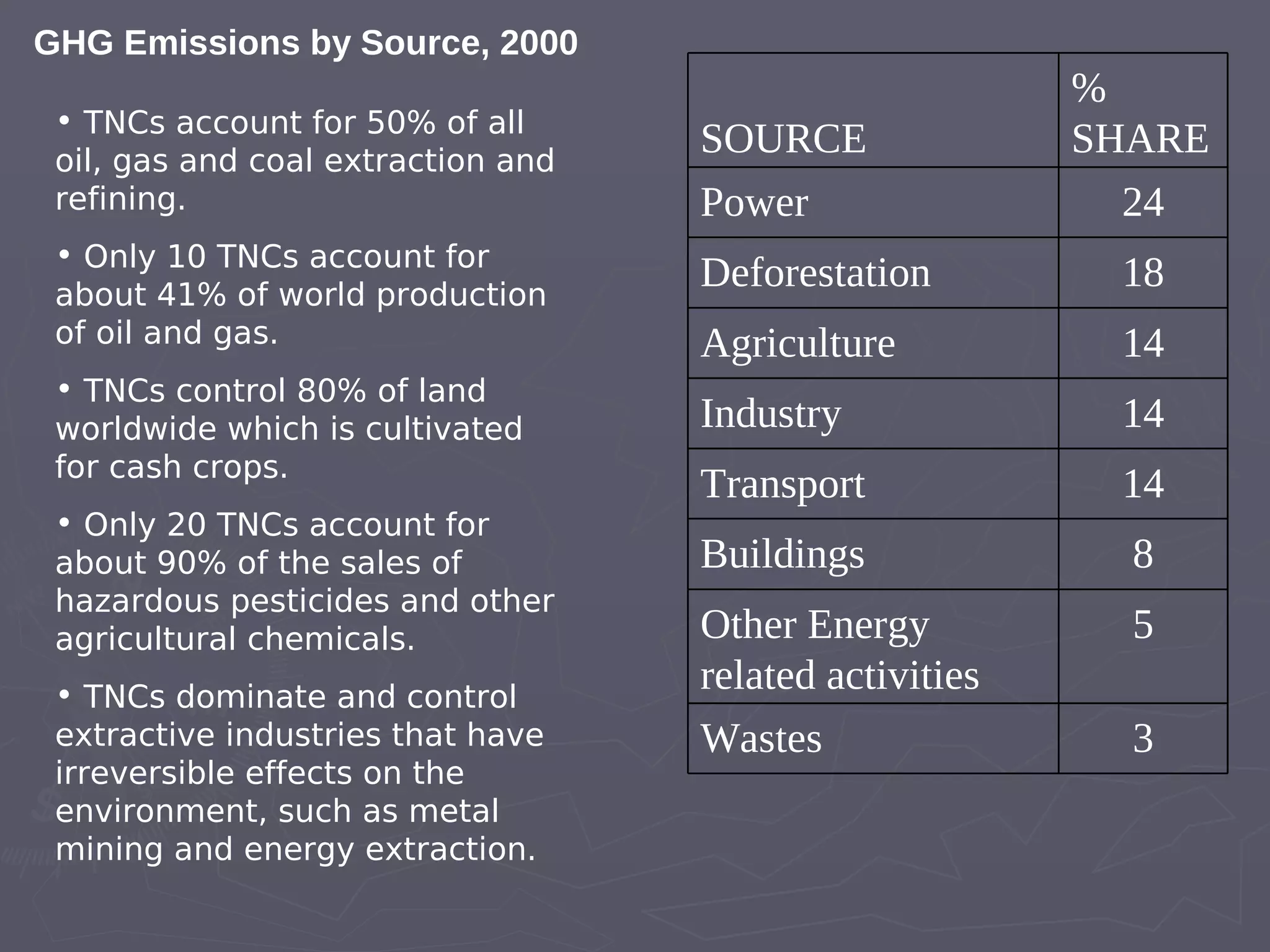




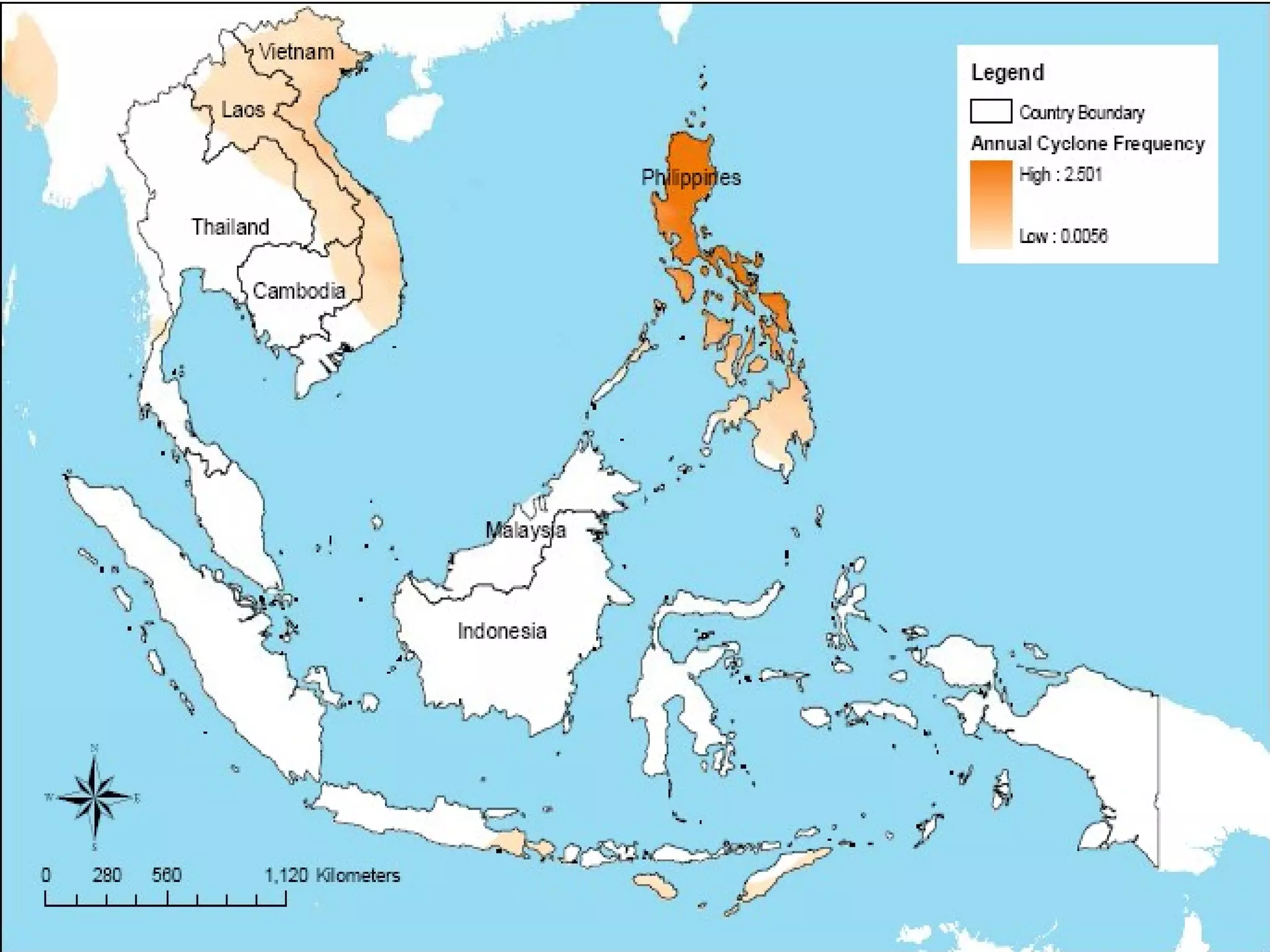
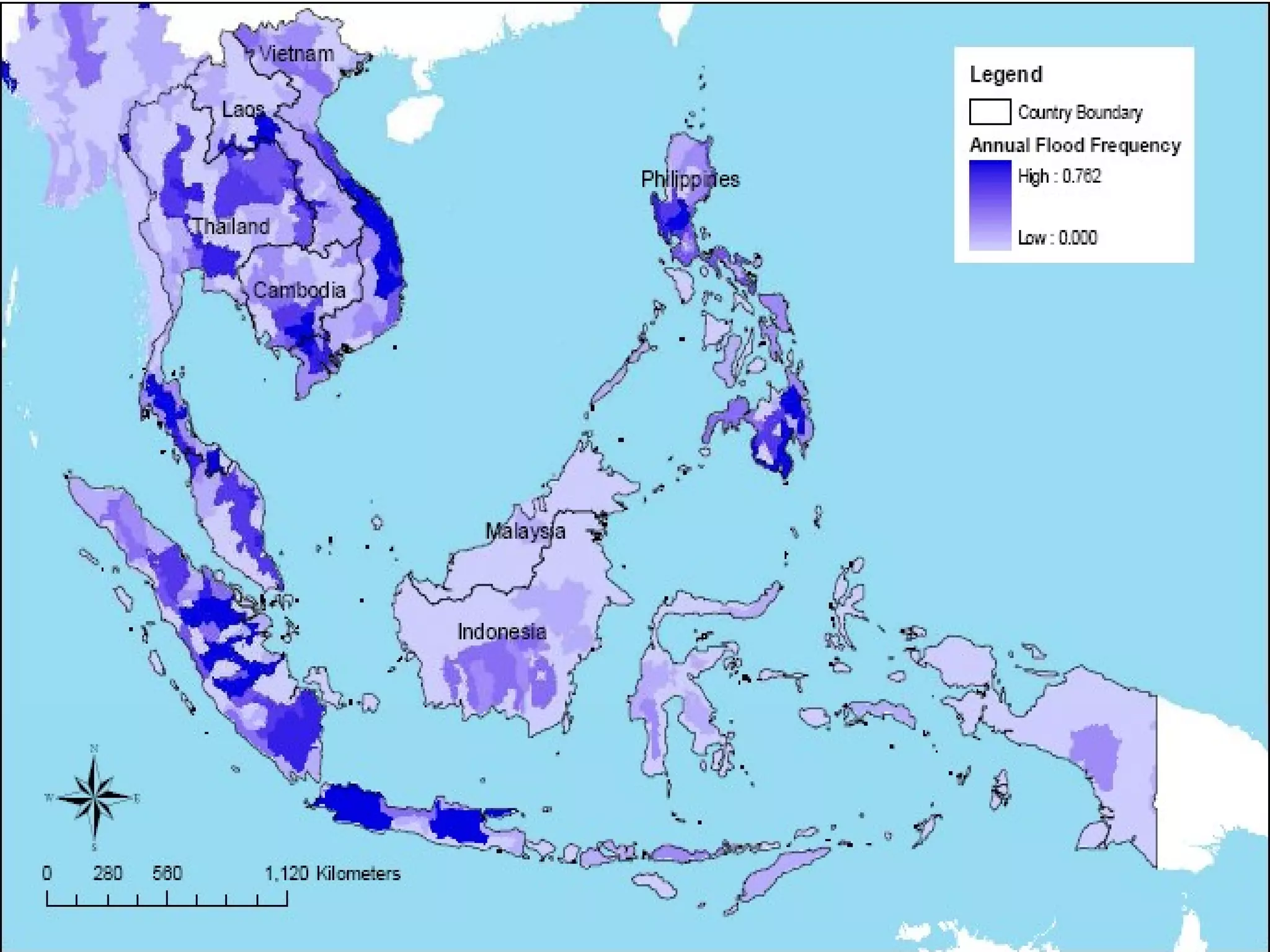
