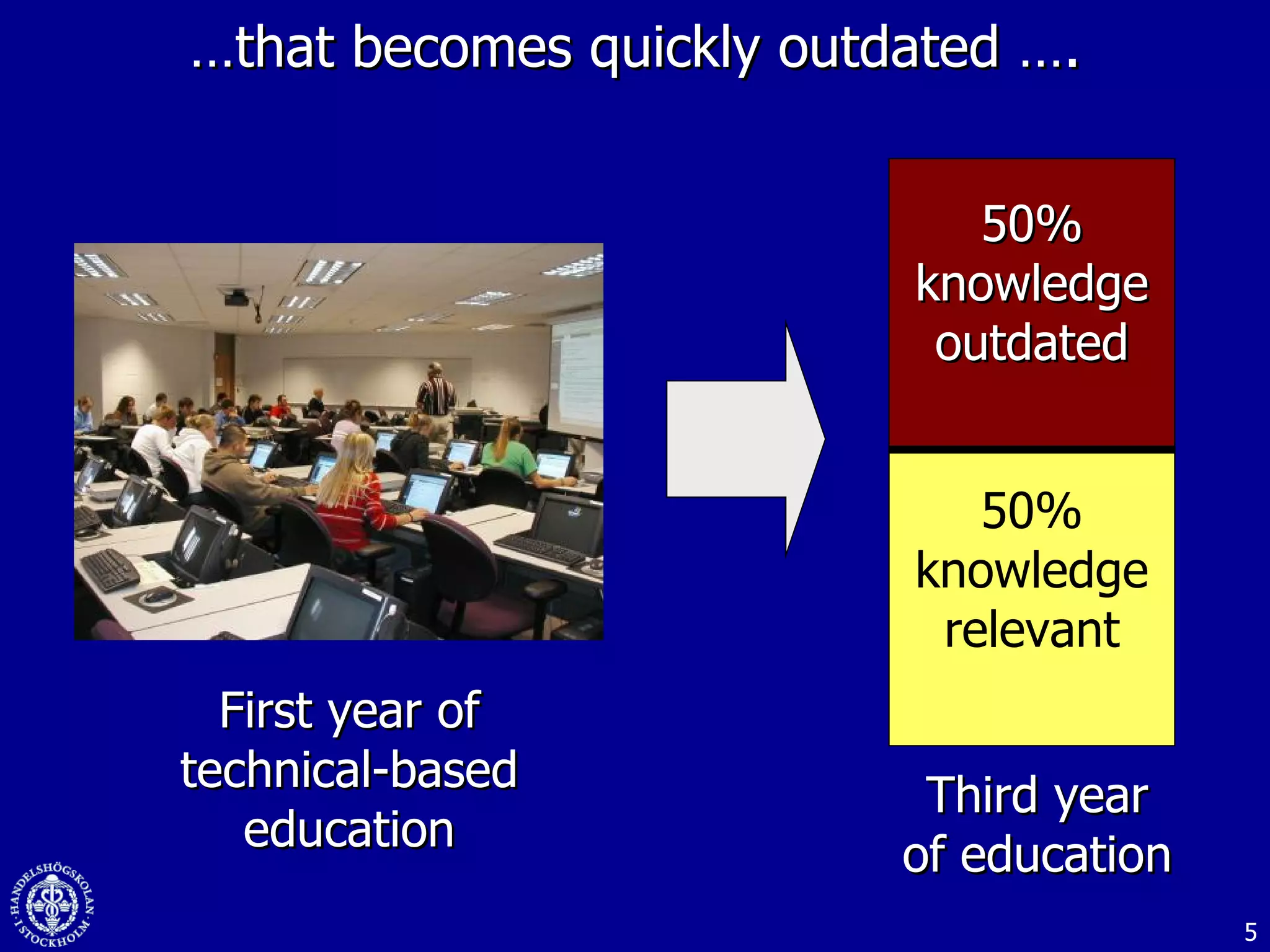
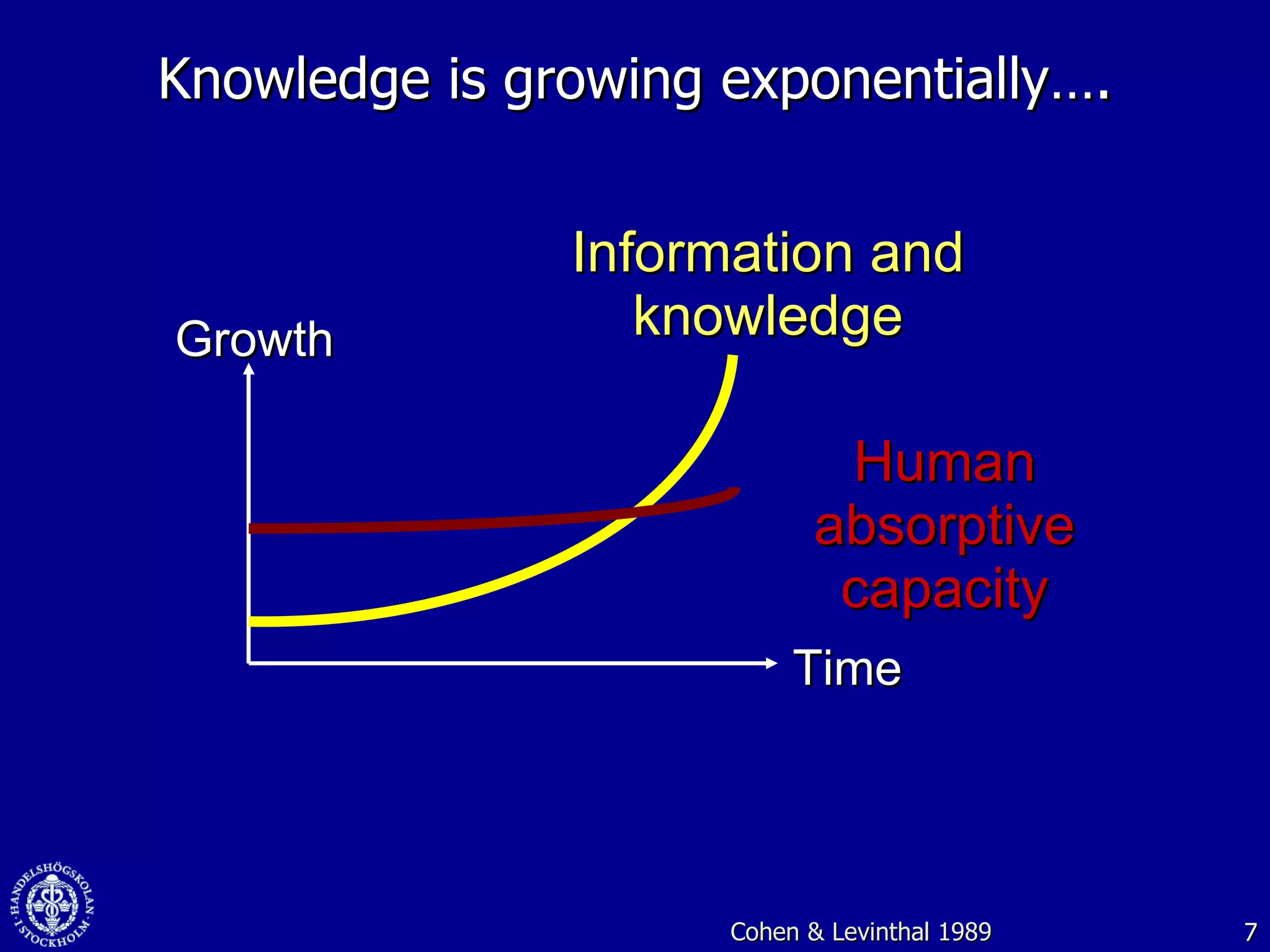
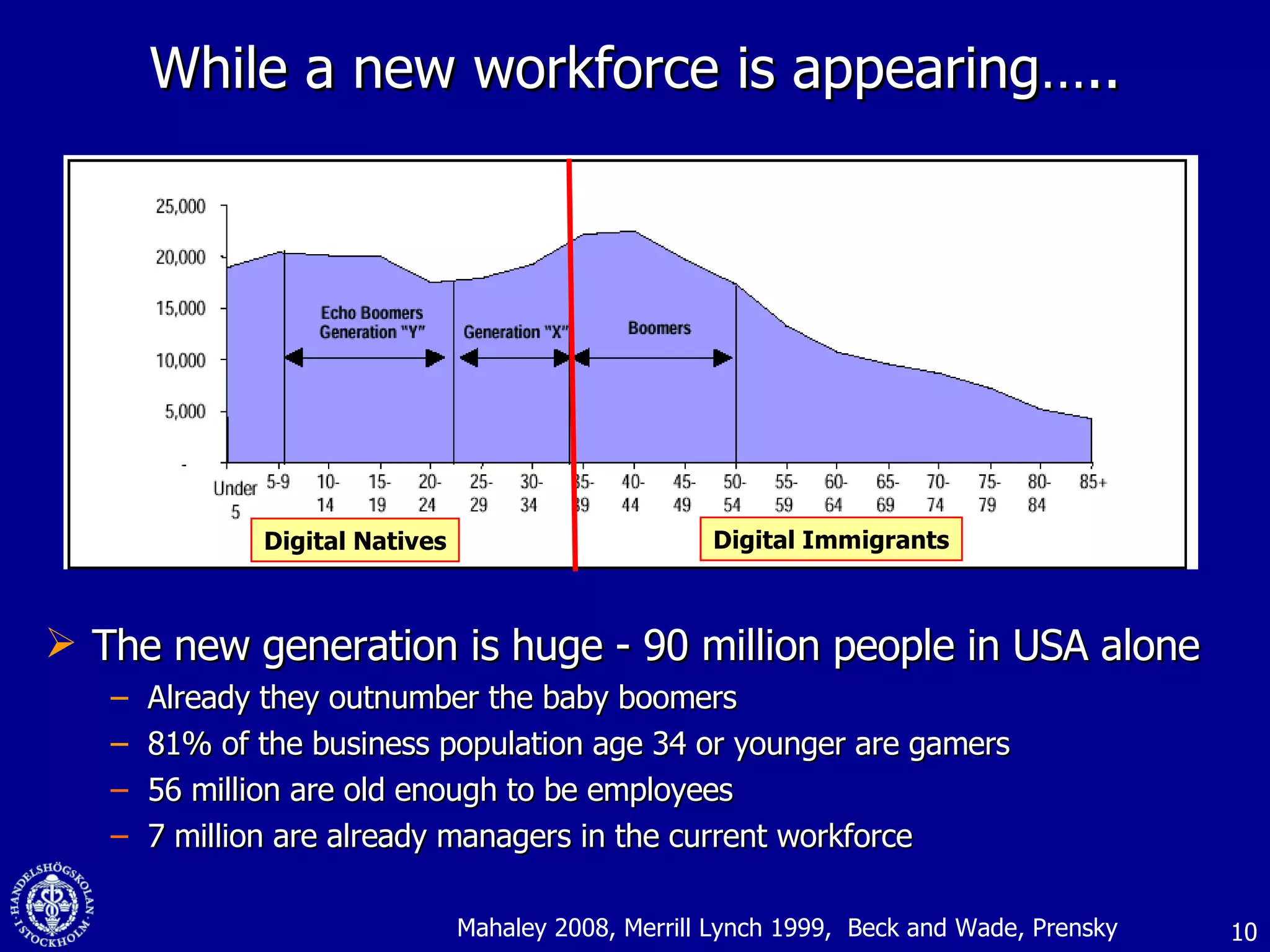
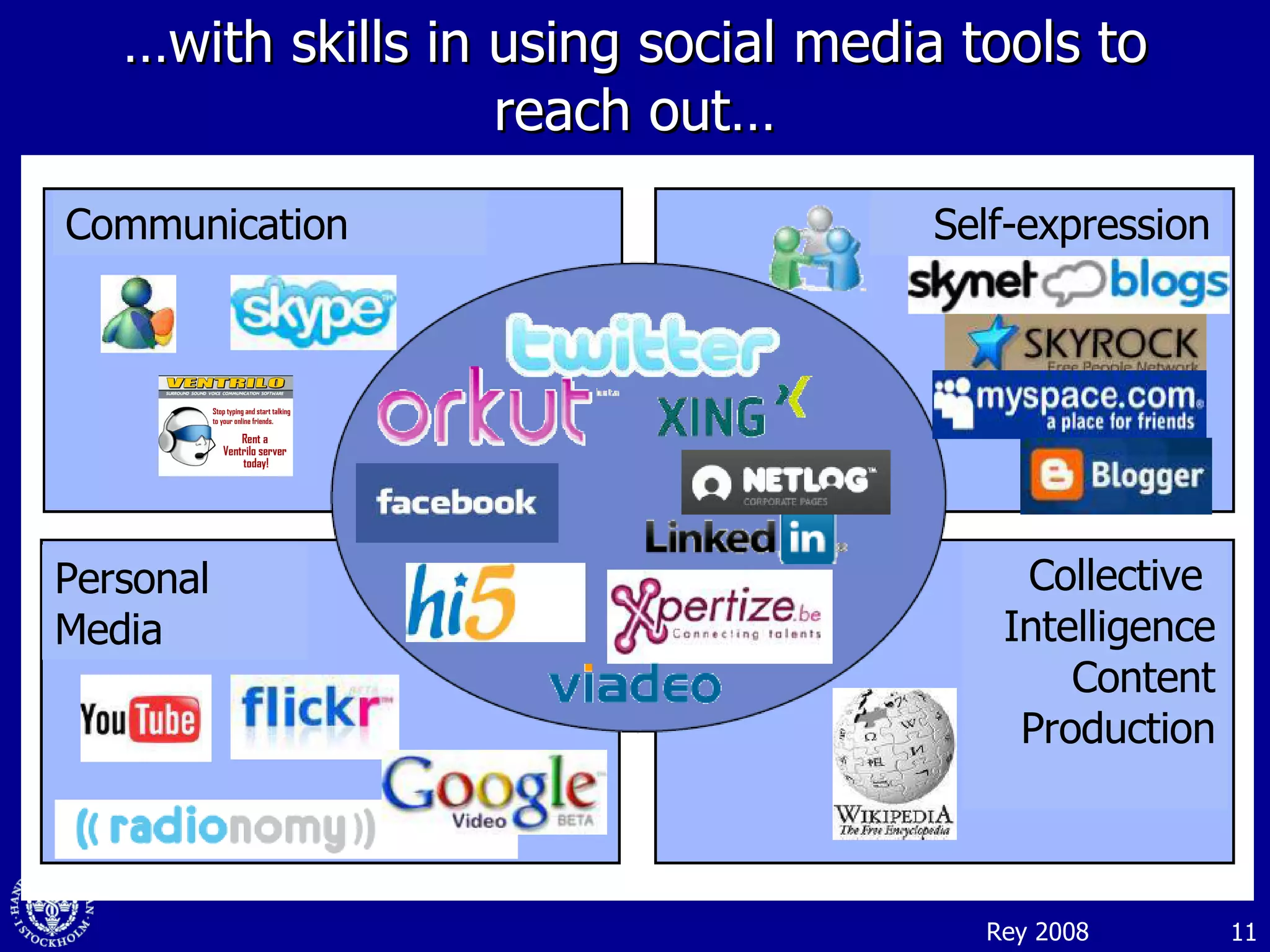
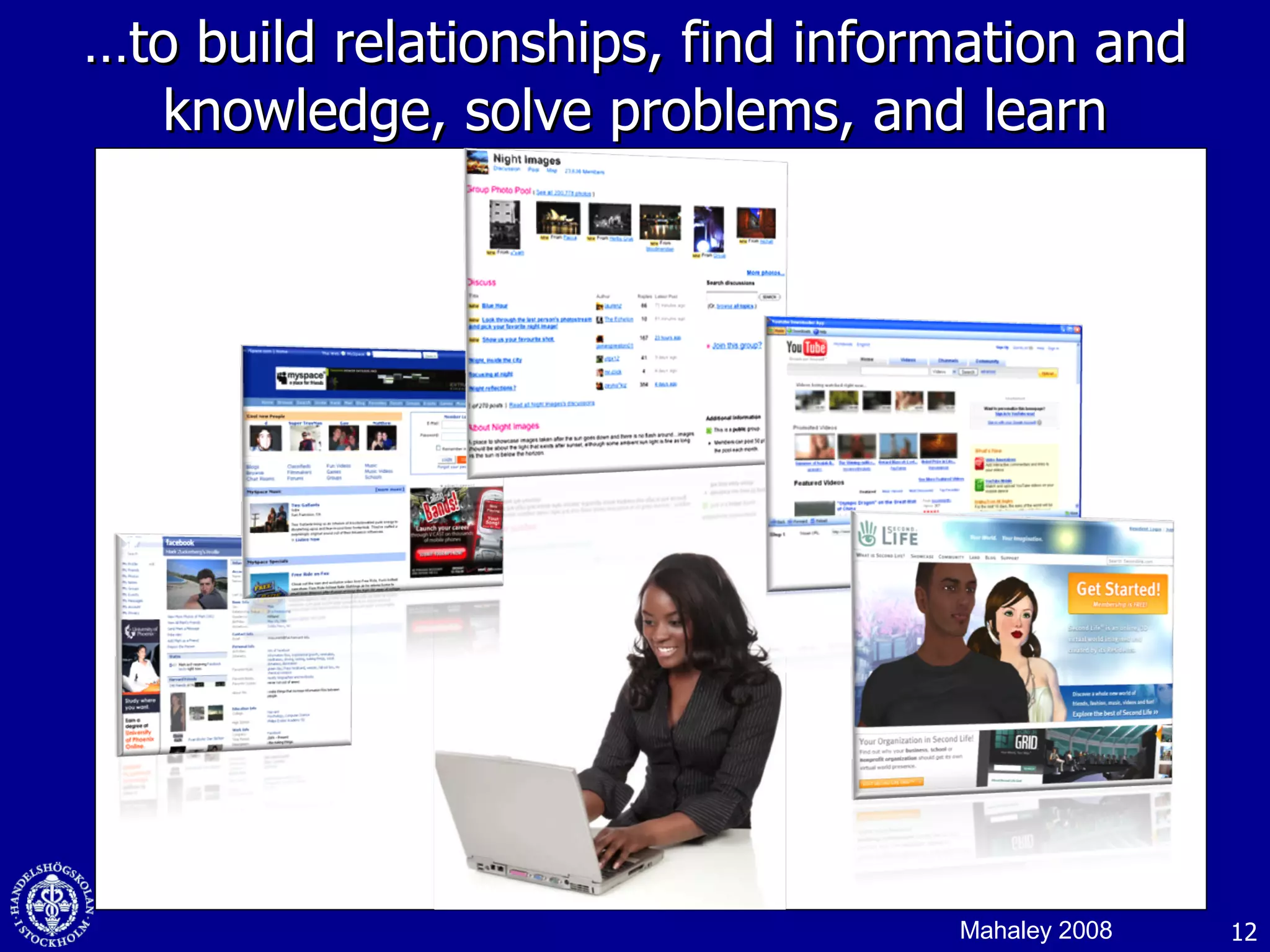
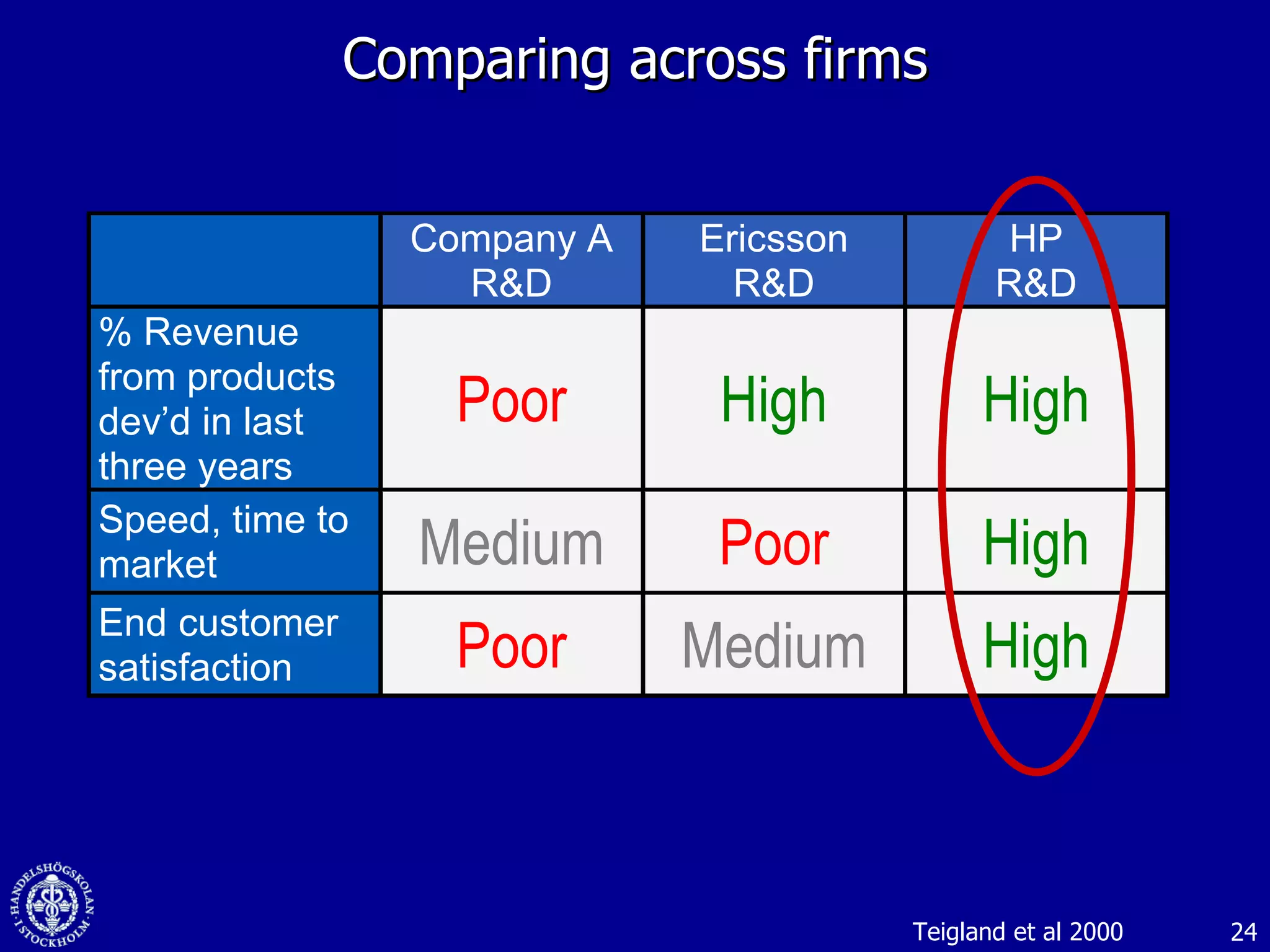
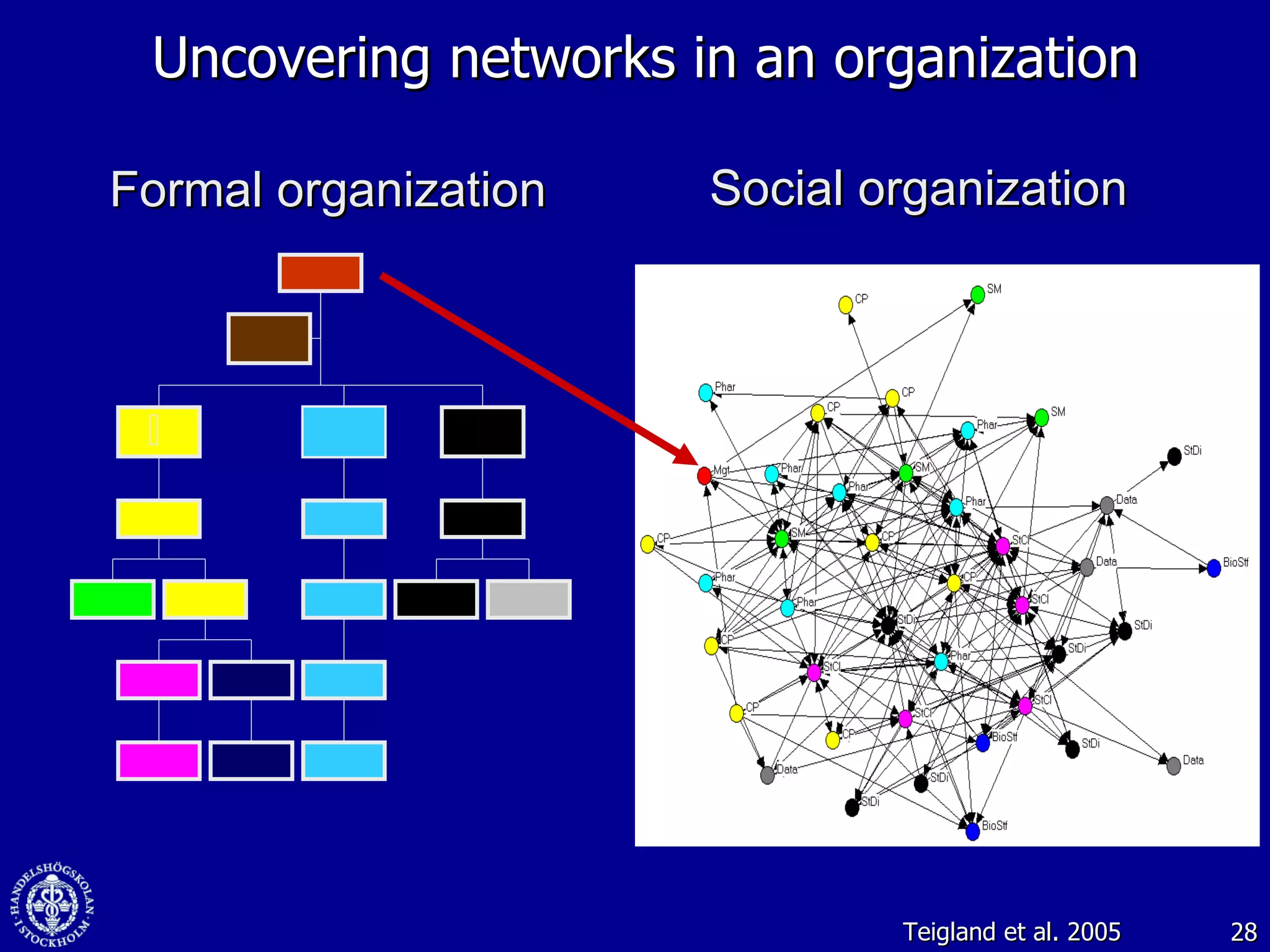
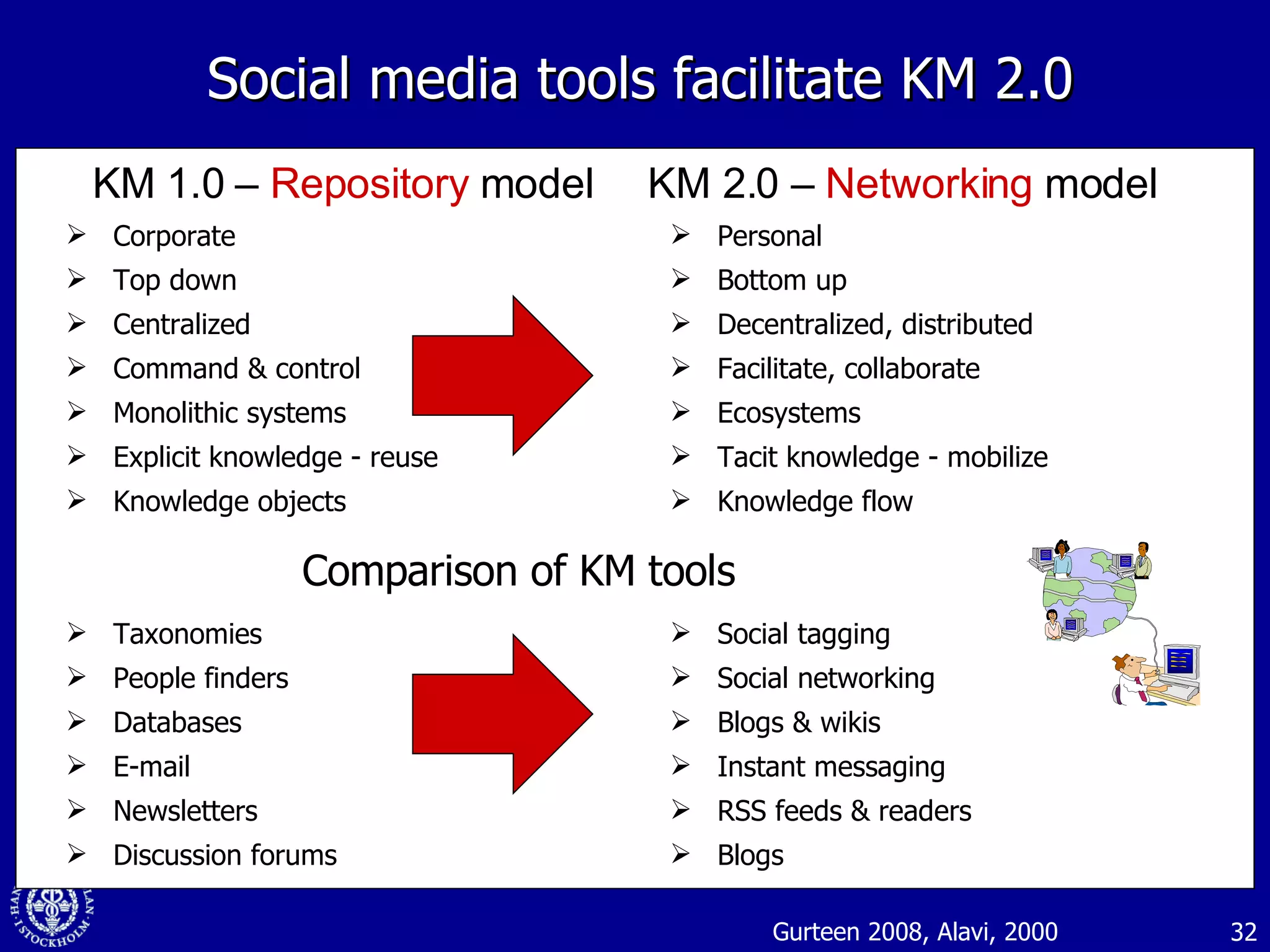
