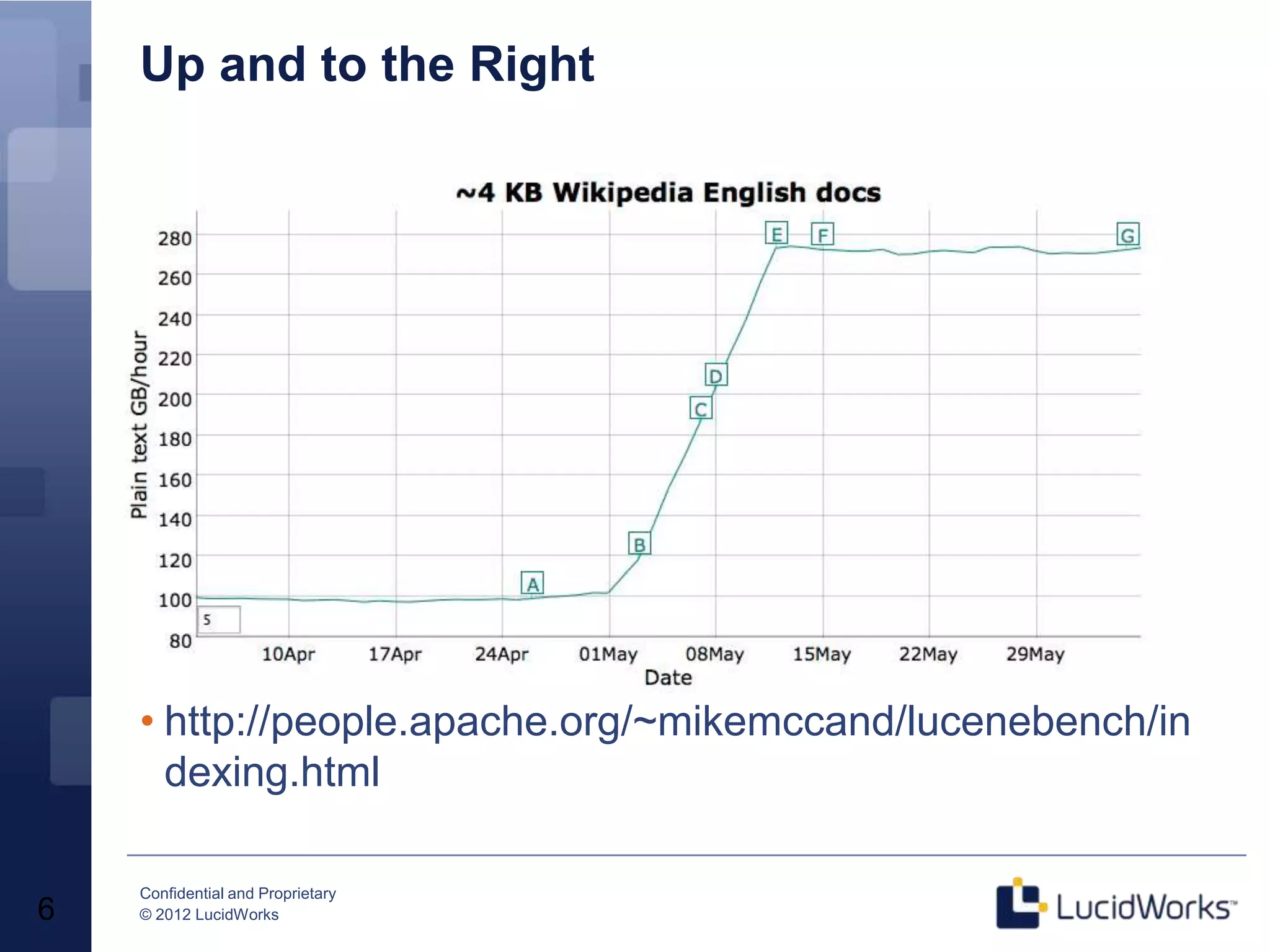
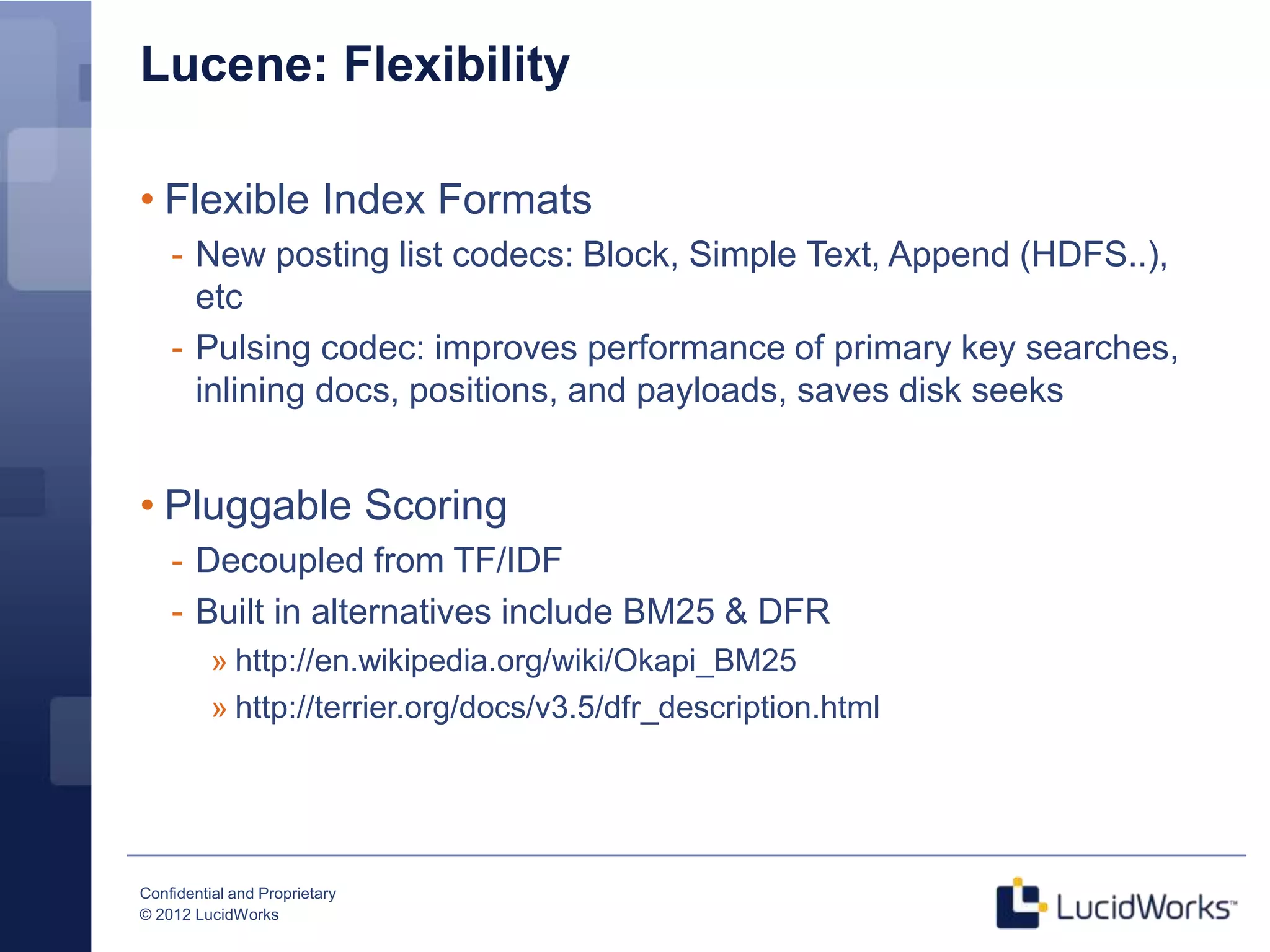
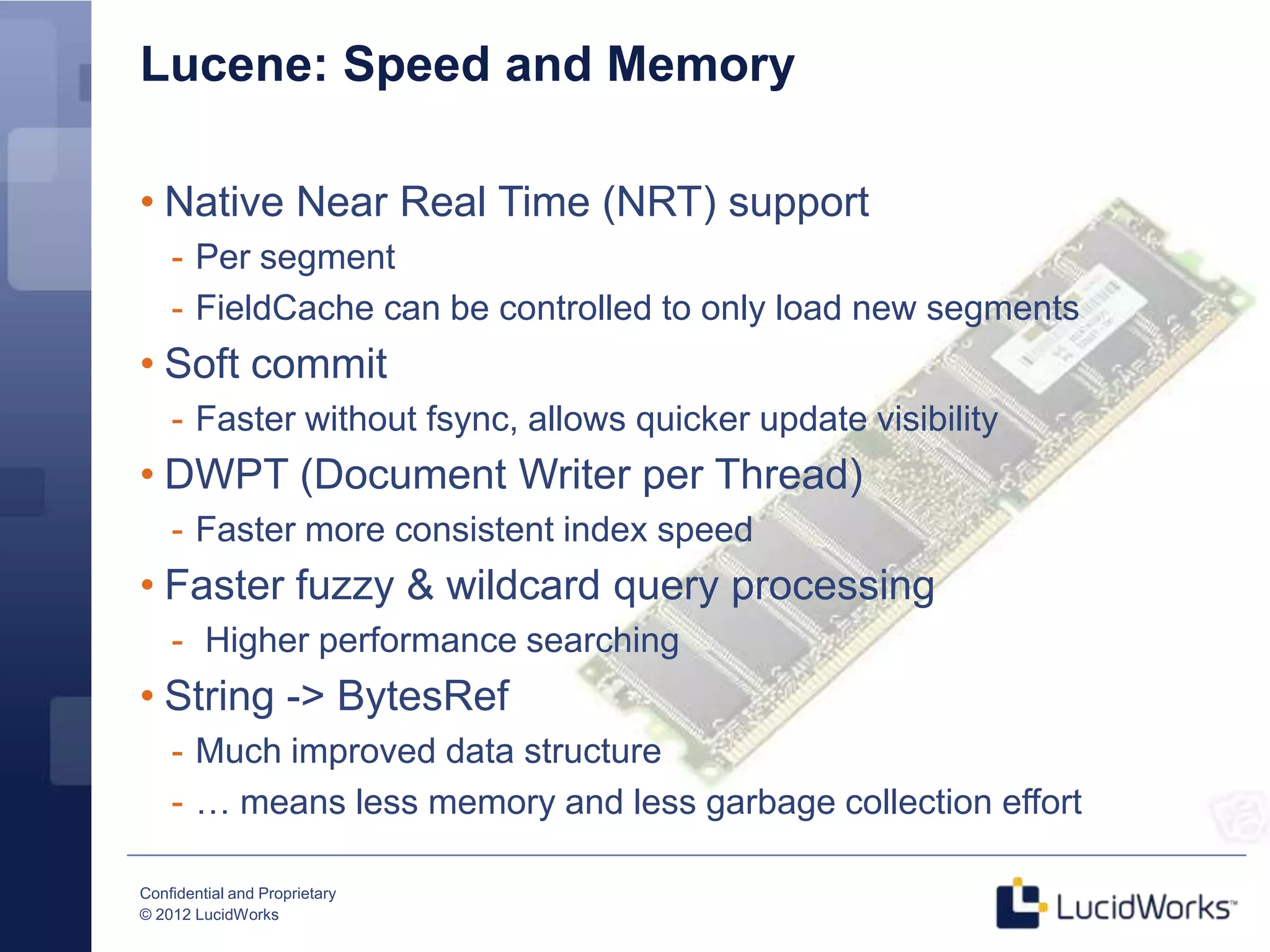
