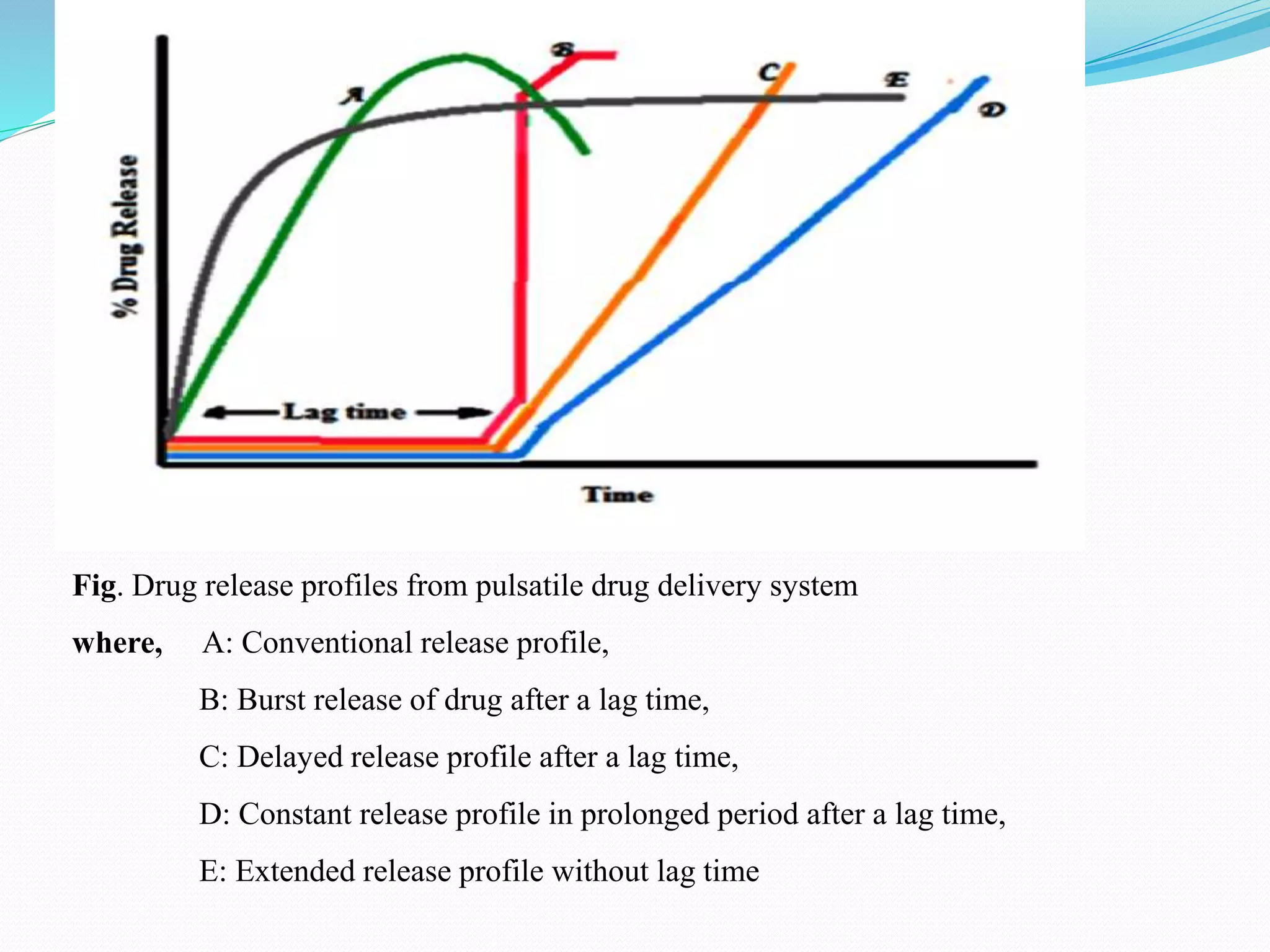
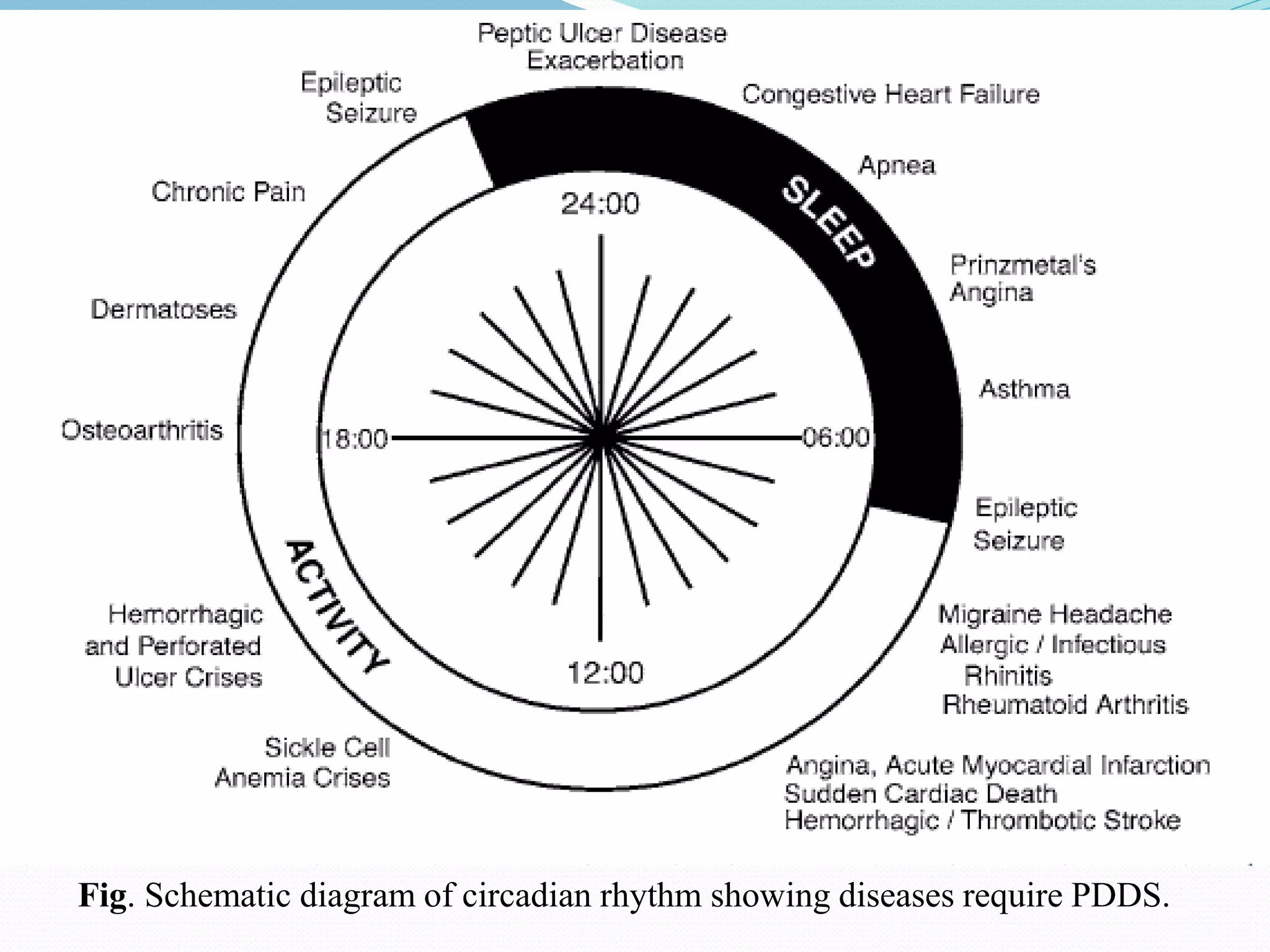
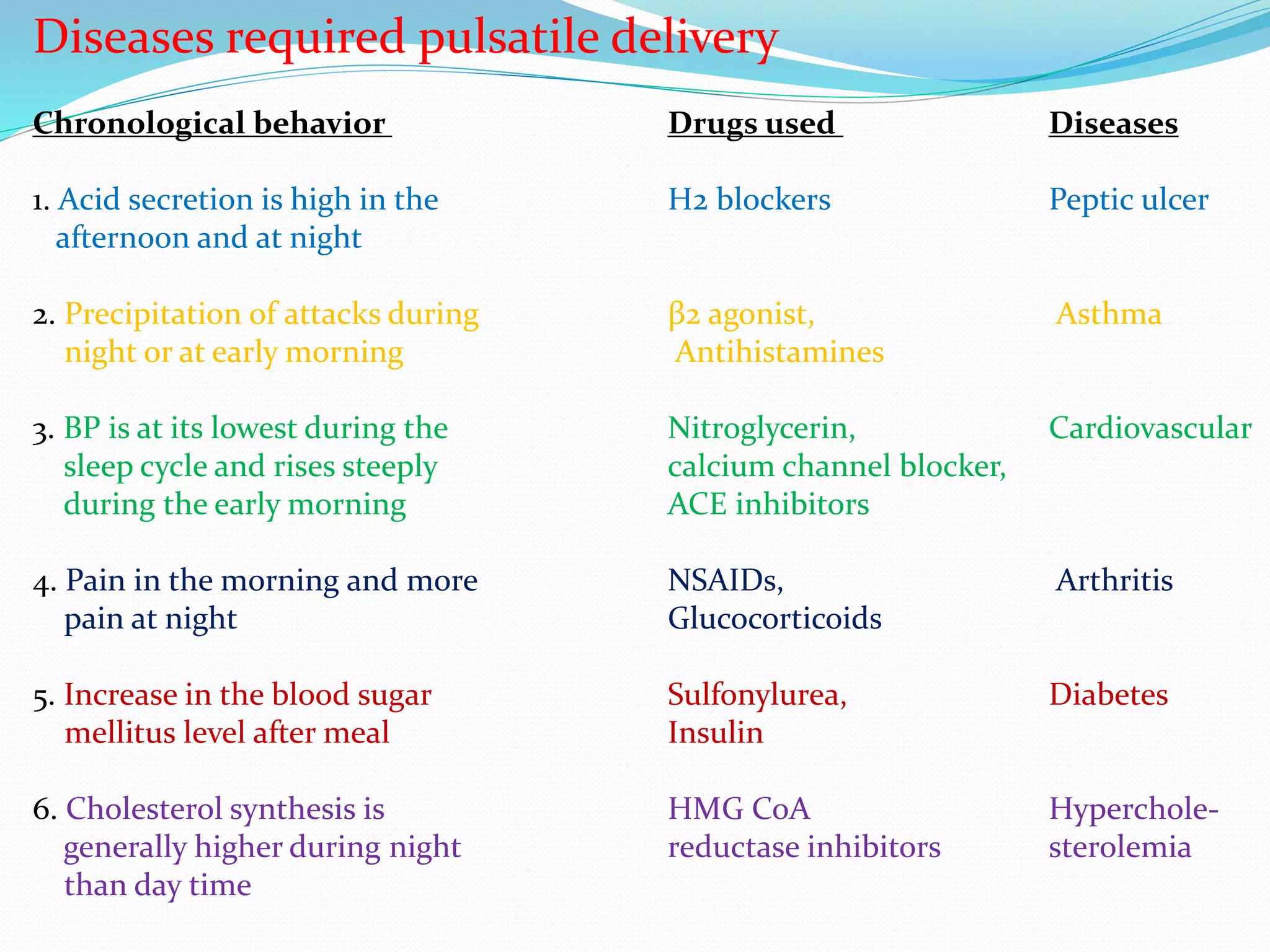