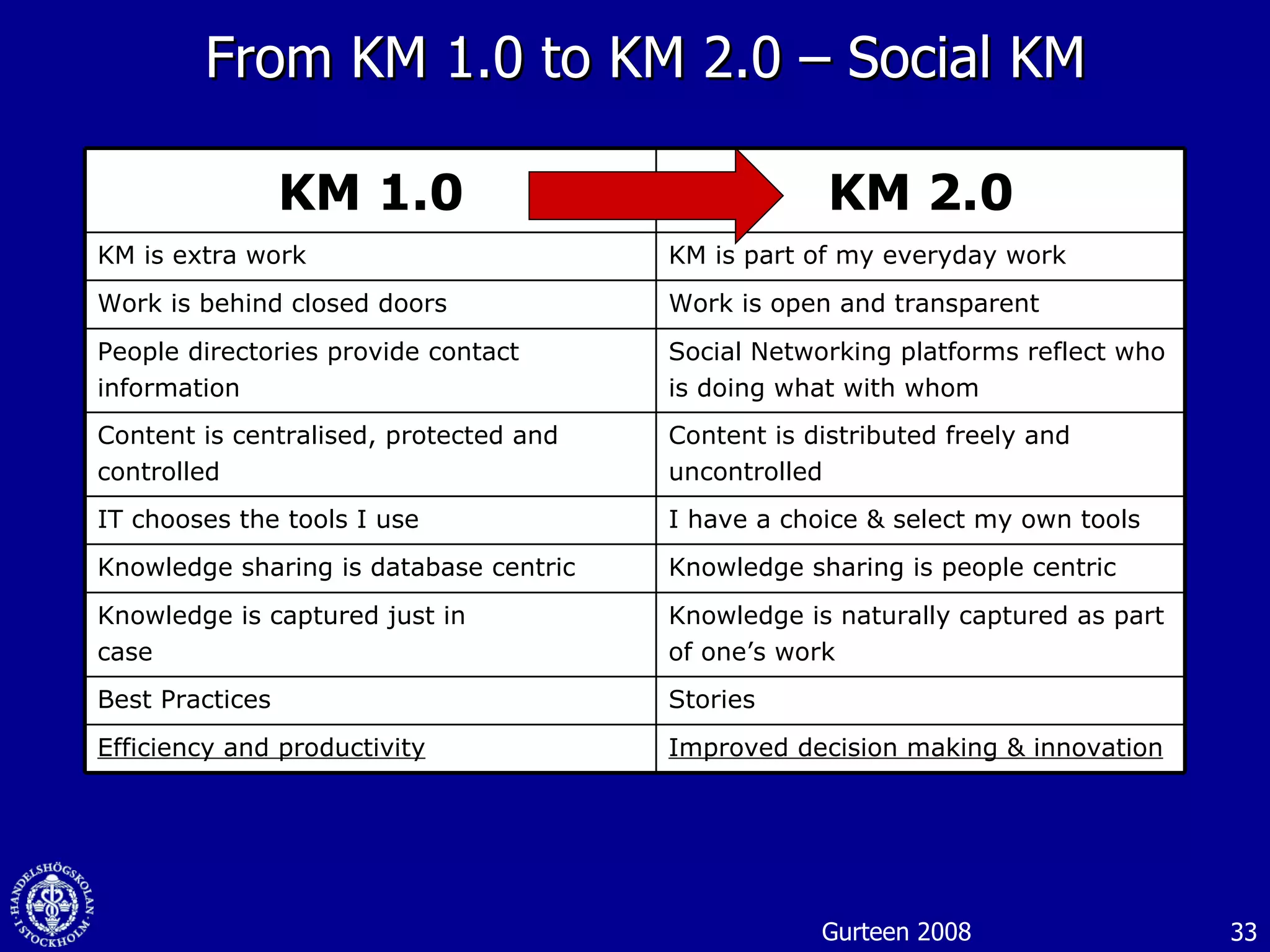
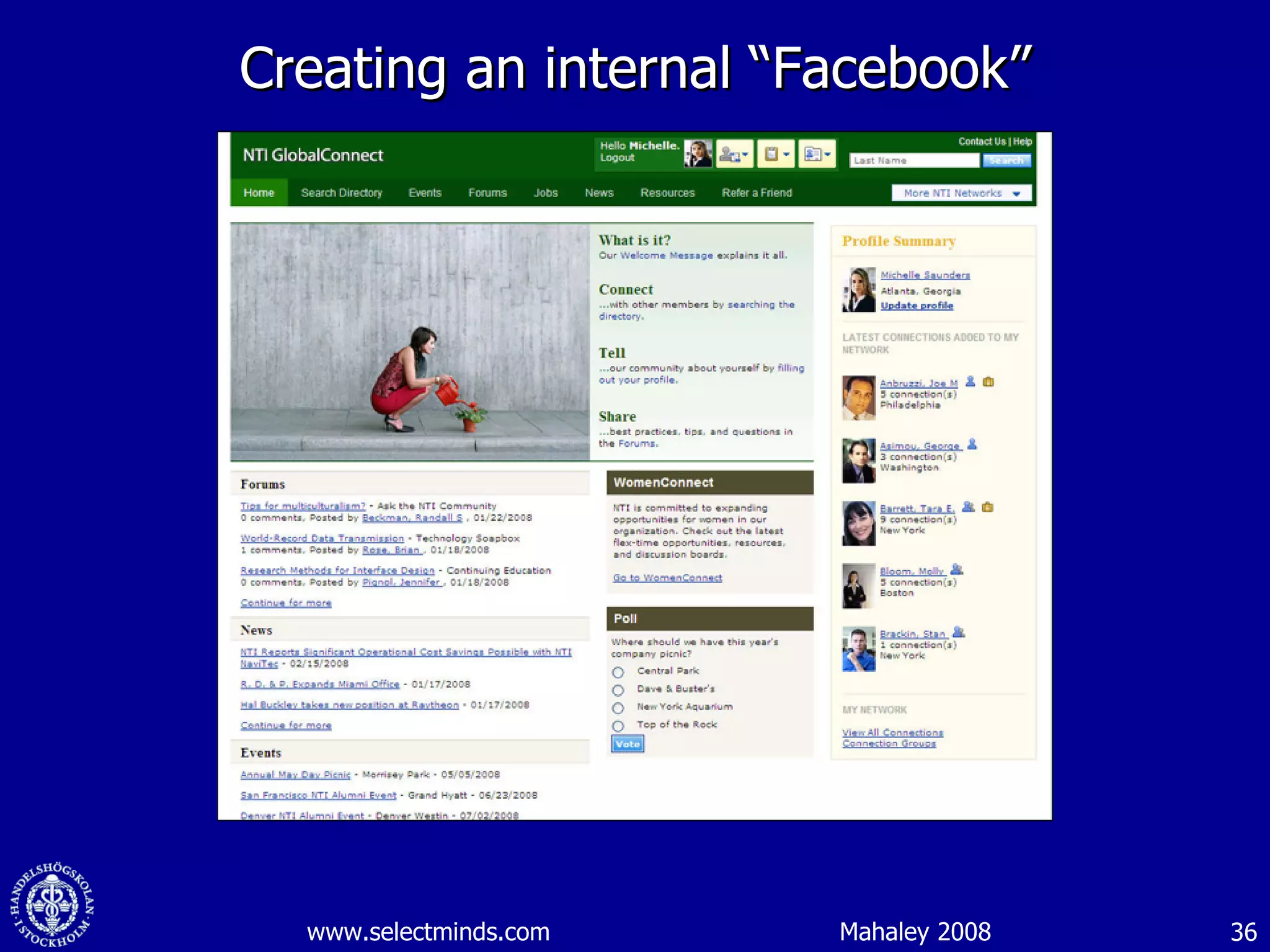
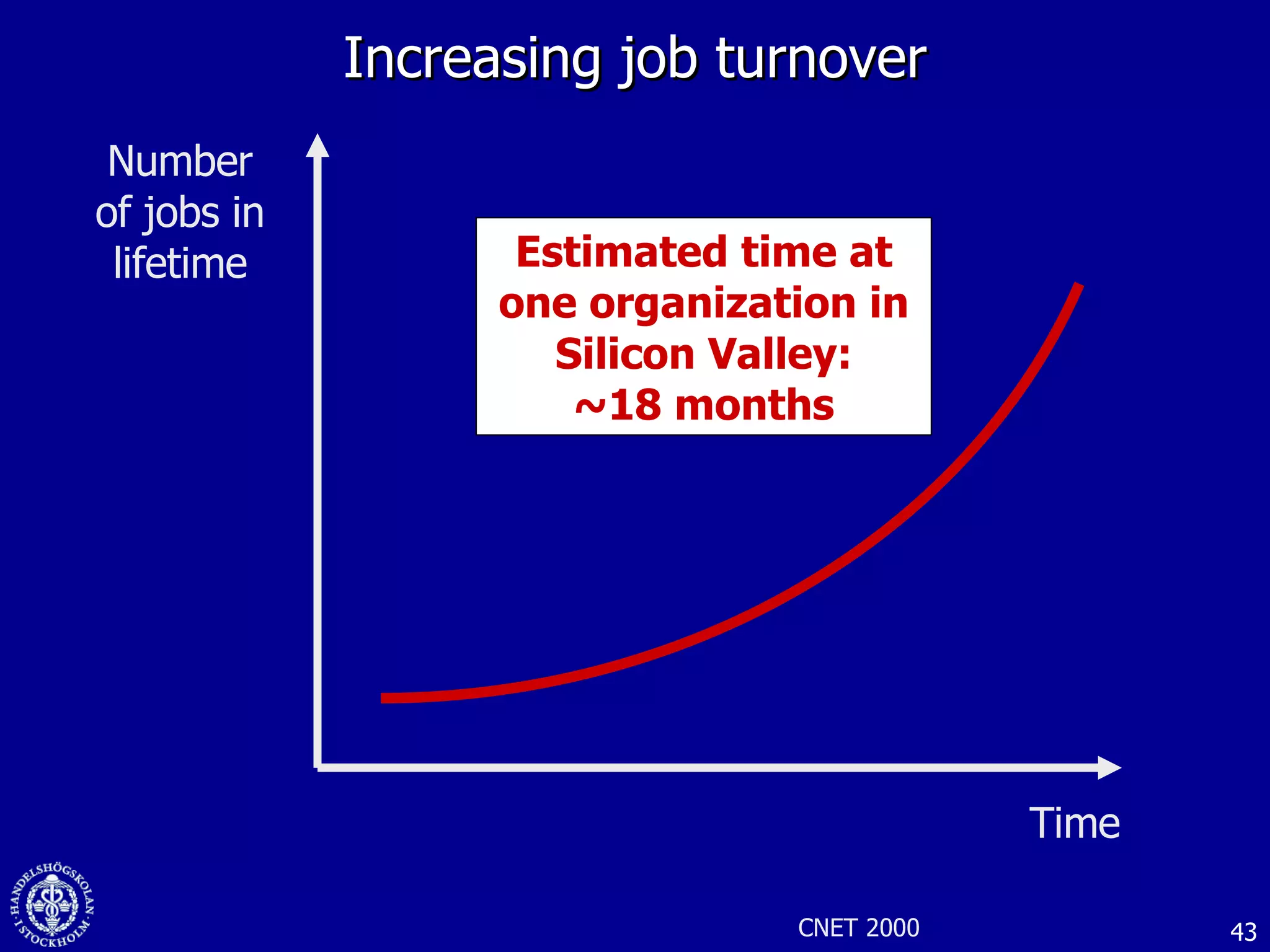
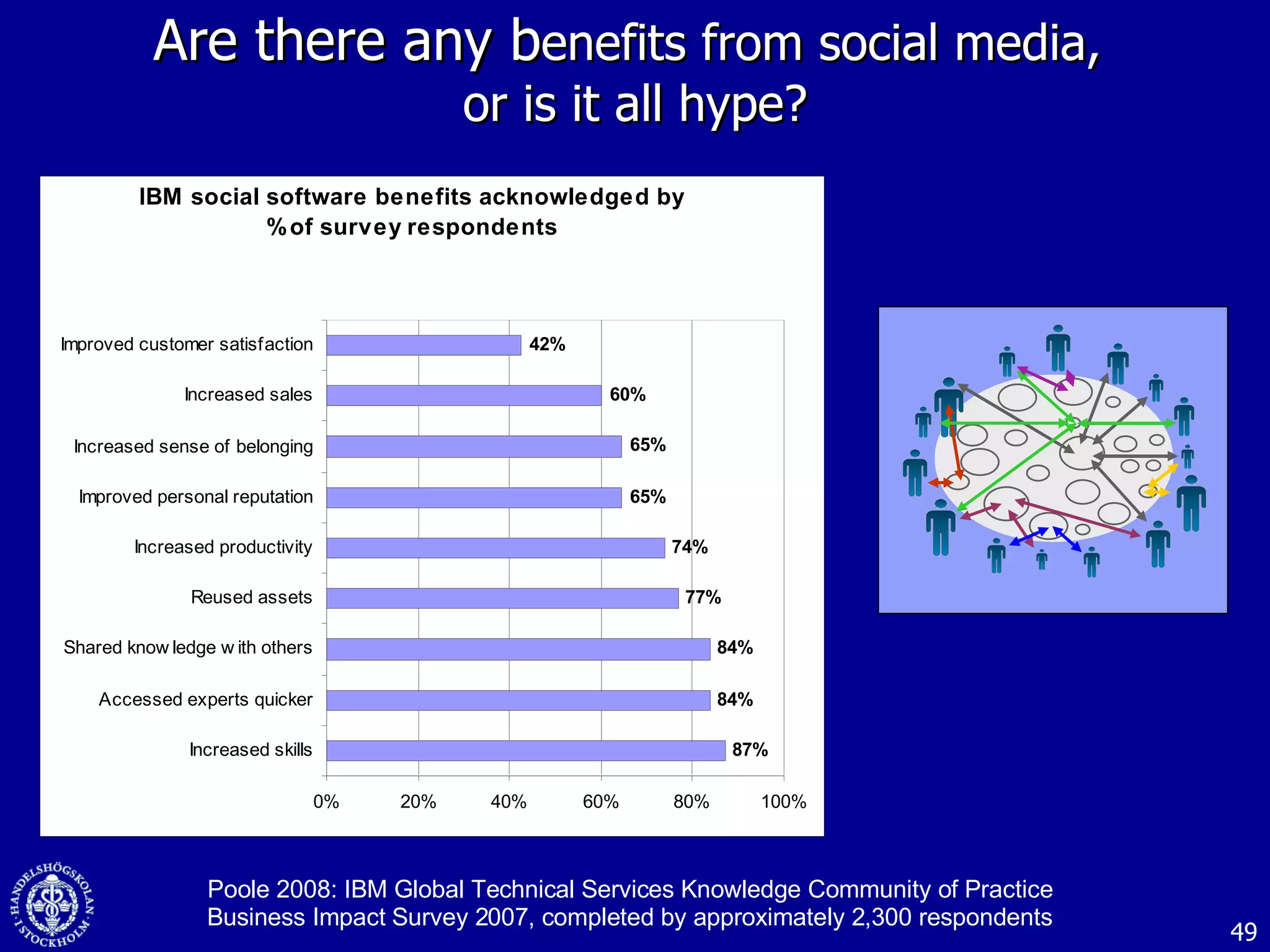
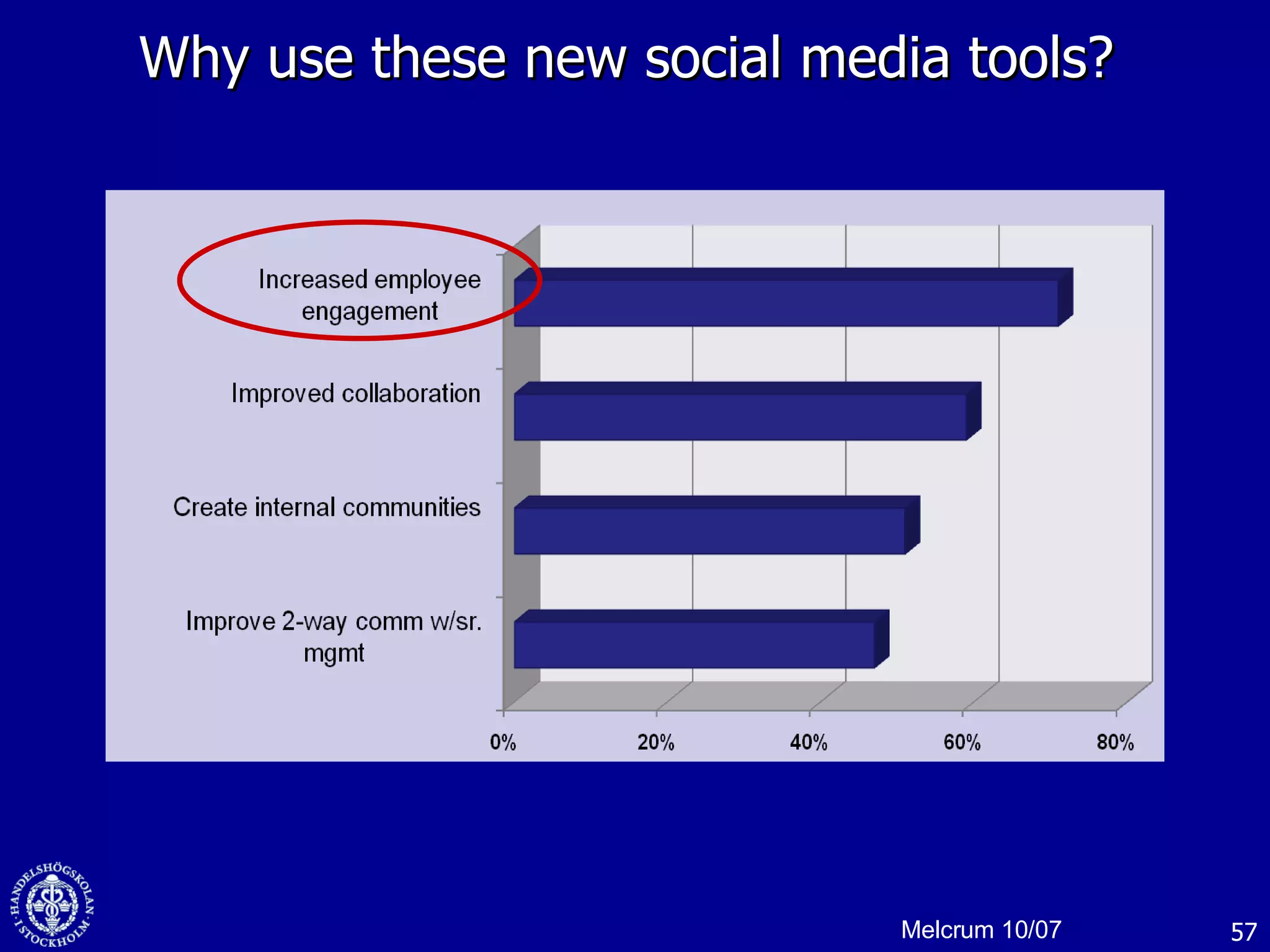
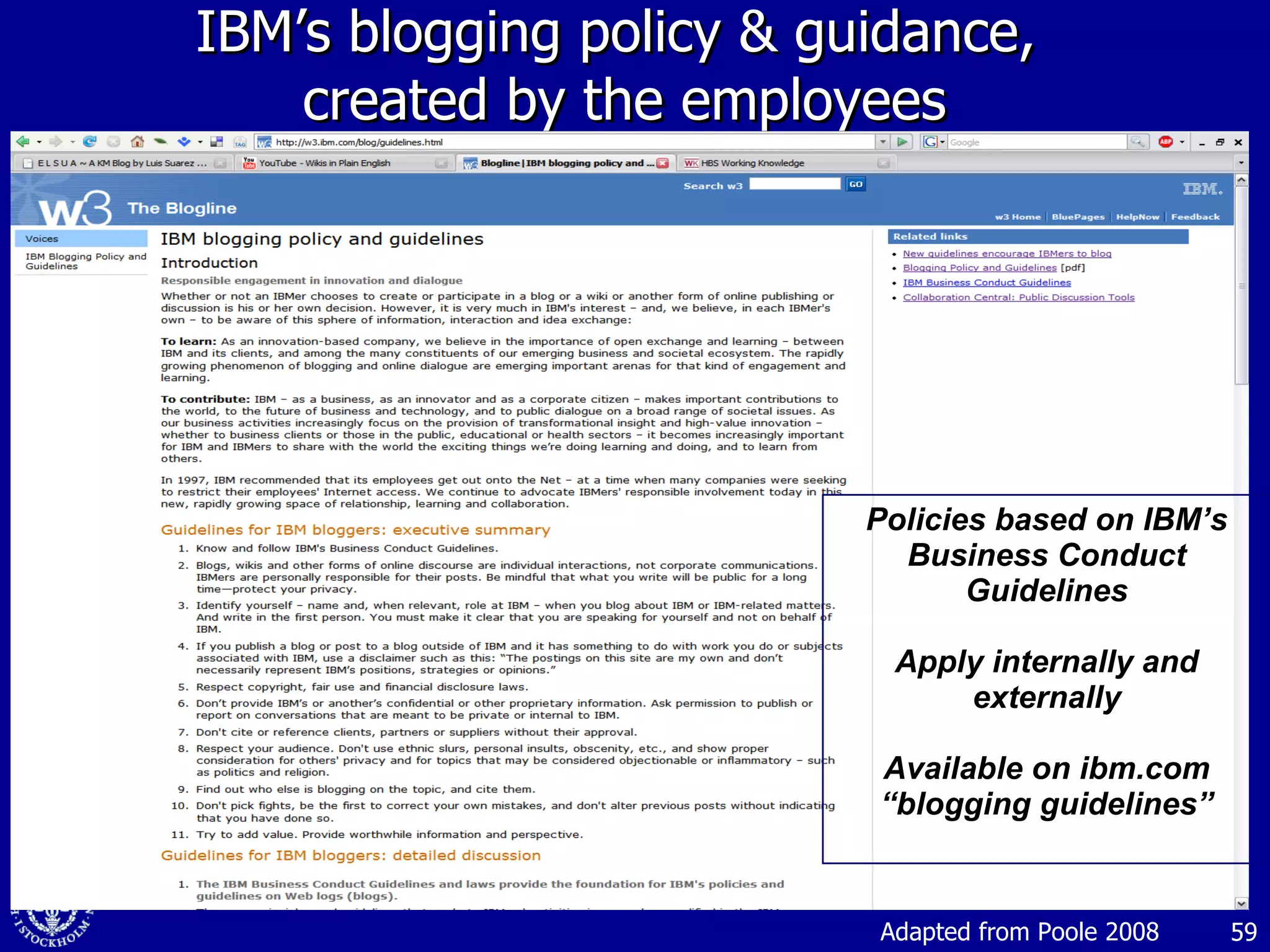
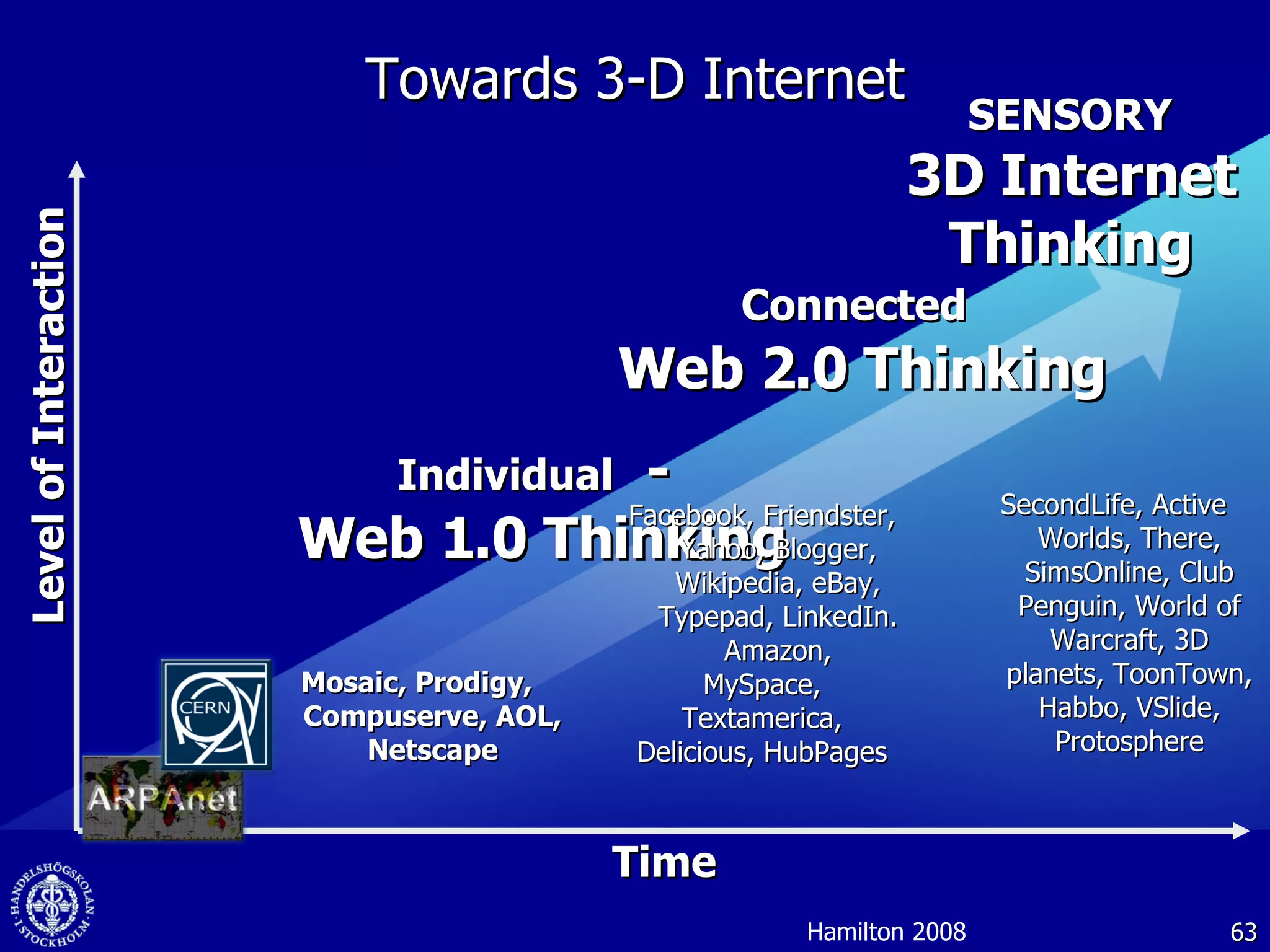
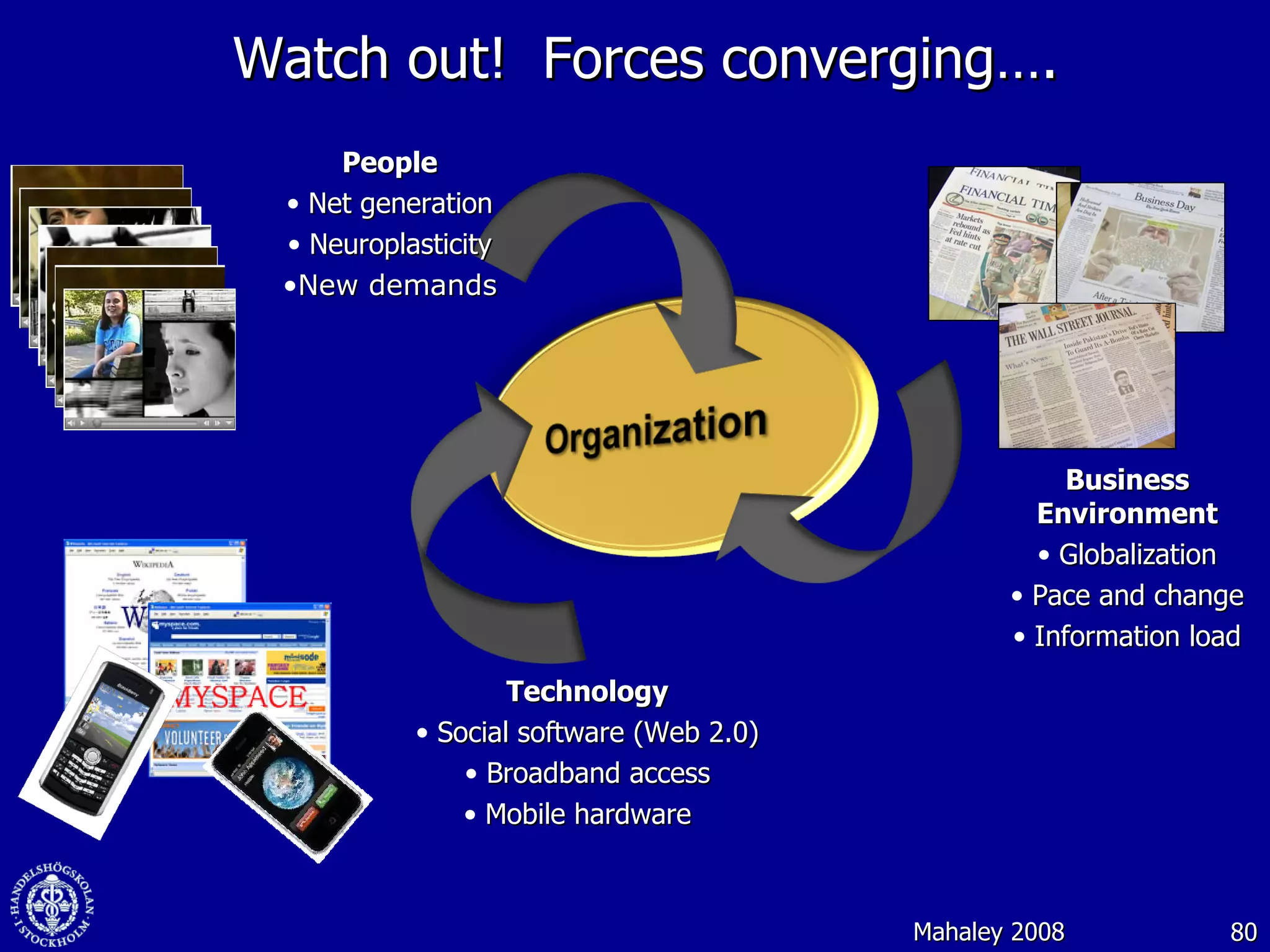
