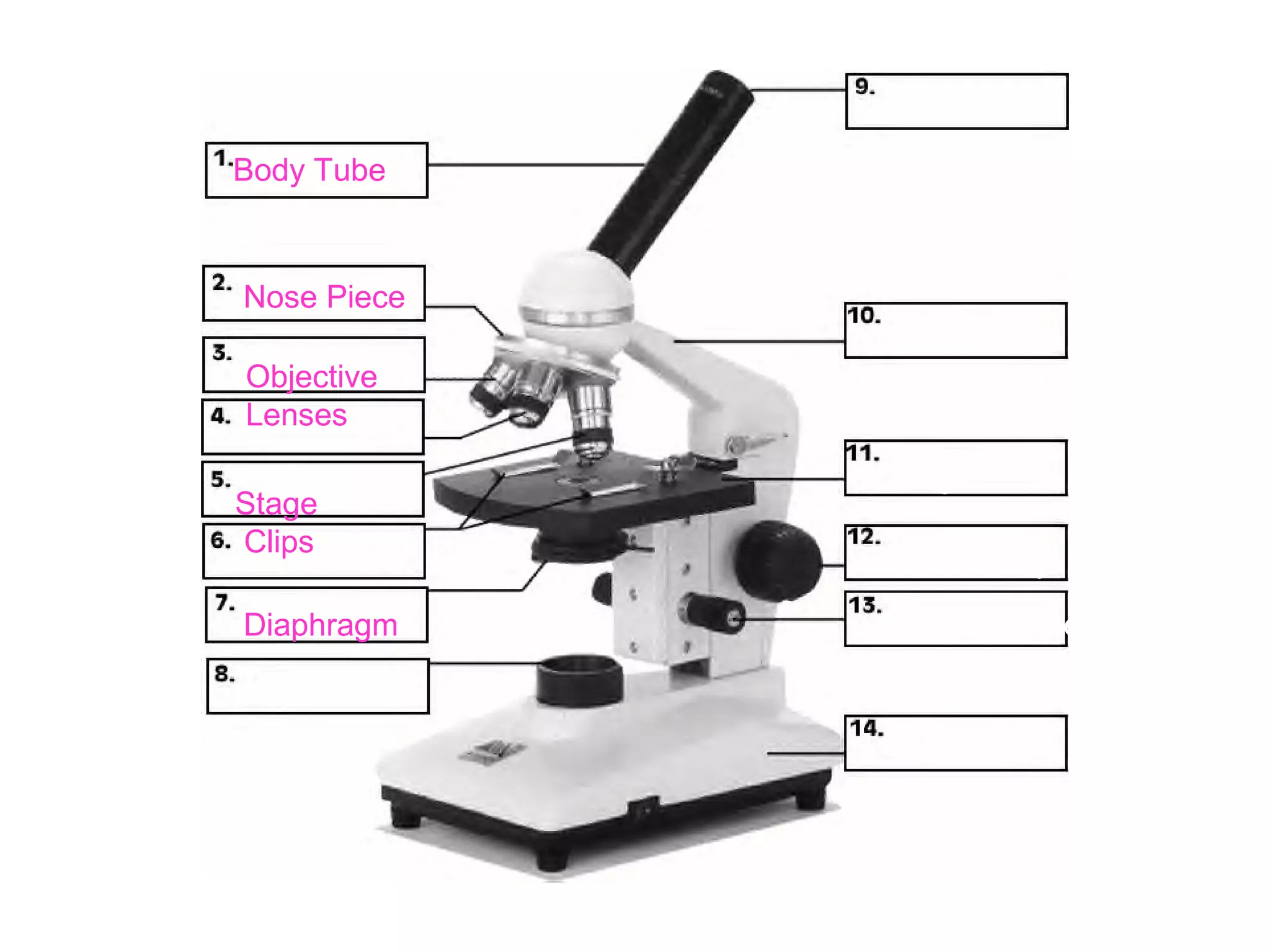
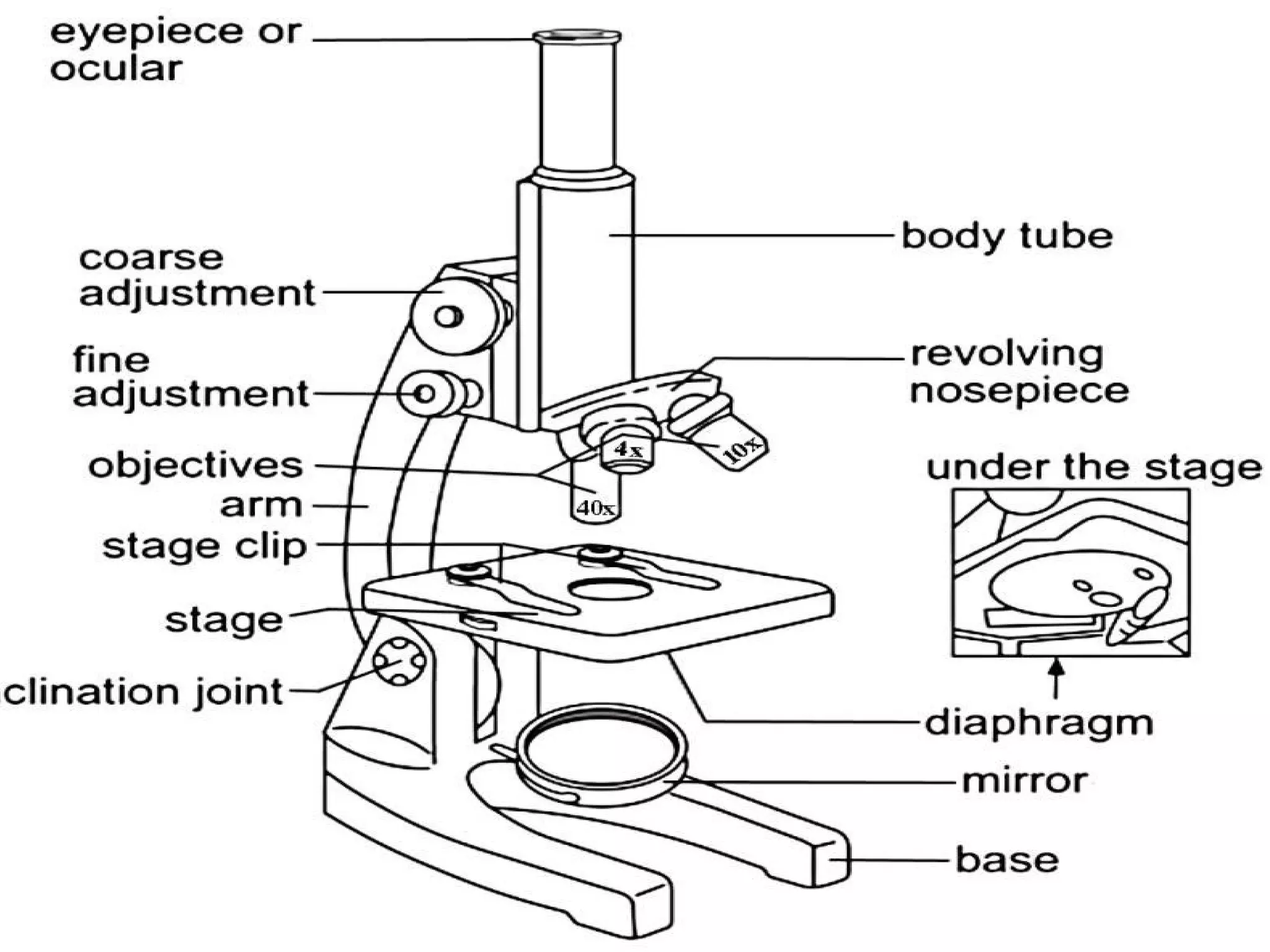
