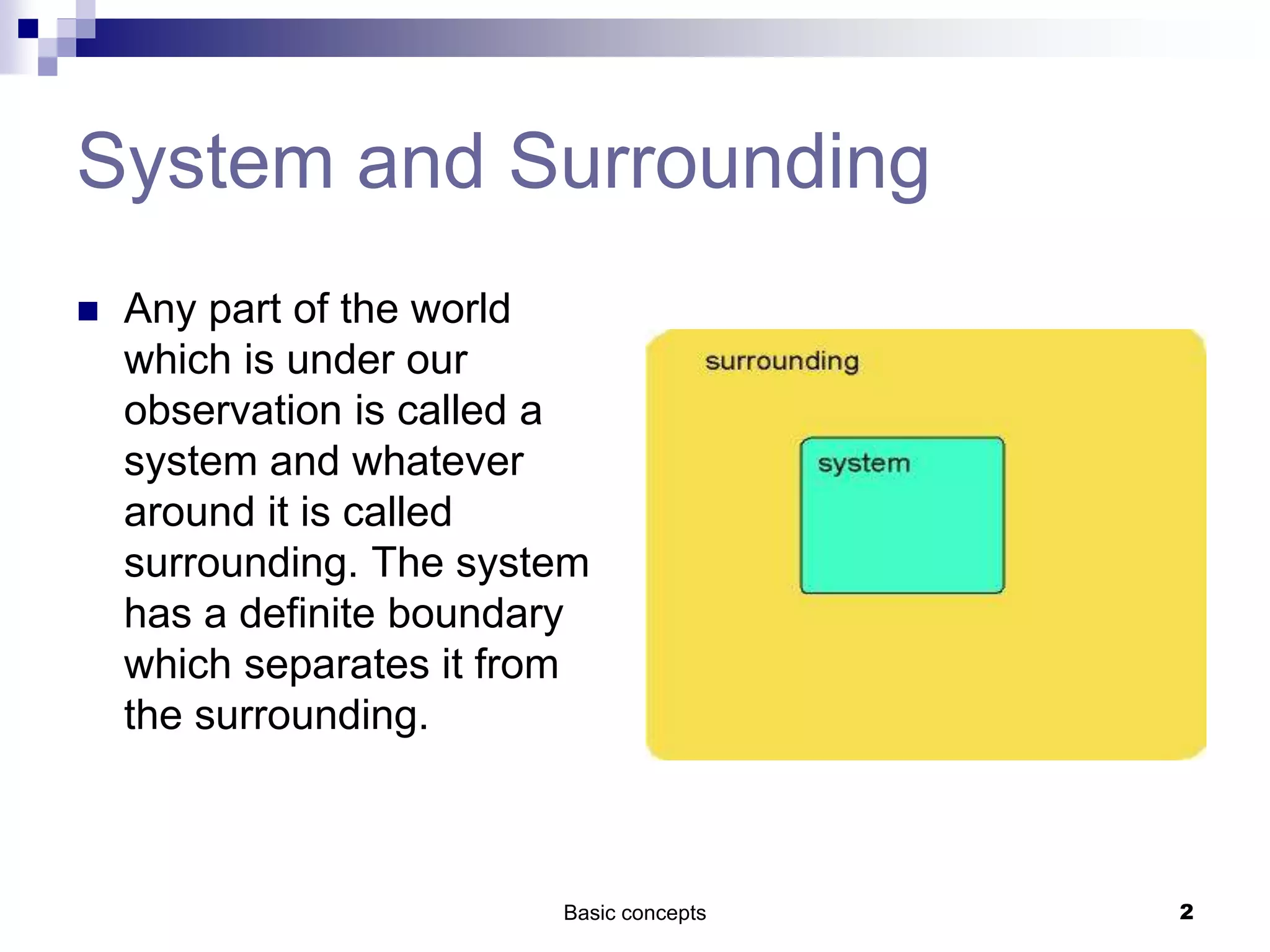
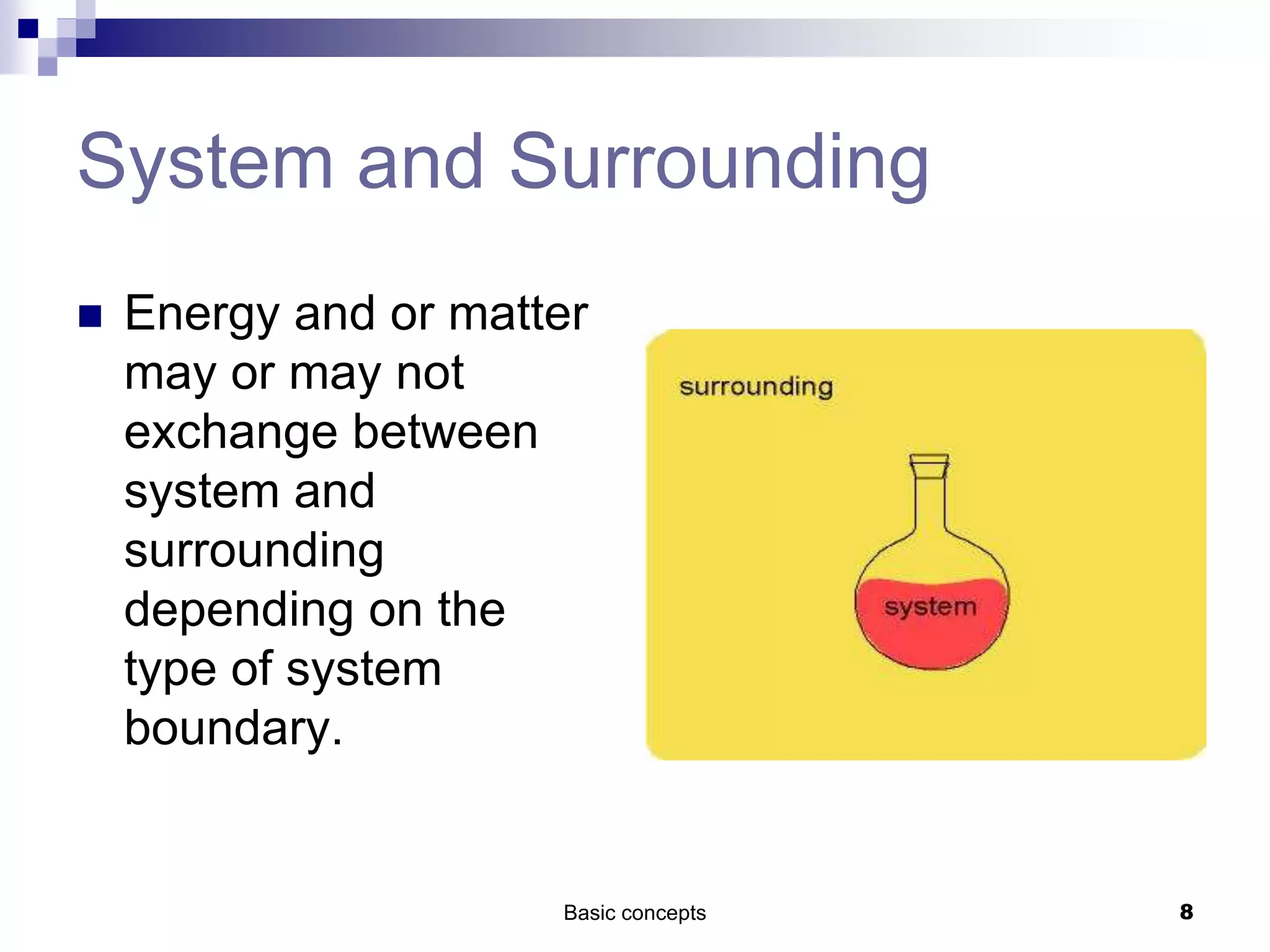
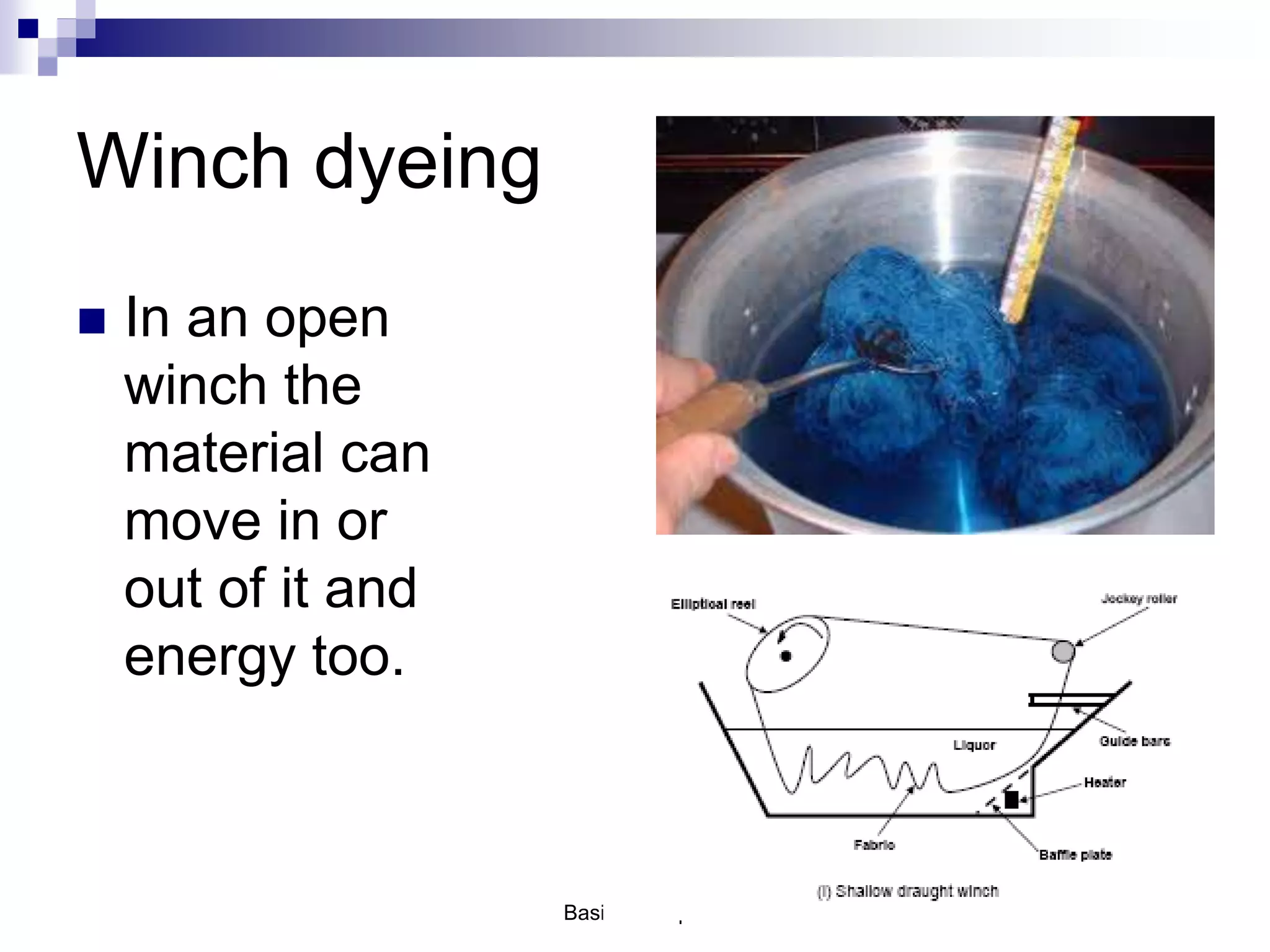
