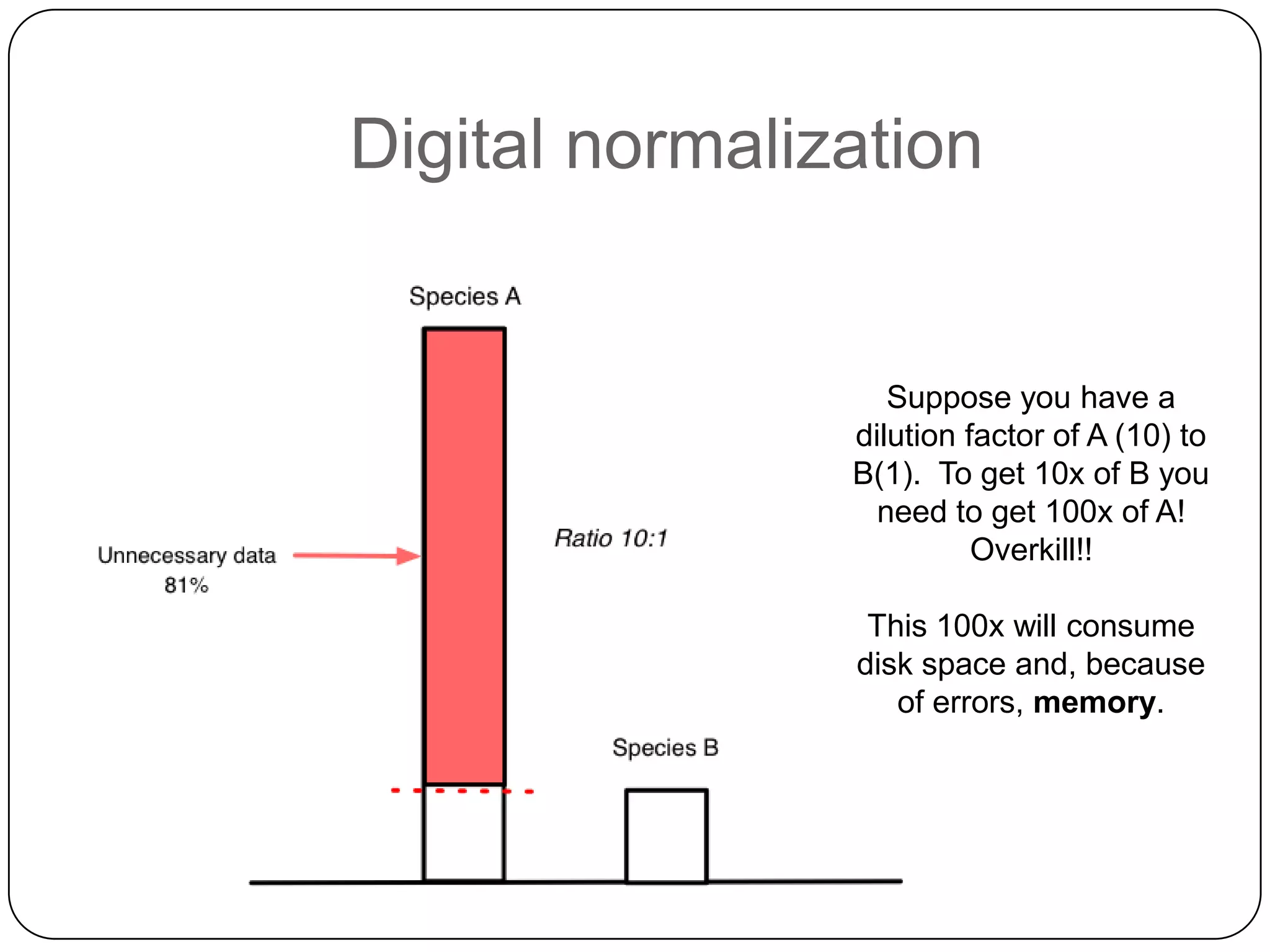
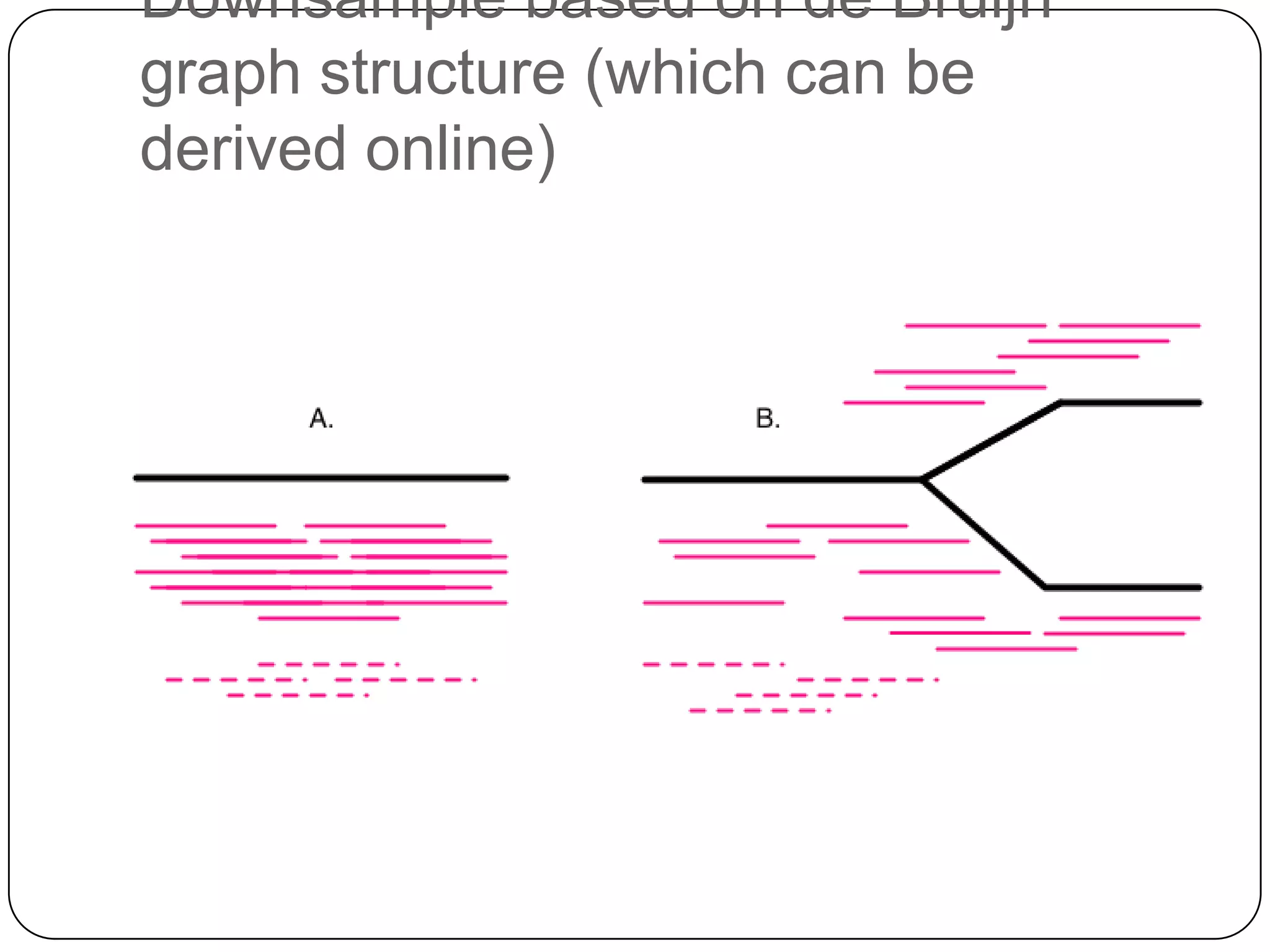
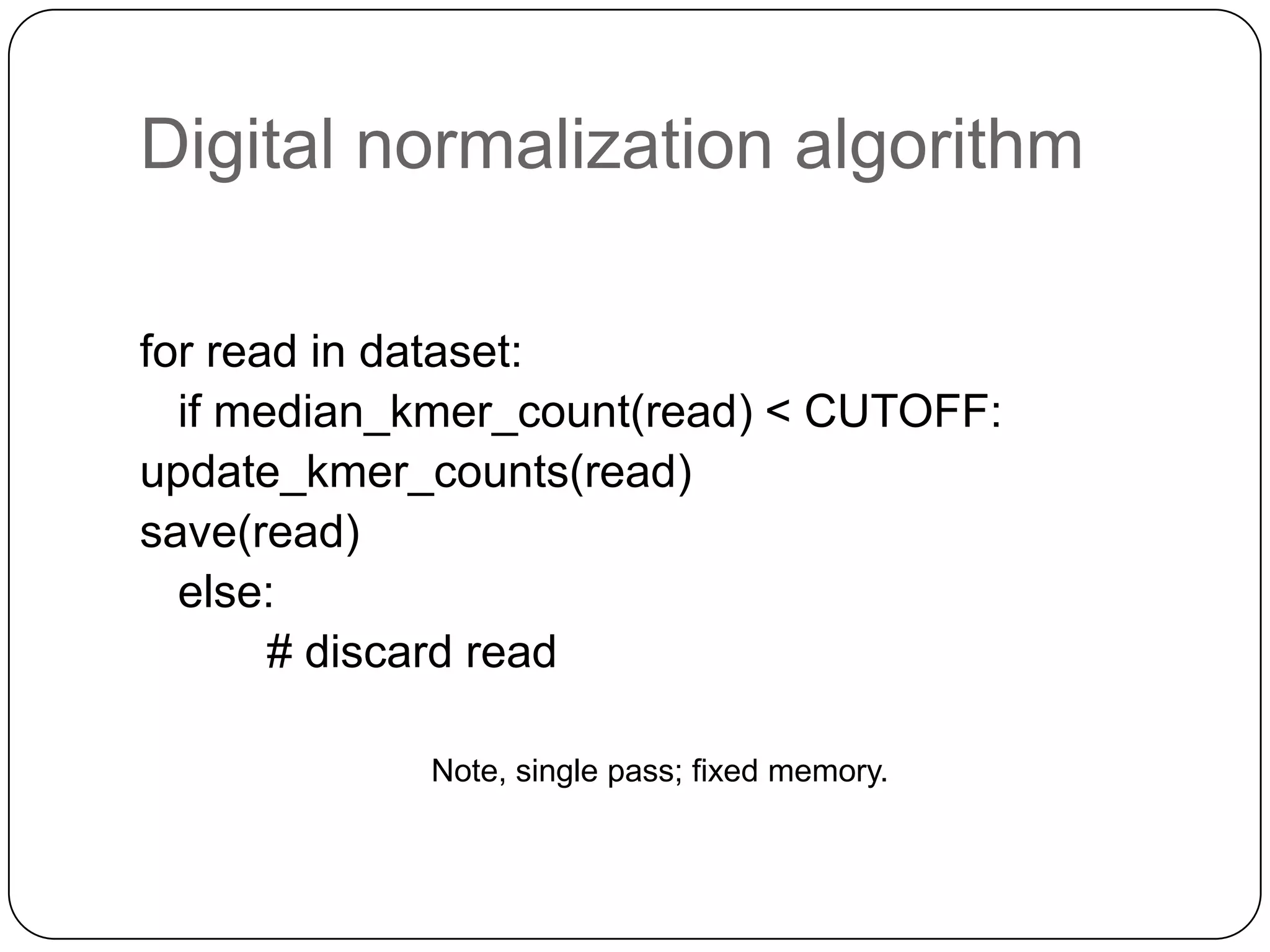