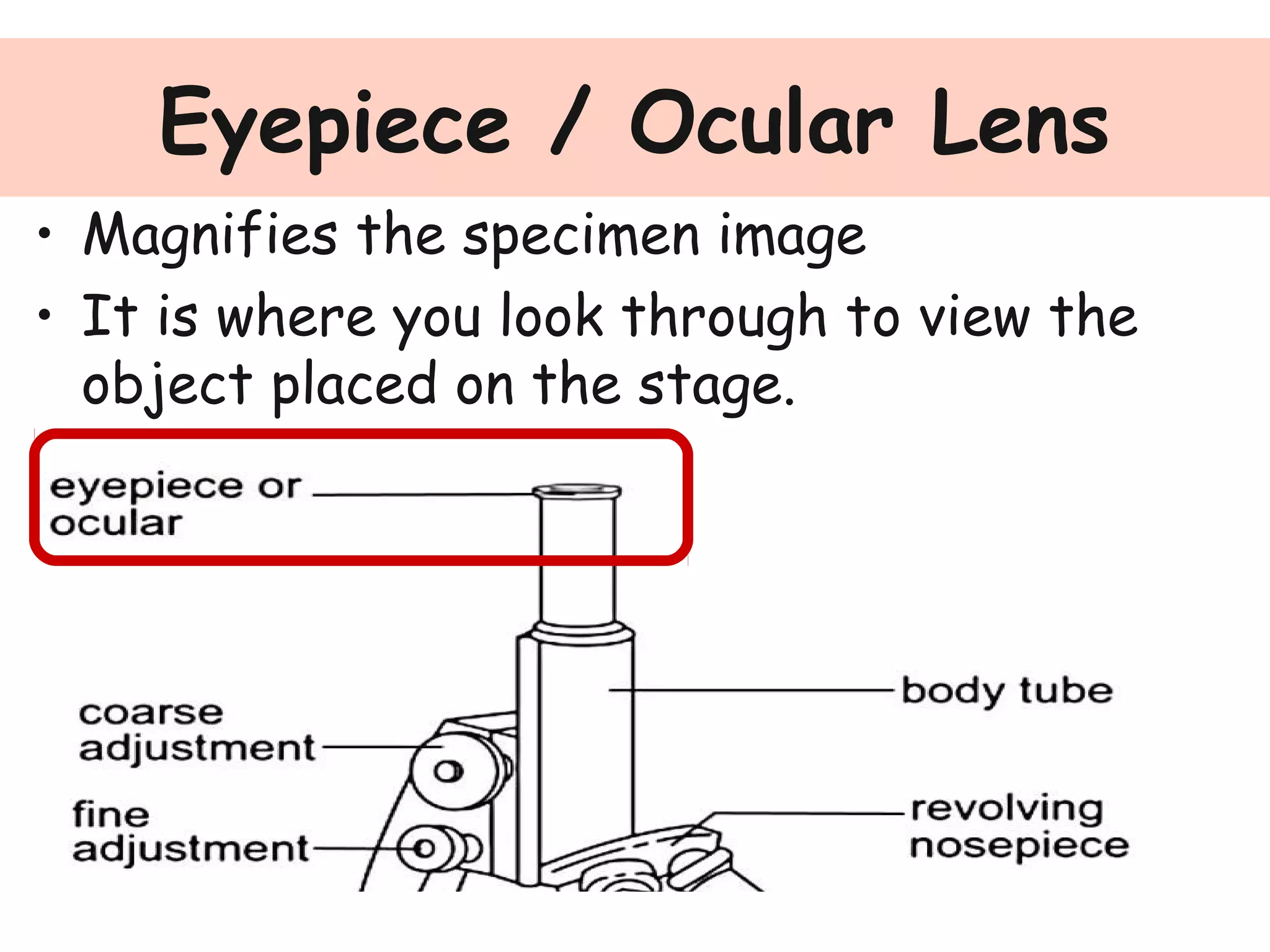