1. The document discusses social media and networks, their benefits for organizations, and challenges in leveraging them. It provides examples of how companies are using social media internally to connect employees, find expertise, and share knowledge.
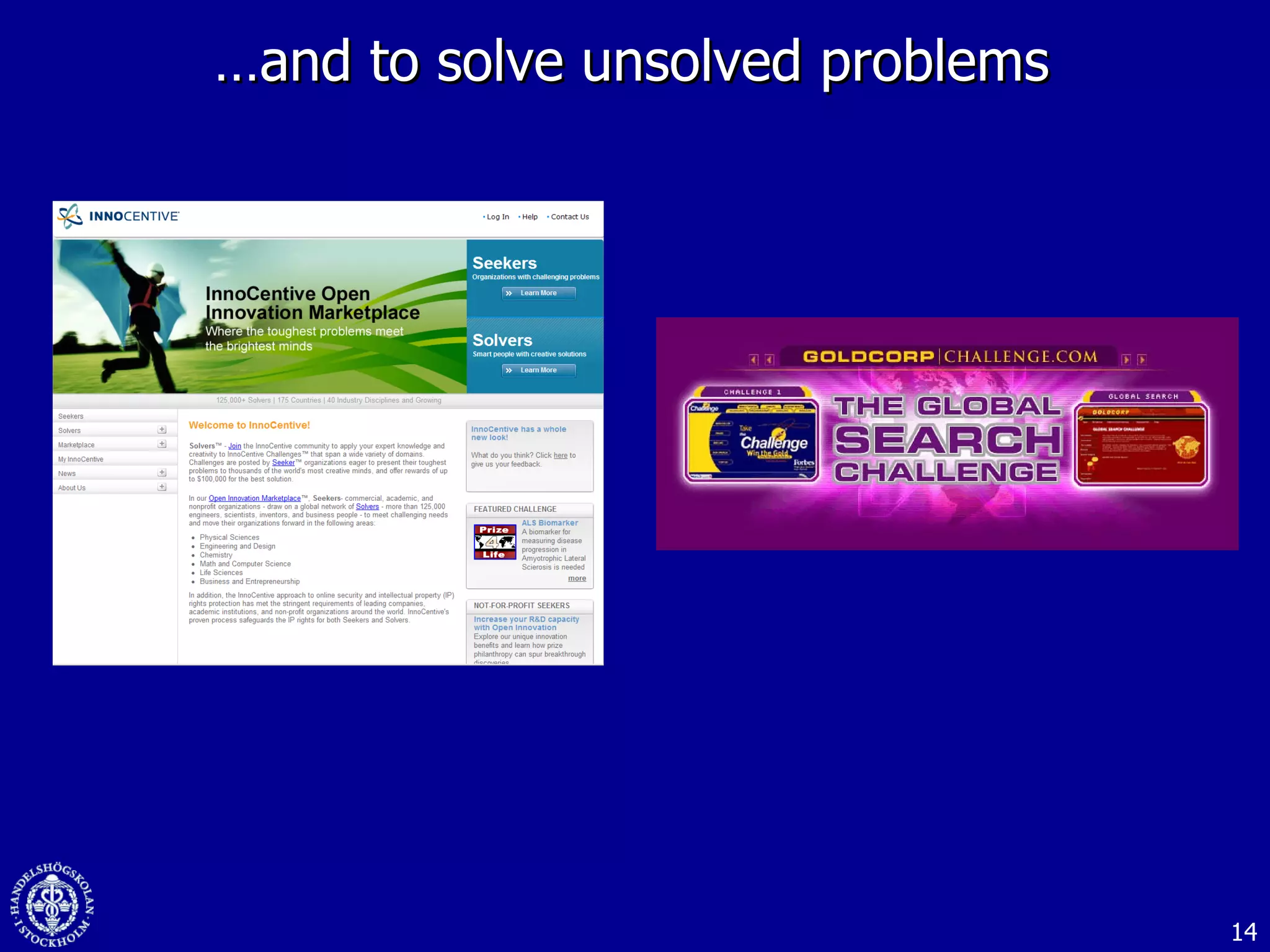