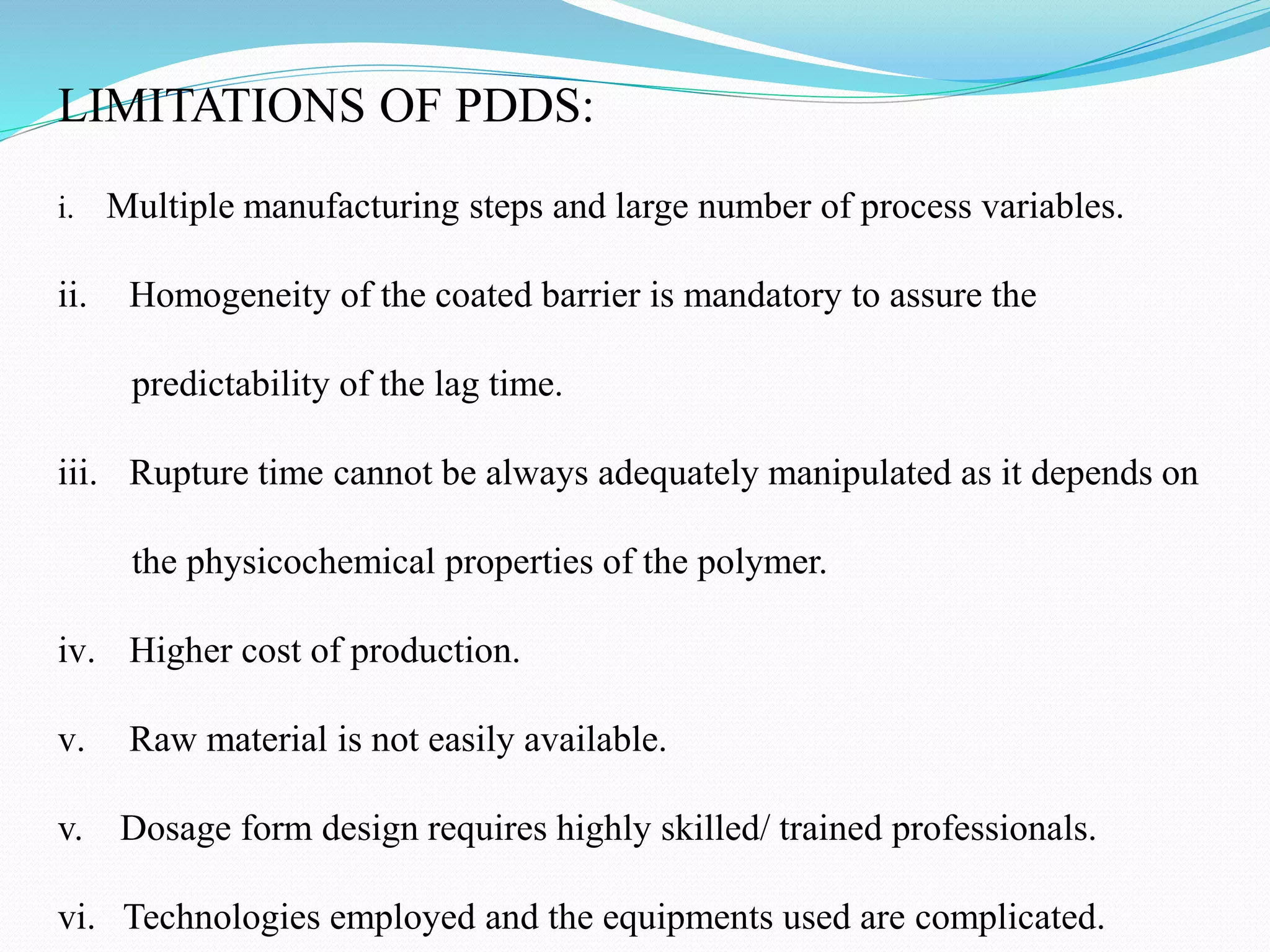
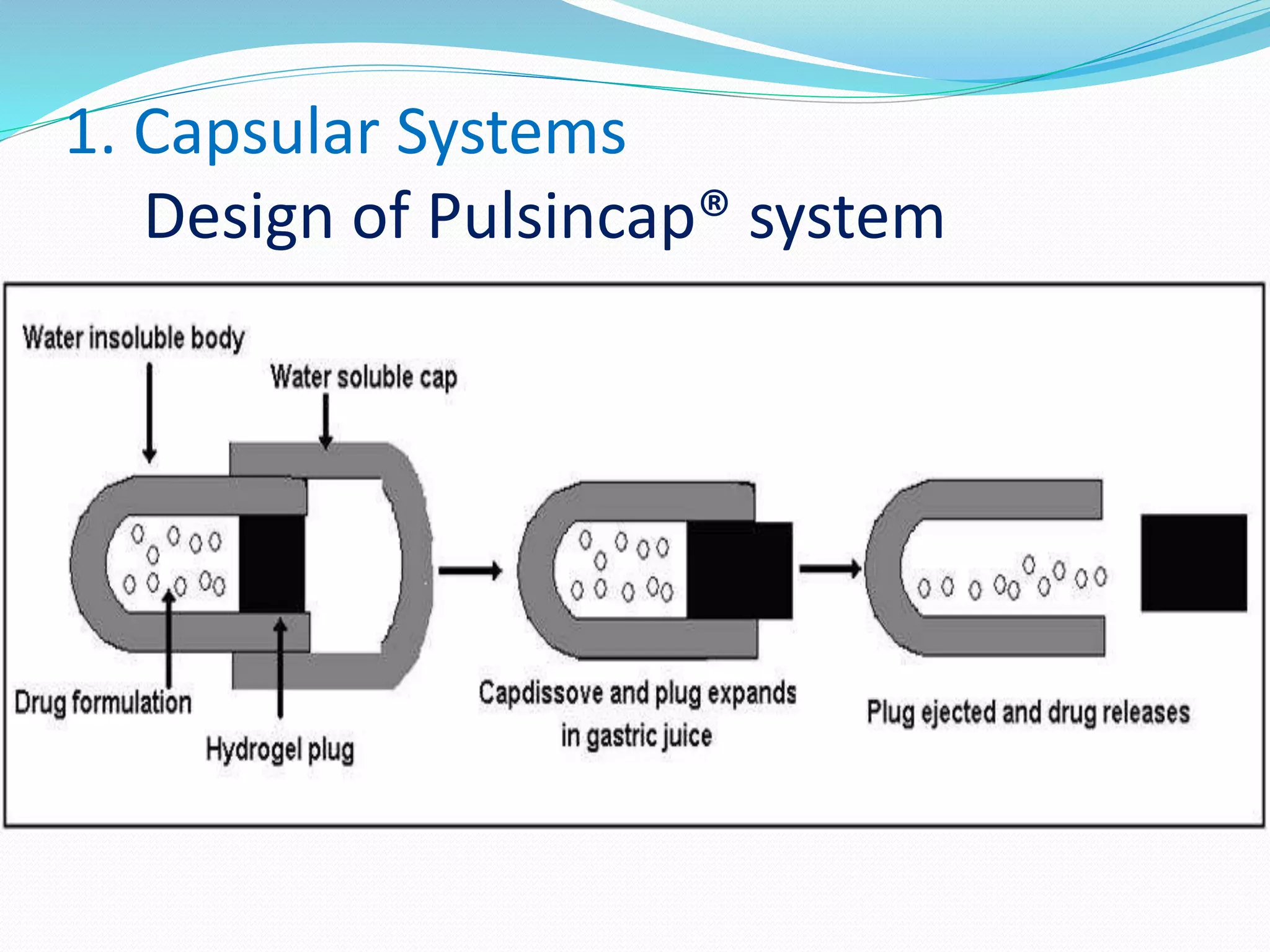
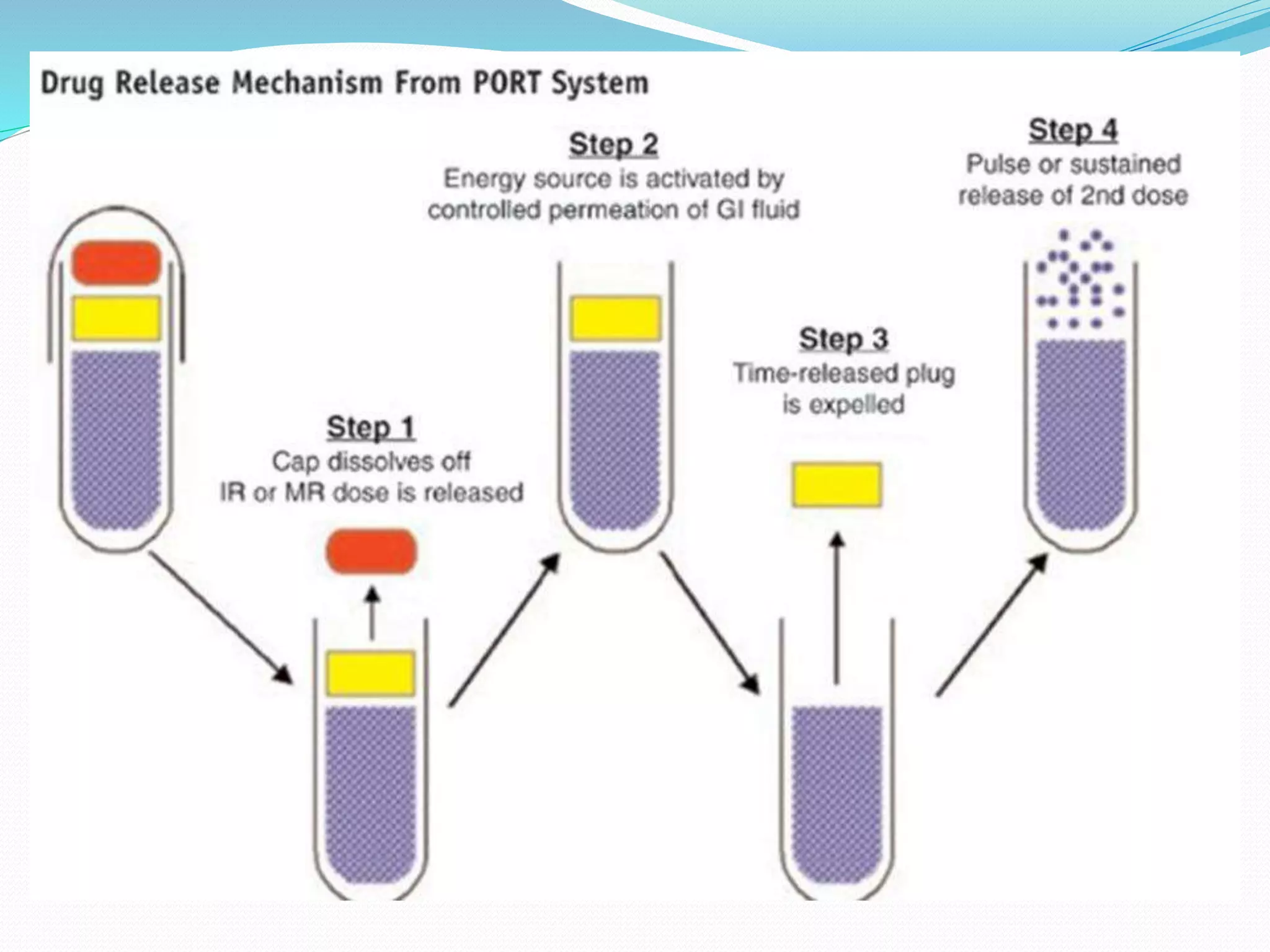
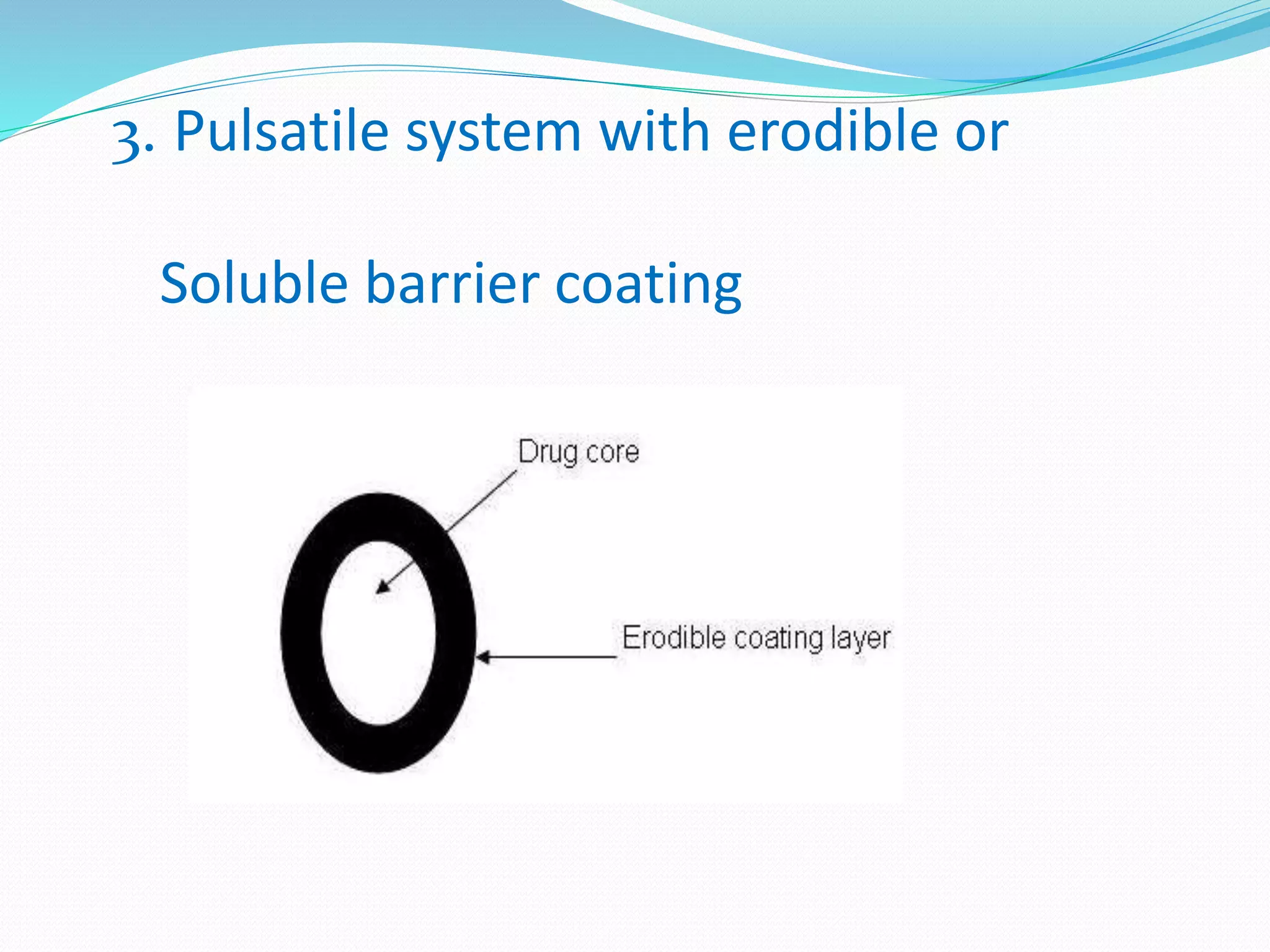