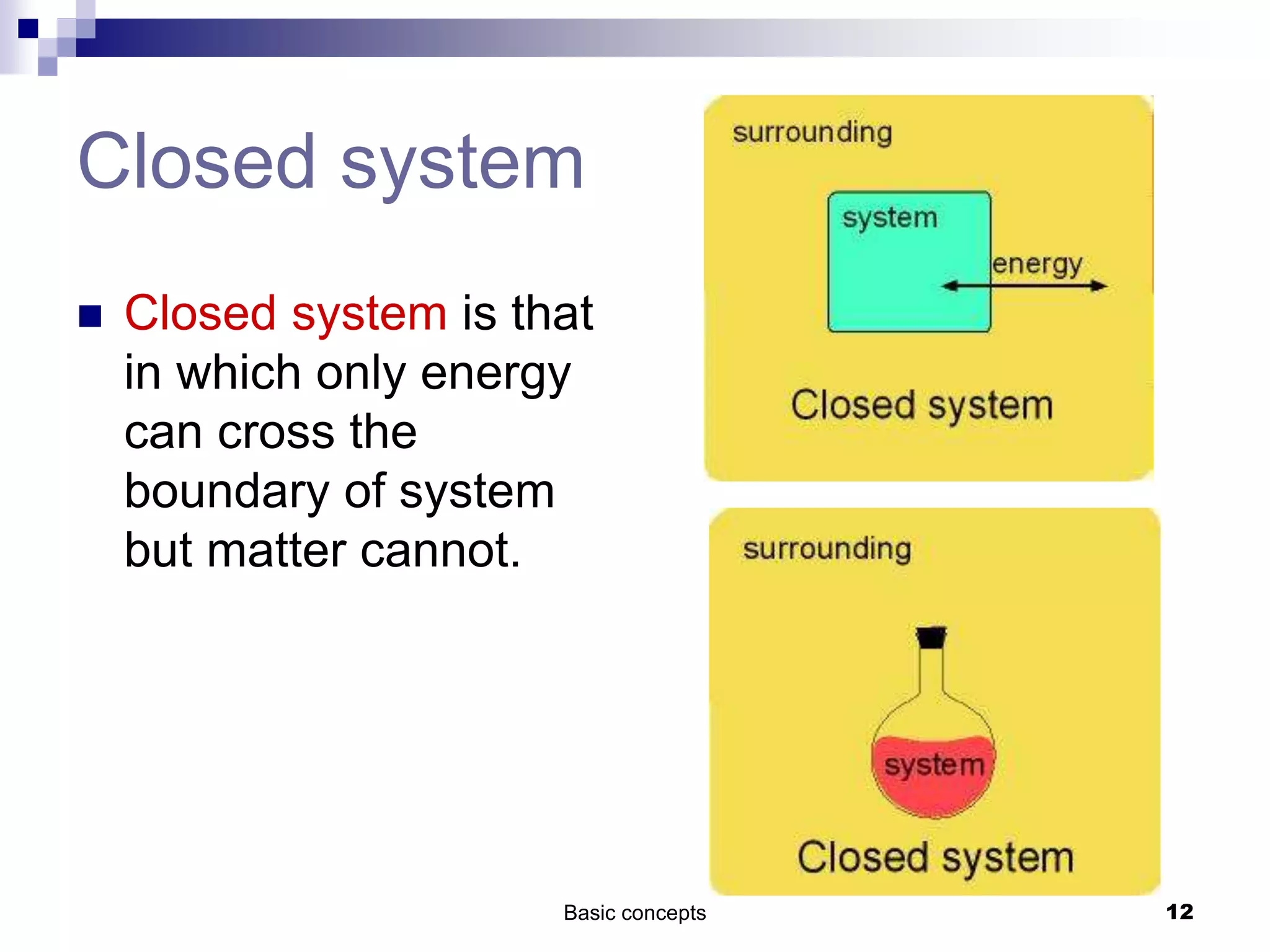
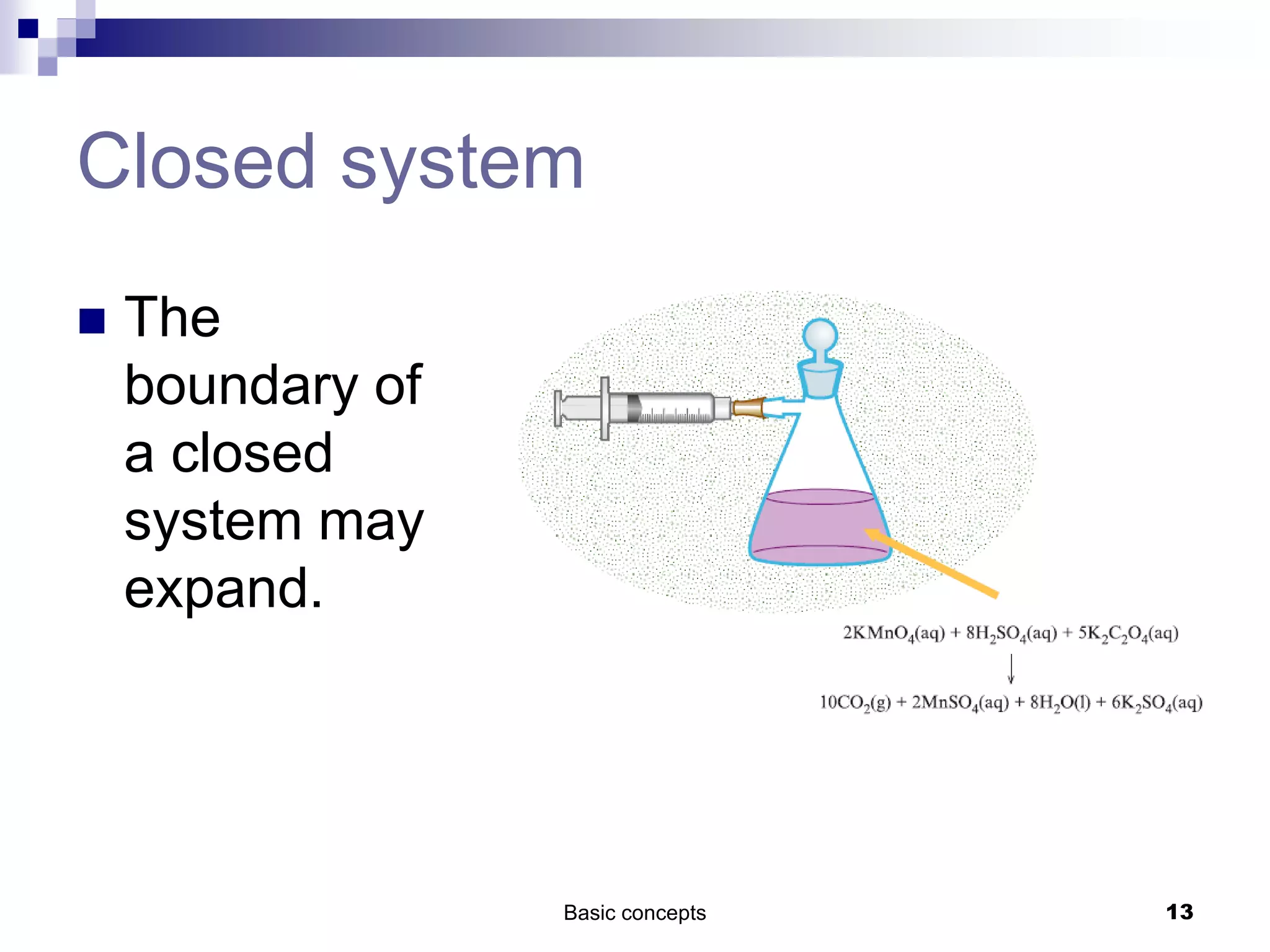
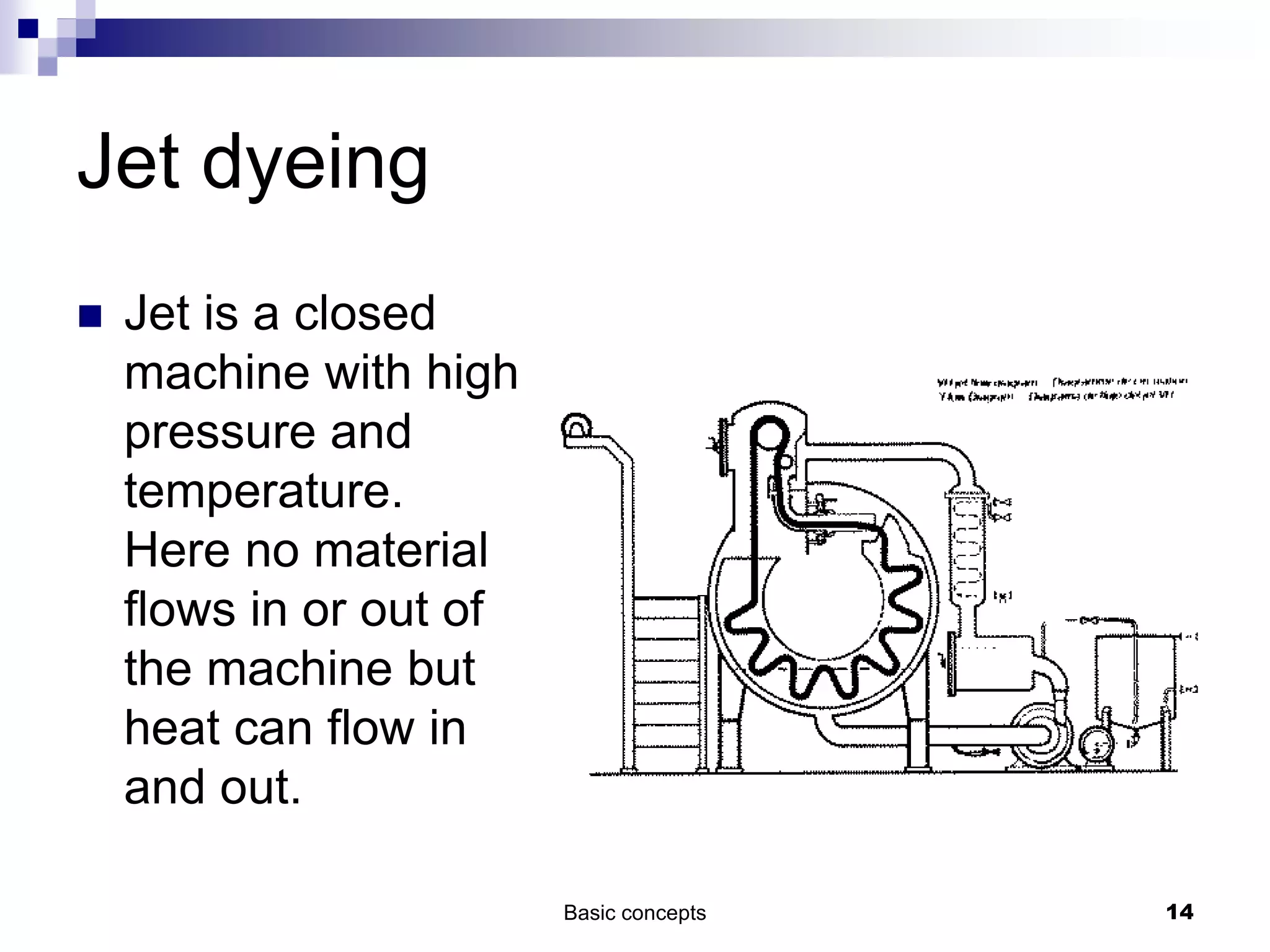
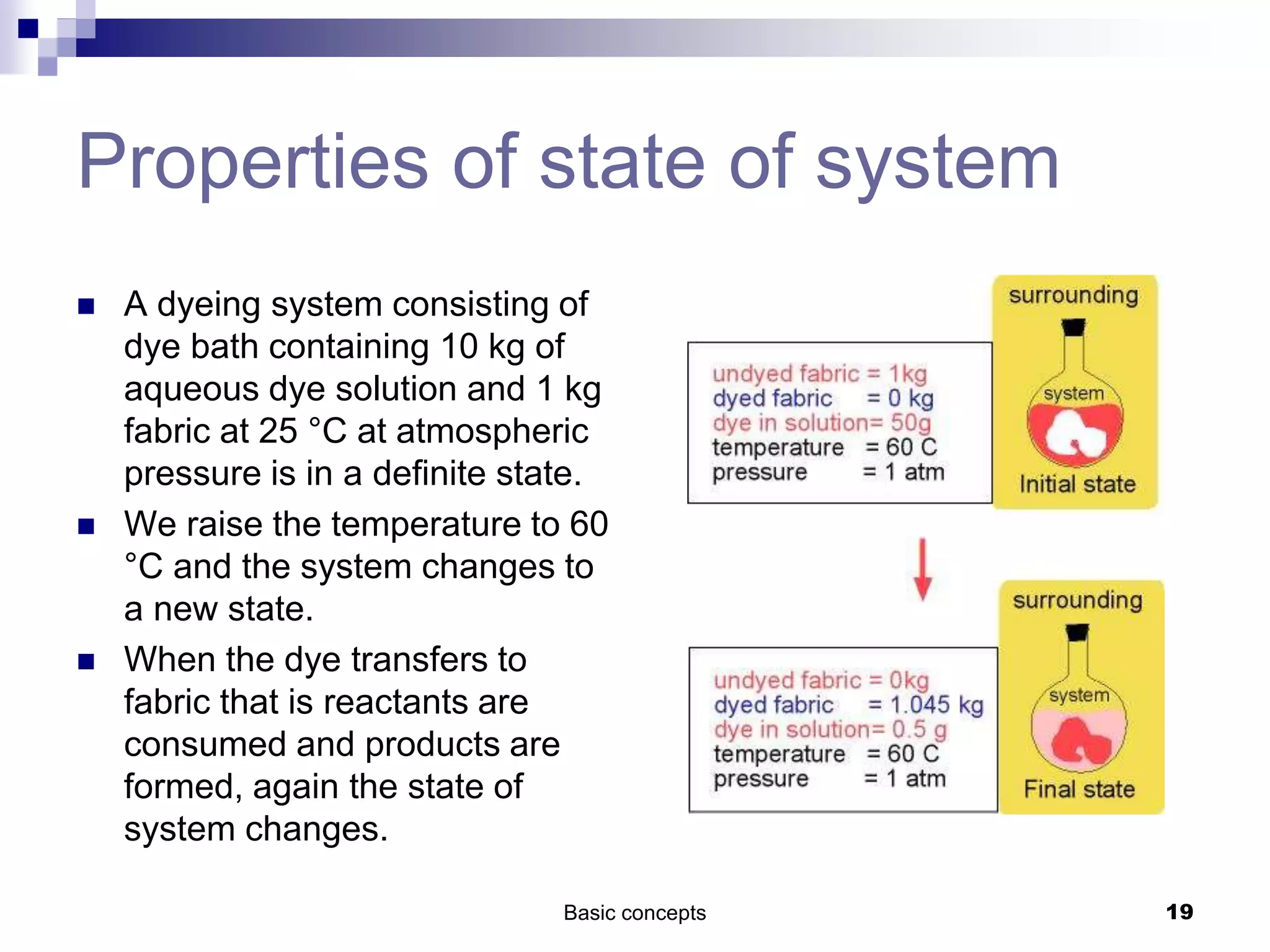