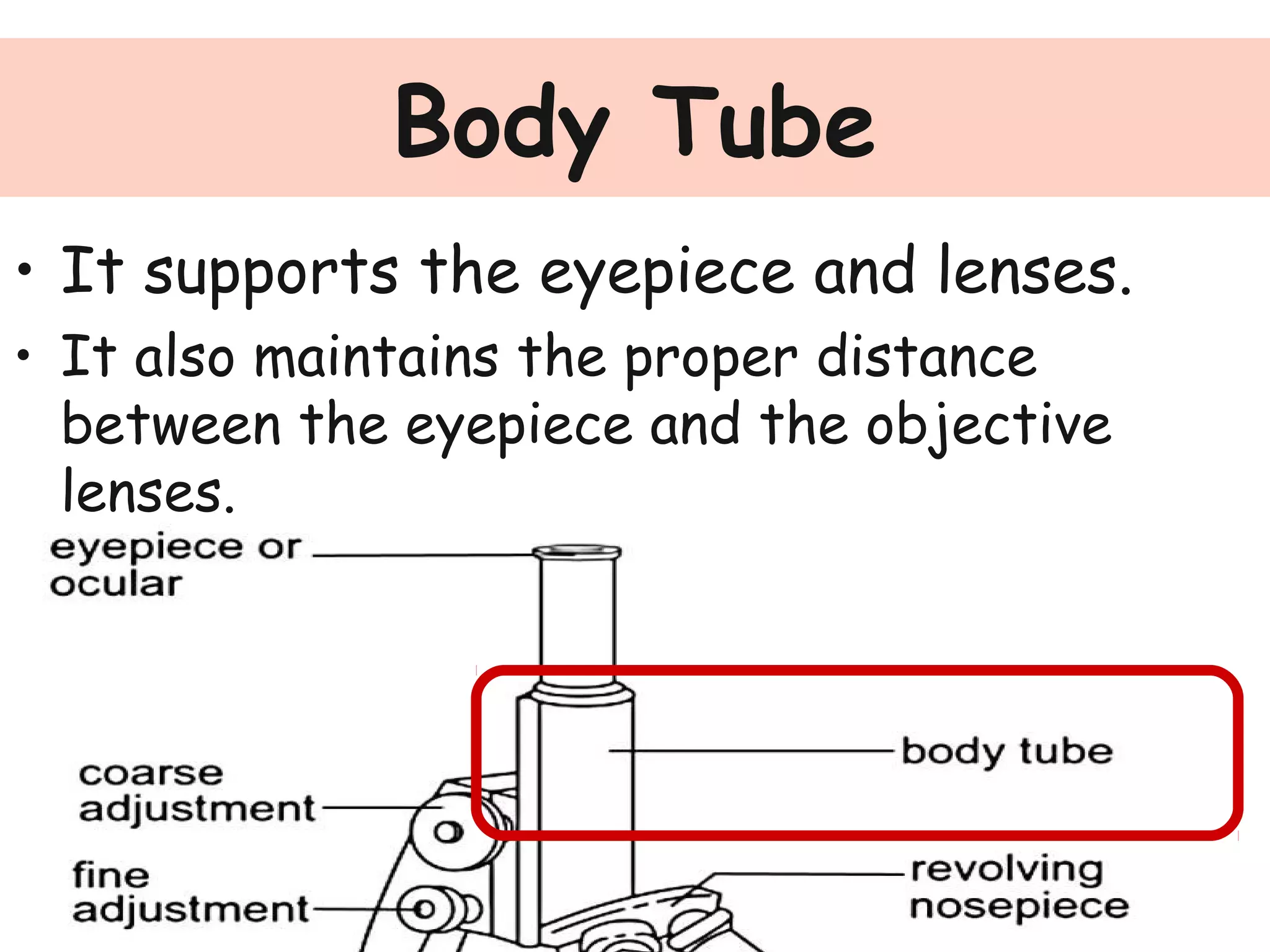