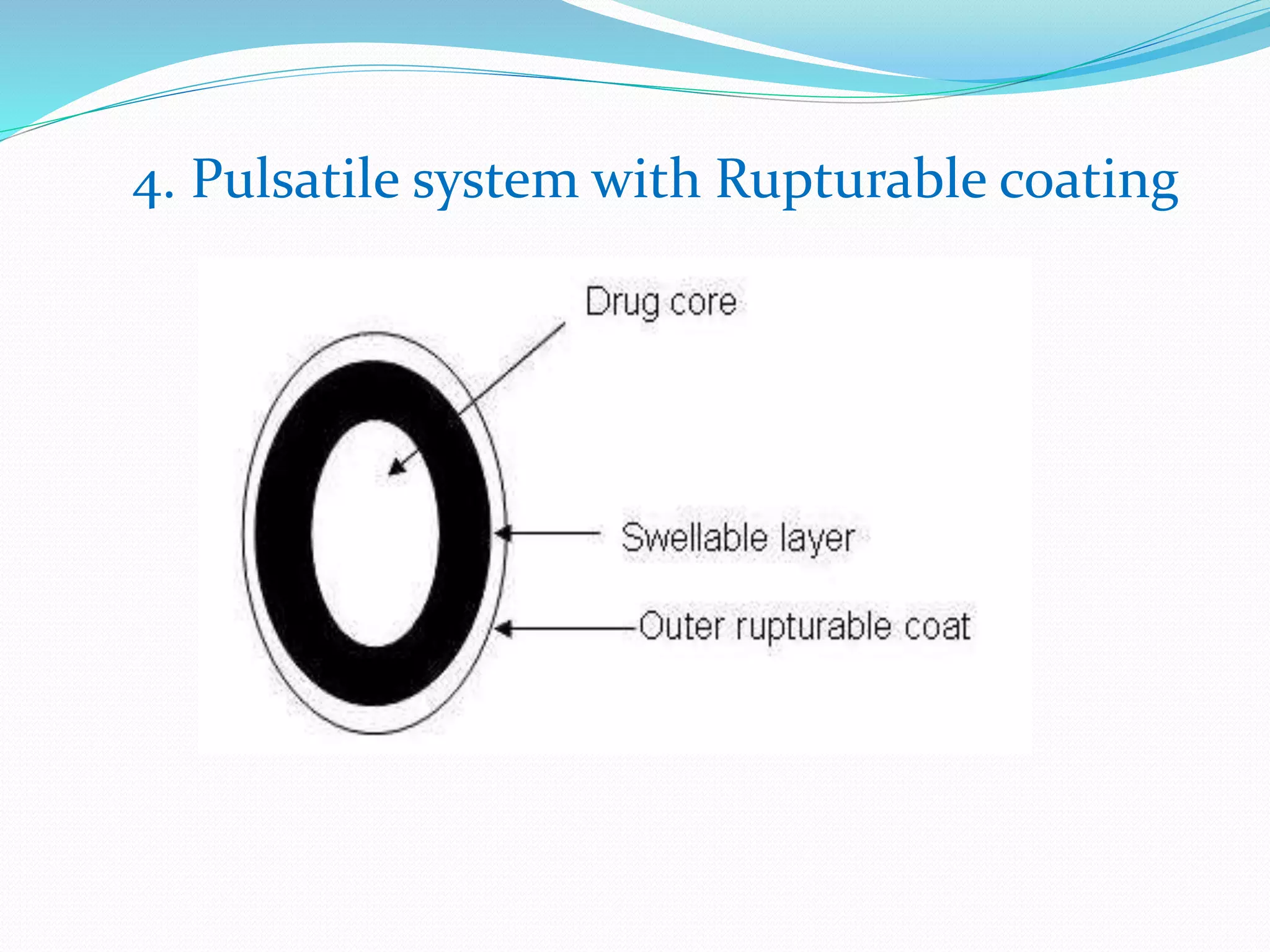
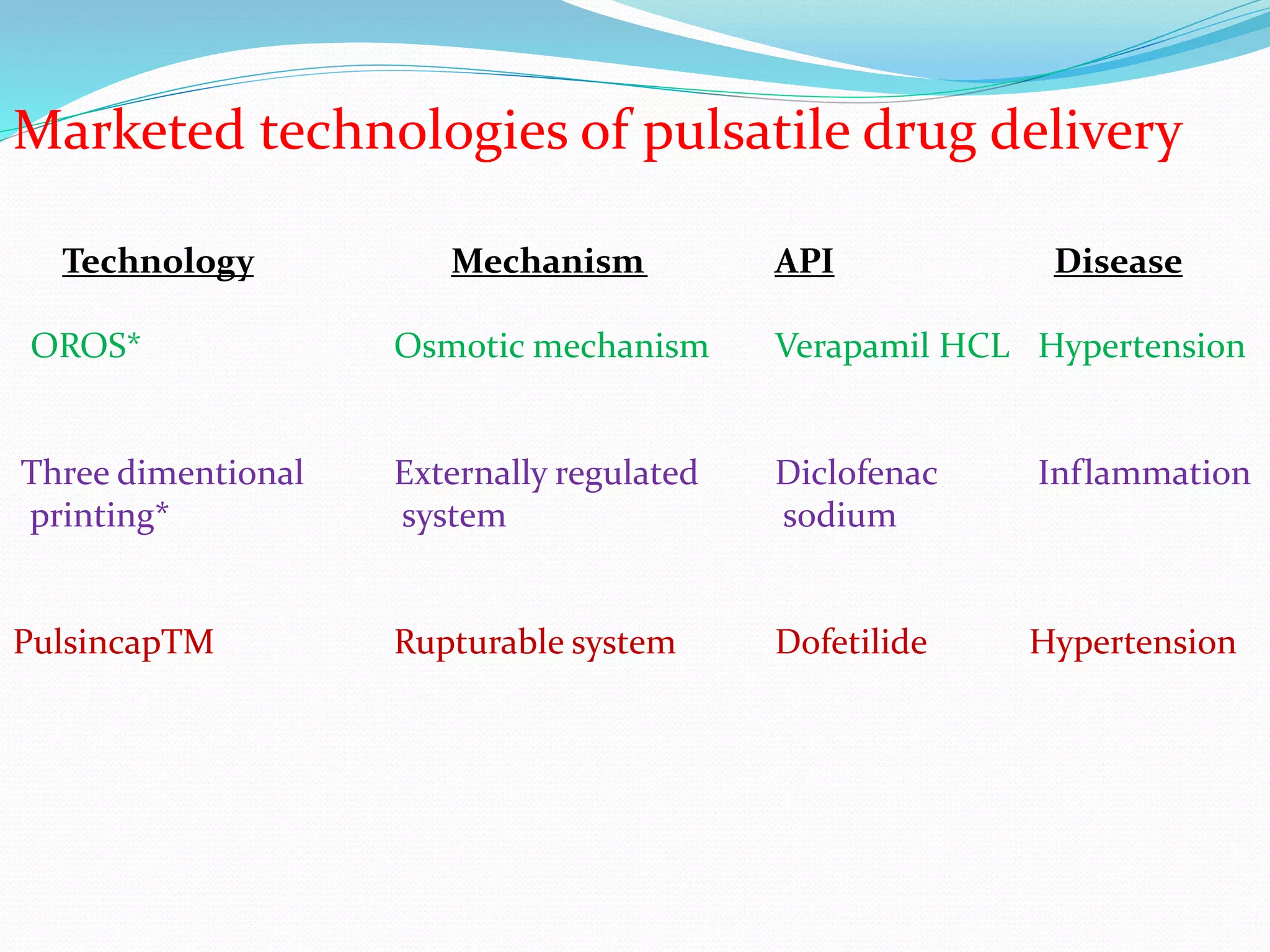
This seminar discusses pulsatile drug delivery systems, which deliver drugs according to circadian rhythms to time their release when diseases are most active. Such systems provide a lag time followed by a rapid and complete drug release. This allows drugs to be delivered at the right time, amount, and site of action. Pulsatile delivery provides benefits like increased absorption, site targeting of drugs, reduced dosing, and less side effects. Various methods were presented including single and multiple unit systems using coatings that erode, rupture or allow osmotic pumping at the desired time. Marketed technologies like OROS and Pulsincap were highlighted. Pulsatile delivery holds promise for improving treatment of chronic diseases like asthma, arthritis and