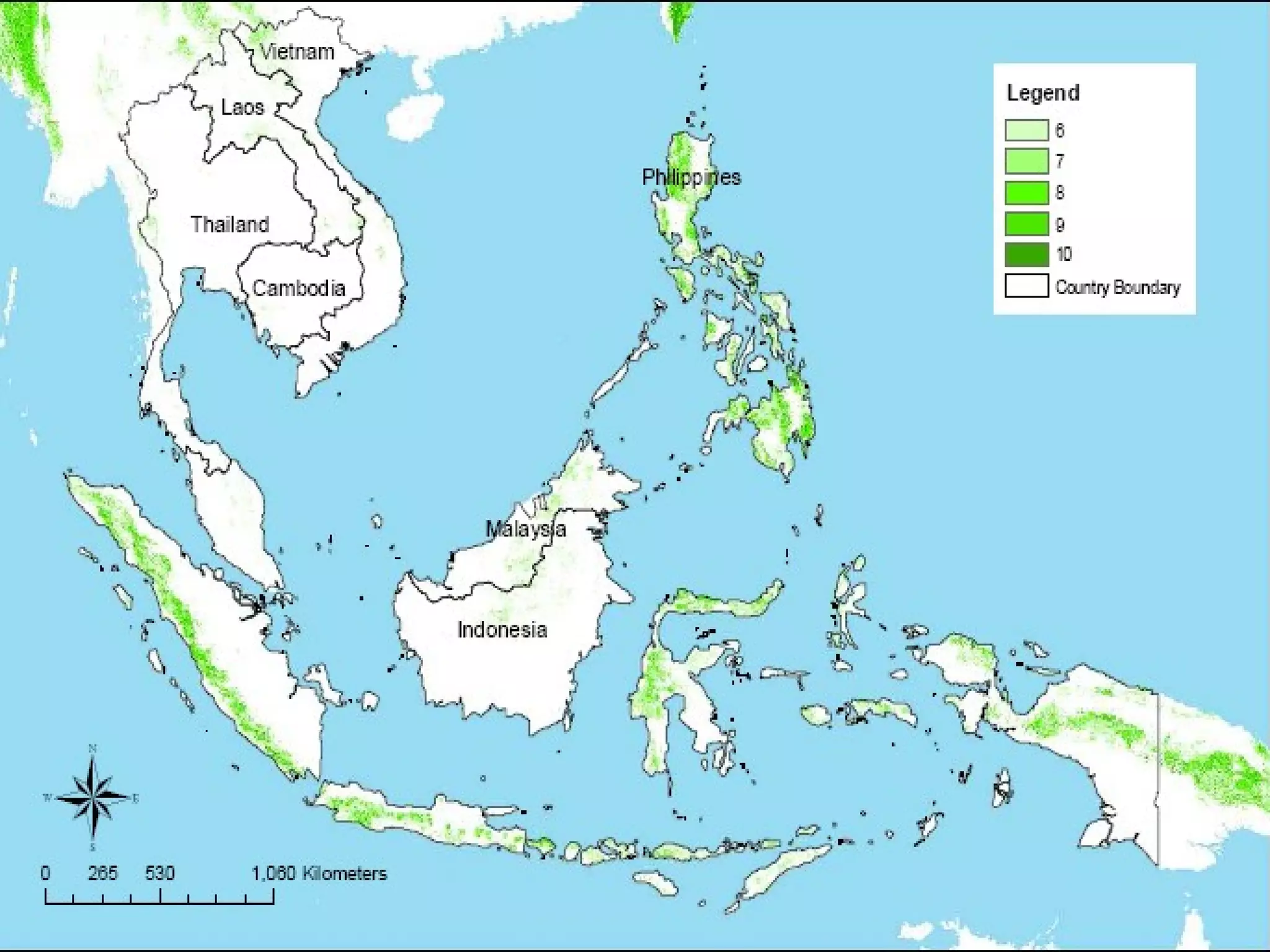
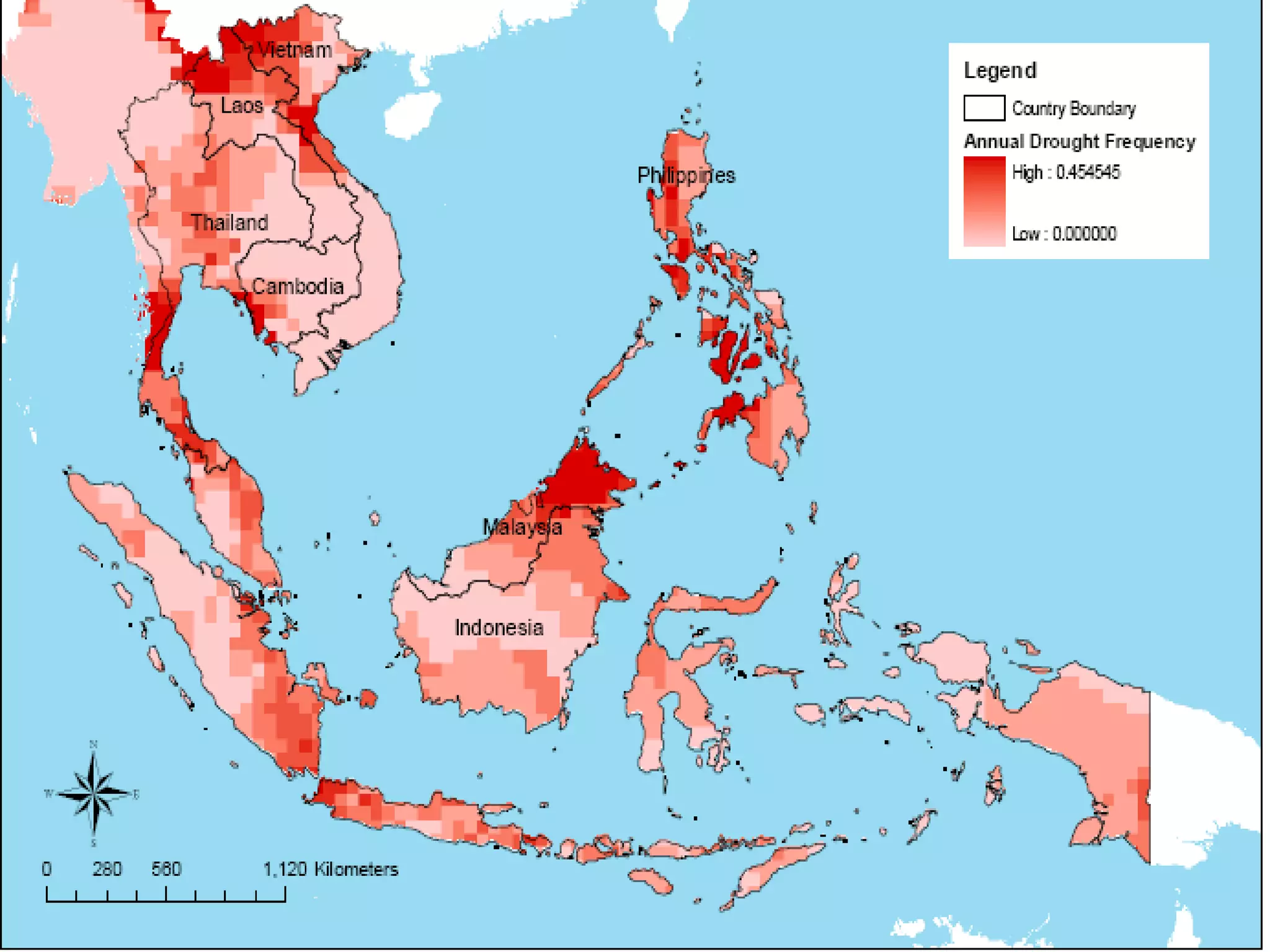
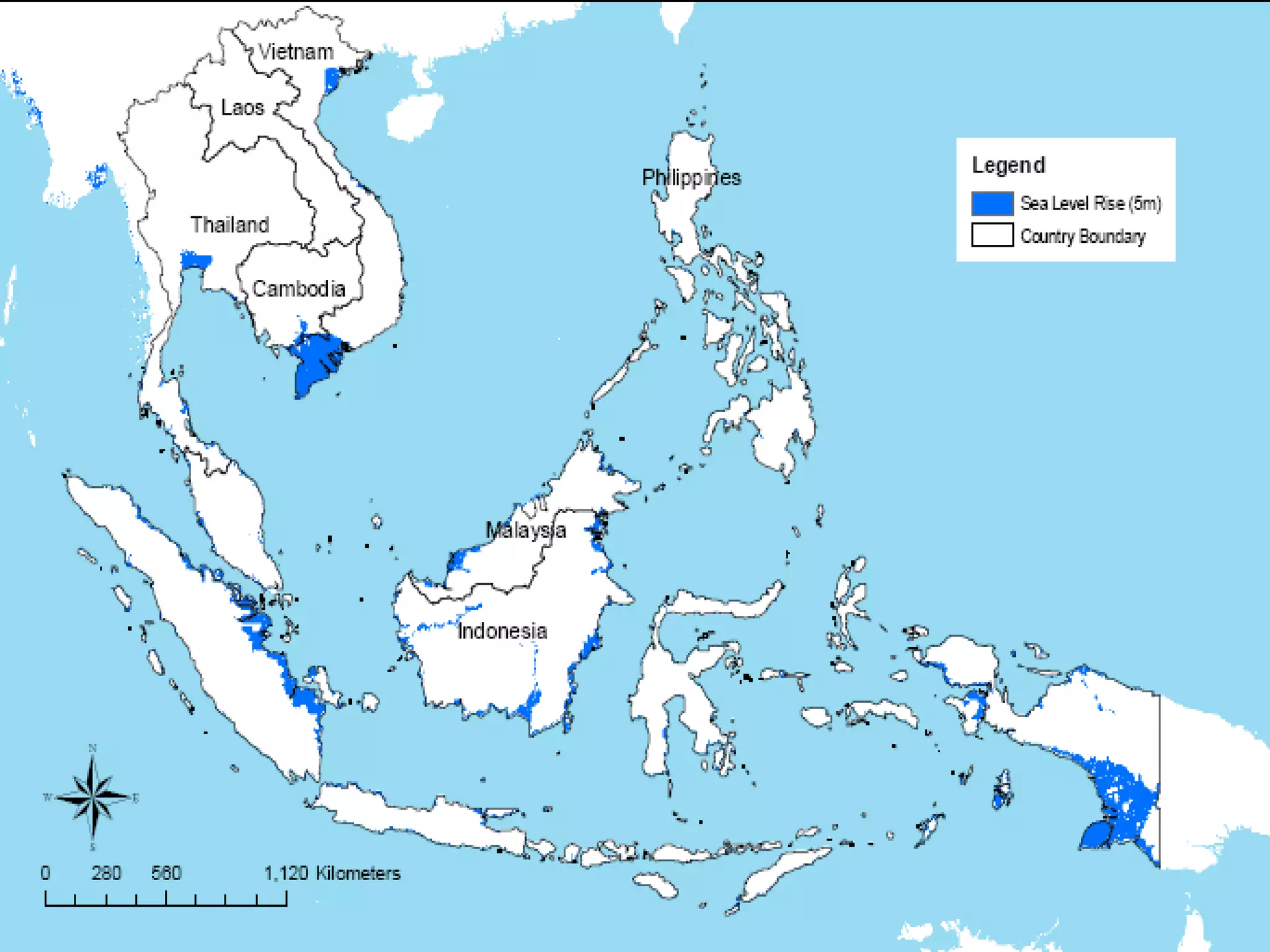
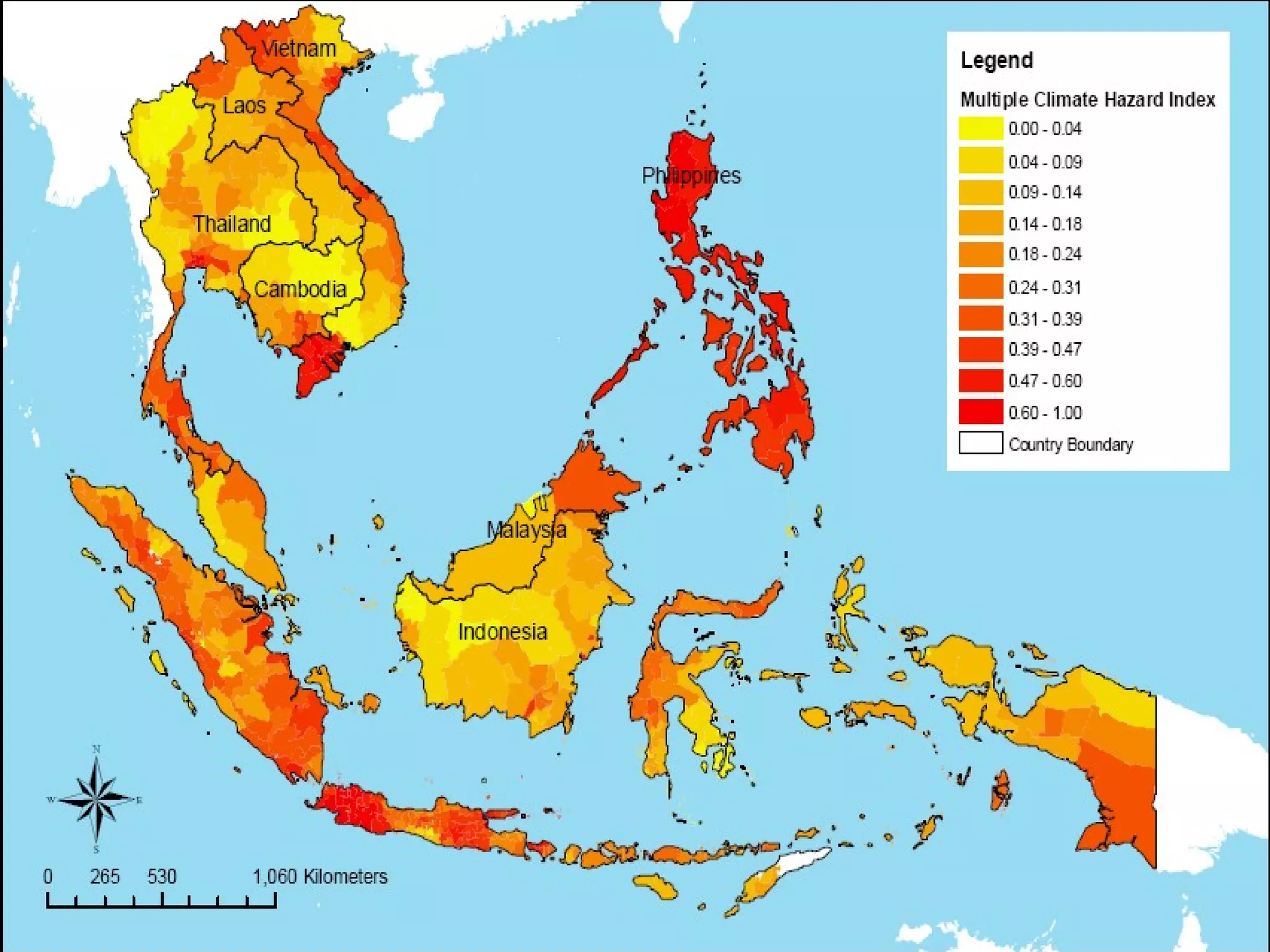