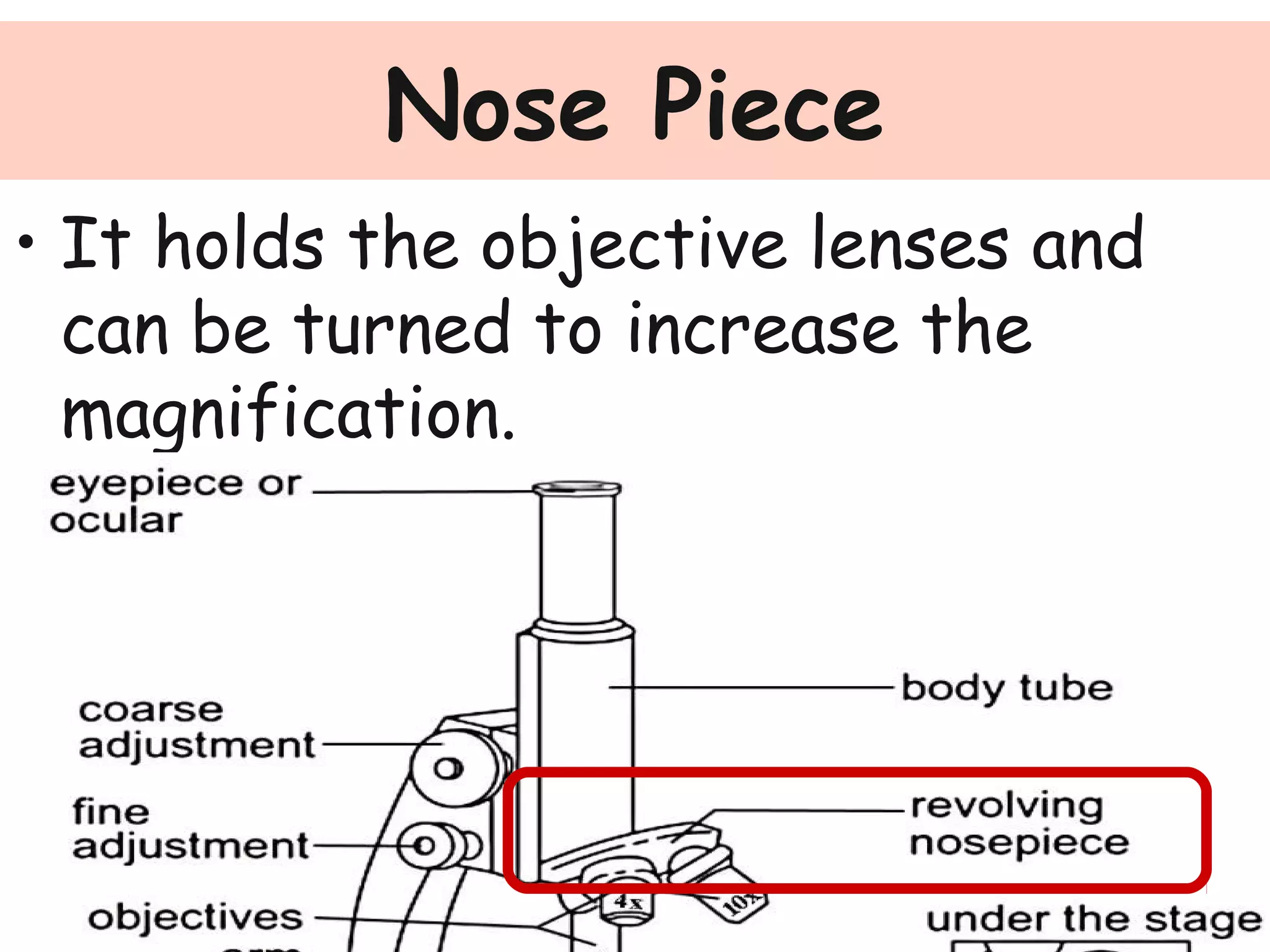
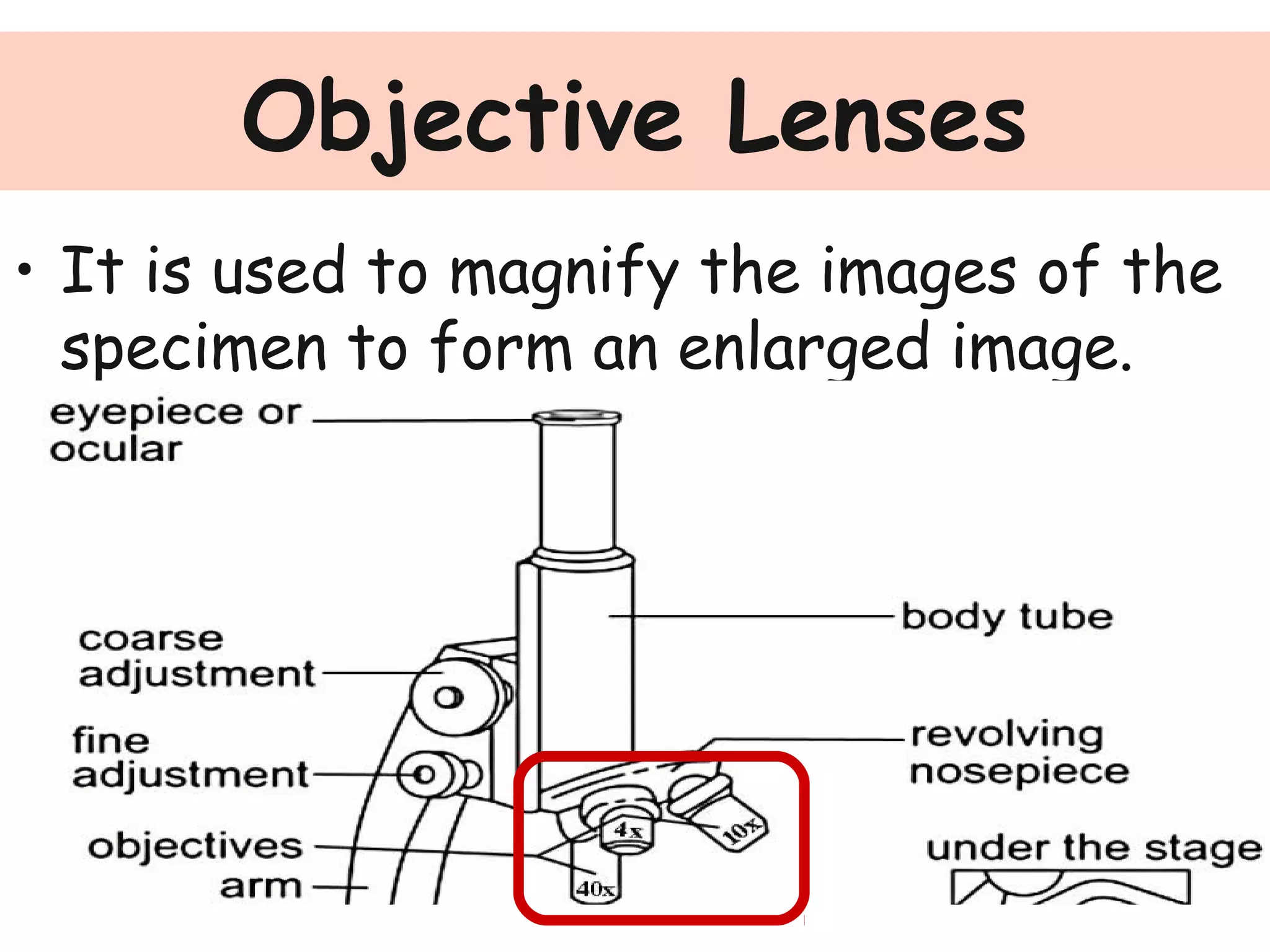