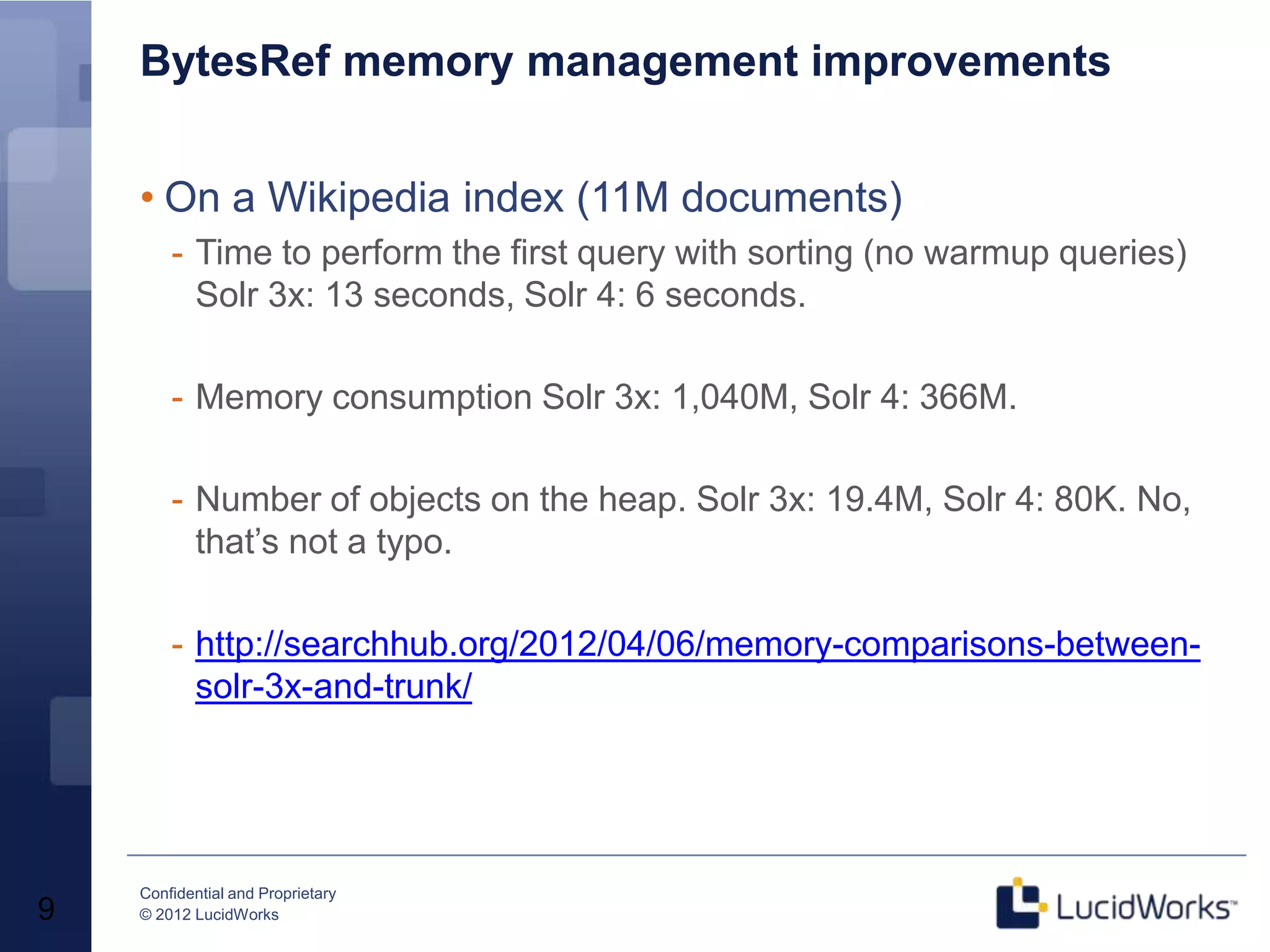
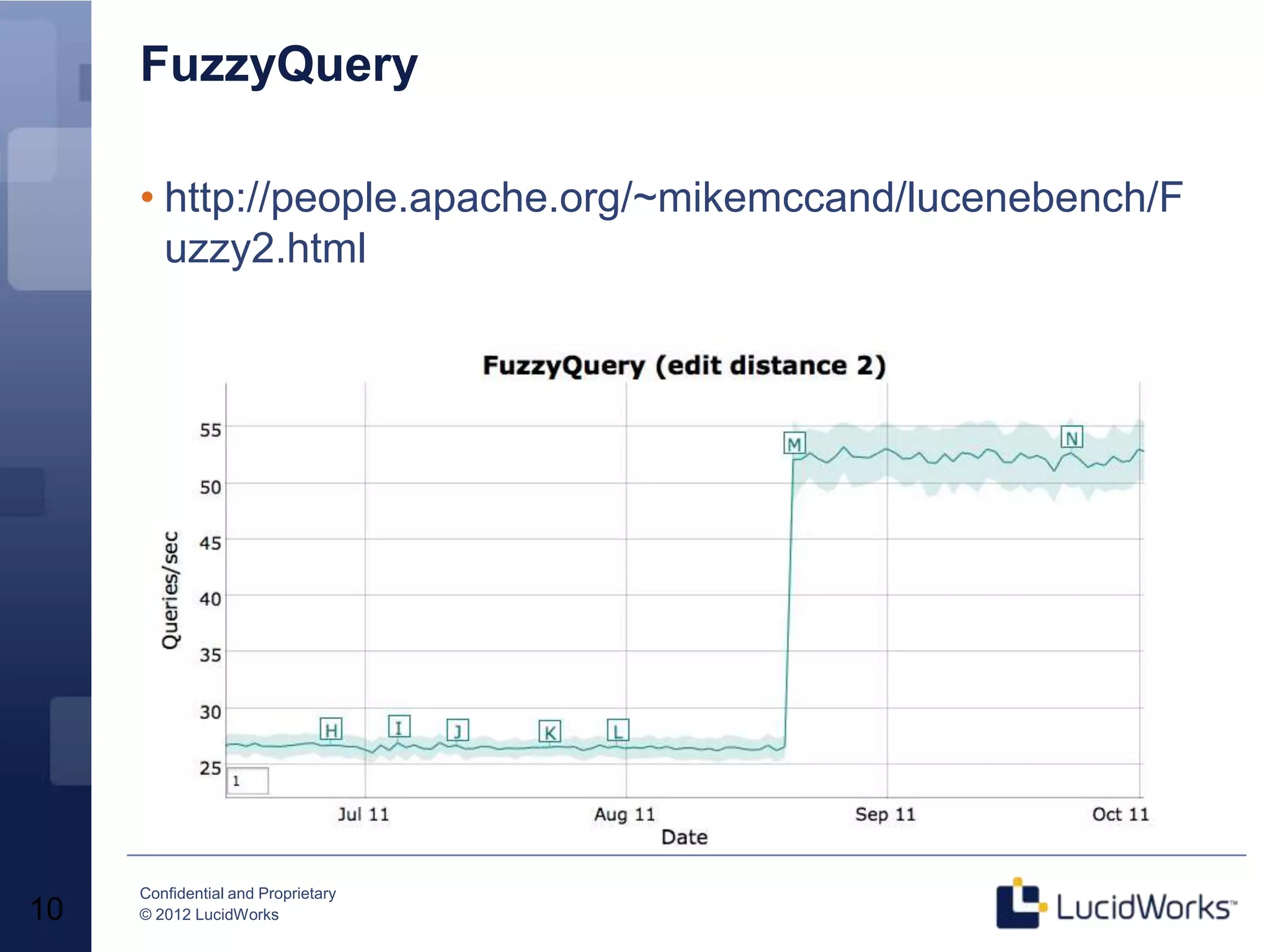
