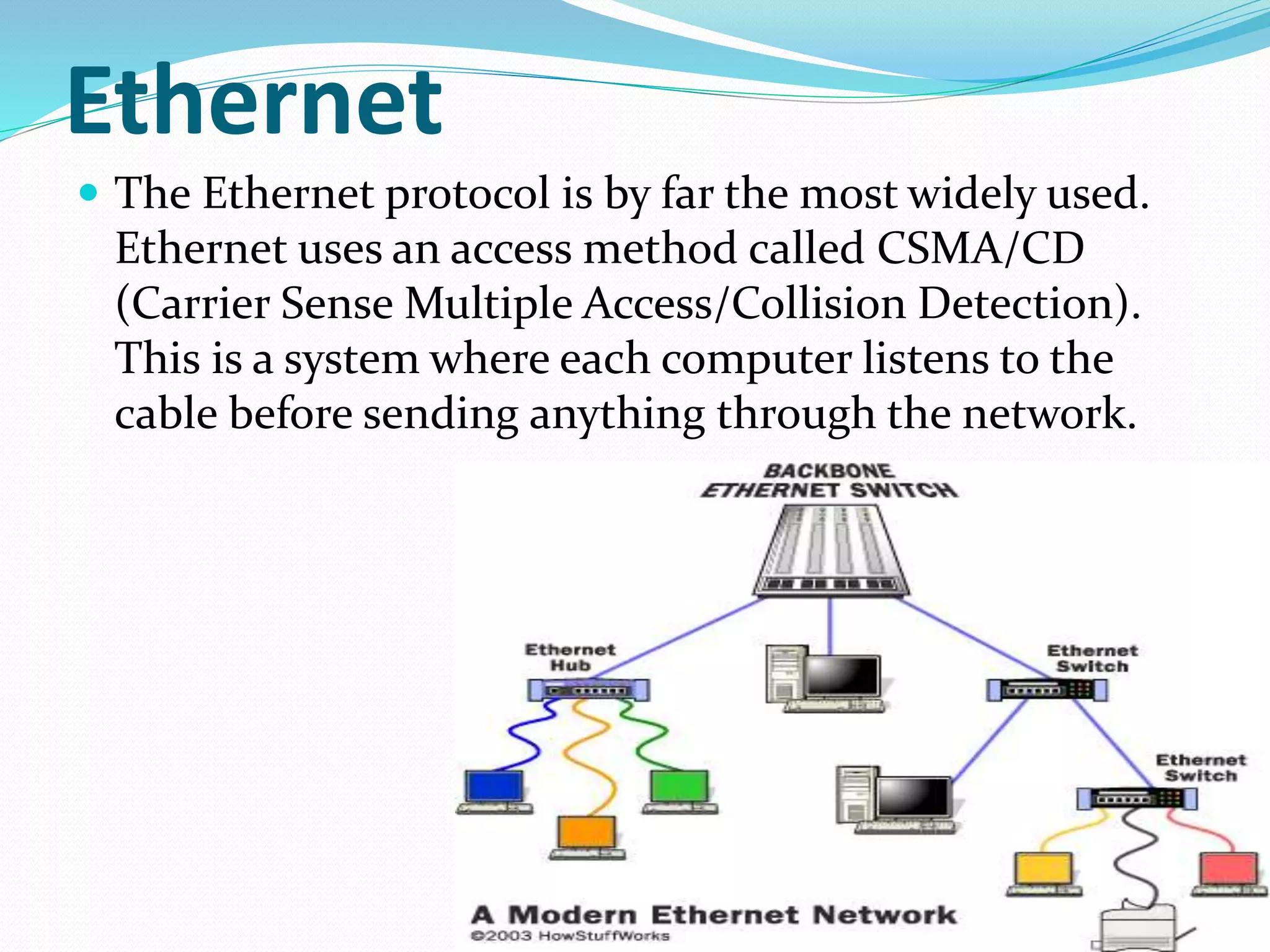
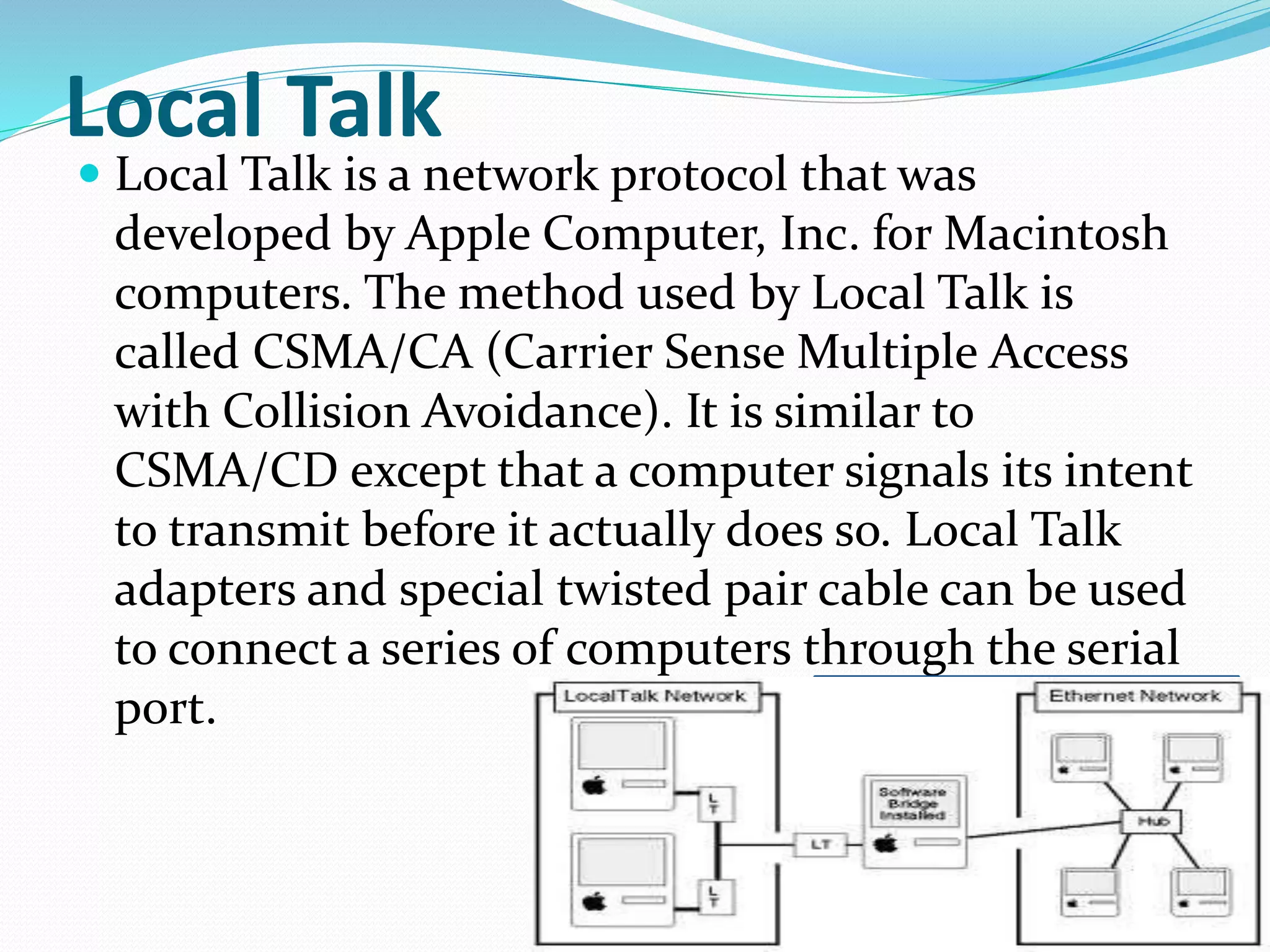
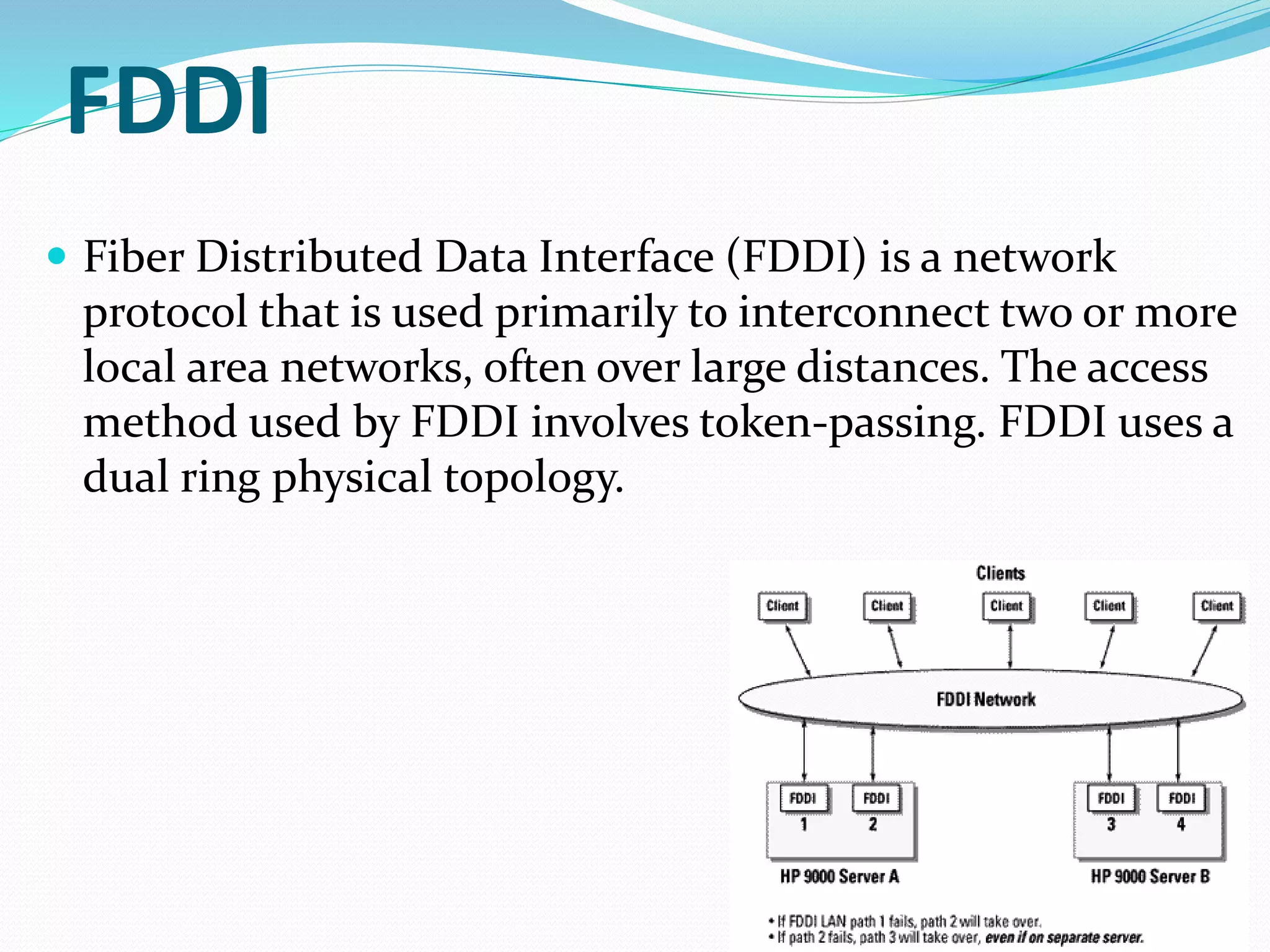
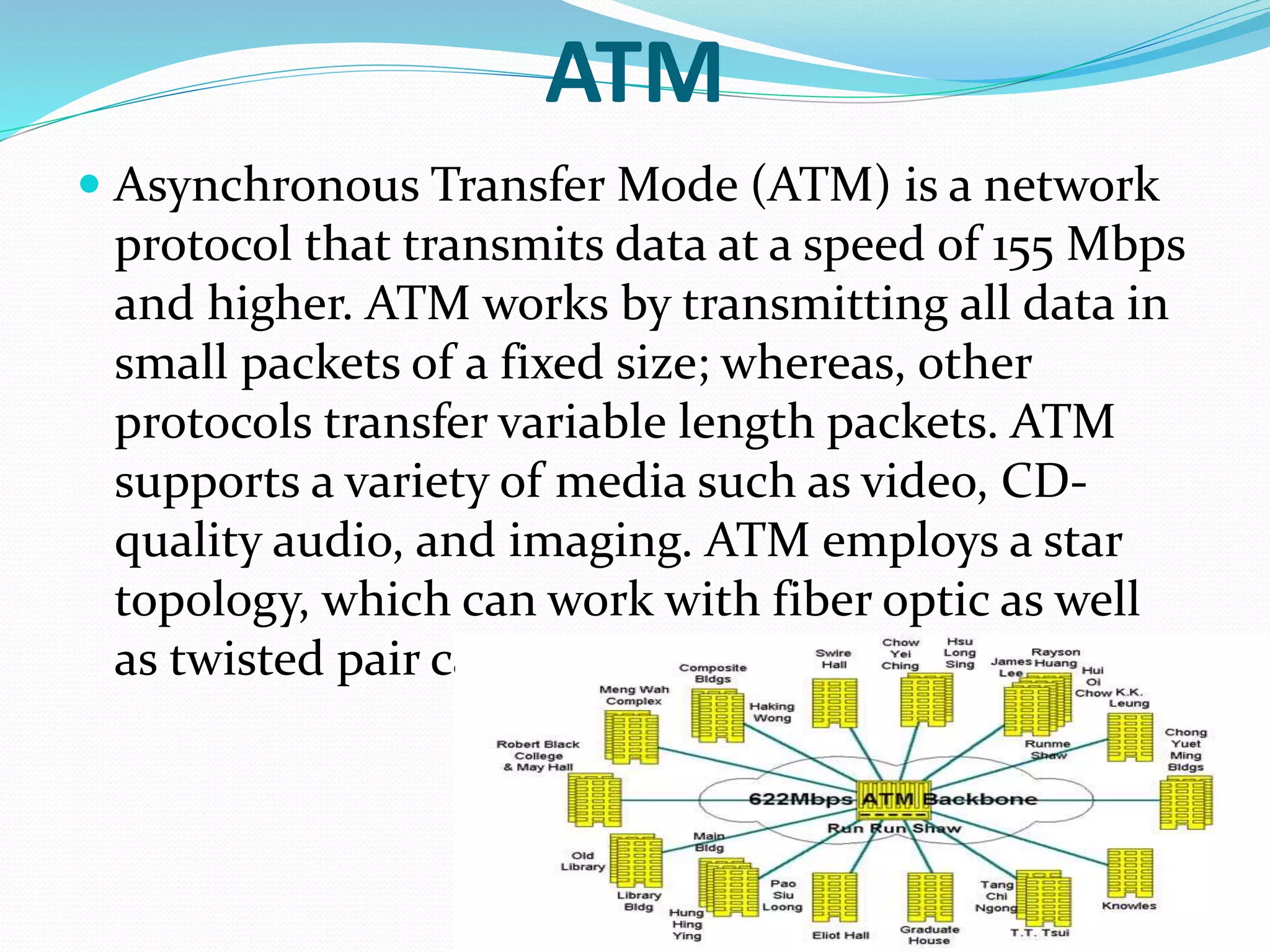
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on network protocols. It defines what a protocol is and discusses some common network protocols like TCP, UDP, HTTP, and Ethernet. It also covers different types of network protocols including Ethernet, LocalTalk, Token Ring, FDDI, and ATM. Benefits of using network protocols include standardized communication between hardware and software. Protocols are needed for computers to effectively communicate over a network.