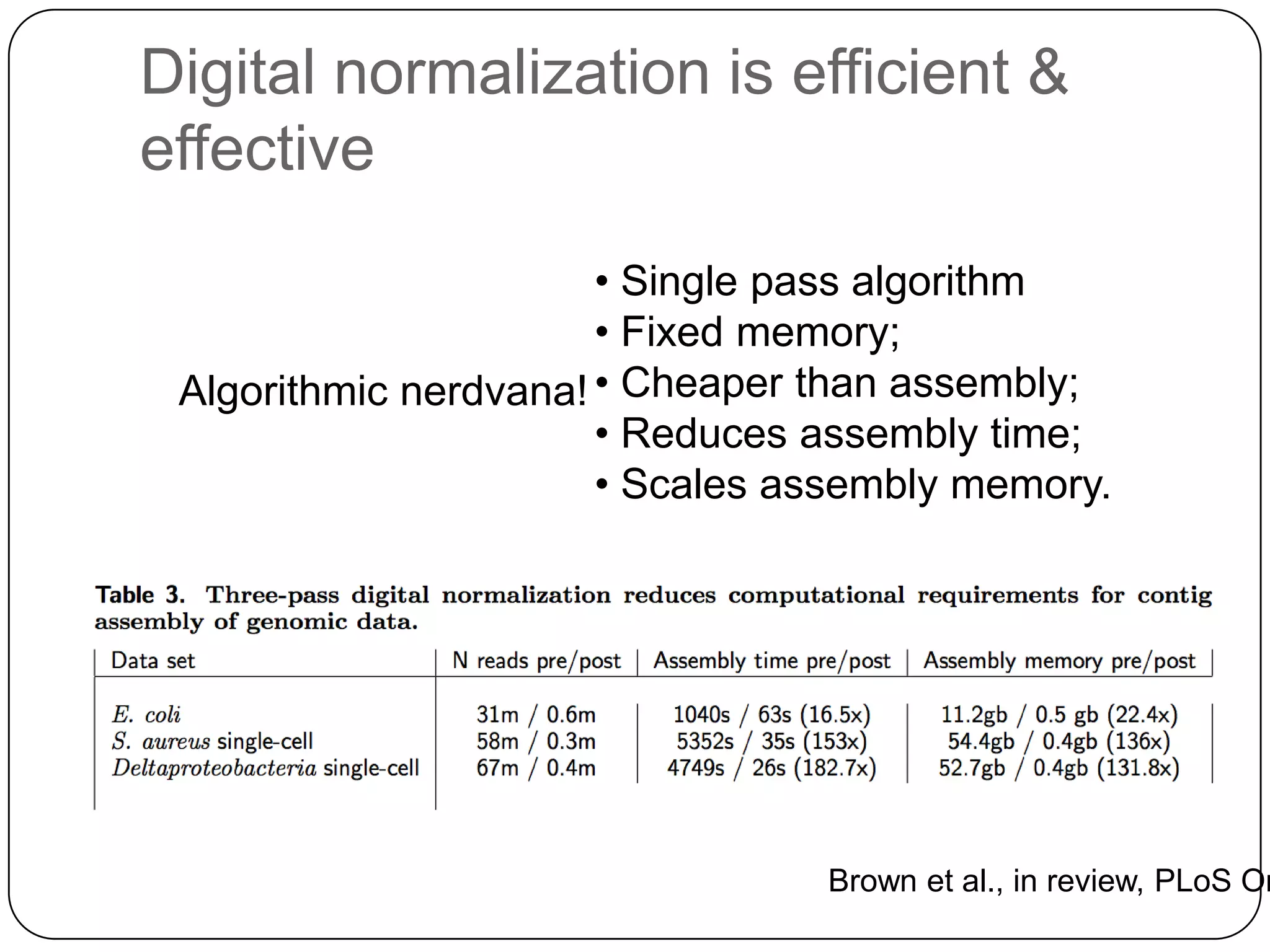
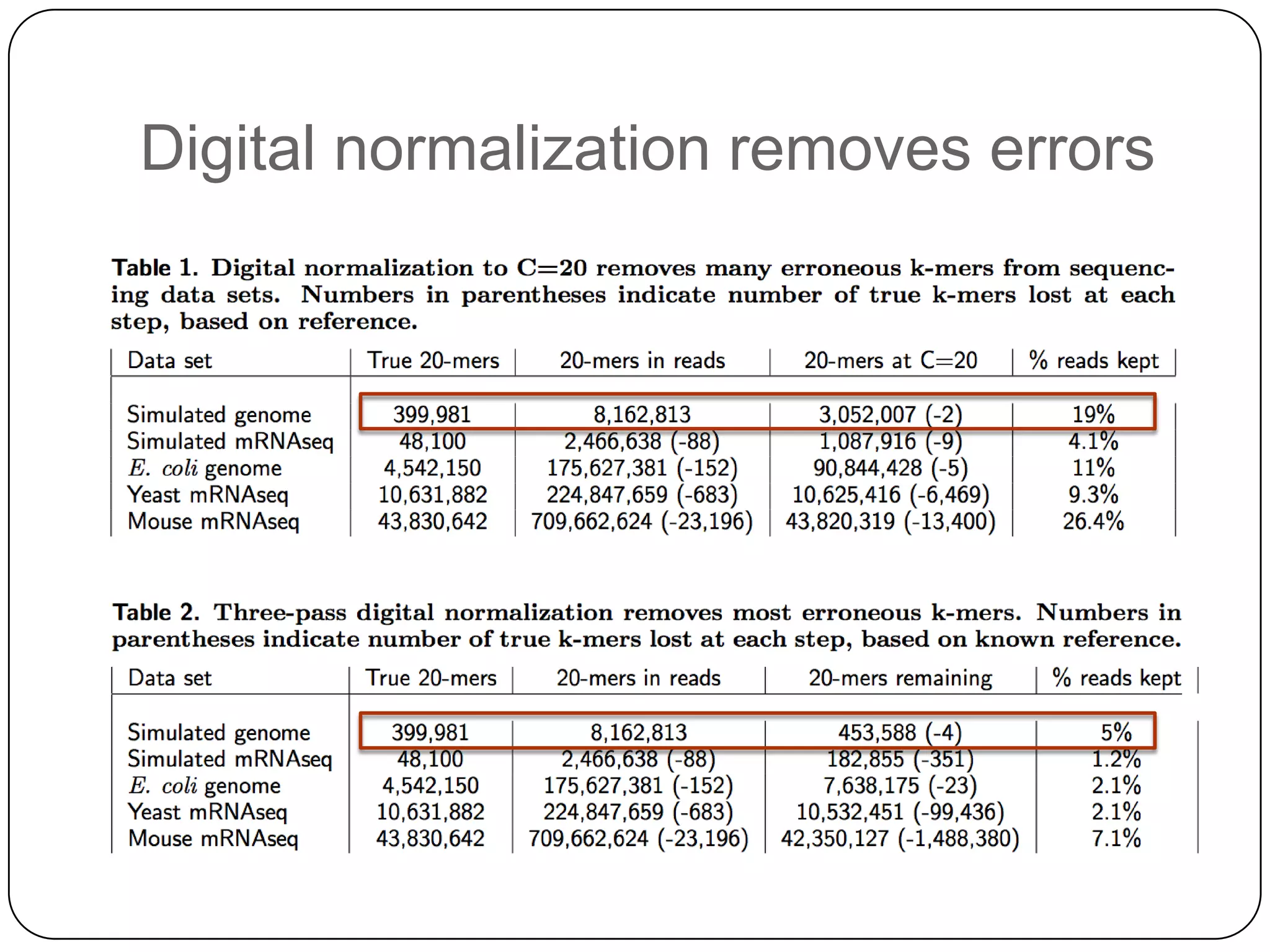
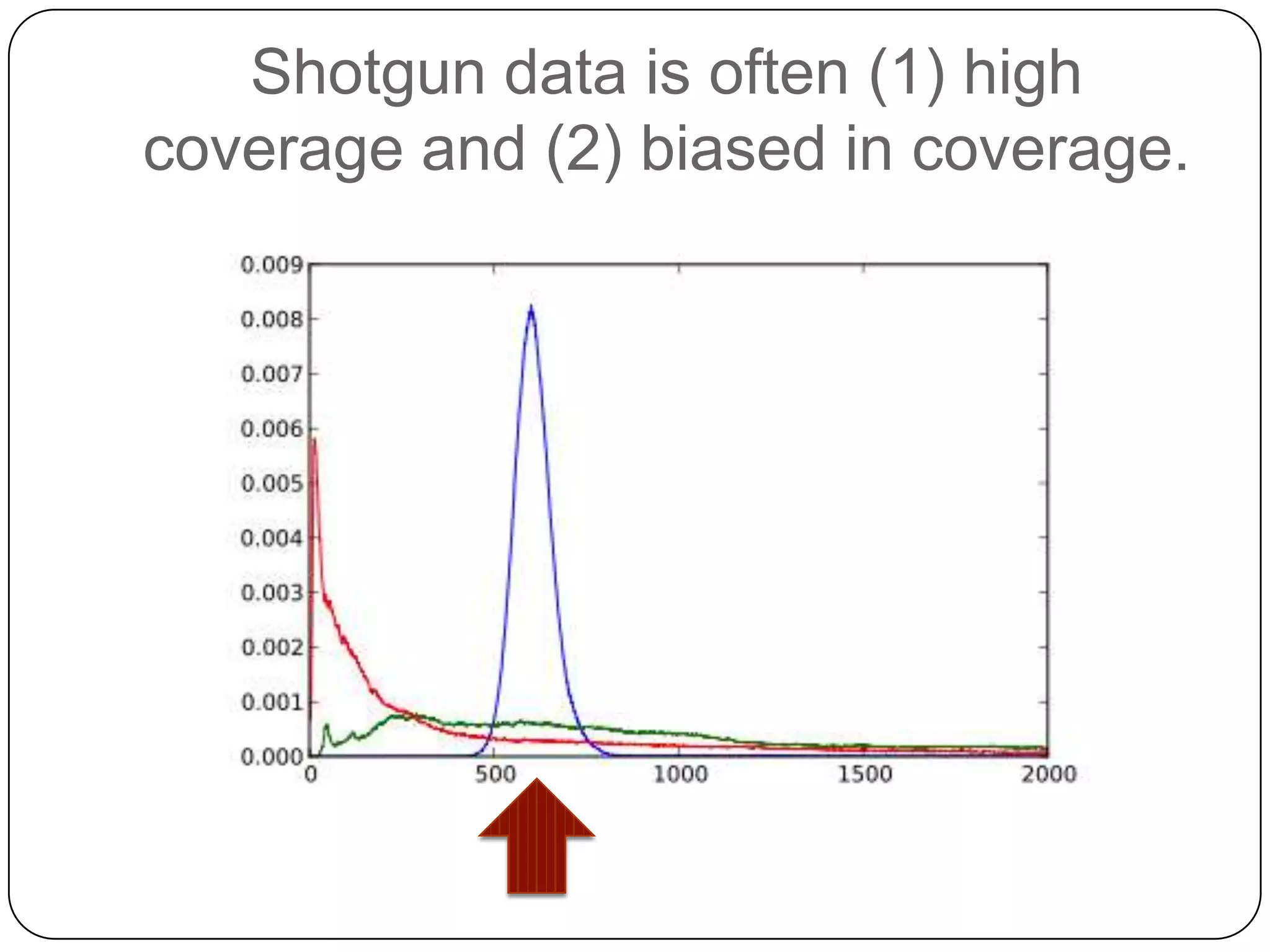
