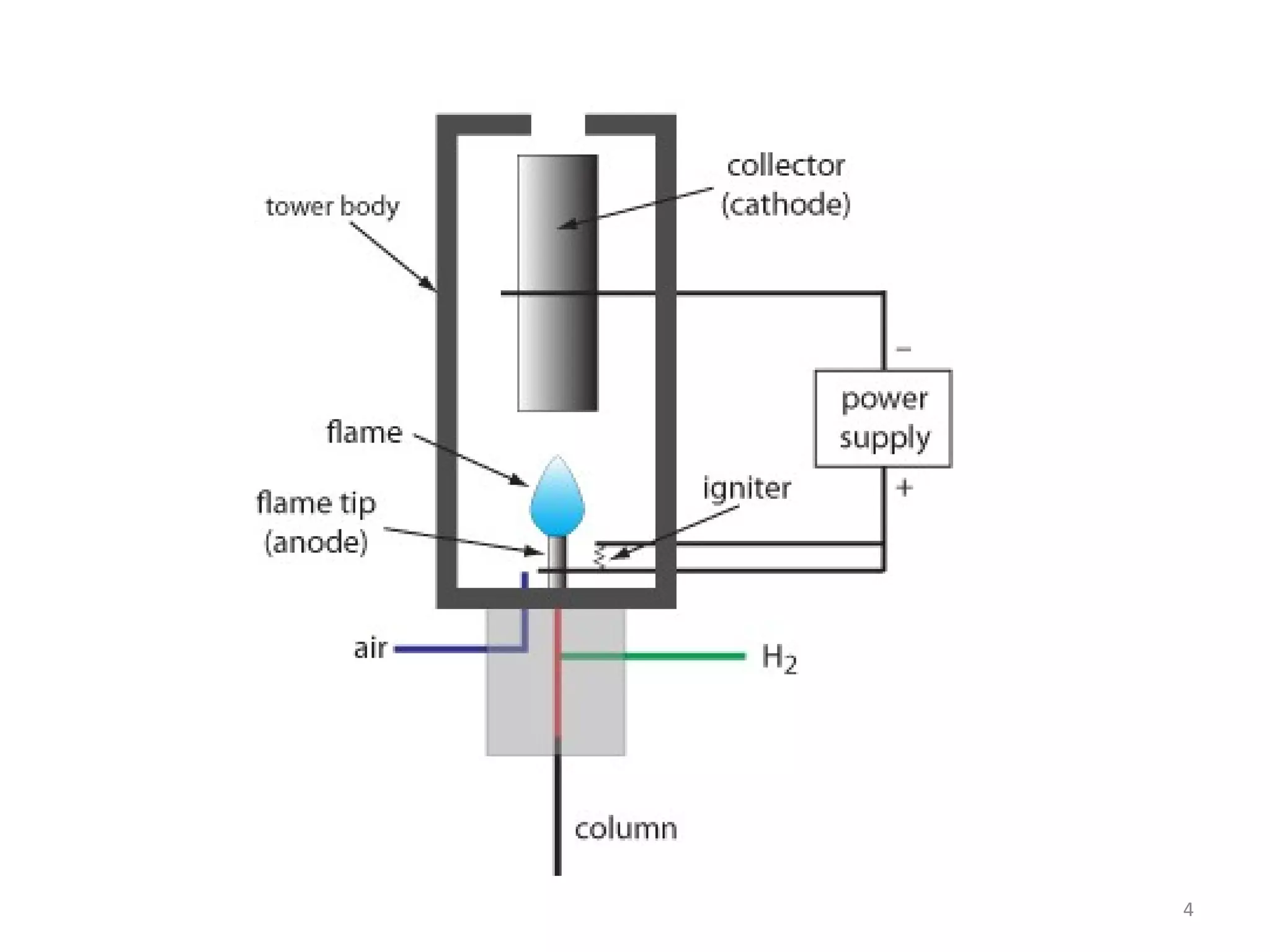
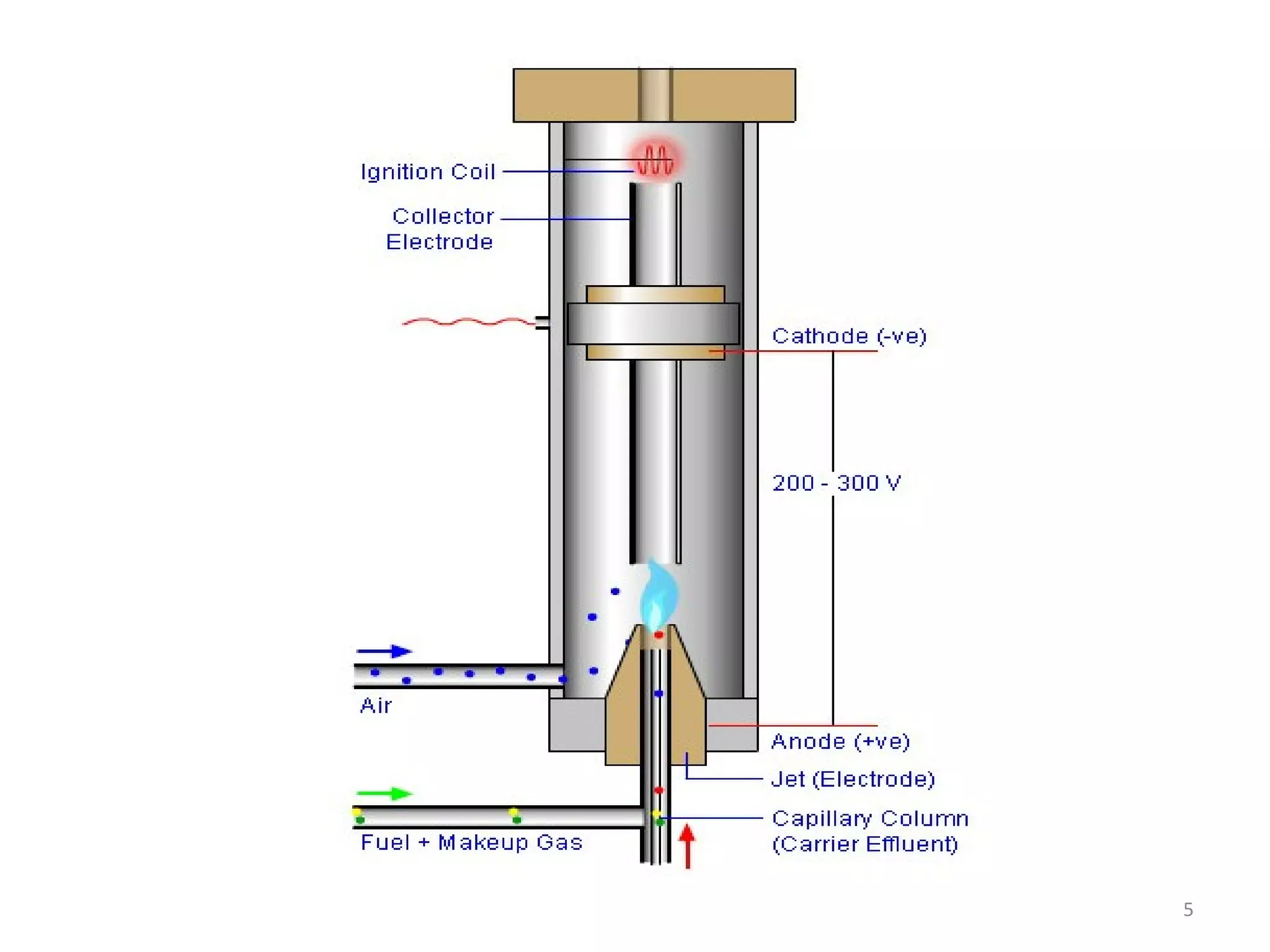
The document discusses the flame ionization detector (FID). It explains that the FID is one of the most sensitive and reliable detectors for gas analysis. It works by ionizing solutes in a flame, with electrons emitted attracted to a positive electrode to produce a current. The FID is responsive only to organic compounds with carbon atoms, making it useful for analyzing volatile solutes in water without pretreatment. It also lists key characteristics of the FID like being rugged, sensitive, having a wide dynamic range, and being destructive. Example applications mentioned include analyzing purge gases and impurities in gas supplies for various industrial processes.