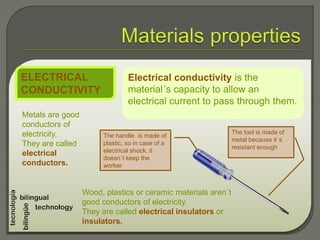
This document discusses various properties of materials, grouping them into physical properties, chemical properties, technological properties, and ecological properties. It provides examples of different materials and their properties related to density, opacity, magnetism, permeability, porosity, hardness, tenacity, elasticity, ductility, weldability, fusibility, thermal and electrical conductivity, acoustic conductivity, recyclability, biodegradability, and toxicity.