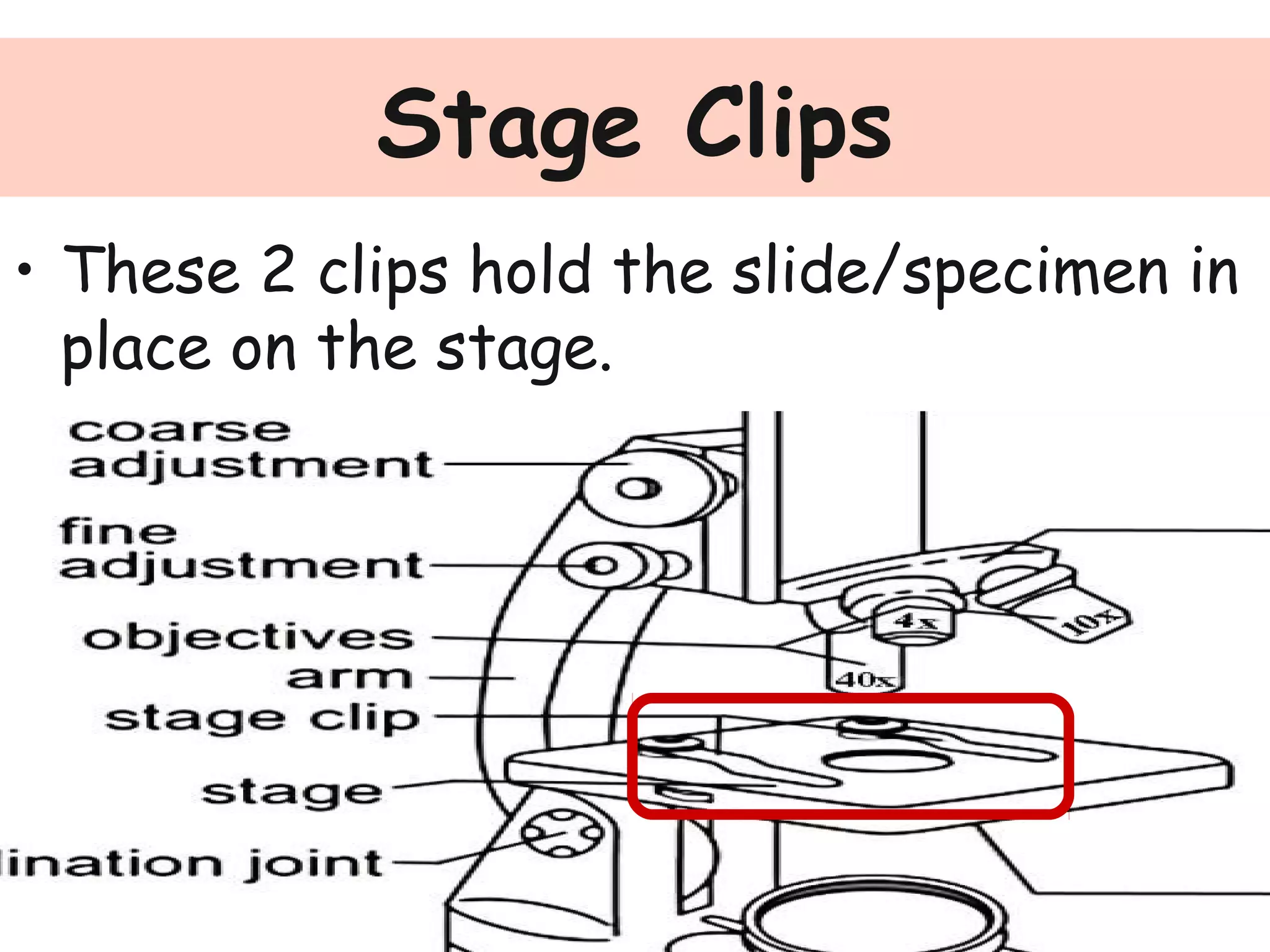
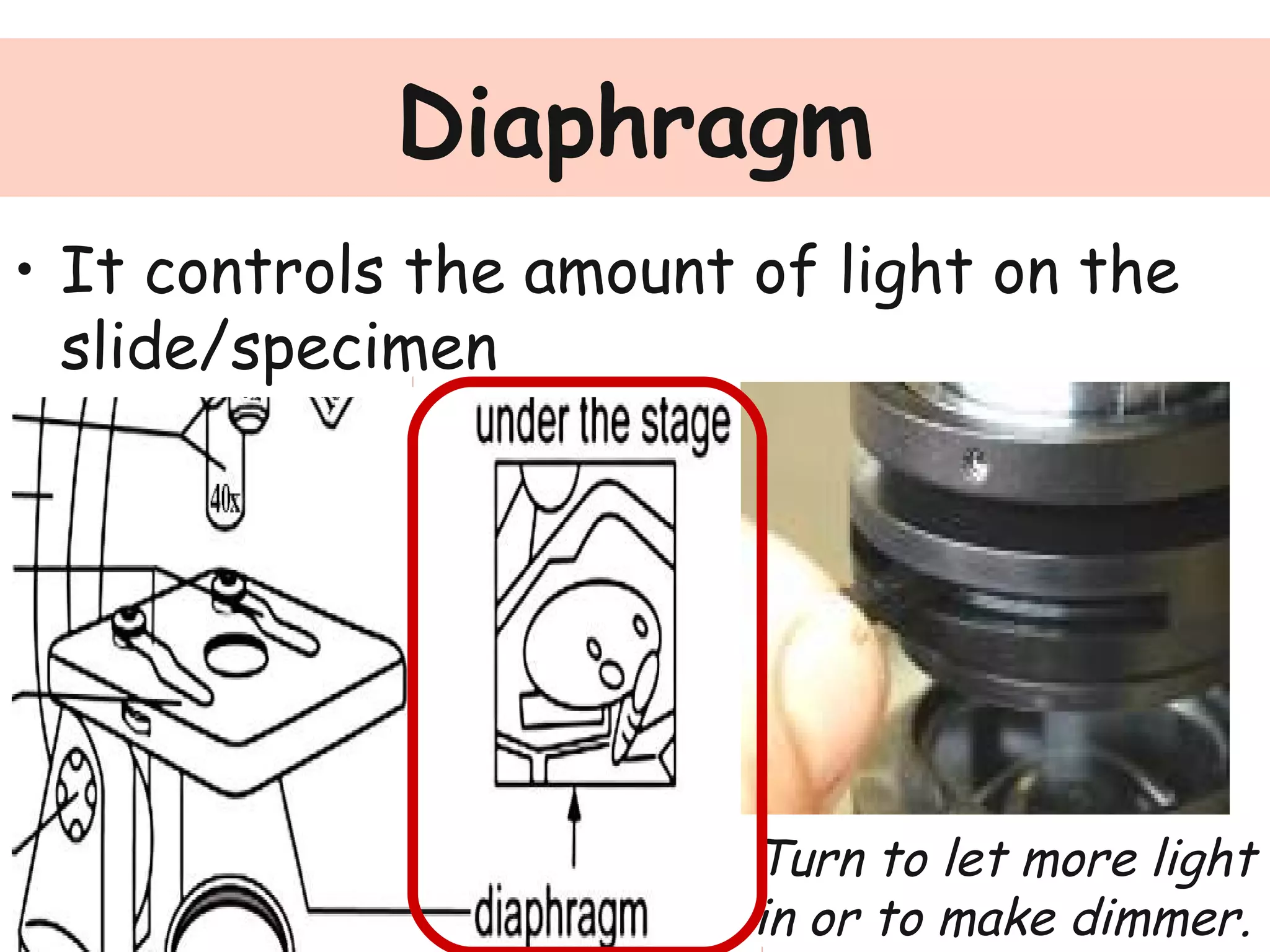
