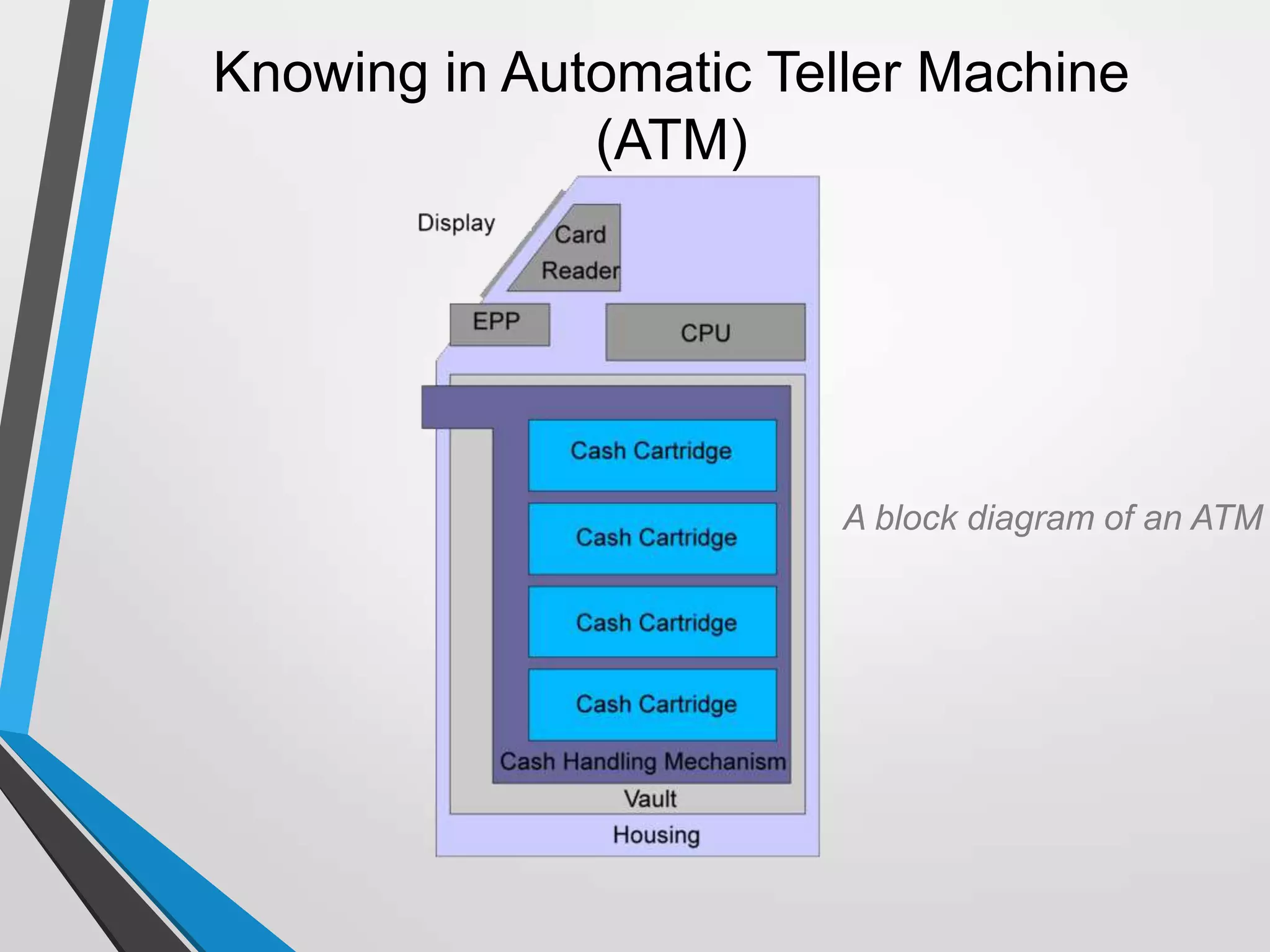
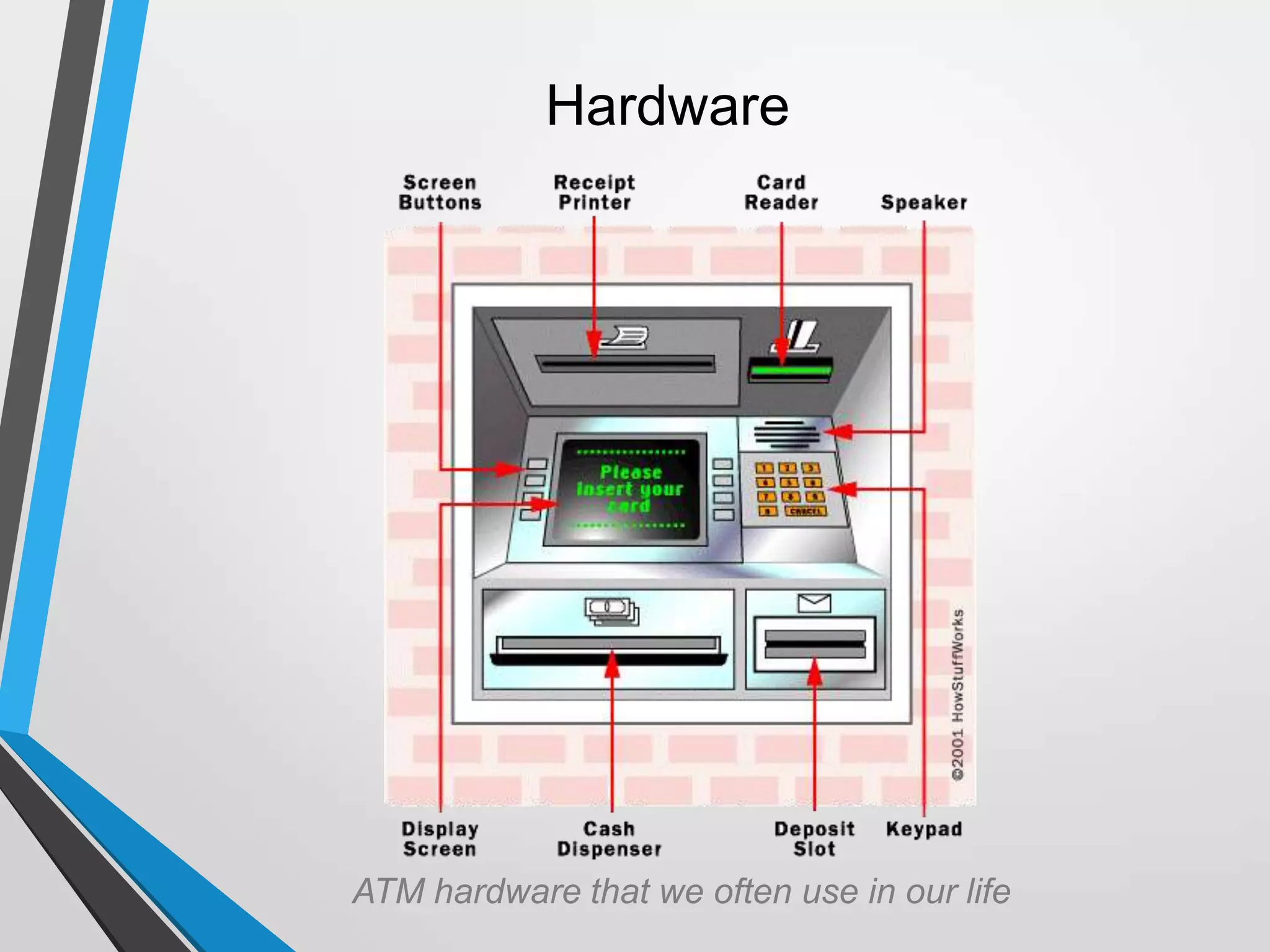
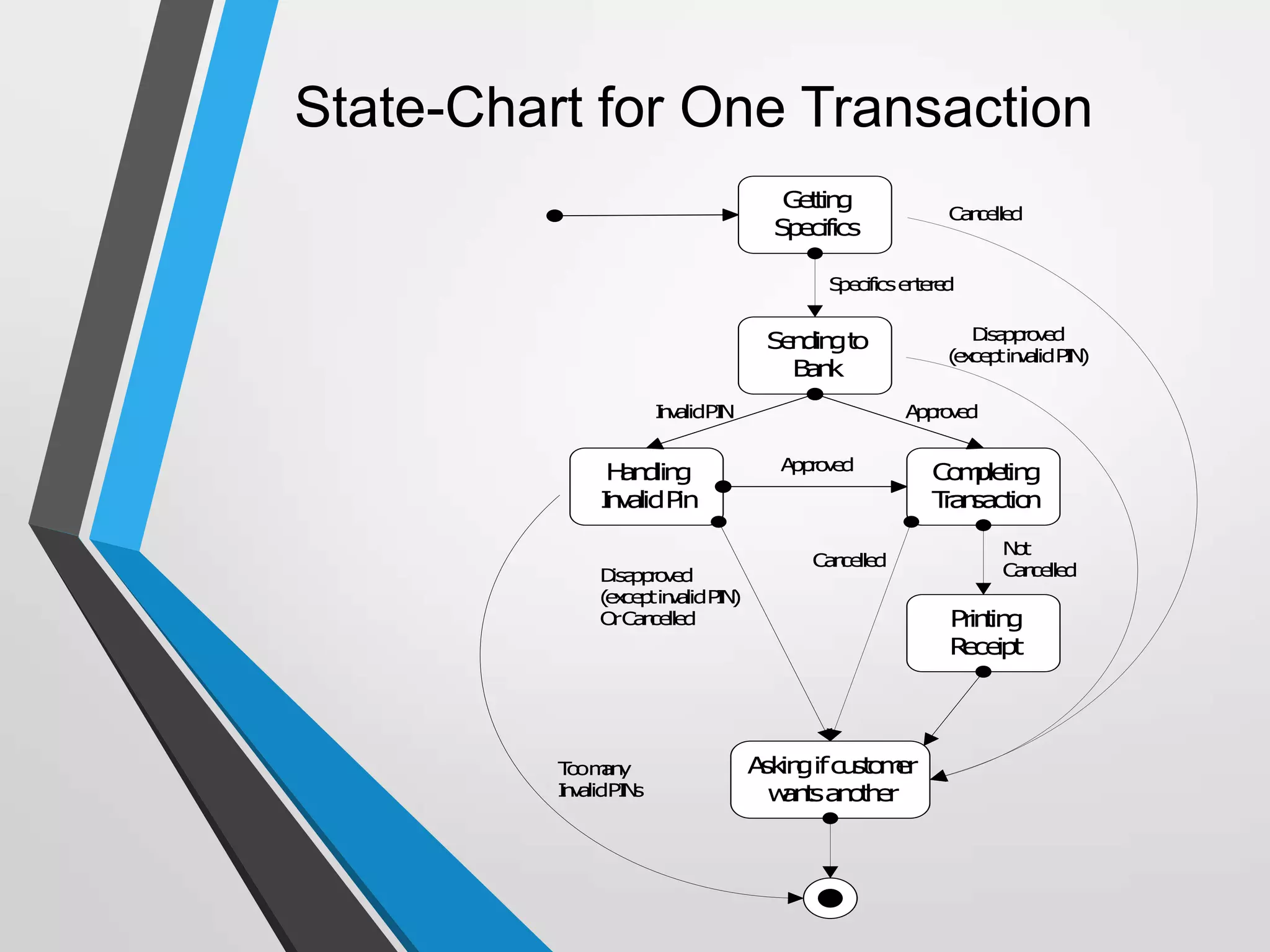