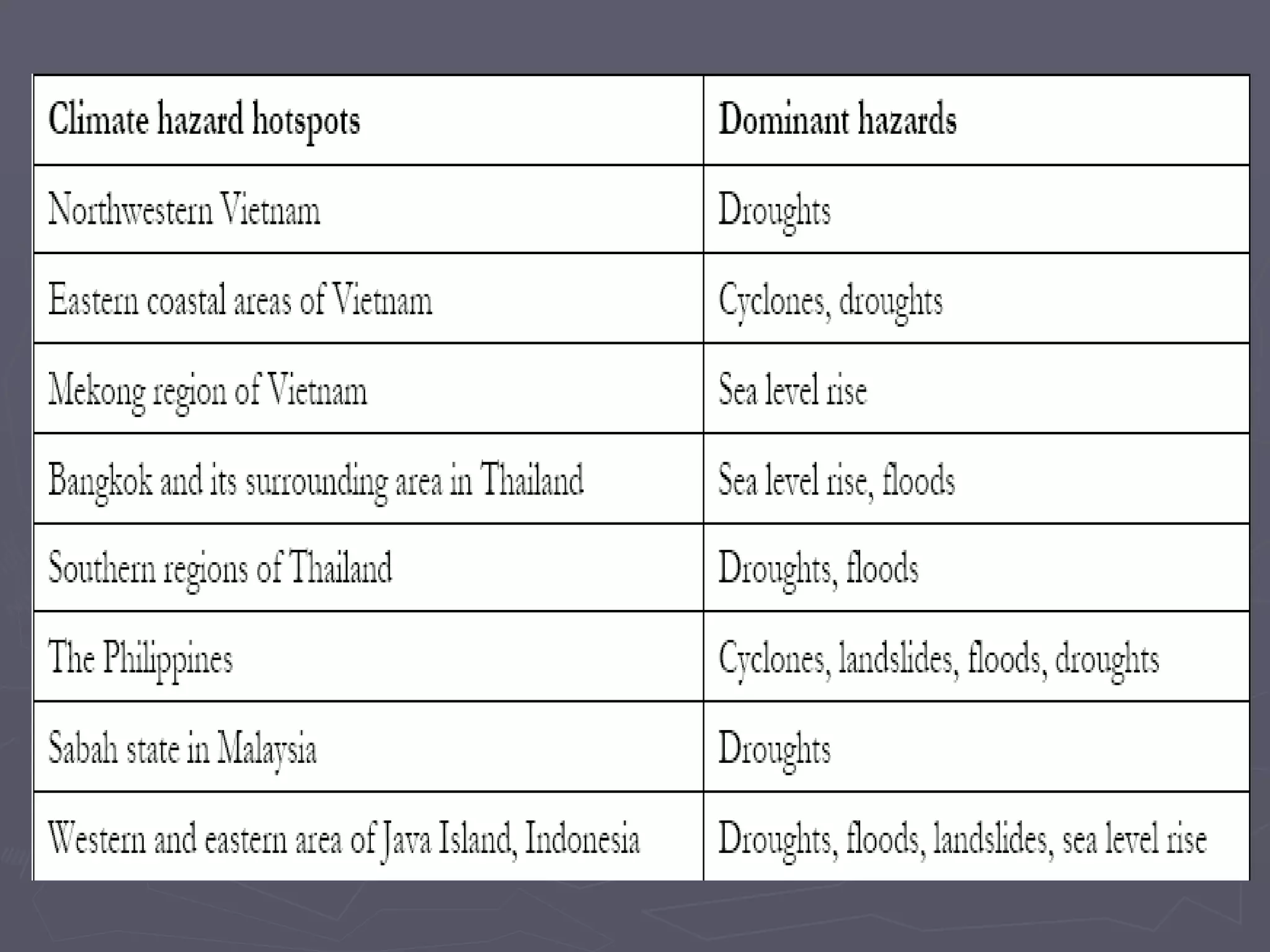
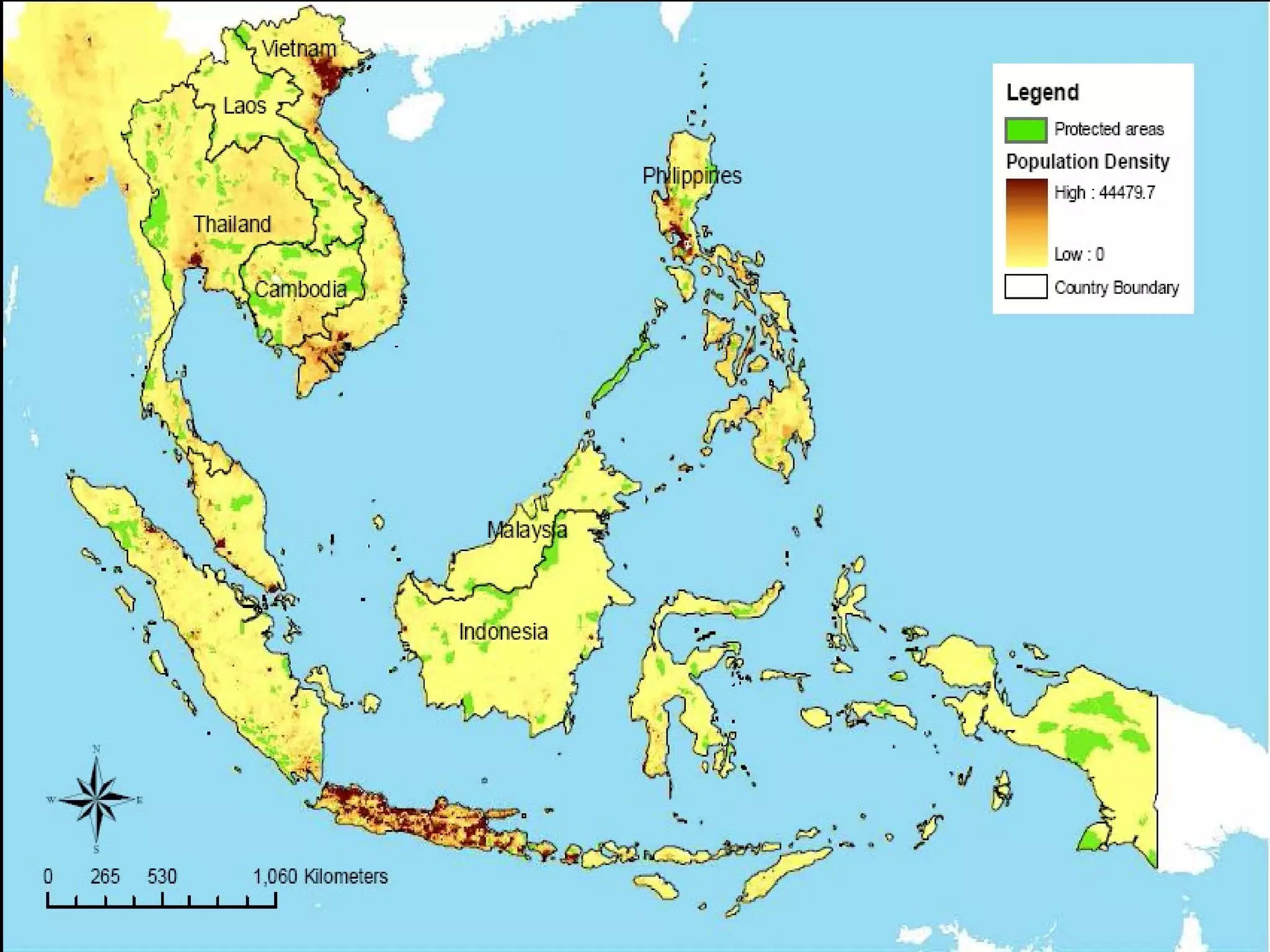














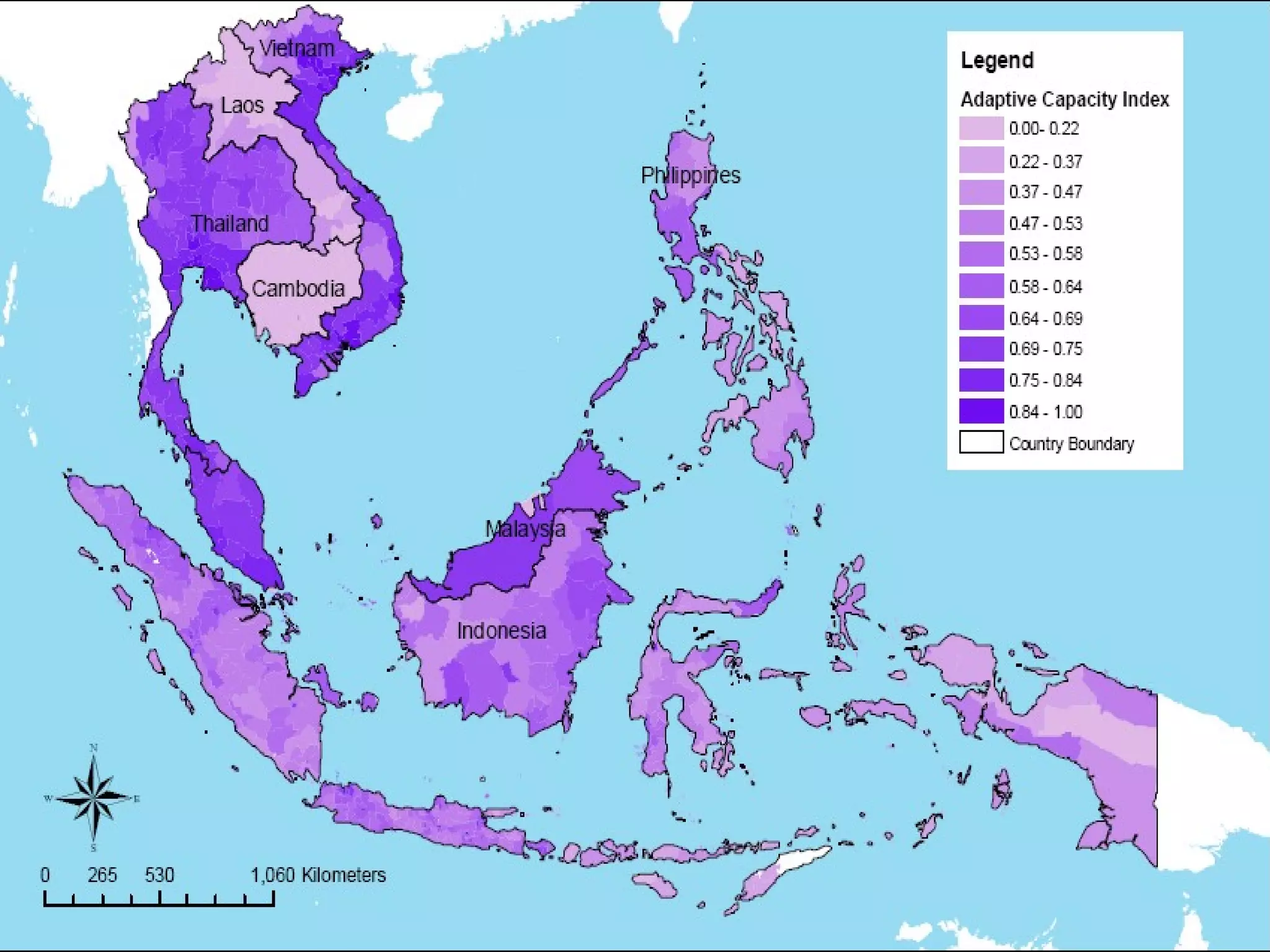