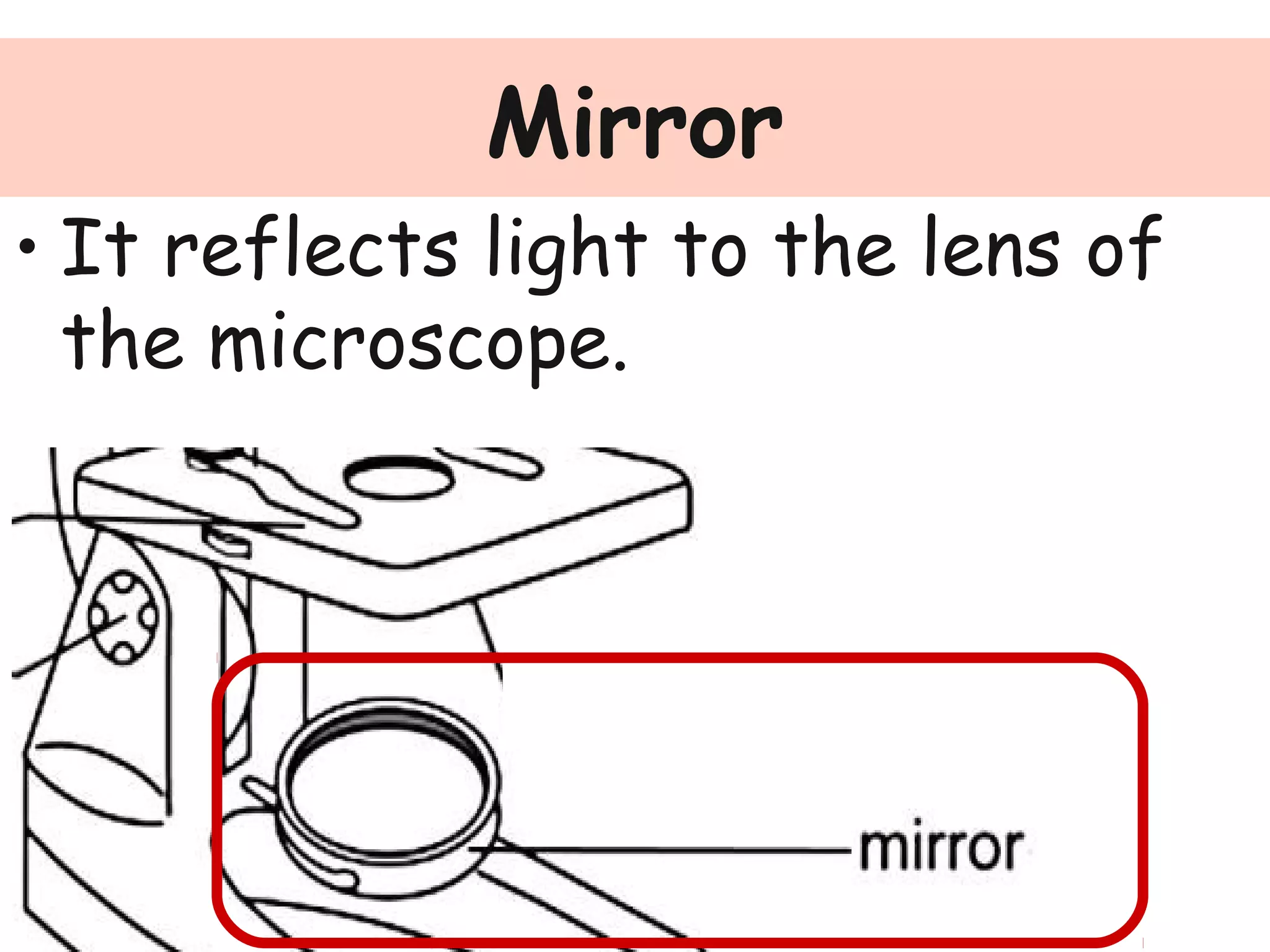