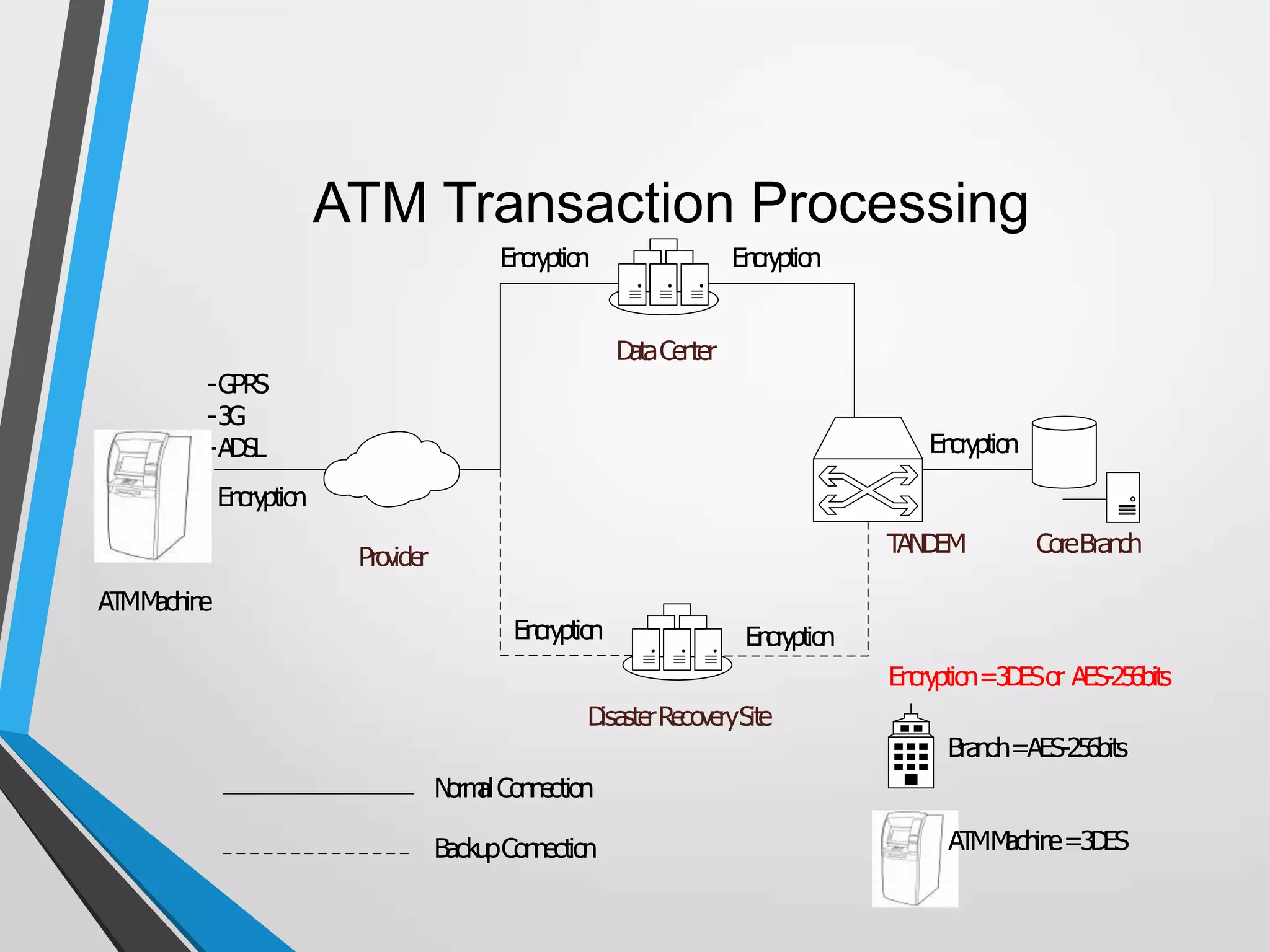
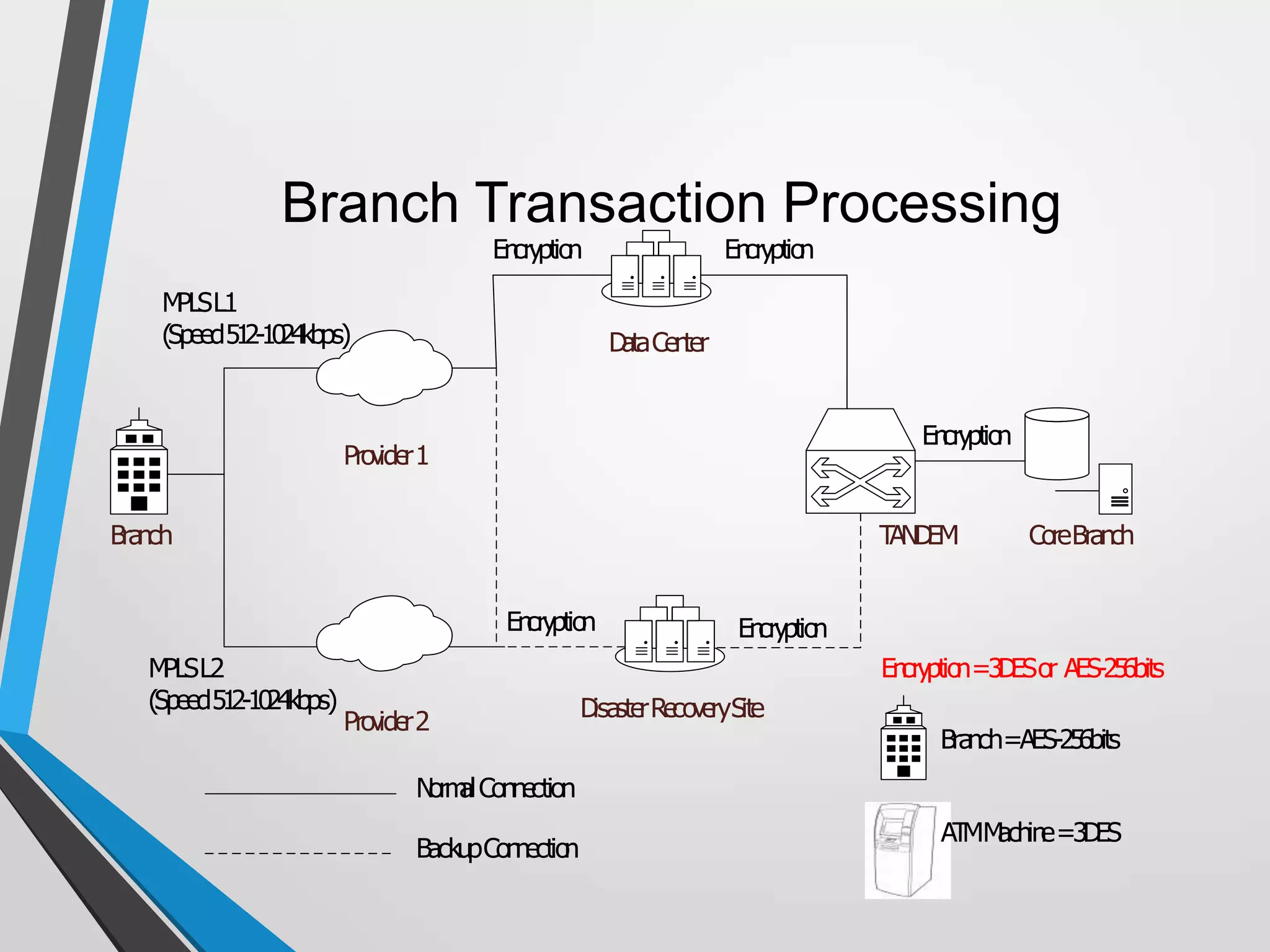
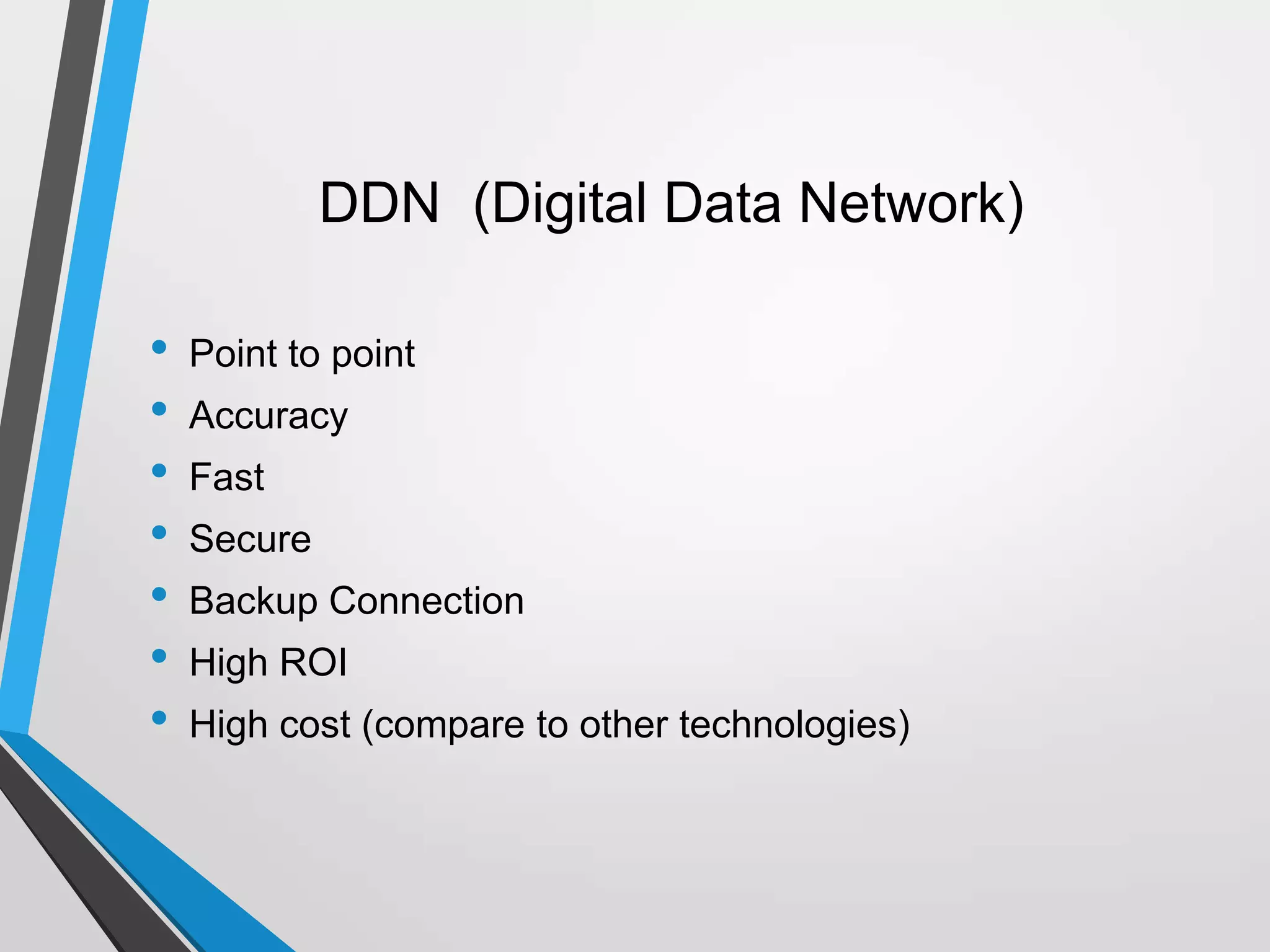