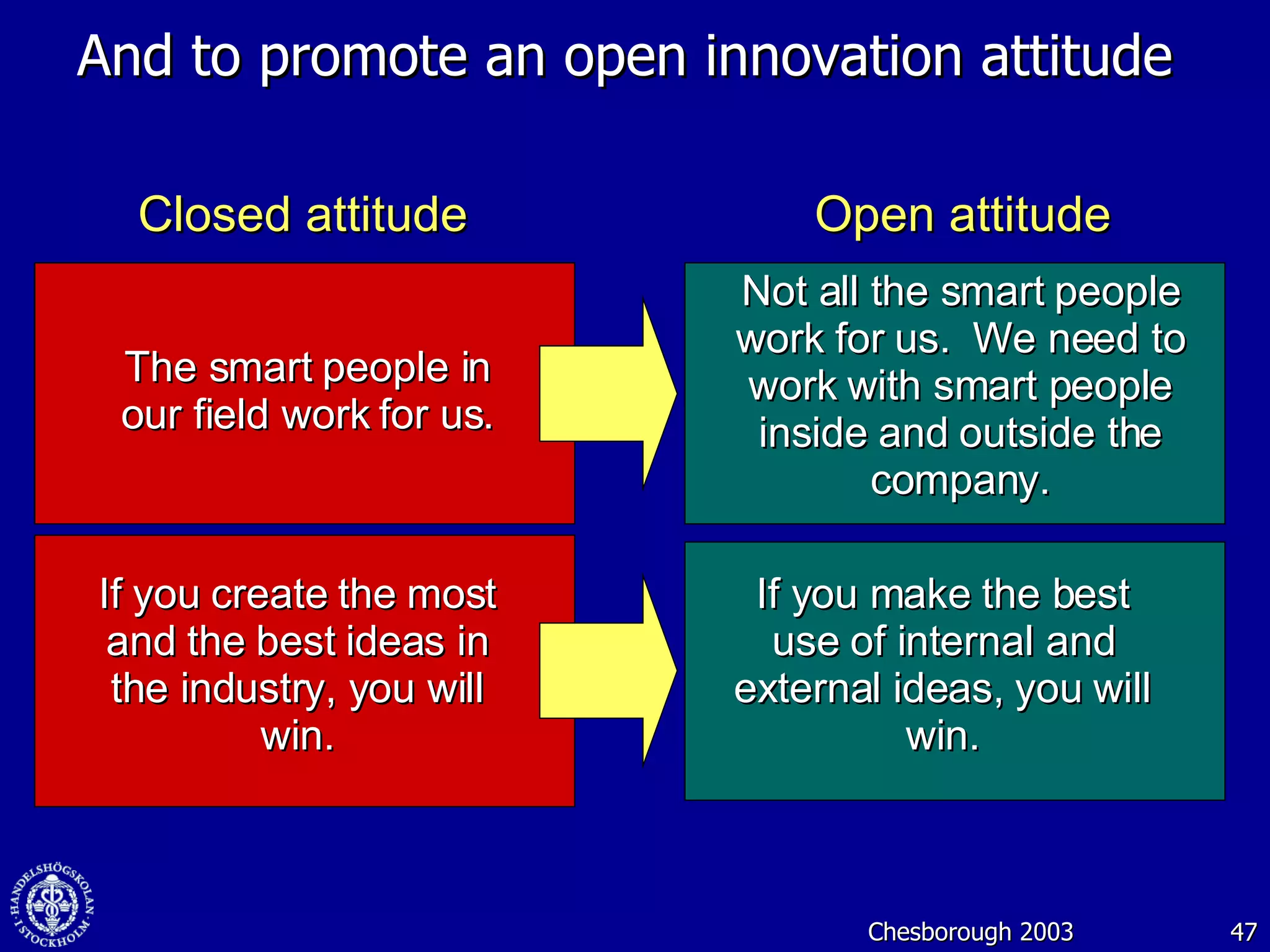
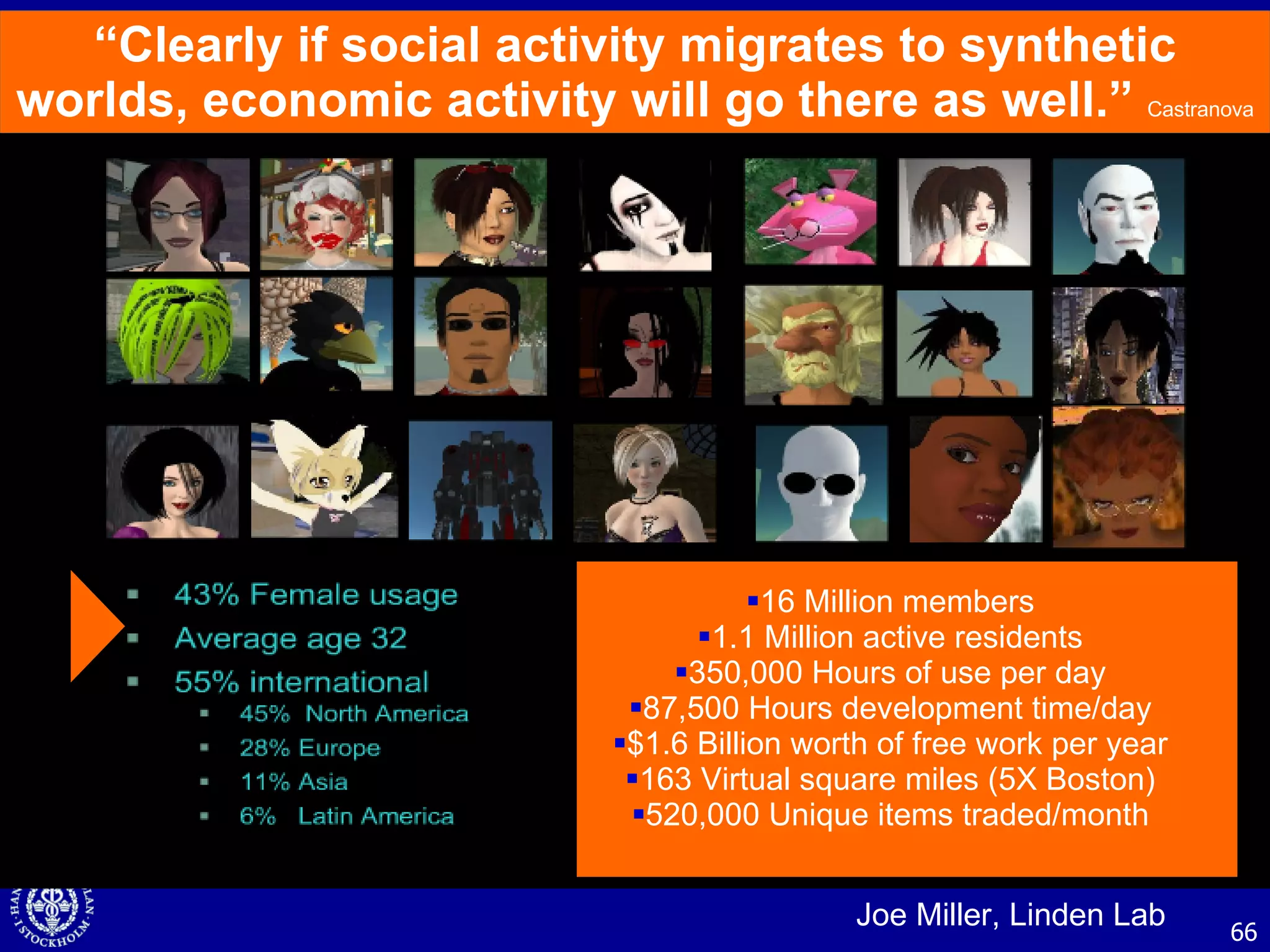
2. Companies are also using virtual worlds and social networks to improve recruiting, collaboration for remote workers, and open innovation by connecting with external partners and communities.
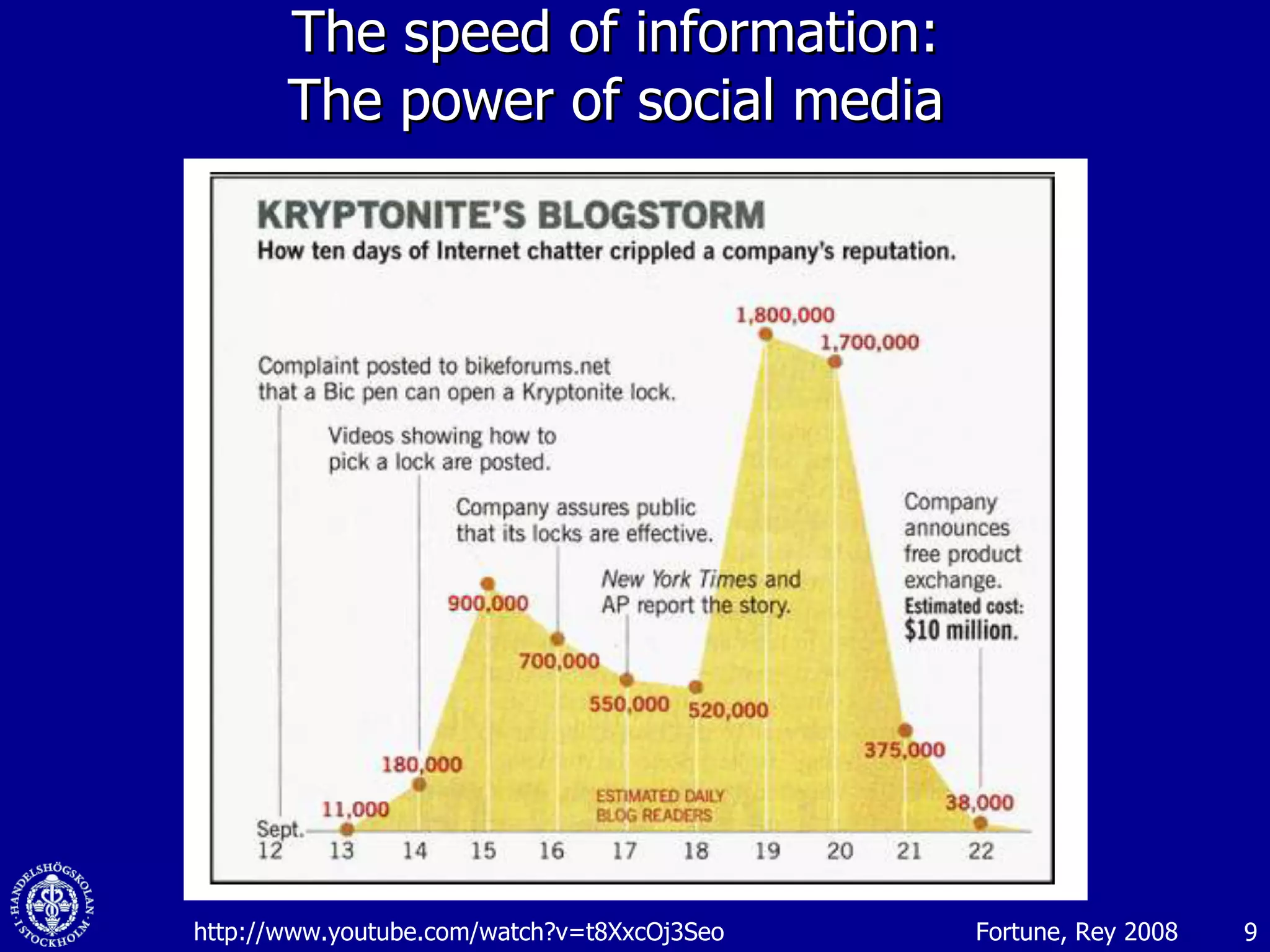