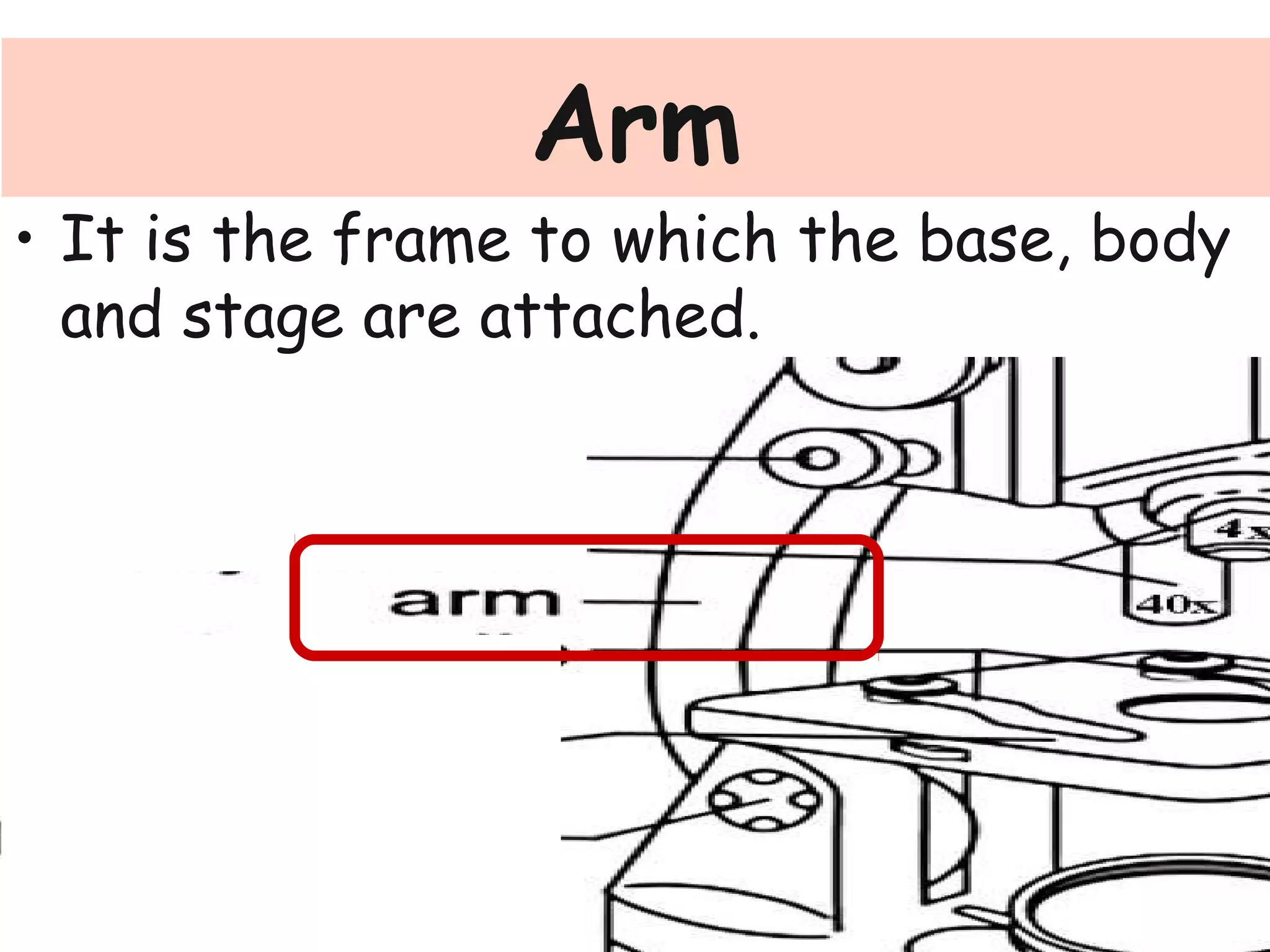