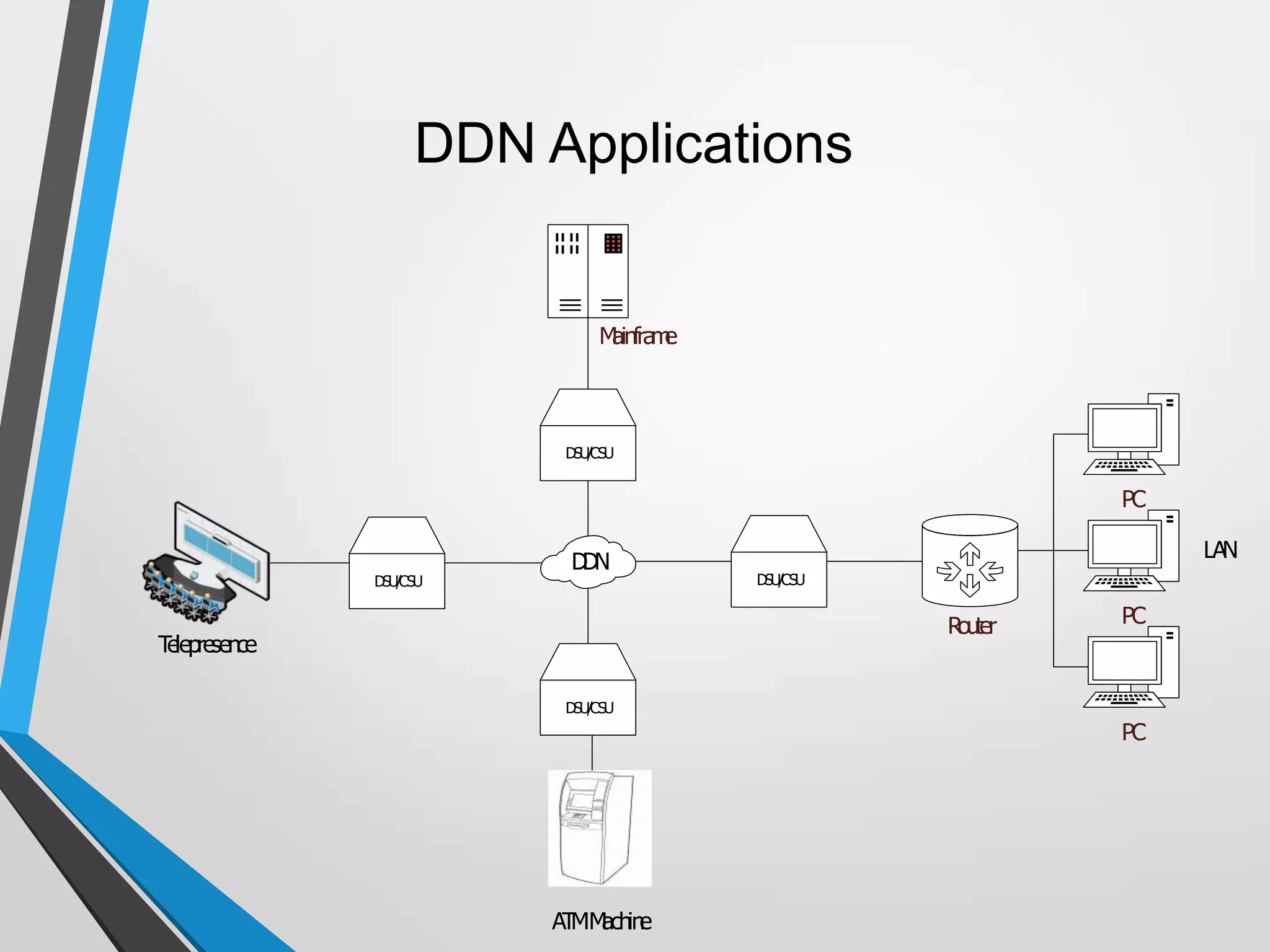
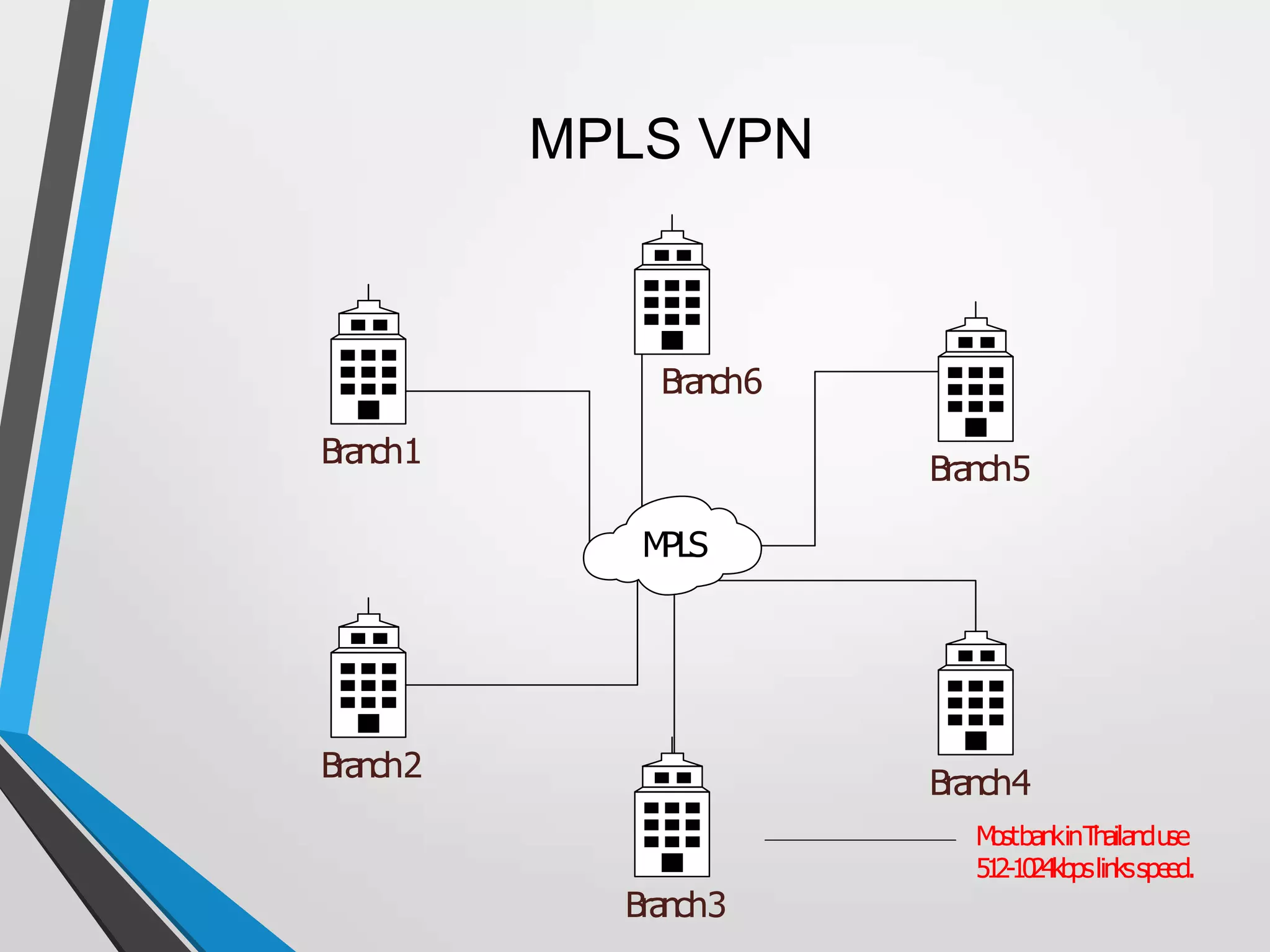