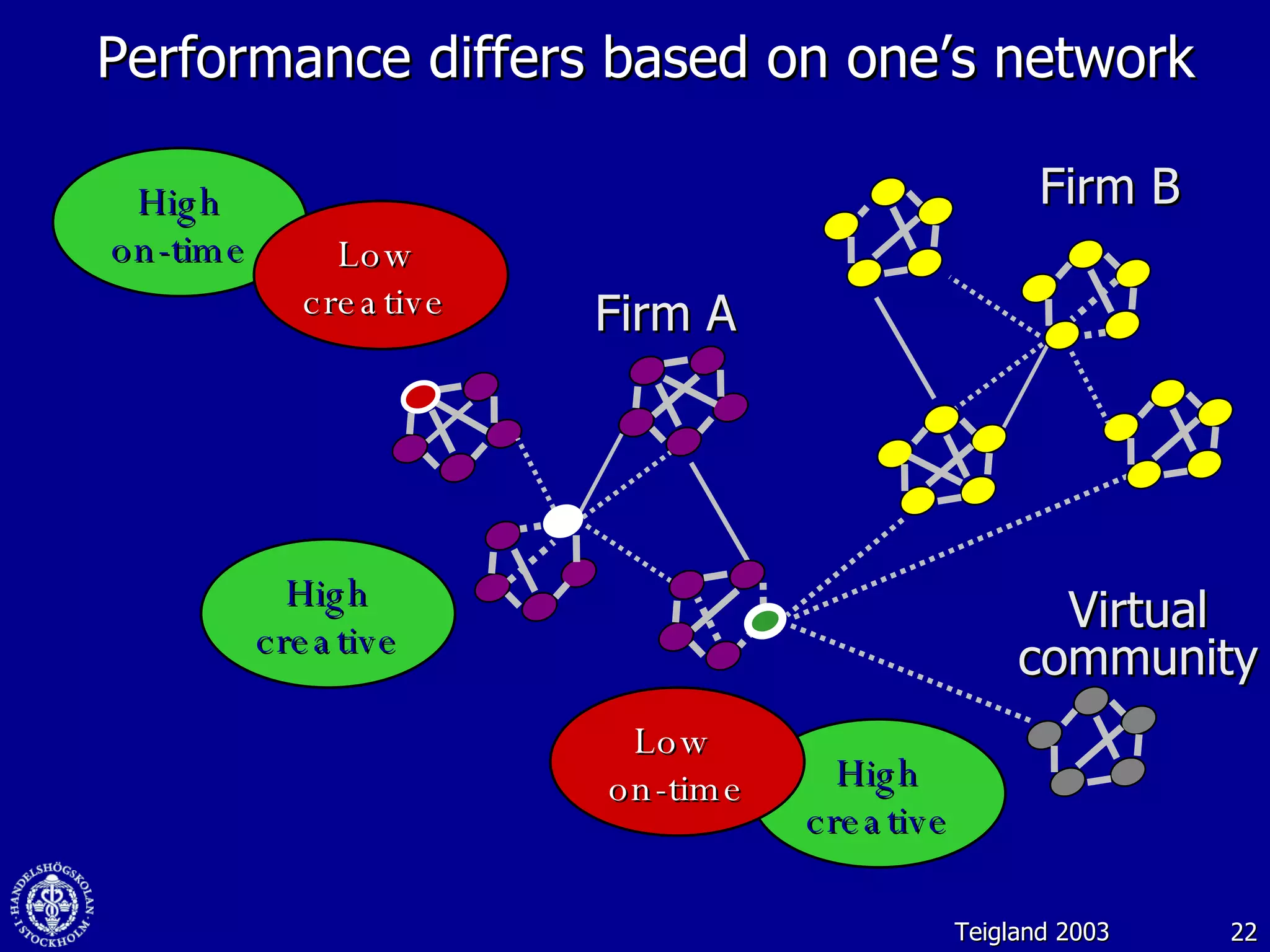
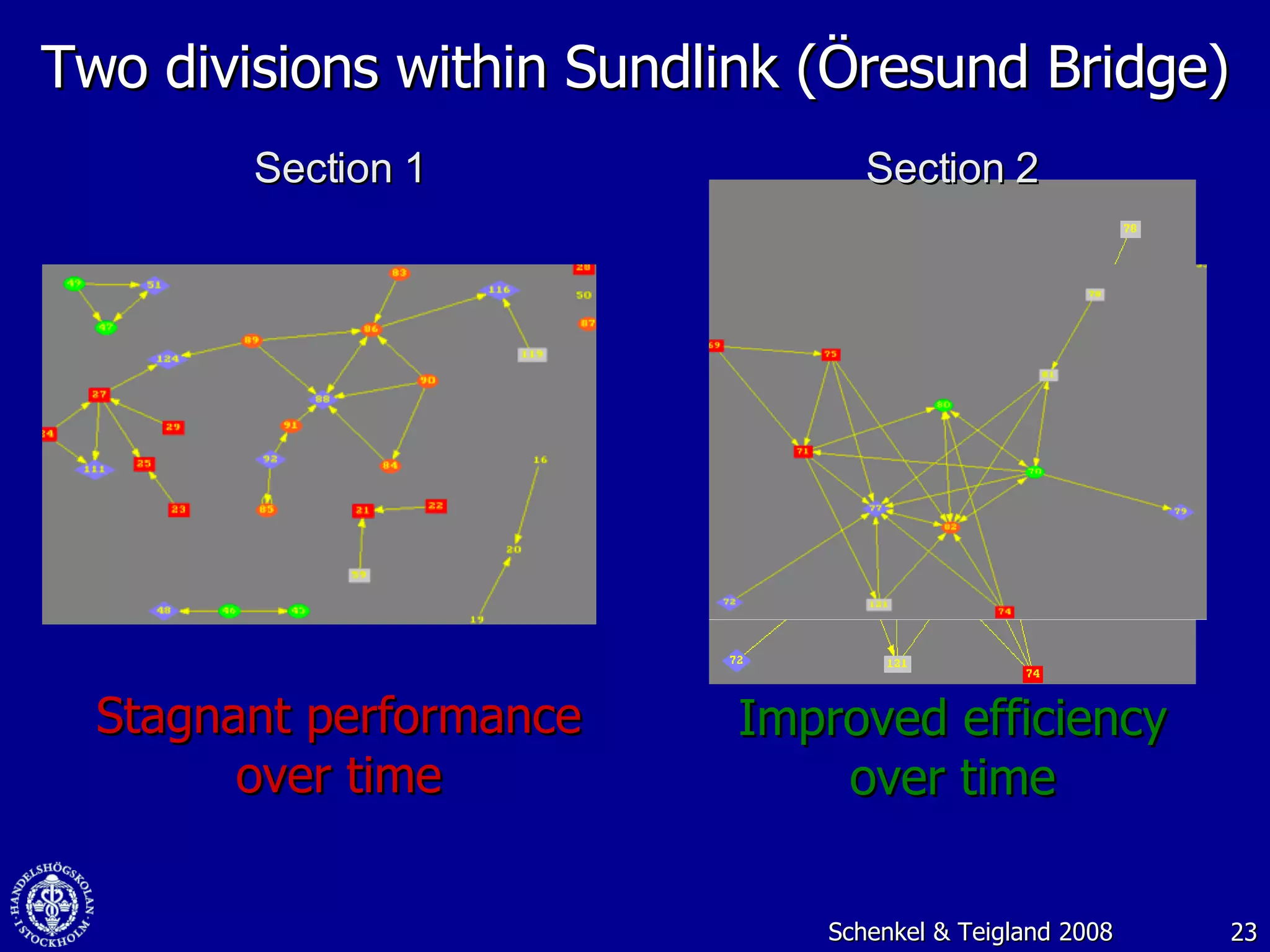
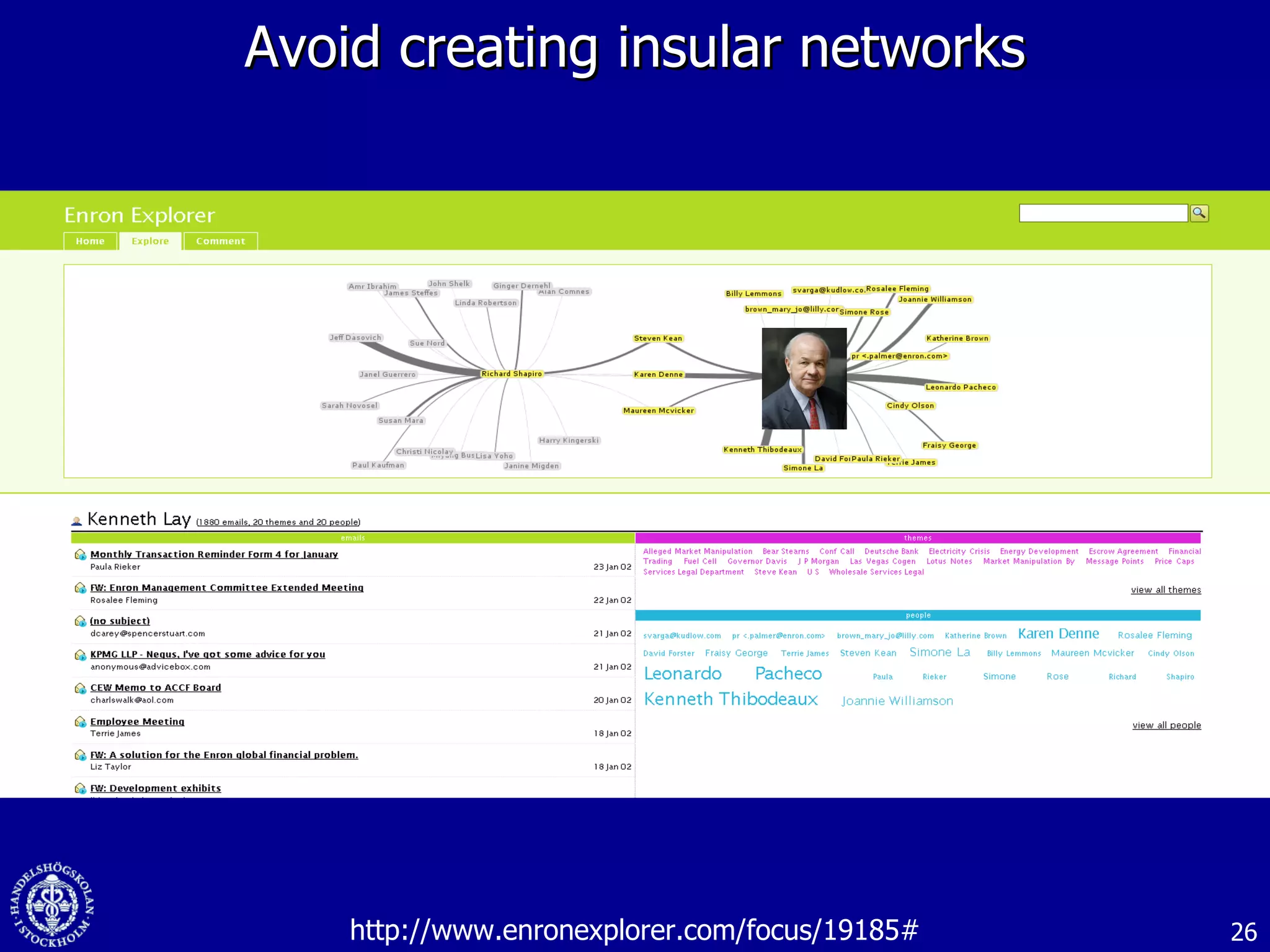
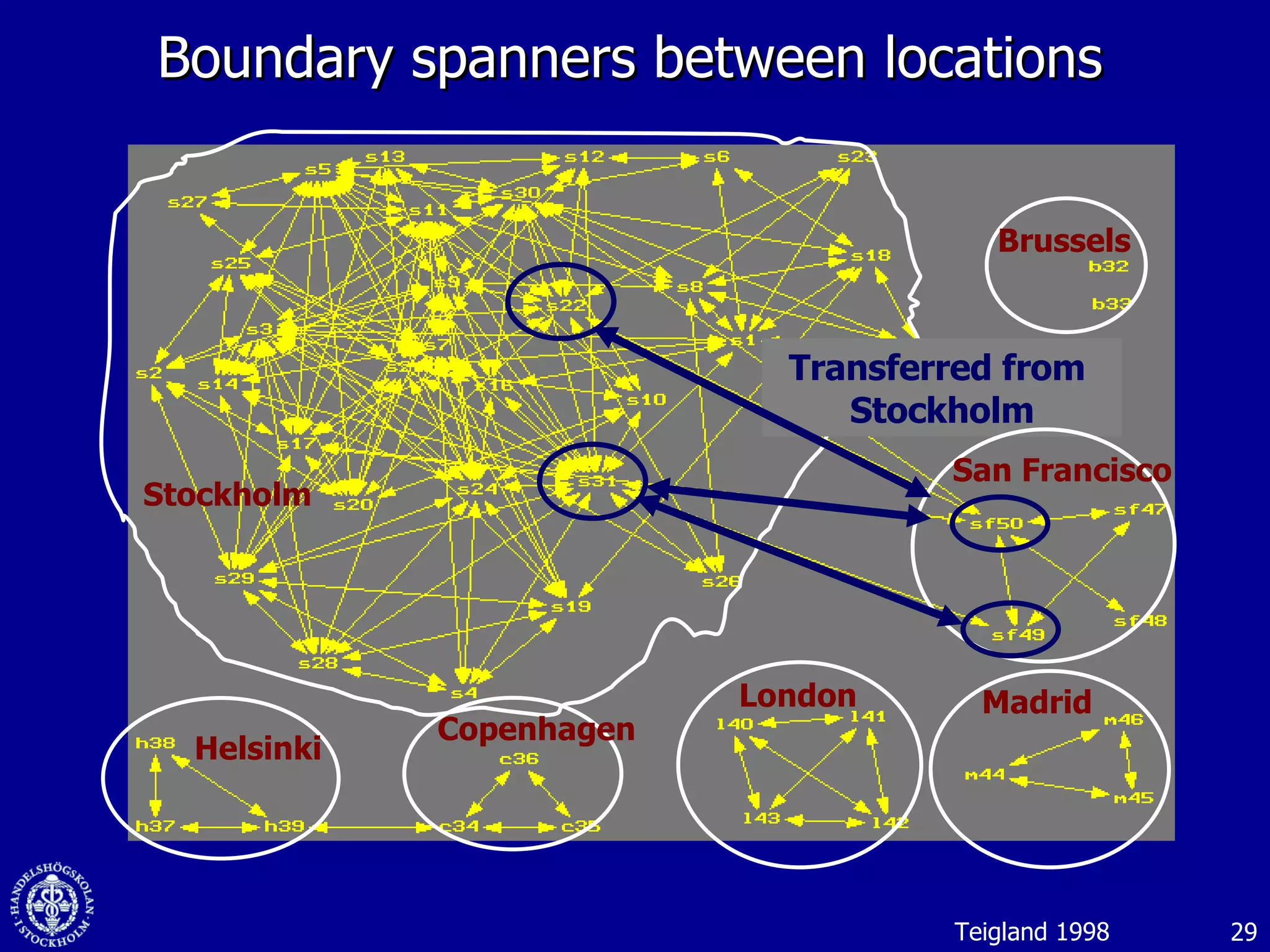
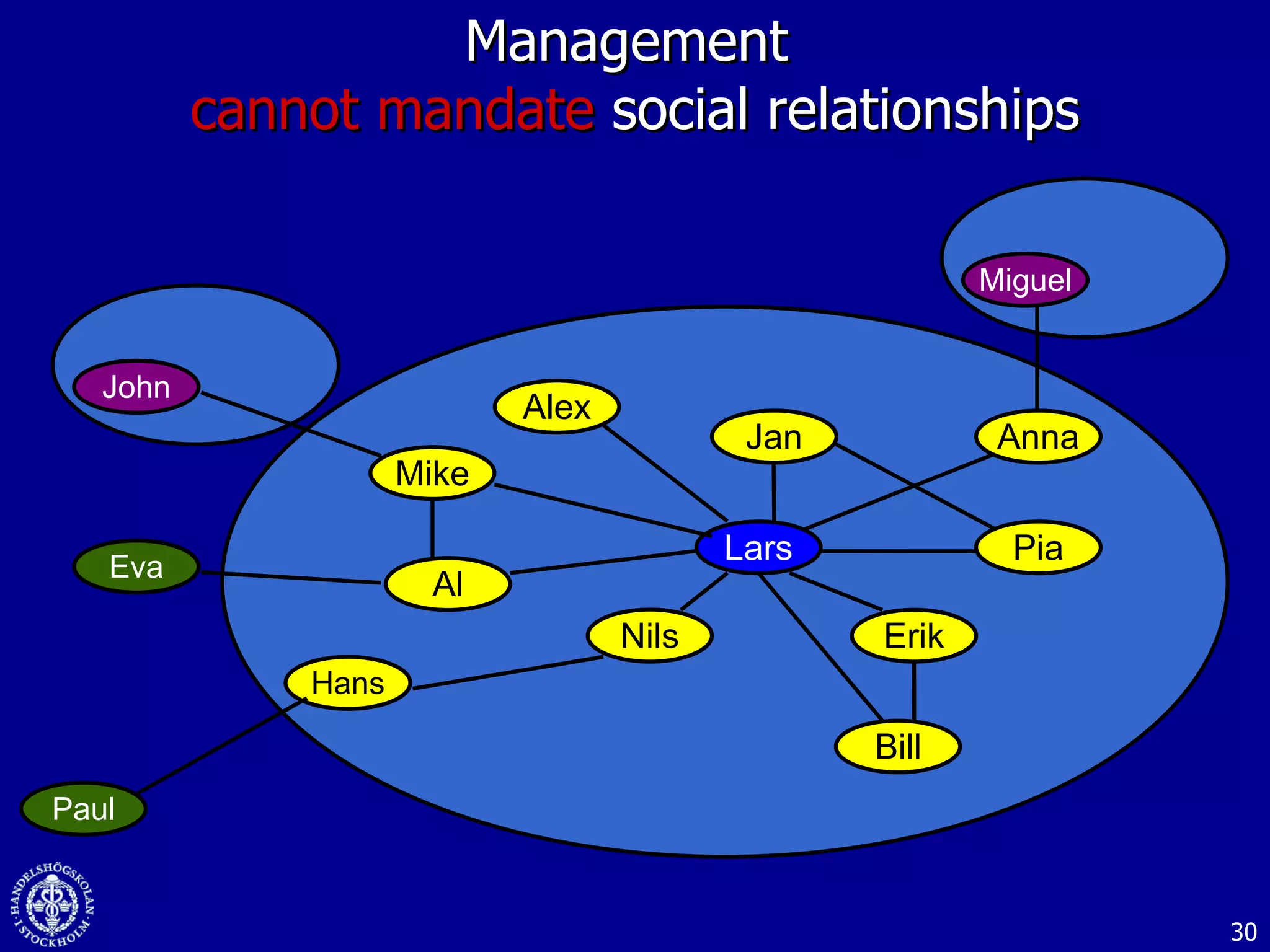
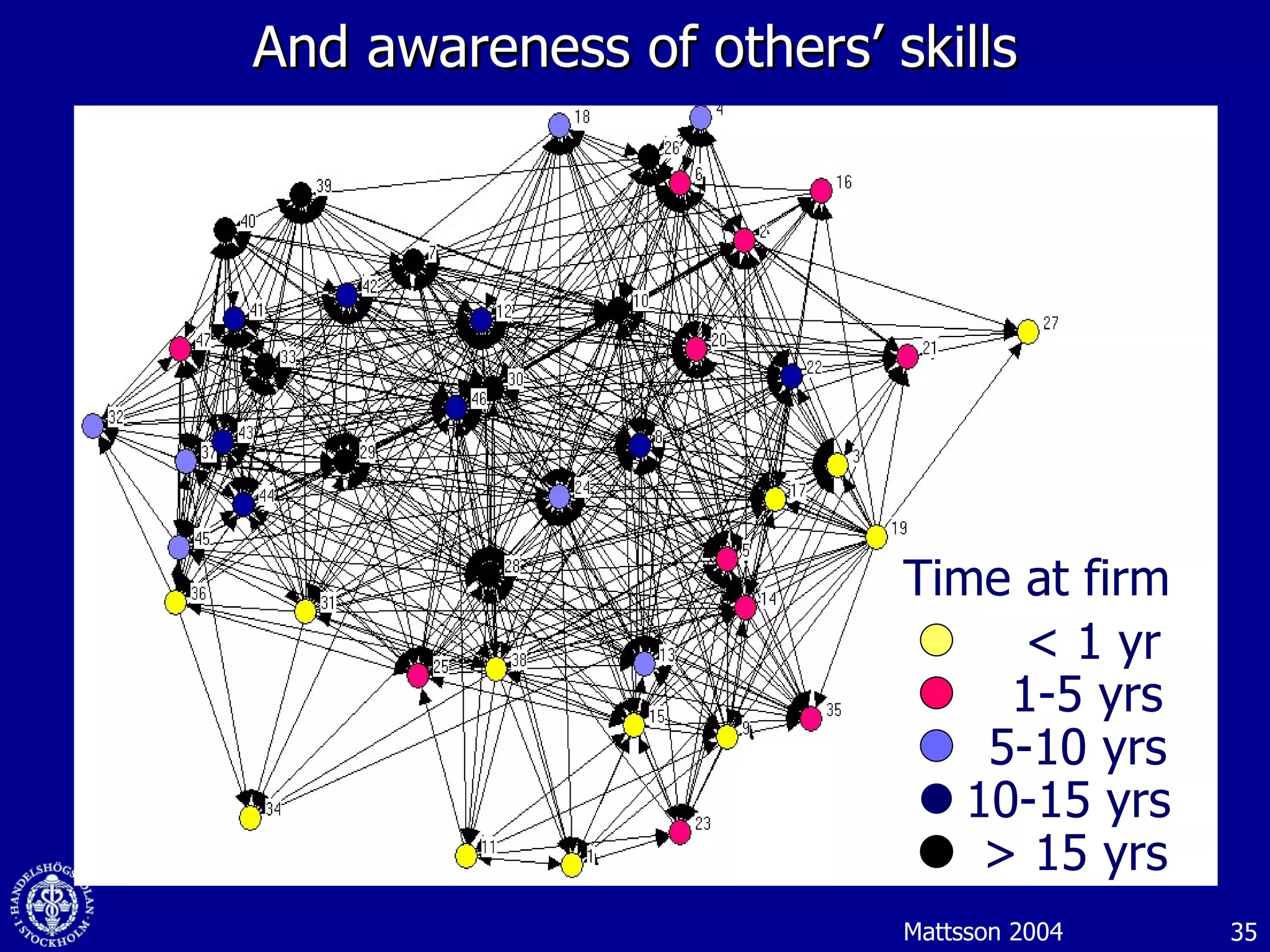
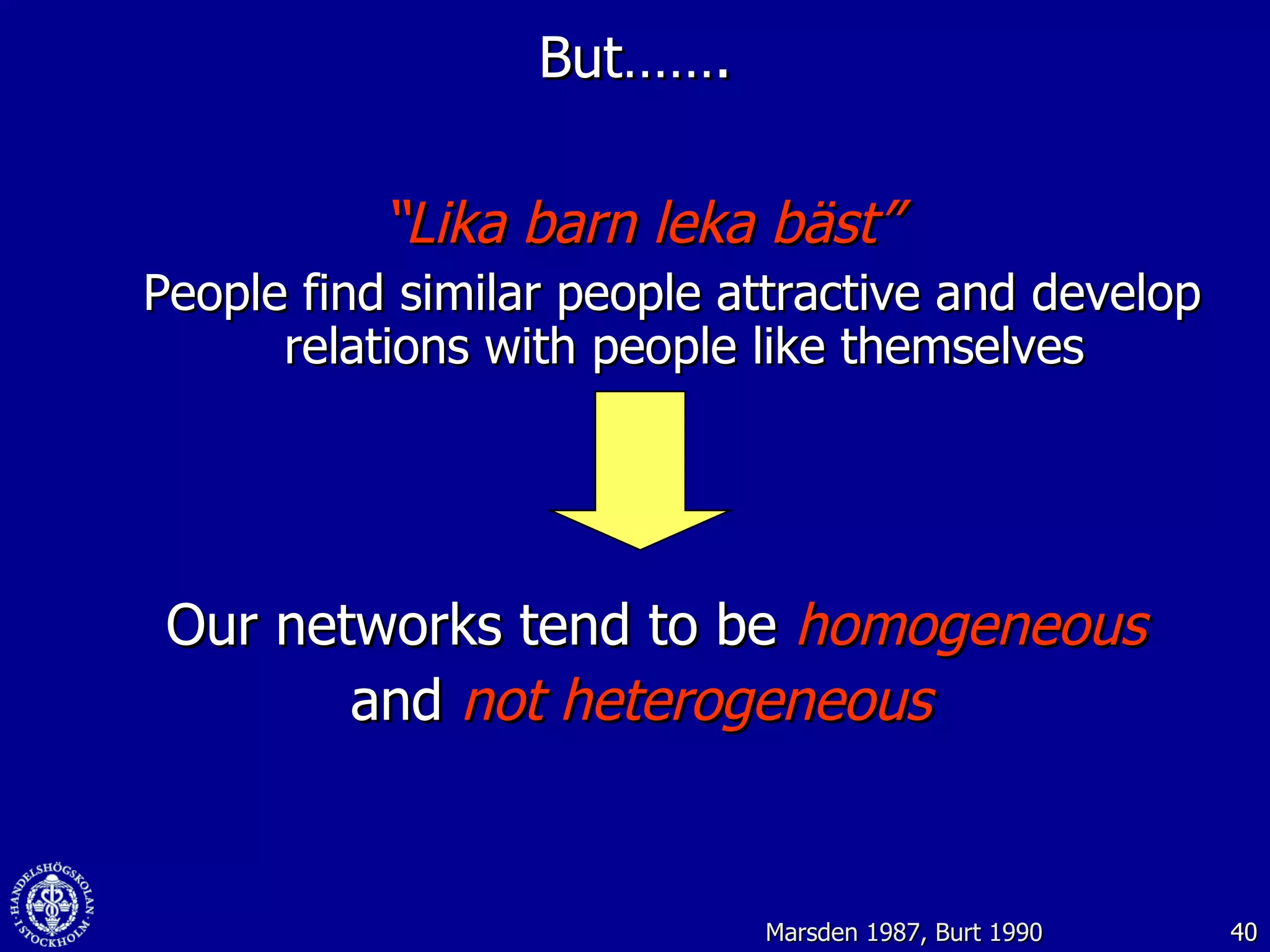
3. While social media provides benefits like knowledge sharing and relationship building, challenges include ensuring diversity in networks and balancing organizational vs individual goals.
![Web 2.0: Creating value through social media and virtual worlds November 2008 Dr. Robin Teigland Stockholm School of Economics [email_address] www.knowledgenetworking.org www.slideshare.net/eteigland 1-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-20-creating-value-through-social-networks-and-virtual-worlds-1225997934819099-9/75/Web-2-0-Creating-Value-Through-Social-Networks-And-Virtual-Worlds-1-2048.jpg)




















































![Thanks and see you in world! Karinda Rhode aka Robin Teigland [email_address] www.knowledgenetworking.org www.slideshare.net/eteigland](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web-20-creating-value-through-social-networks-and-virtual-worlds-1225997934819099-9/75/Web-2-0-Creating-Value-Through-Social-Networks-And-Virtual-Worlds-86-2048.jpg)