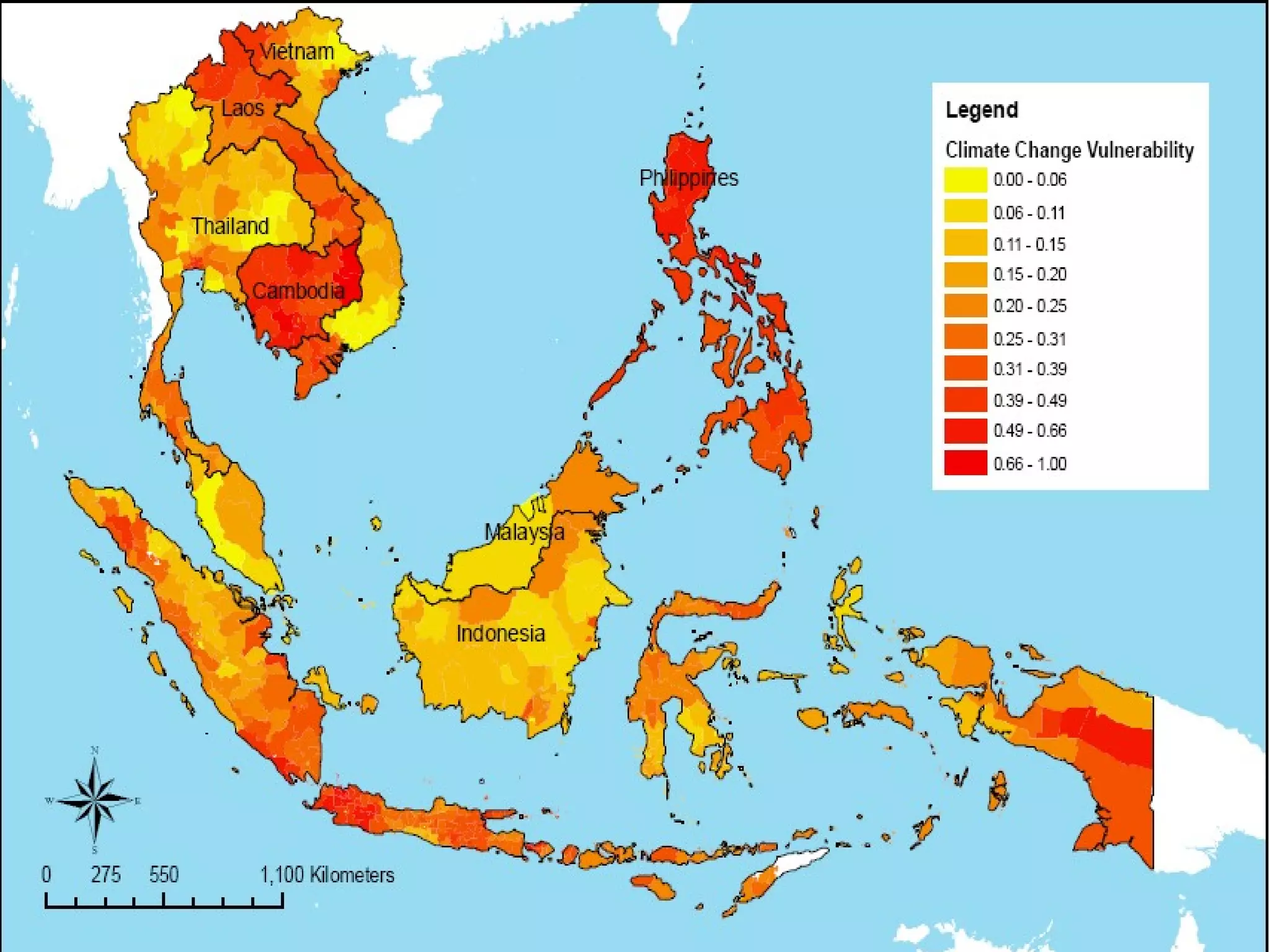
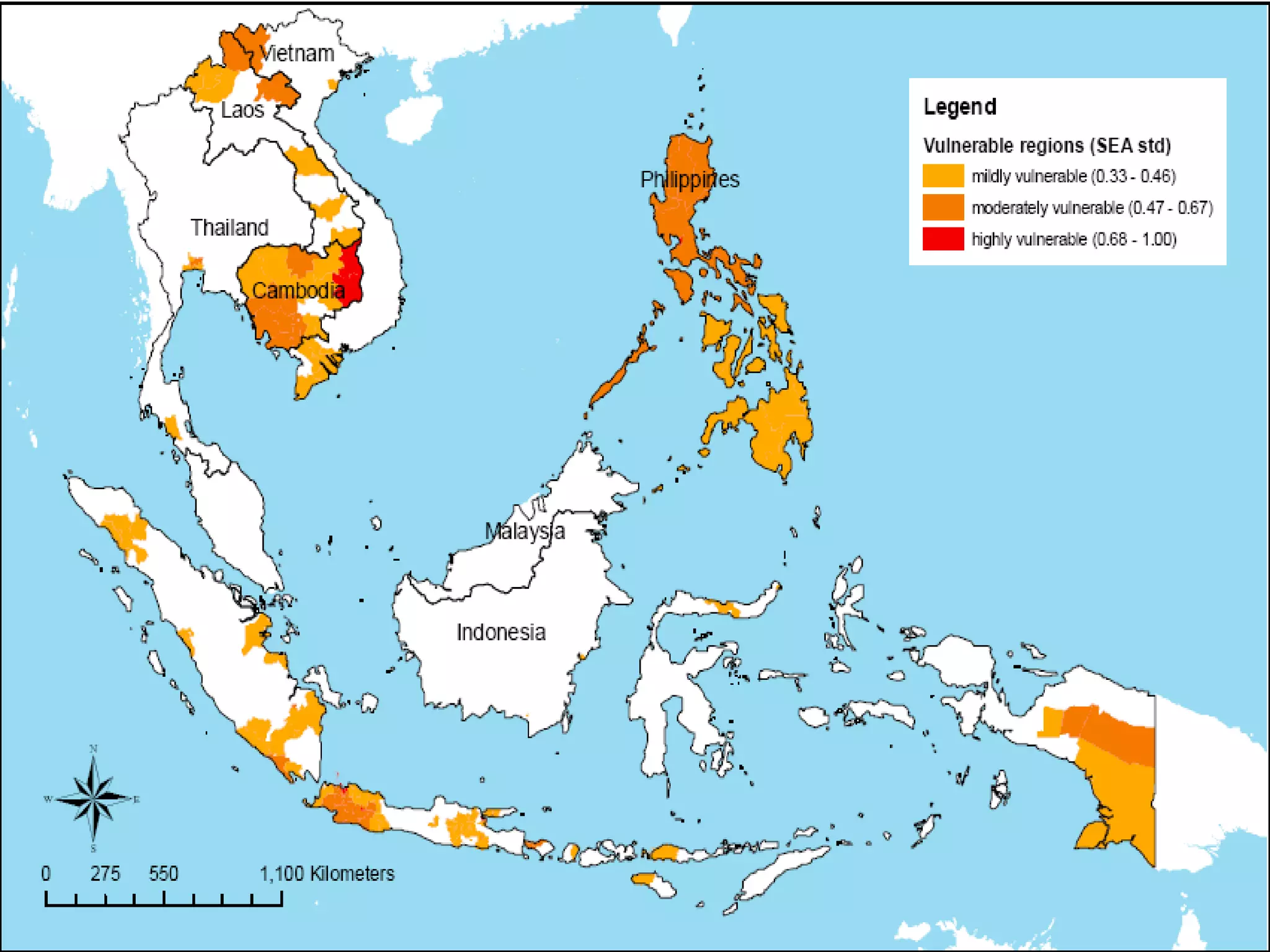
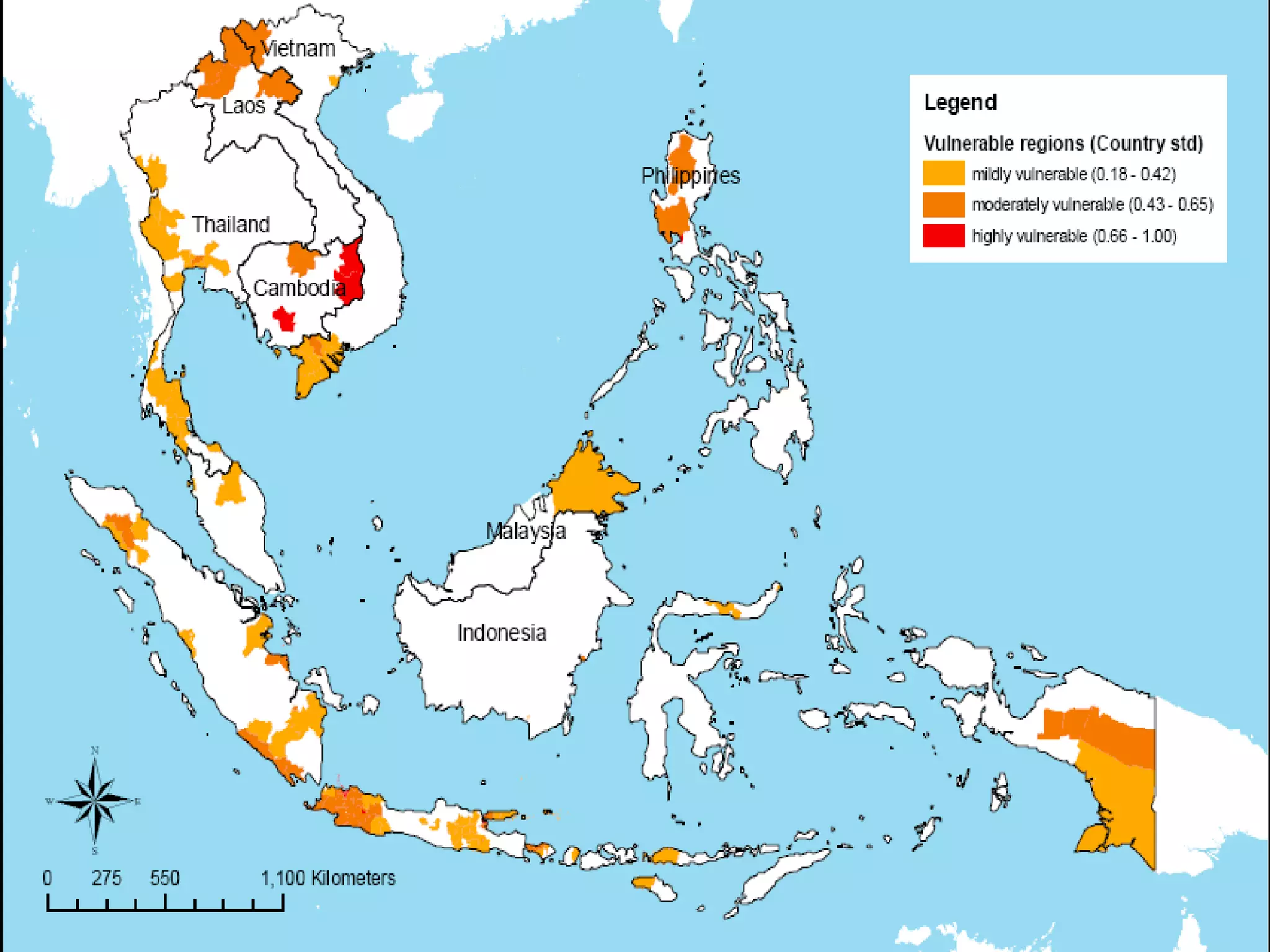






The document discusses the accountability of industrialized countries and transnational corporations (TNCs) for climate change, highlighting their unsustainable production and consumption patterns. It emphasizes that poorer nations, particularly in Asia and the Pacific, are more vulnerable to climate impacts due to their economic conditions and lack of resources, exacerbated by globalization. The text critiques global governance structures that prioritize TNC profits over sustainable development and adaptation measures in affected regions.











































