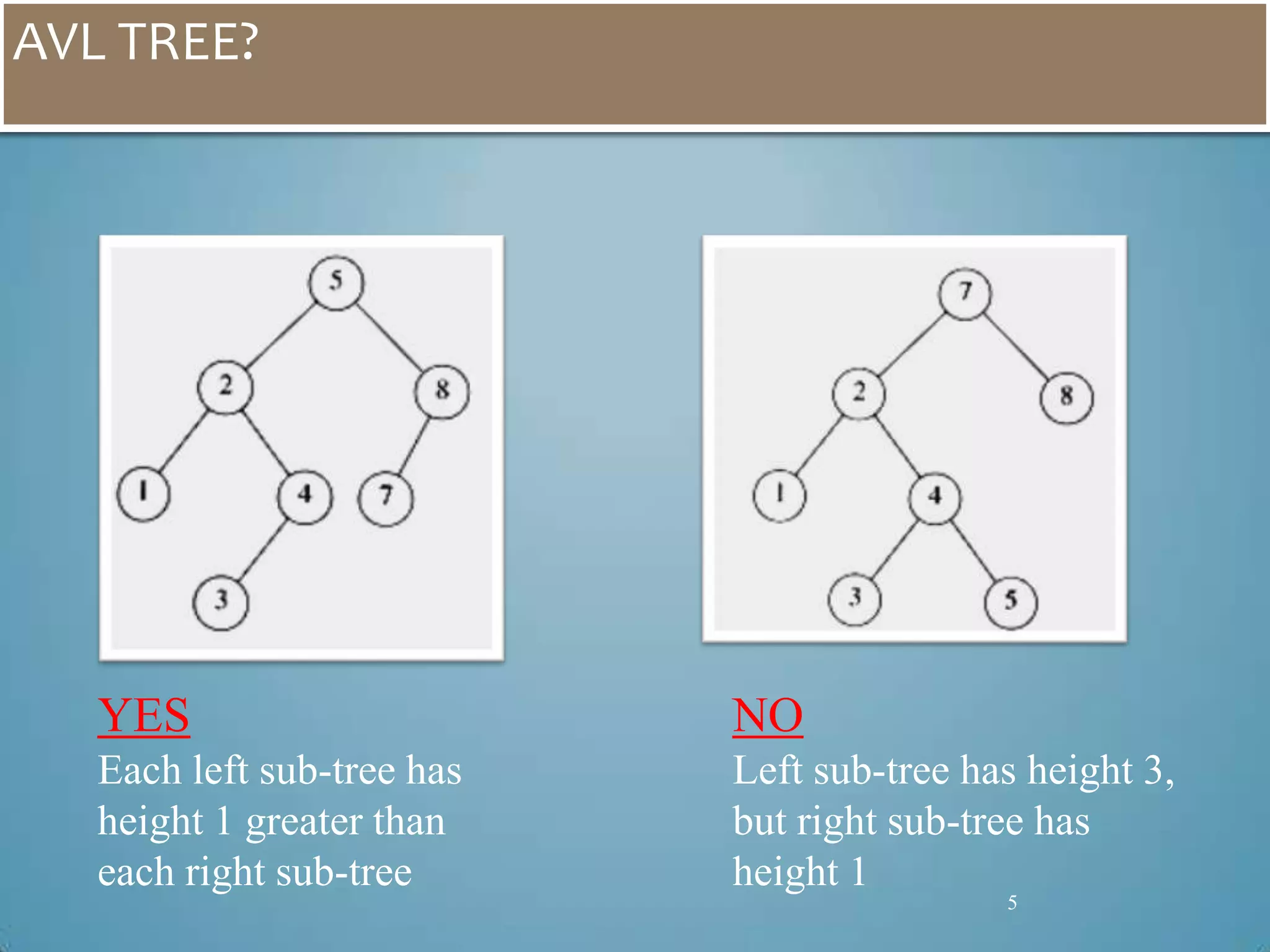
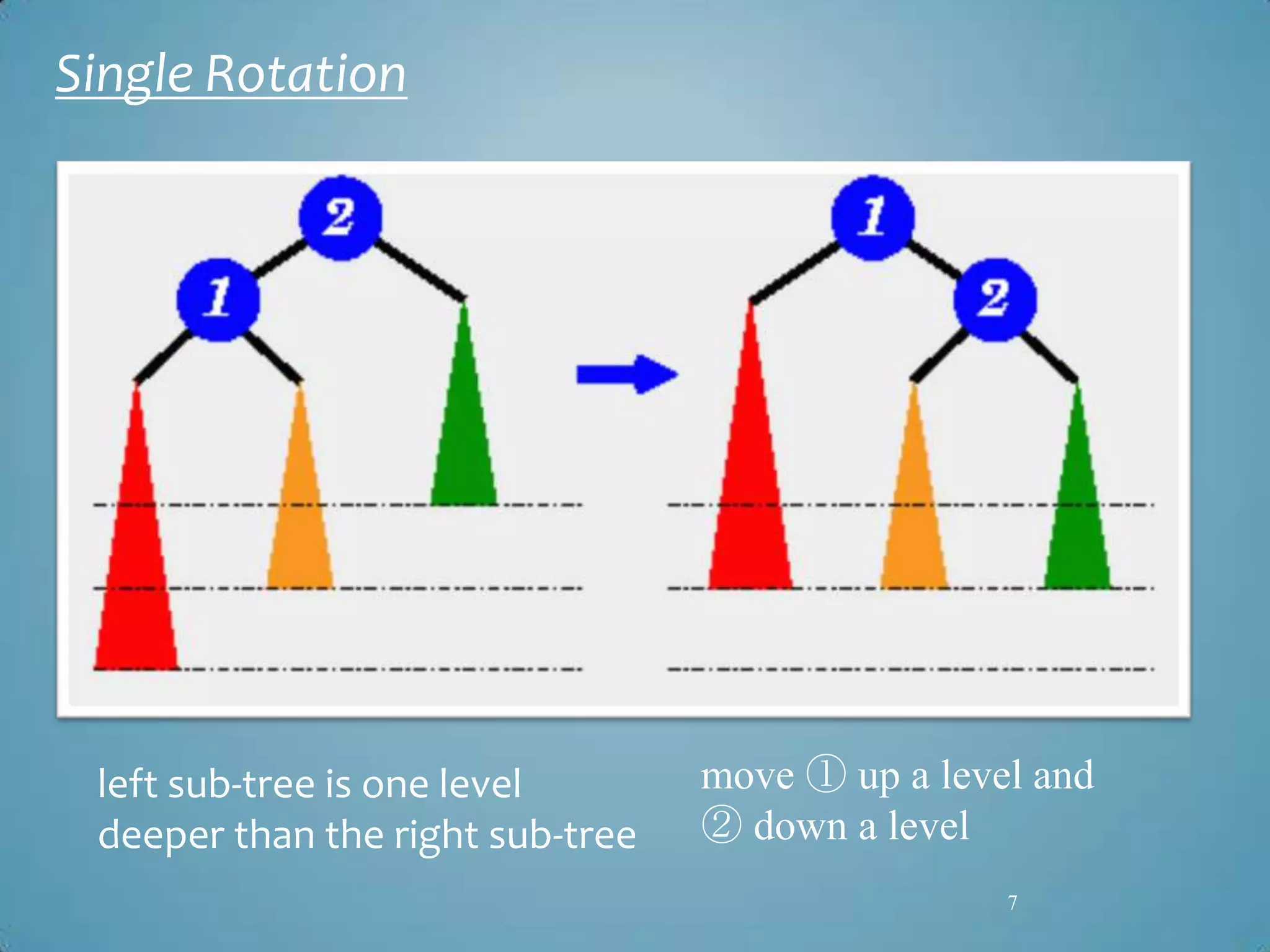
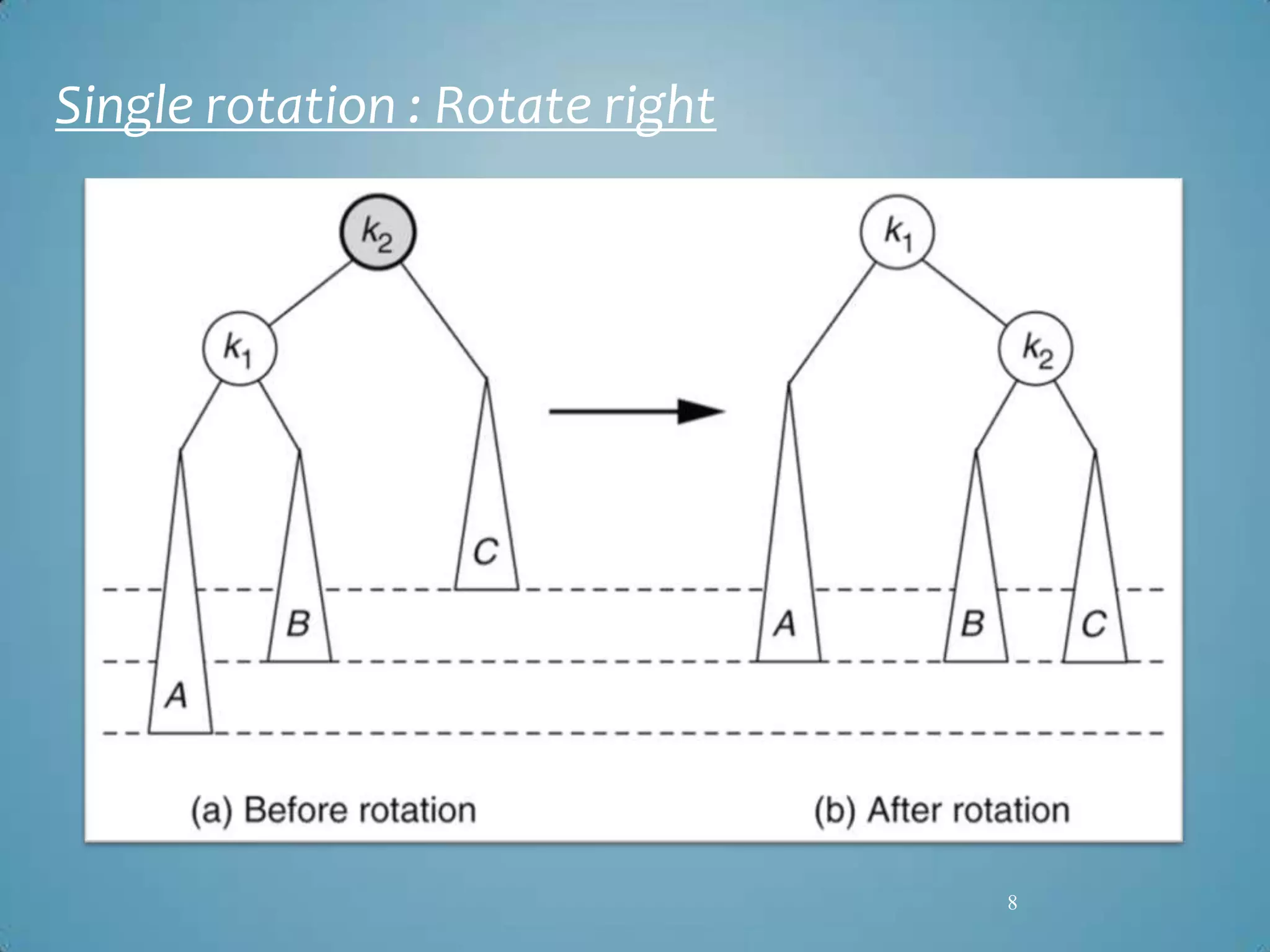
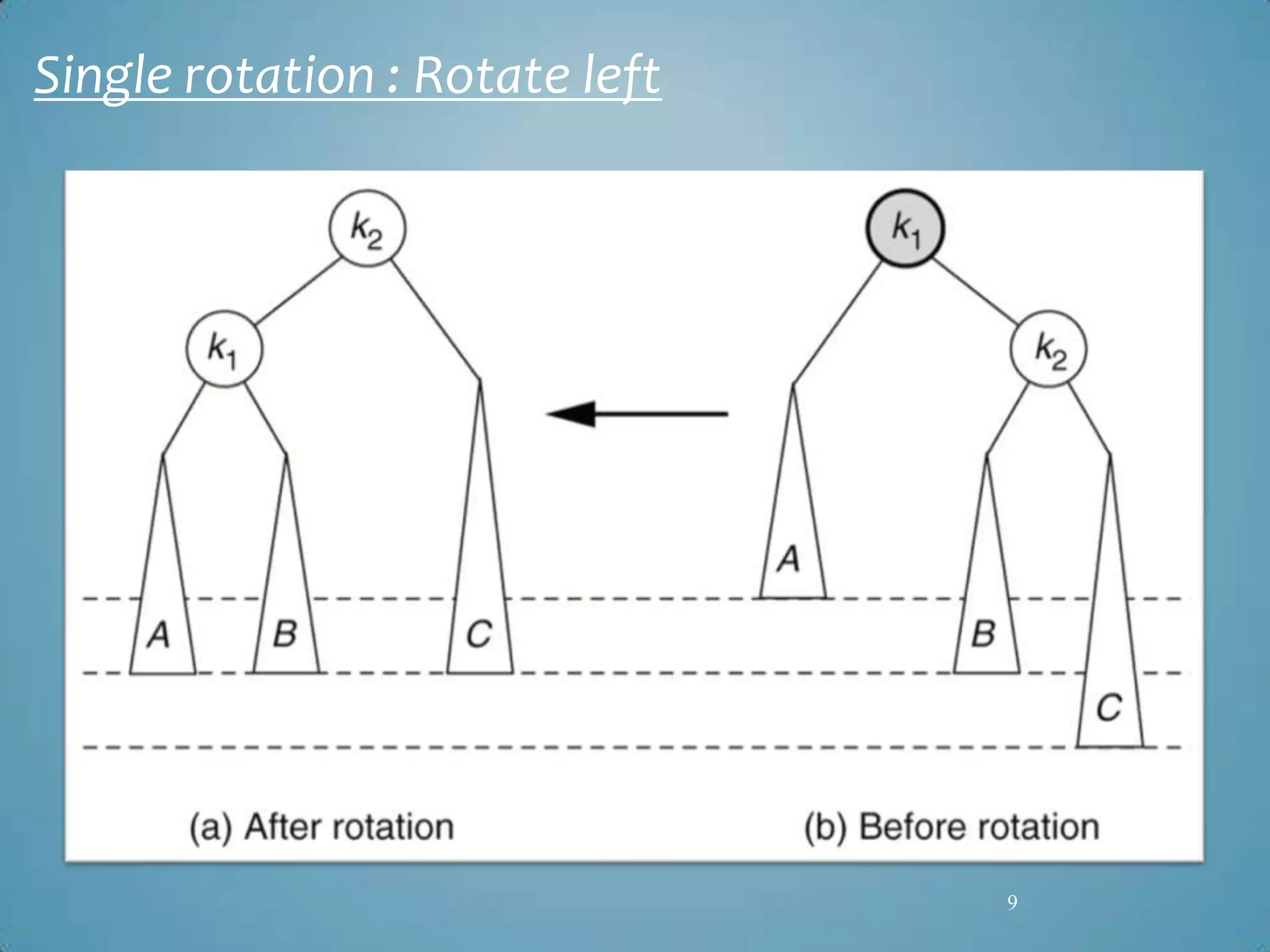
Transport Layer Security (TLS) was designed to provide security at the transport layer and was derived from Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). TLS operates at the transport layer of the internet model and consists of four protocols: the handshake protocol for authentication and key exchange, the change cipher spec protocol for transitioning to the negotiated cryptographic settings, the alert protocol for transmitting error messages, and the record protocol for encapsulation of higher level protocols.