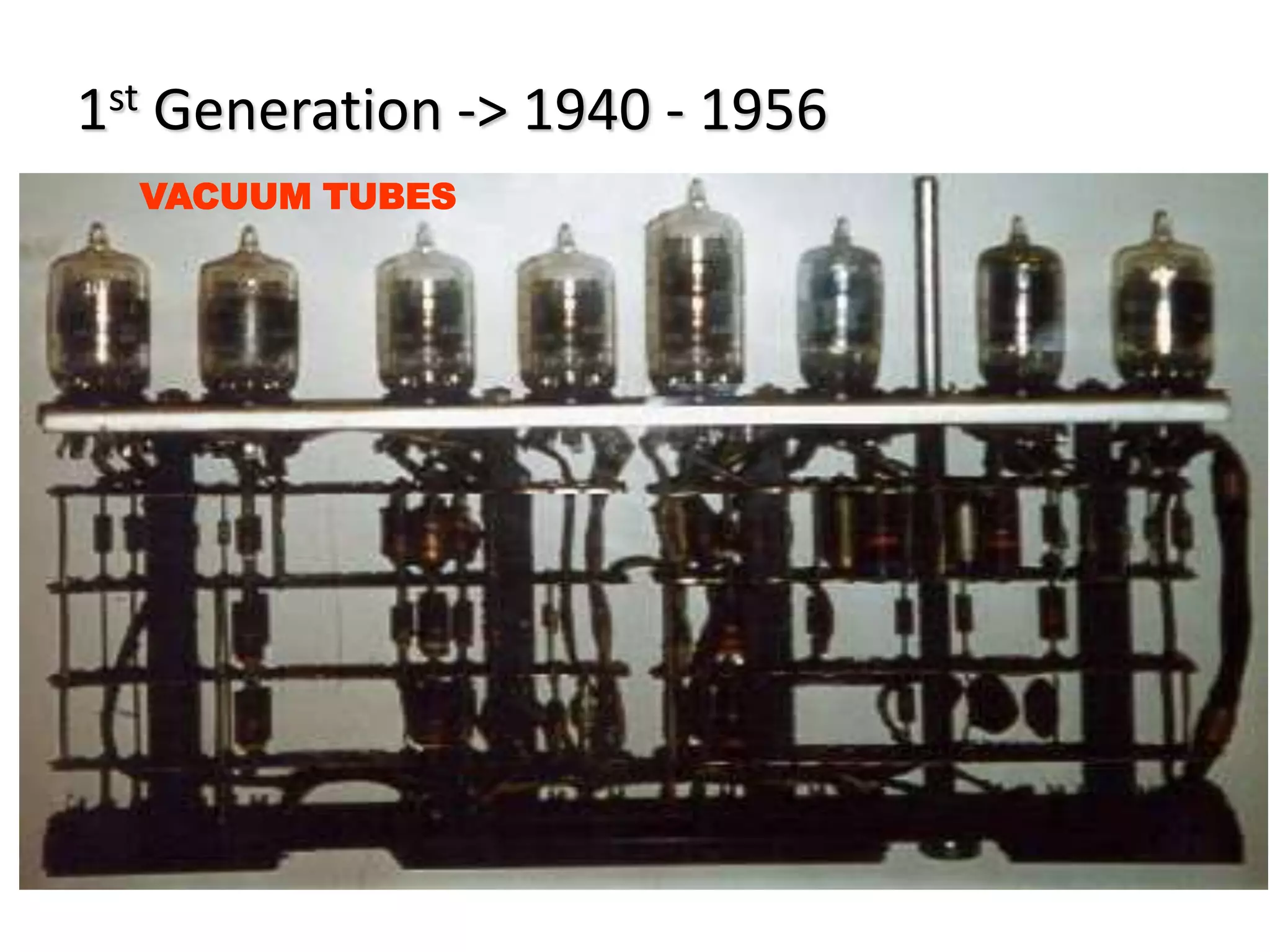
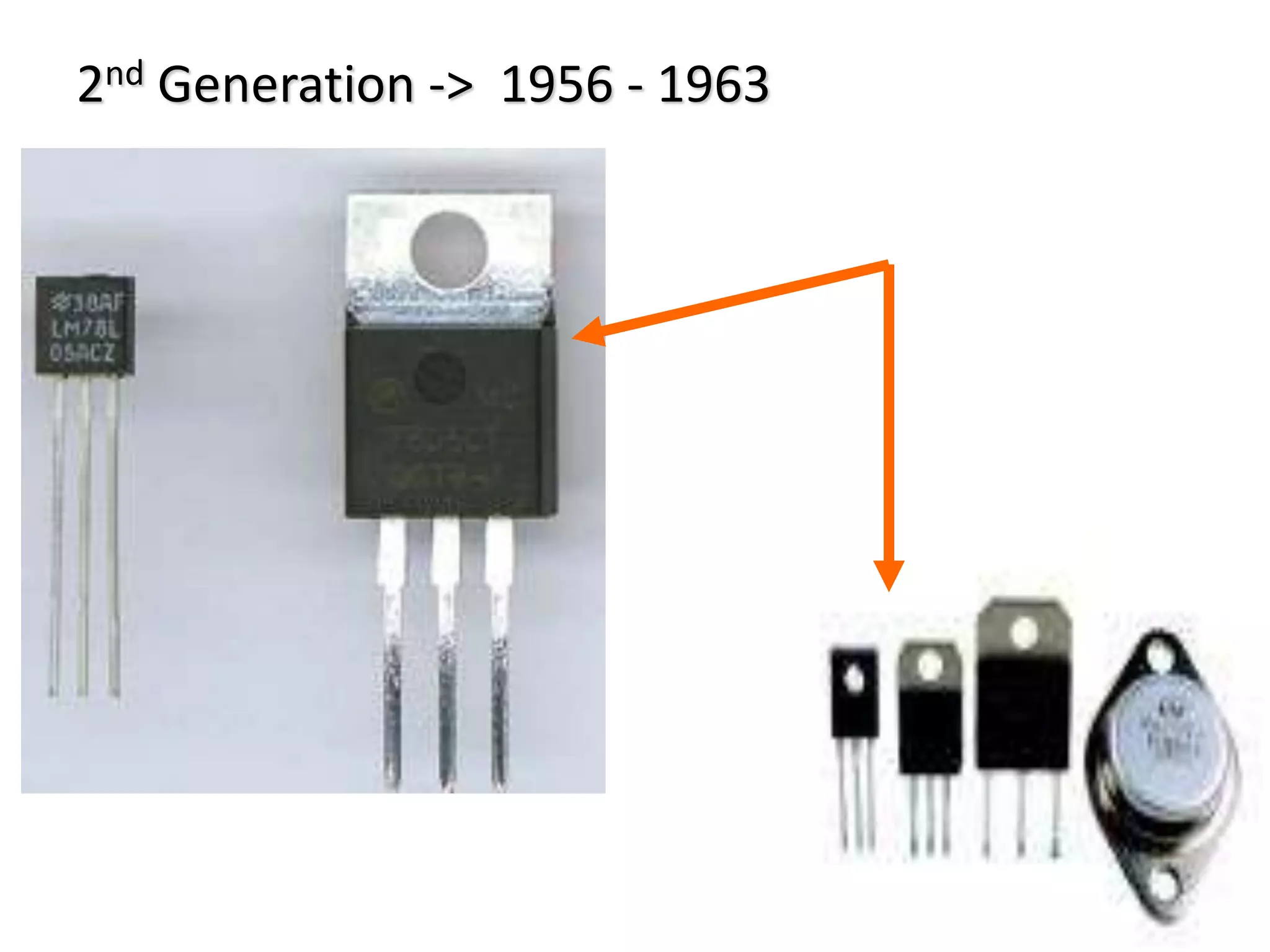
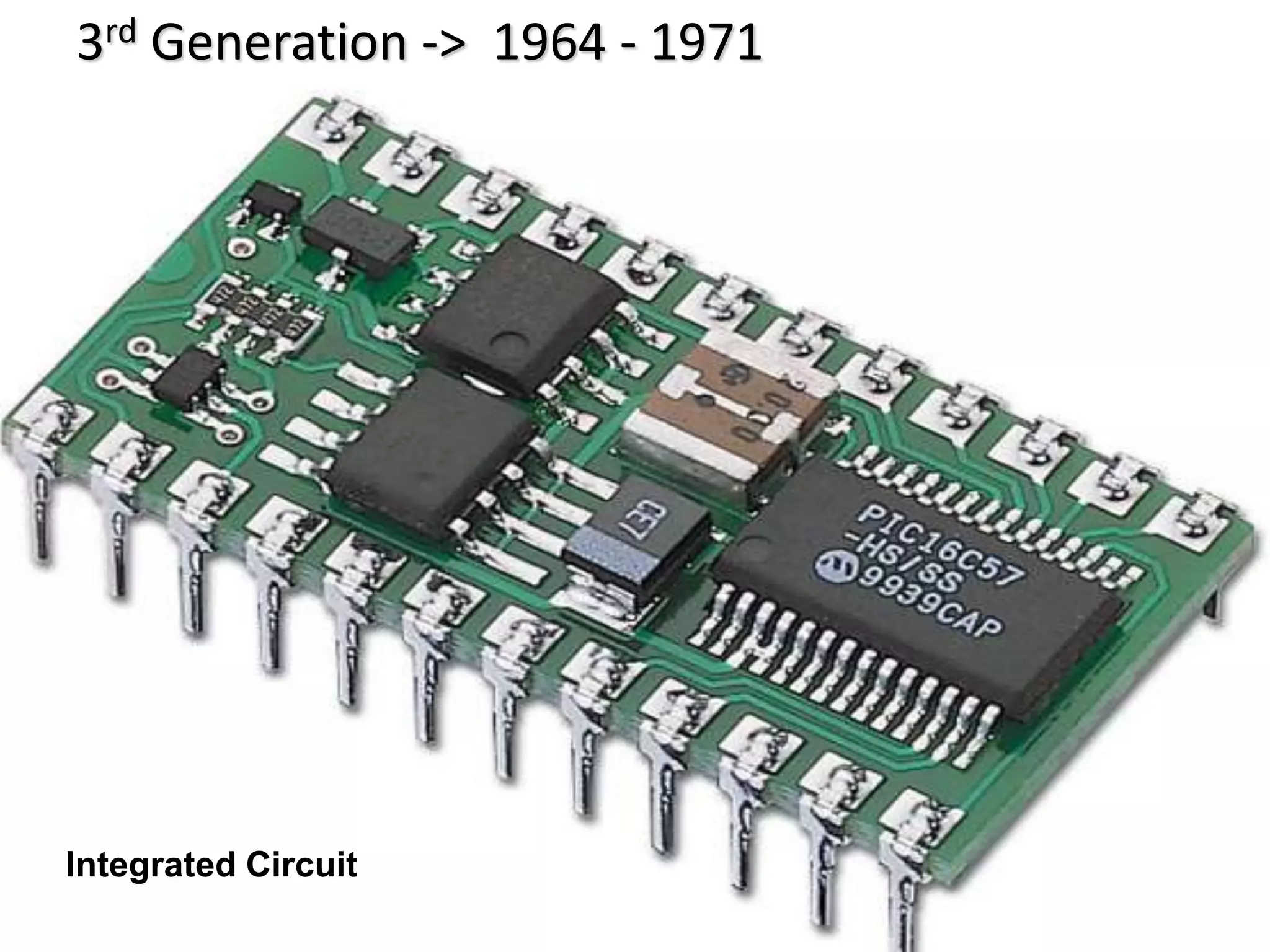
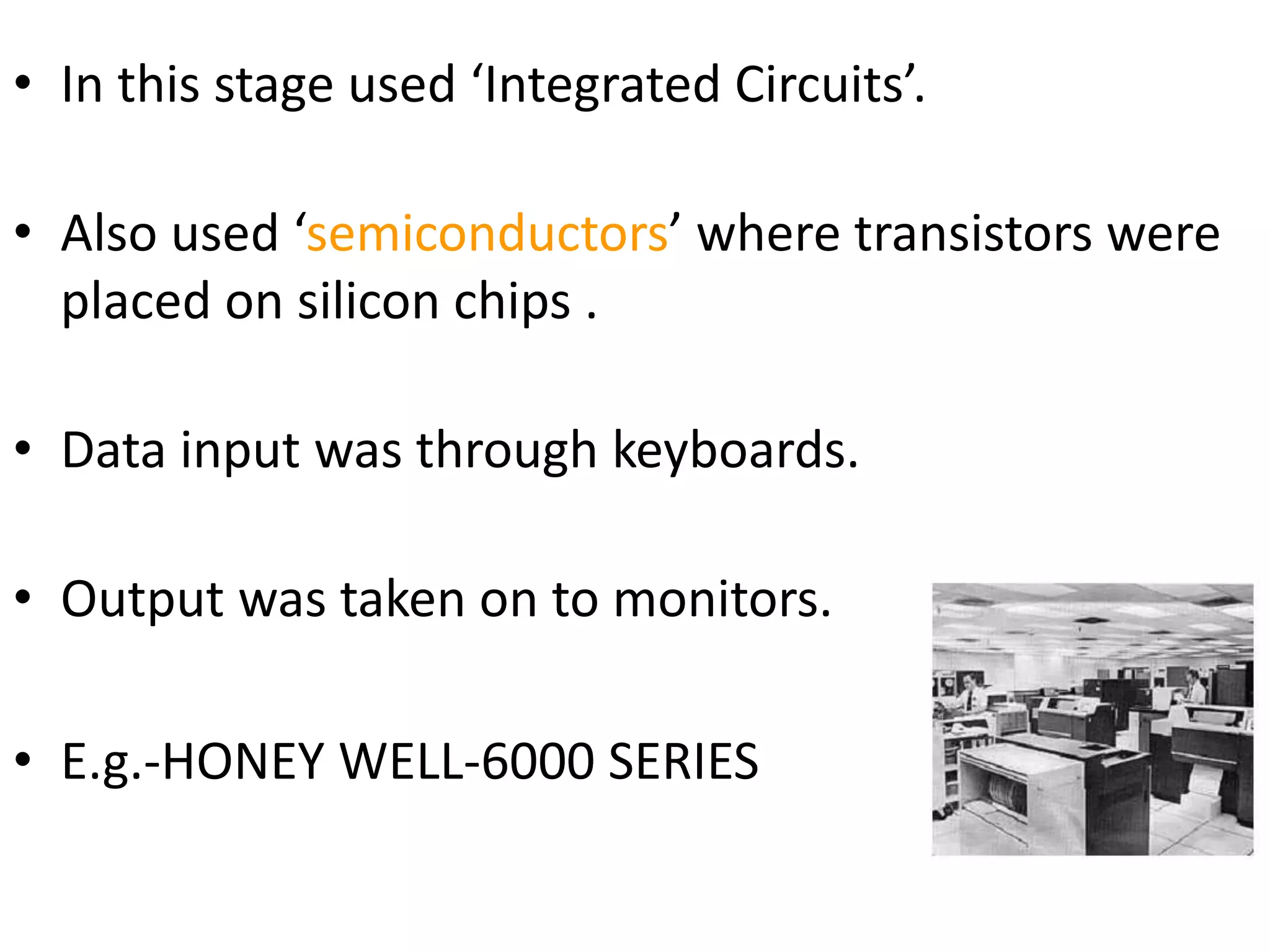
The document discusses the five generations of computers from 1940 to present. The 1st generation used vacuum tubes and were large, expensive to operate, and could only solve one problem at a time. The 2nd generation used transistors, which made computers smaller, faster, cheaper, and more energy efficient. The 3rd generation used integrated circuits and silicon chips, allowing input via keyboards and output to monitors. The 4th generation used microprocessors and were more user friendly with graphical interfaces. Current 5th generation computers are still in development and focus on artificial intelligence.