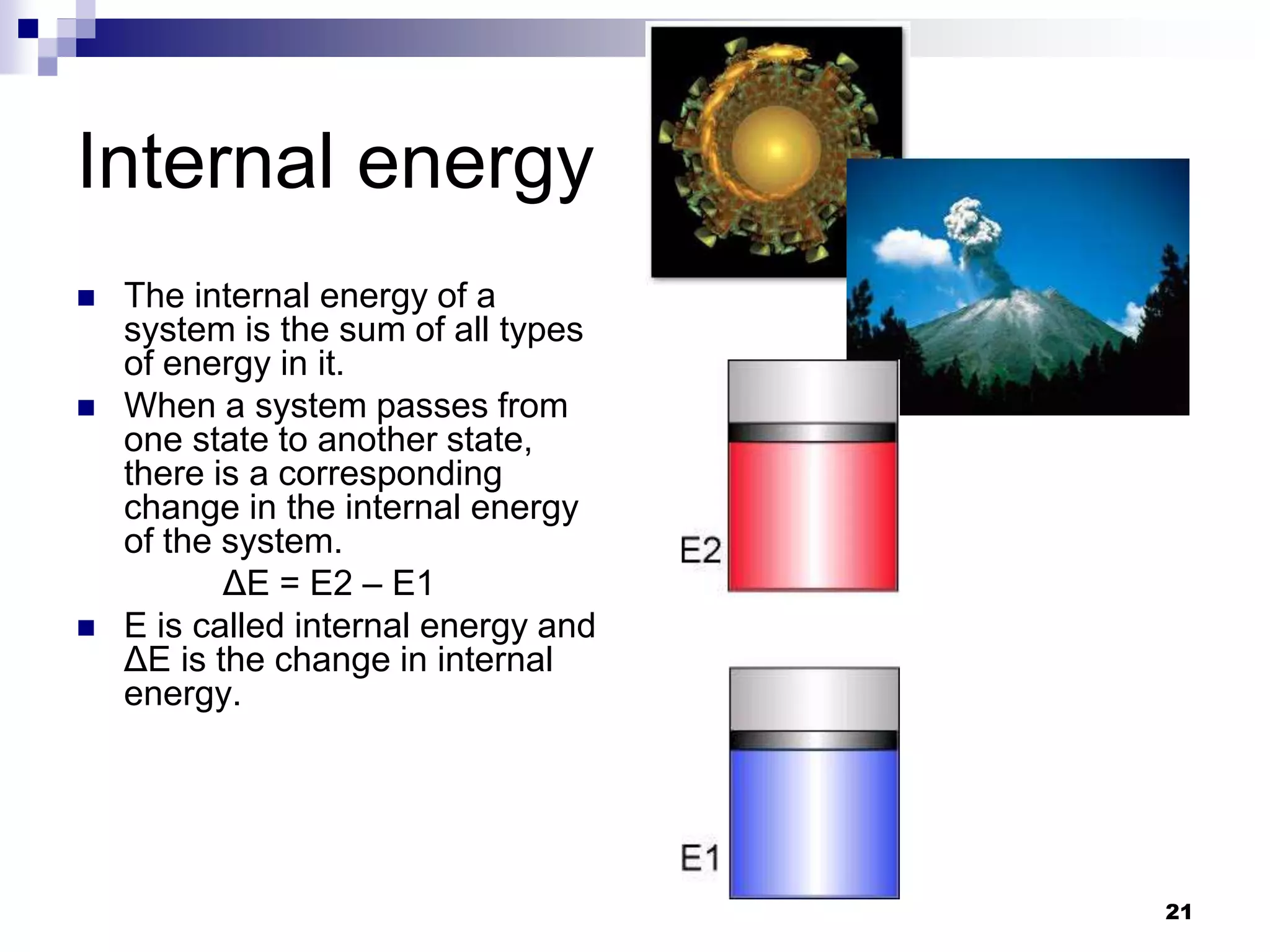
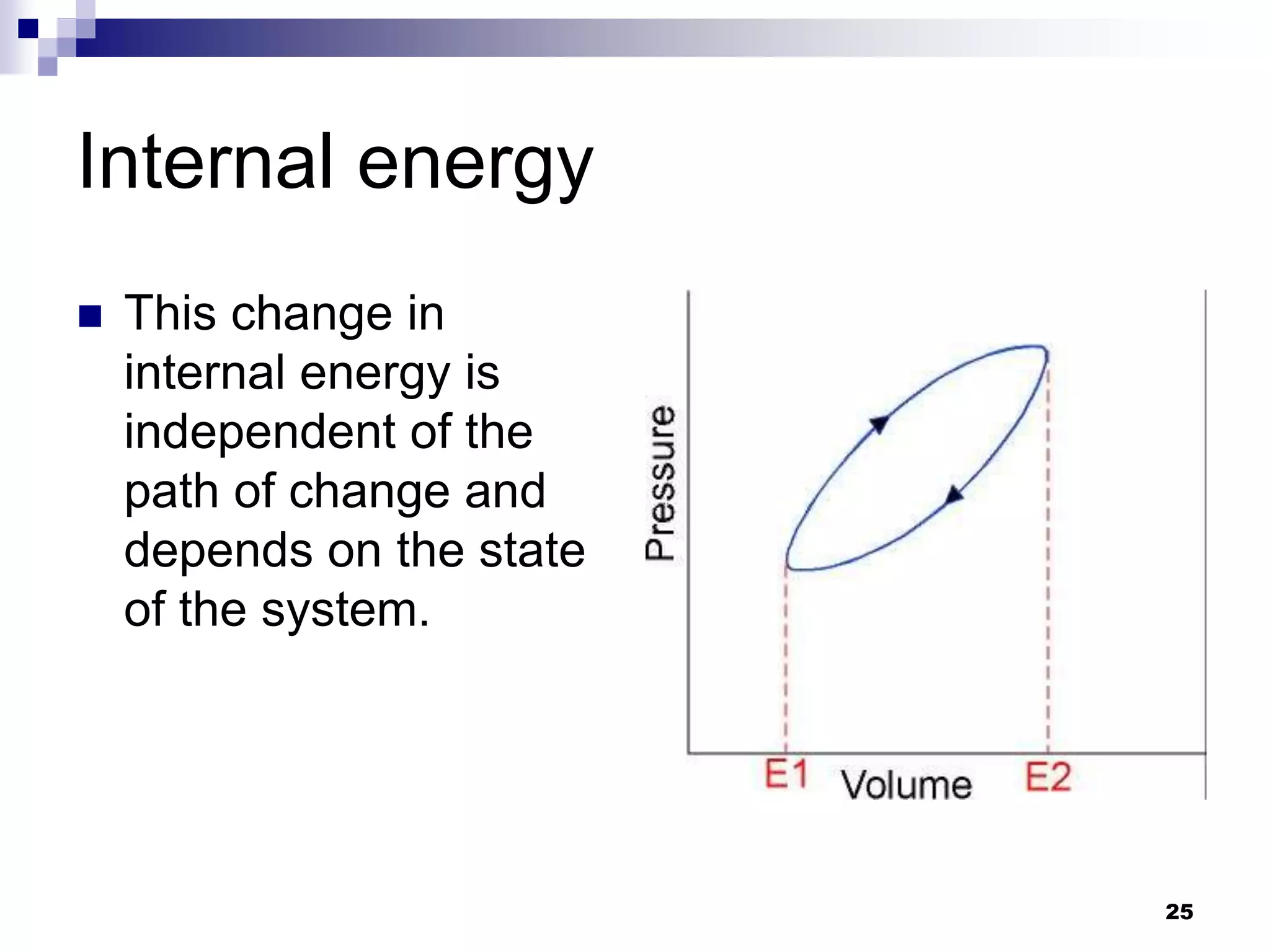
The document discusses systems, surroundings, and various thermodynamic concepts. It defines a system as any part of the world under observation with a boundary separating it from its surroundings. Systems can exchange both energy and matter with surroundings (open), just energy (closed), or neither (isolated). The state of a system is defined by properties like temperature, pressure, and volume. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved and can change forms but not be created or destroyed. Internal energy depends on the state of the system, not the path to get there. Heat and work are path dependent terms related to changes in internal energy. Enthalpy accounts for pressure-volume work. Specific heat is the energy to raise 1g