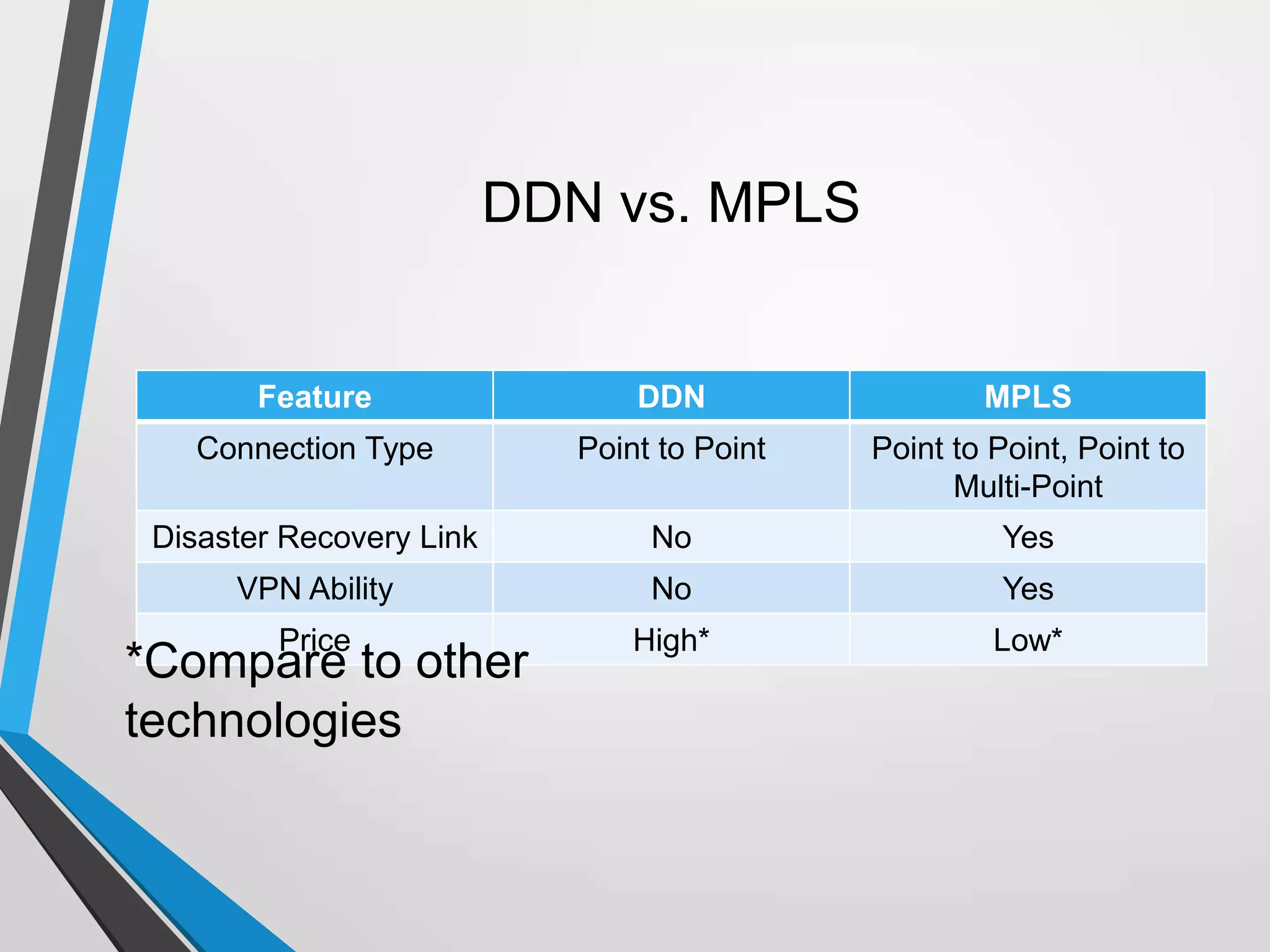
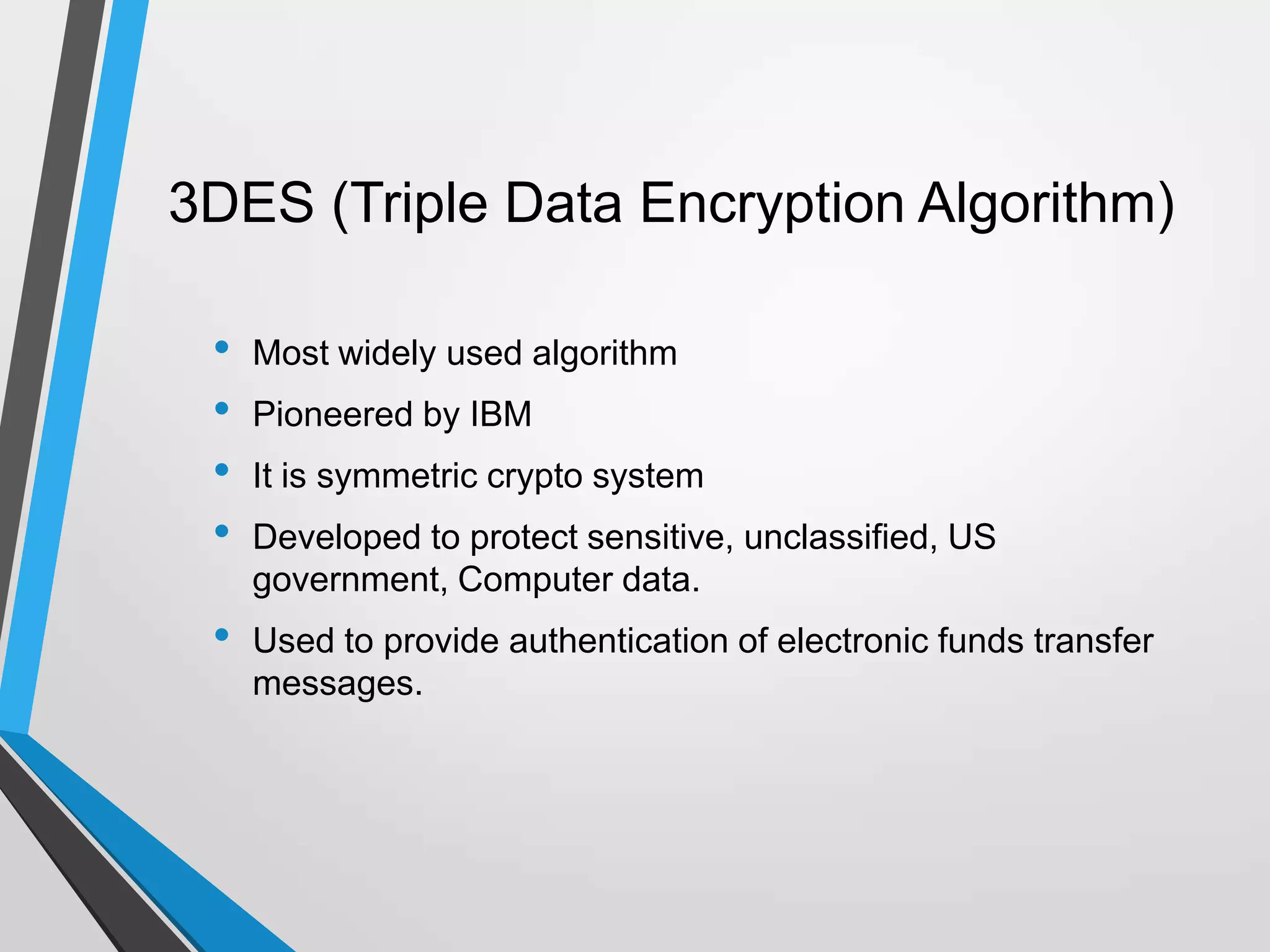
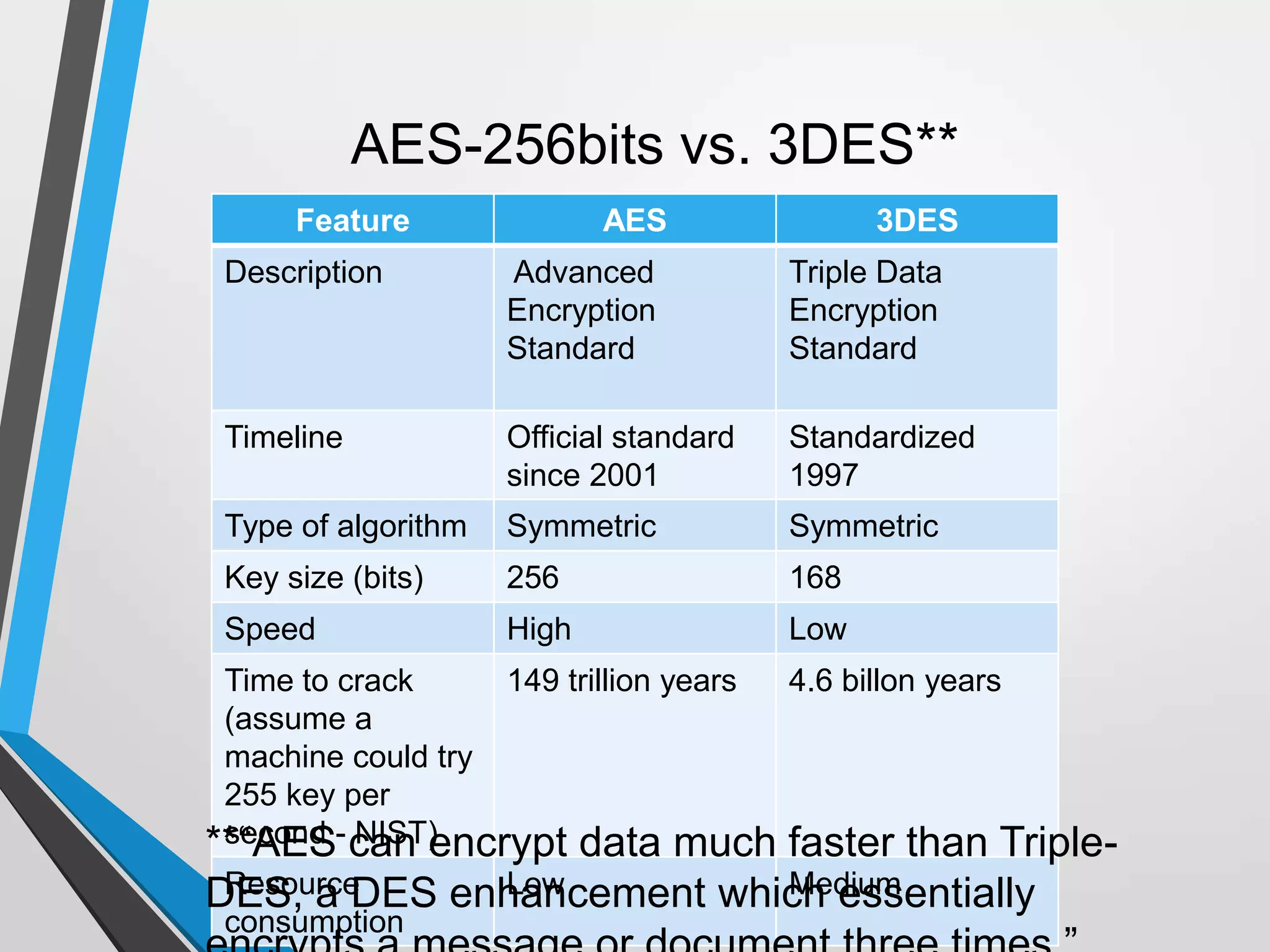
The document discusses the architecture and communication systems of Automatic Teller Machines (ATMs), including their hardware, software, and encryption methods. It contrasts different technologies like DDN and MPLS for ATM connectivity, highlighting their features and costs, as well as comparing encryption standards AES-256 and 3DES. The document emphasizes the importance of security in ATM transactions and the efficiency of various data transmission methods.