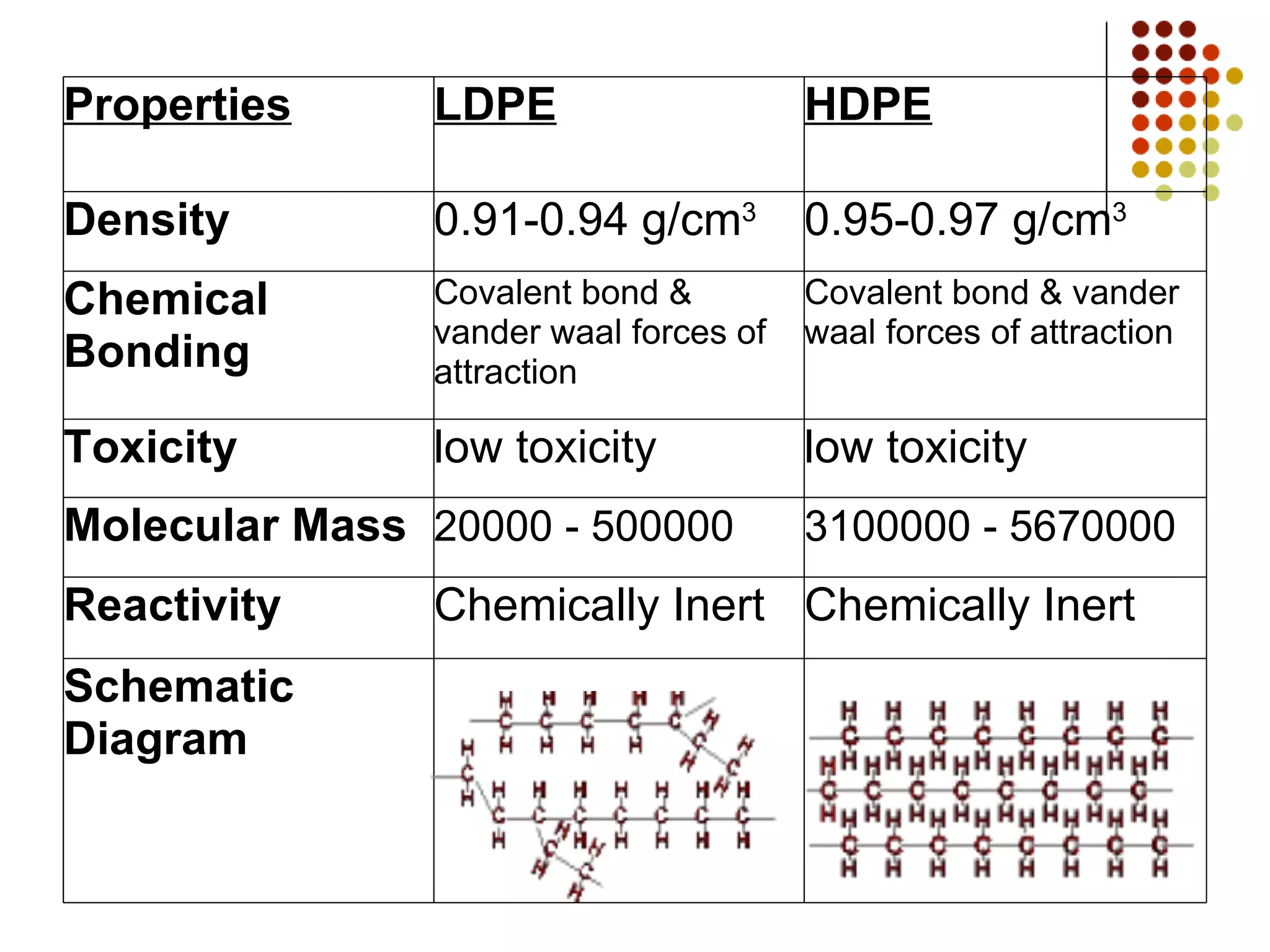
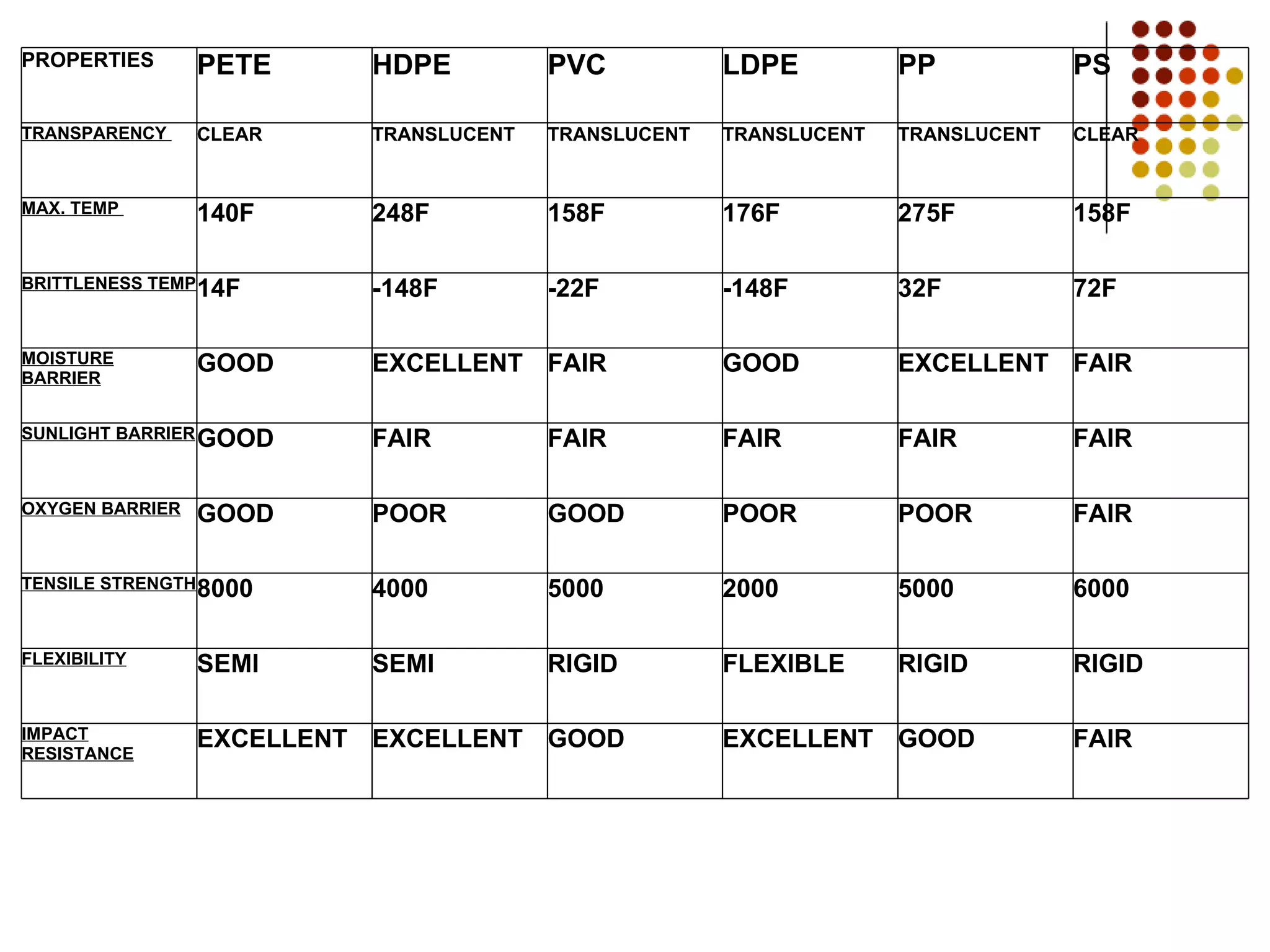
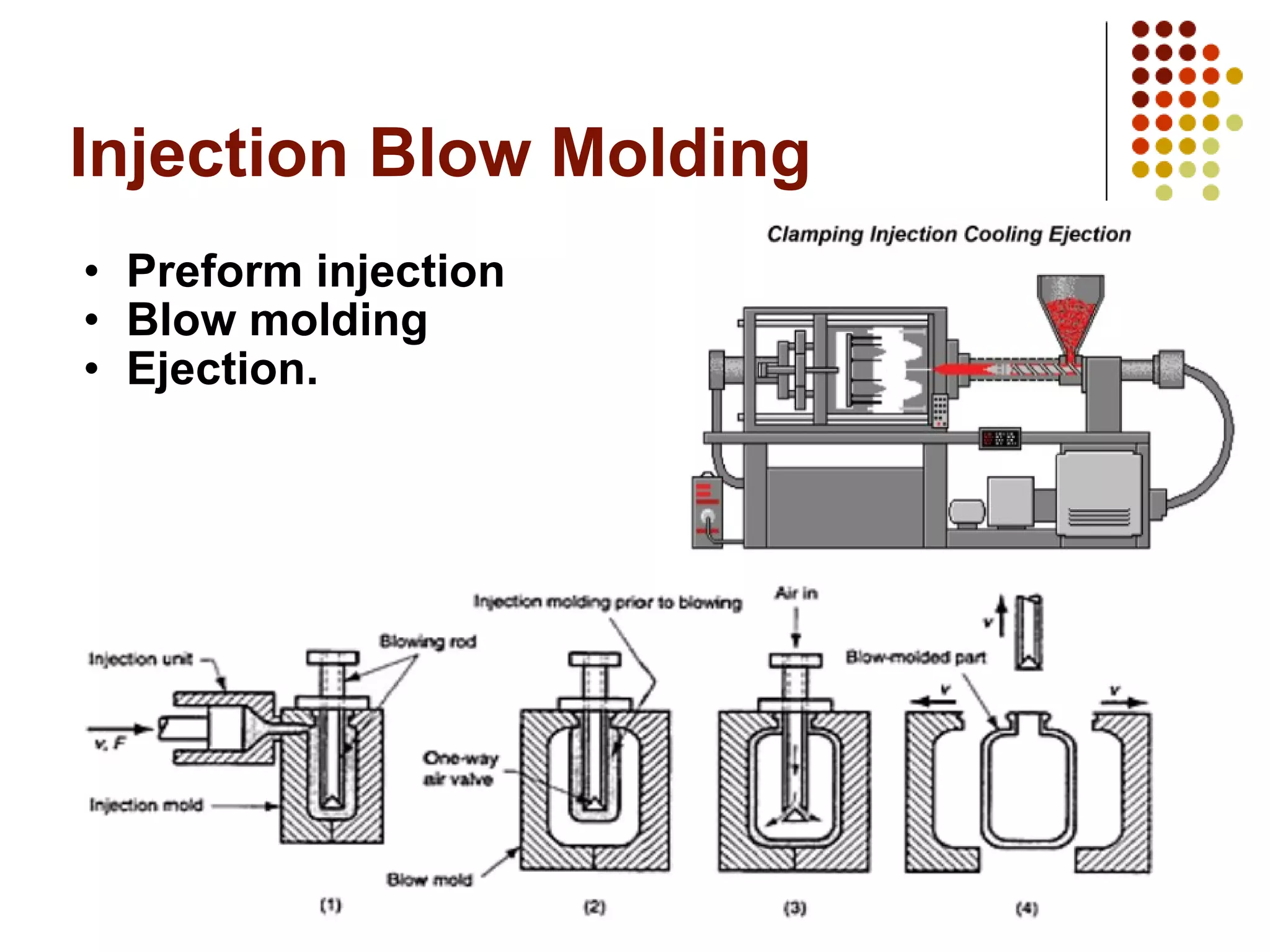
Plastic bottles were developed in the early 20th century and became widely used after World War II. The key materials used are polyethylene terephthalate (PETE), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and polypropylene (PP). These materials are chosen based on their properties like strength, flexibility, and barrier effectiveness. Plastic bottles are manufactured using blow molding processes and come in various colors, shapes, and sizes to suit different applications like water, soda, detergents and more. However, plastic waste is an environmental issue as most plastics do not decompose and recycling rates need improvement.