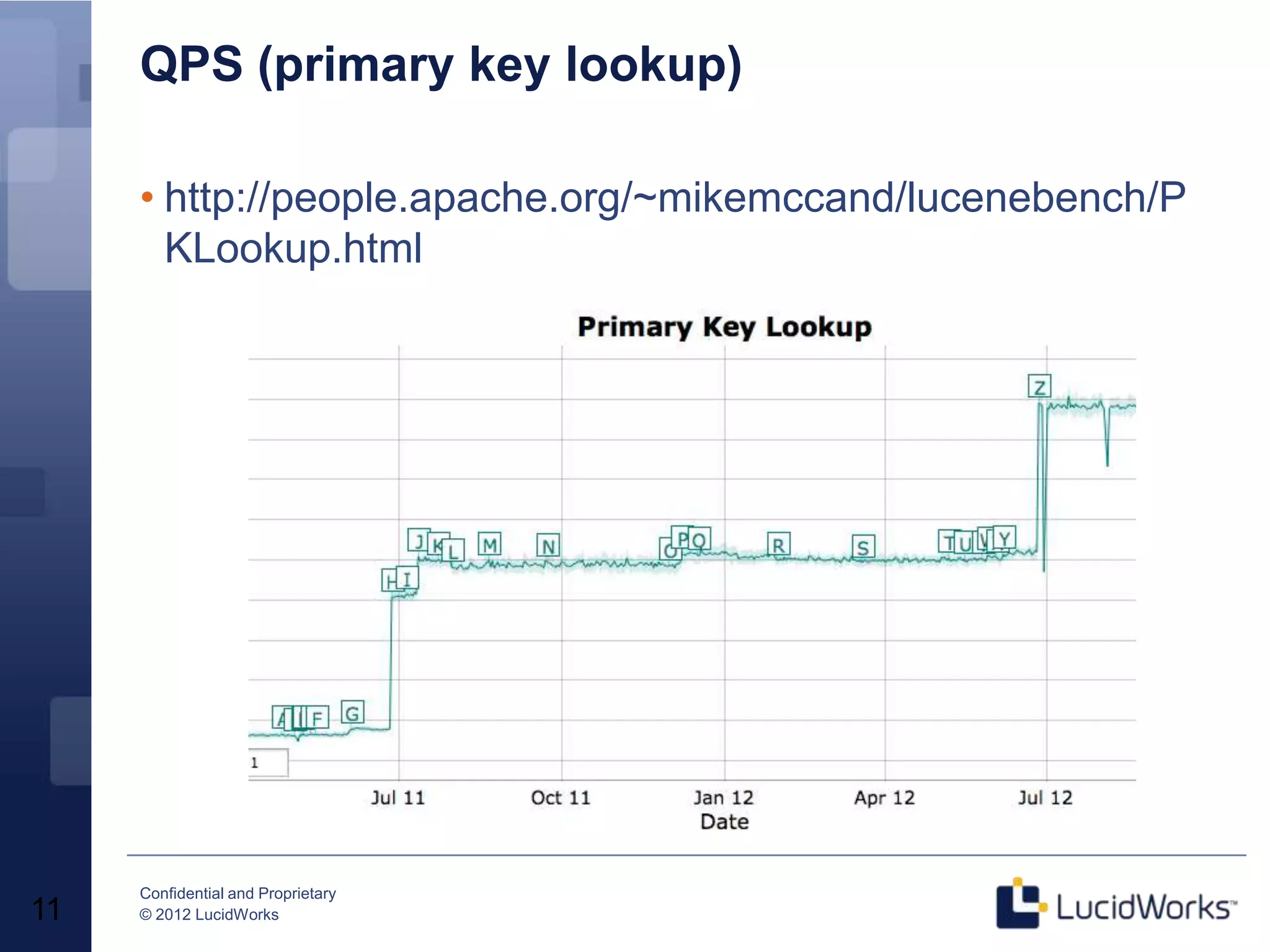
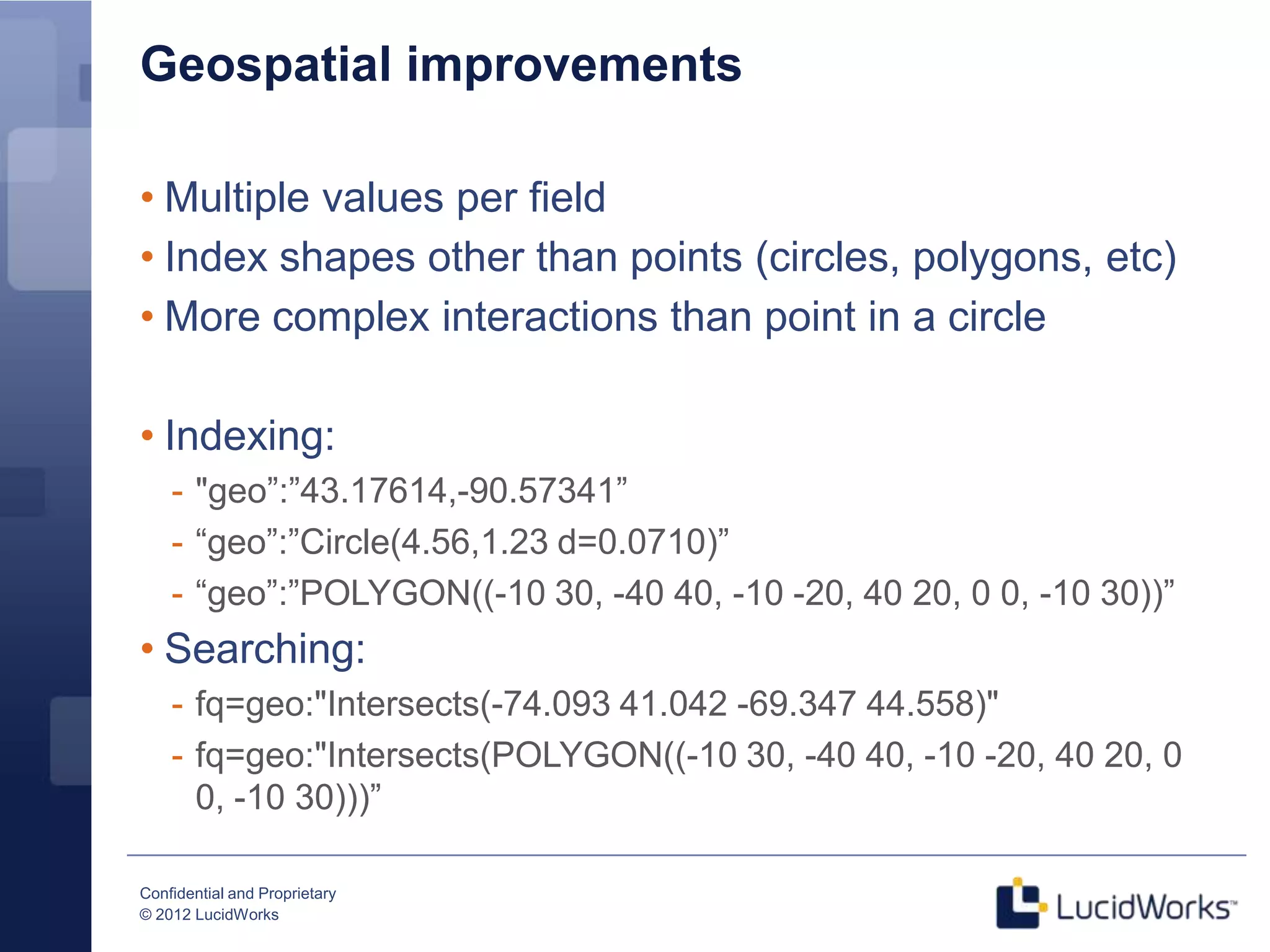
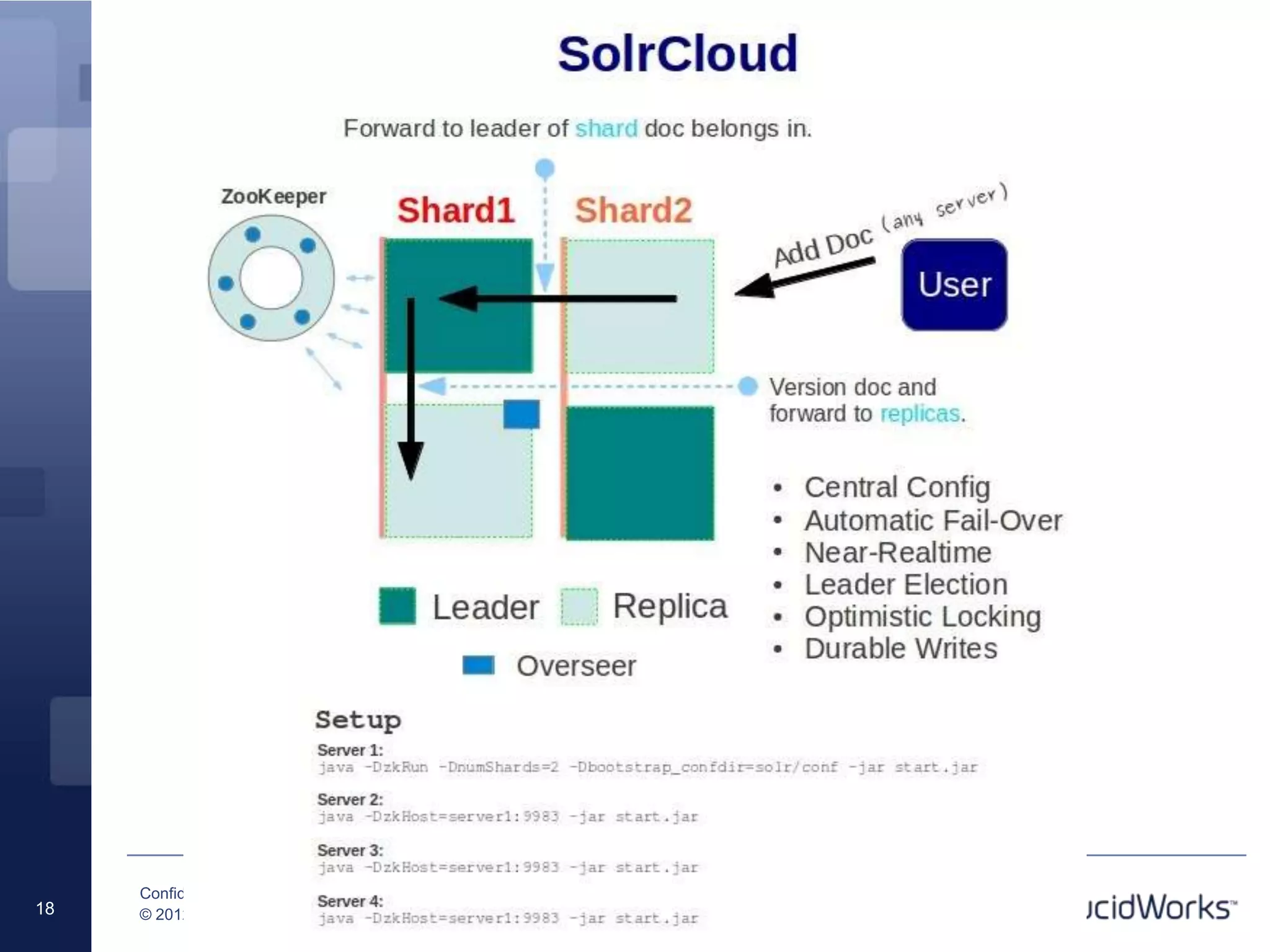
Grant Ingersoll, CTO of LucidWorks, presented on new features and capabilities in Lucene 4 and Solr 4. Key highlights include major performance improvements in Lucene through optimizations like DocValues and native Near Real Time support. Solr 4 features faster indexing and querying, improved geospatial support, and enhancements to SolrCloud including transaction logging for reliability. LucidWorks is continuing to advance Lucene and Solr to provide more flexible, scalable, and robust open source search capabilities.