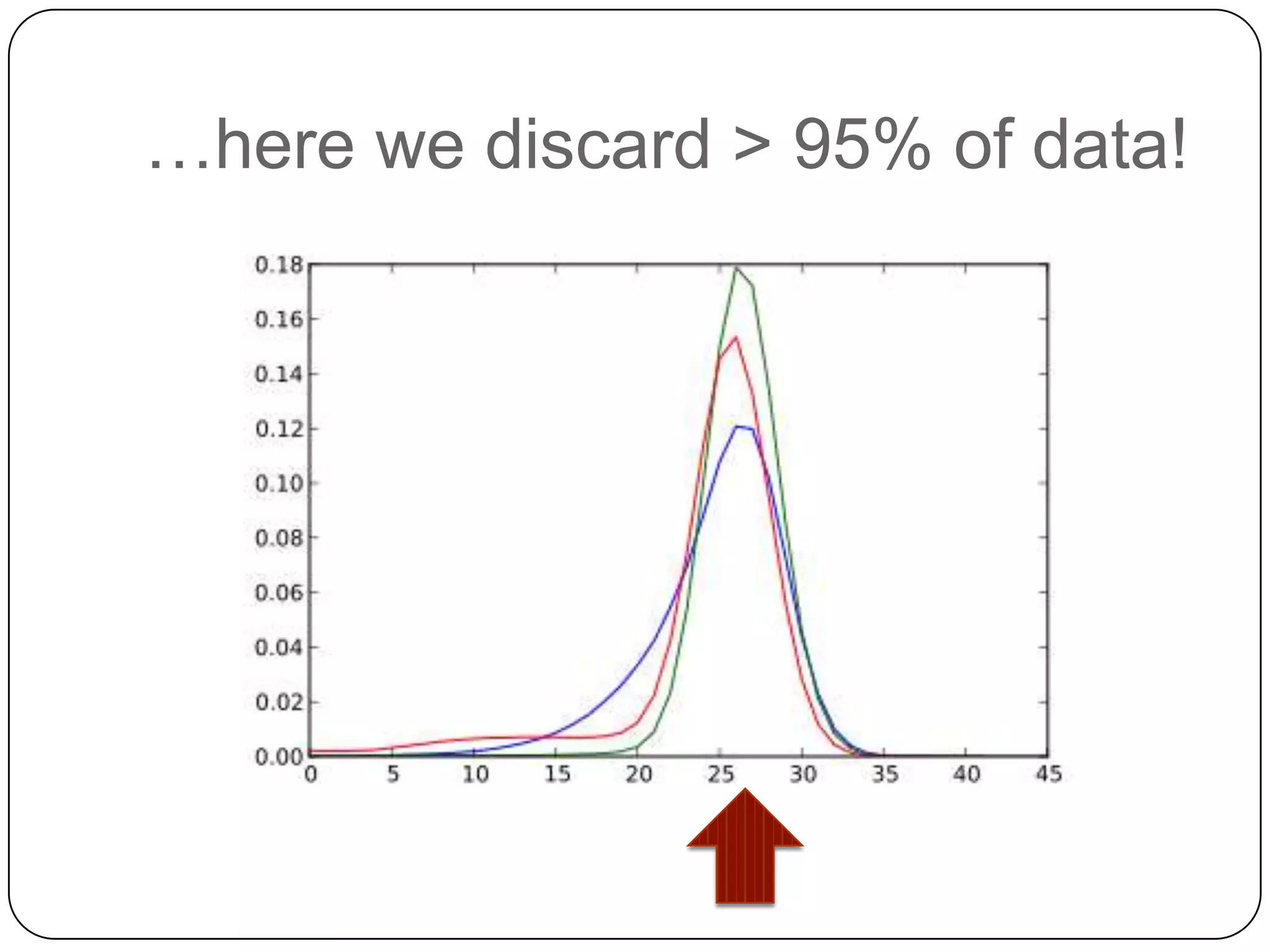
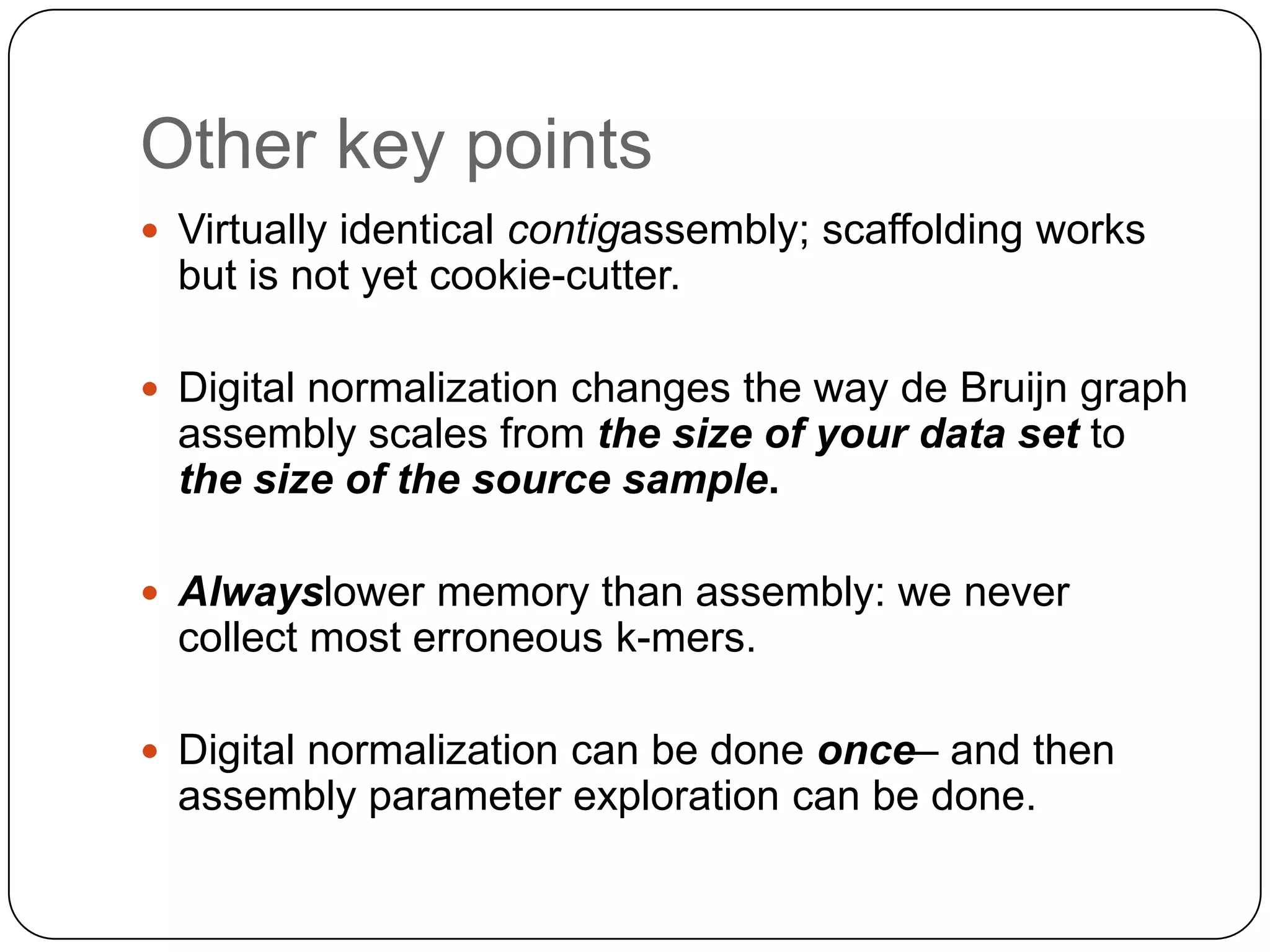
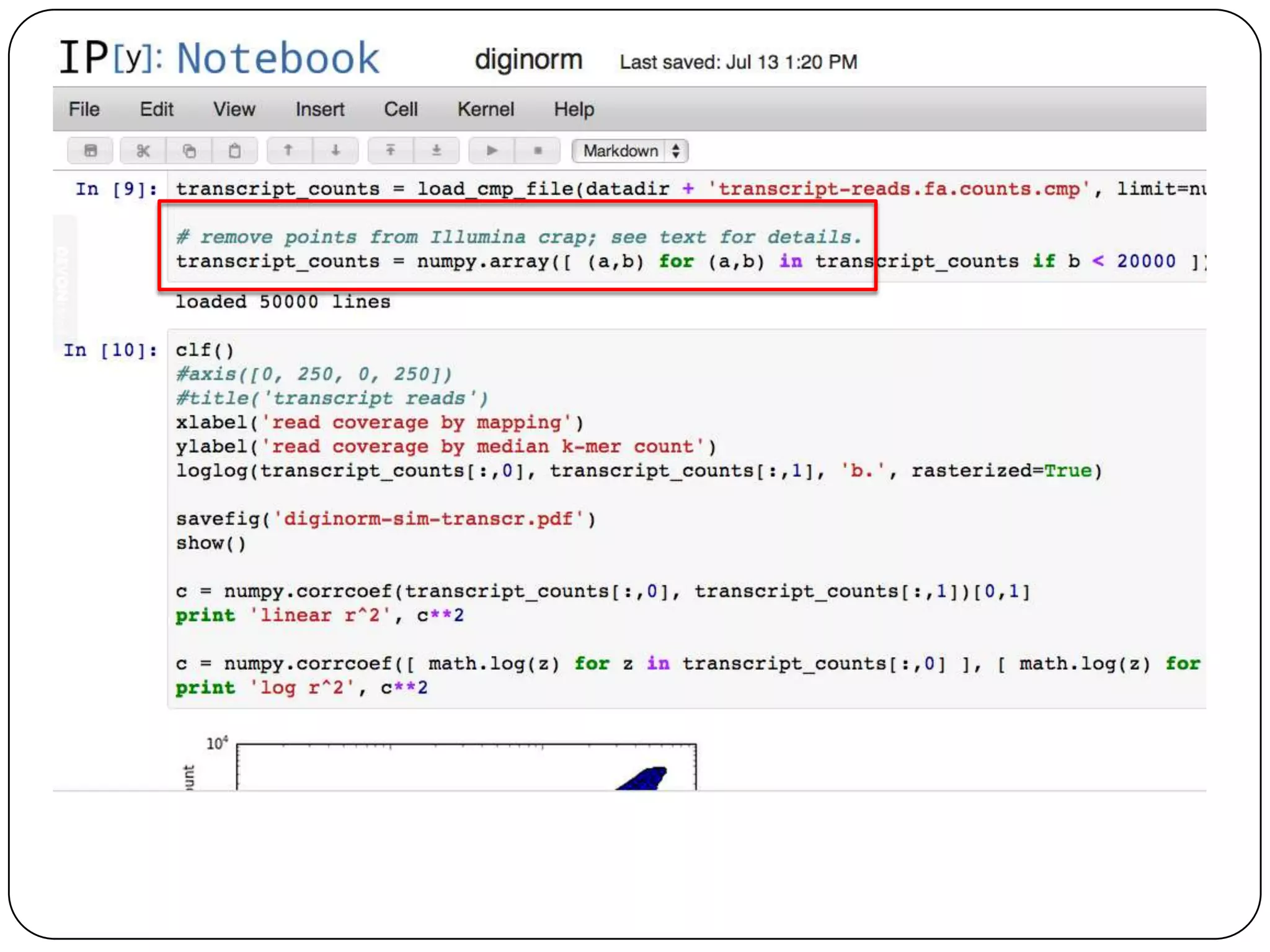
This document summarizes work on digital normalization, a technique for reducing sequencing data size prior to assembly. Digital normalization works by discarding reads whose k-mer counts are below a cutoff, based on analysis of k-mer abundances across the dataset. It can remove over 95% of data in a single pass with fixed memory. This makes genome and metagenome assembly scalable to larger datasets using cloud computing resources. The work is done in an open science manner, with all code, data, and manuscripts openly accessible online.