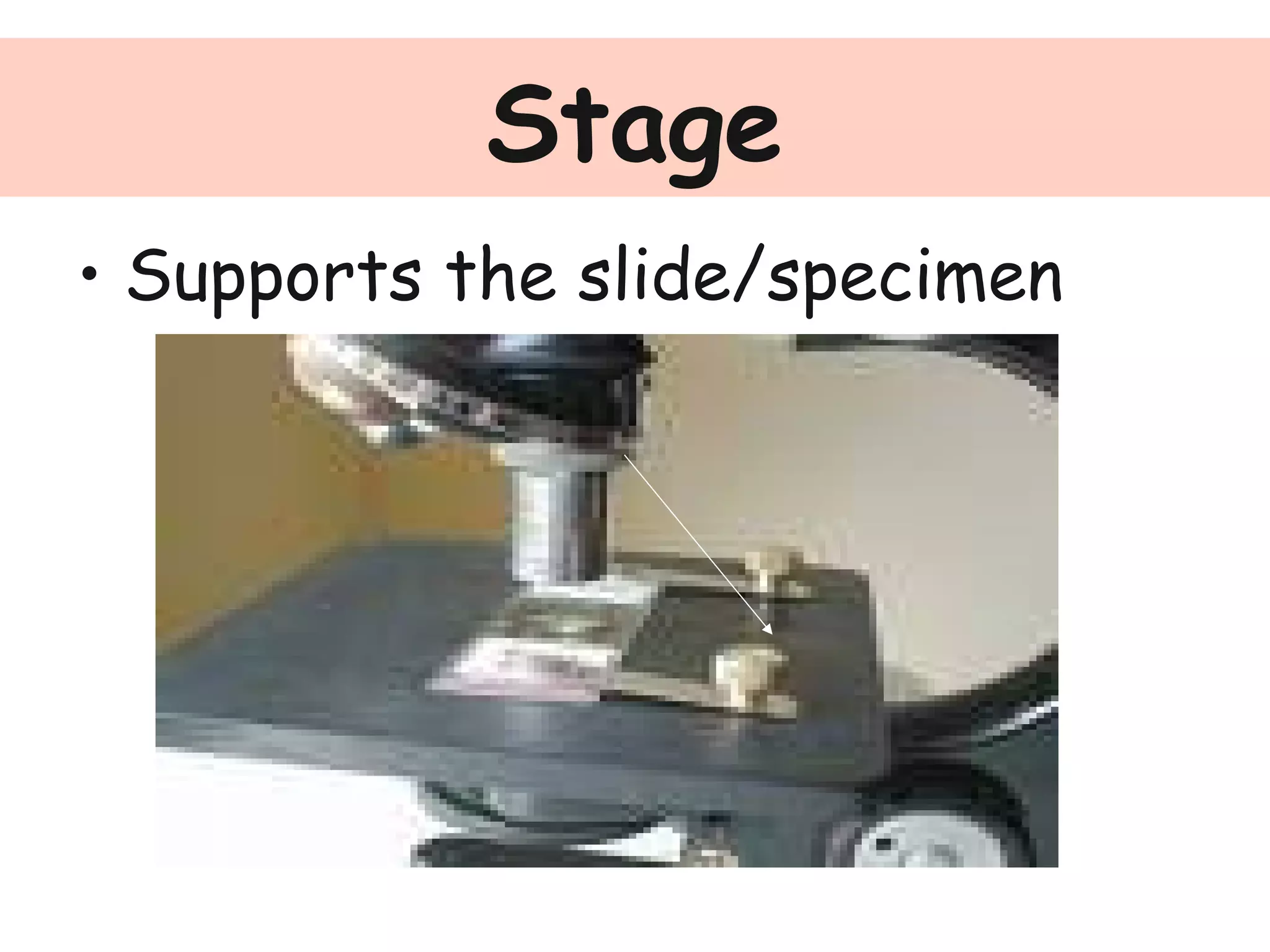
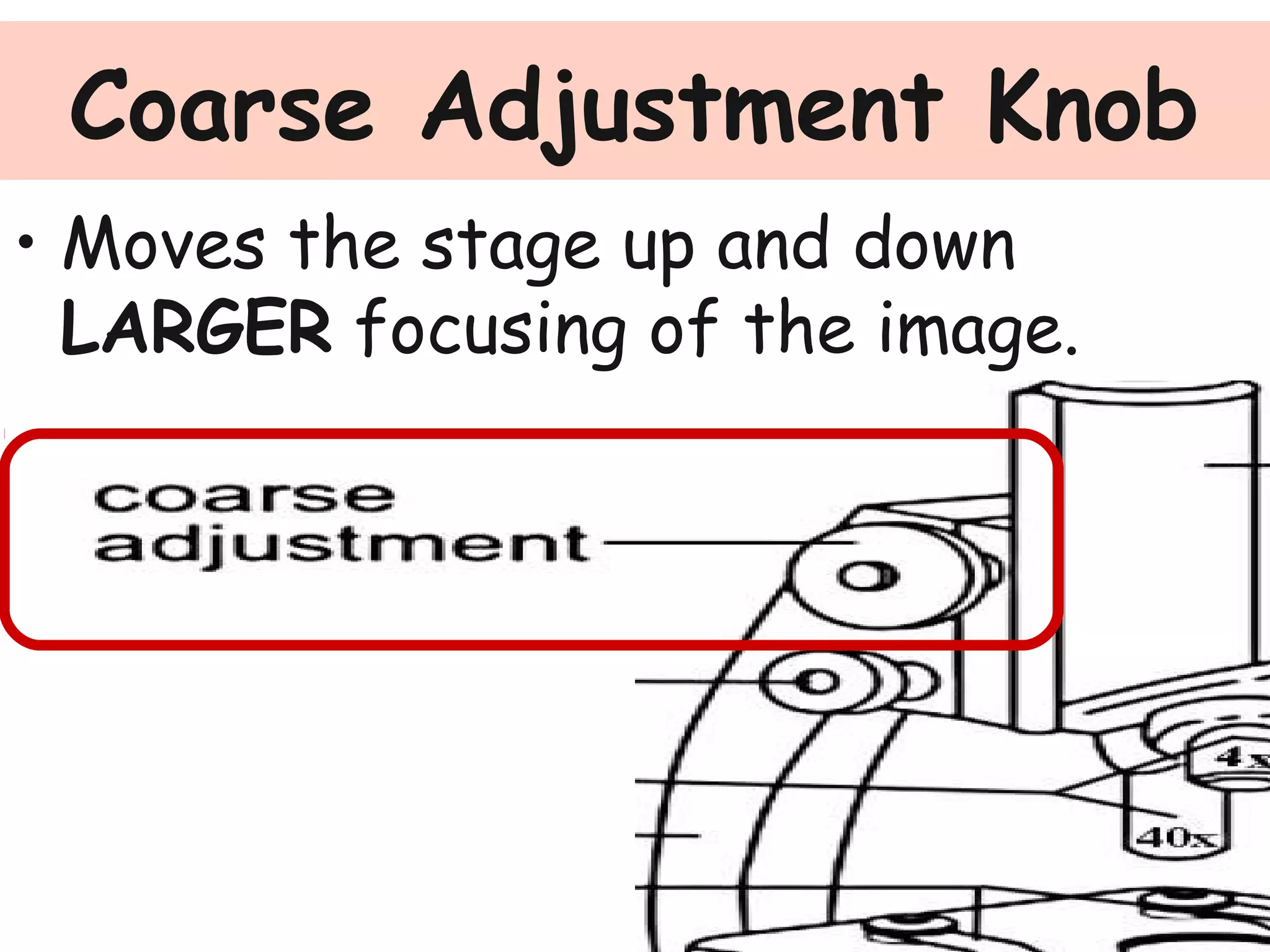
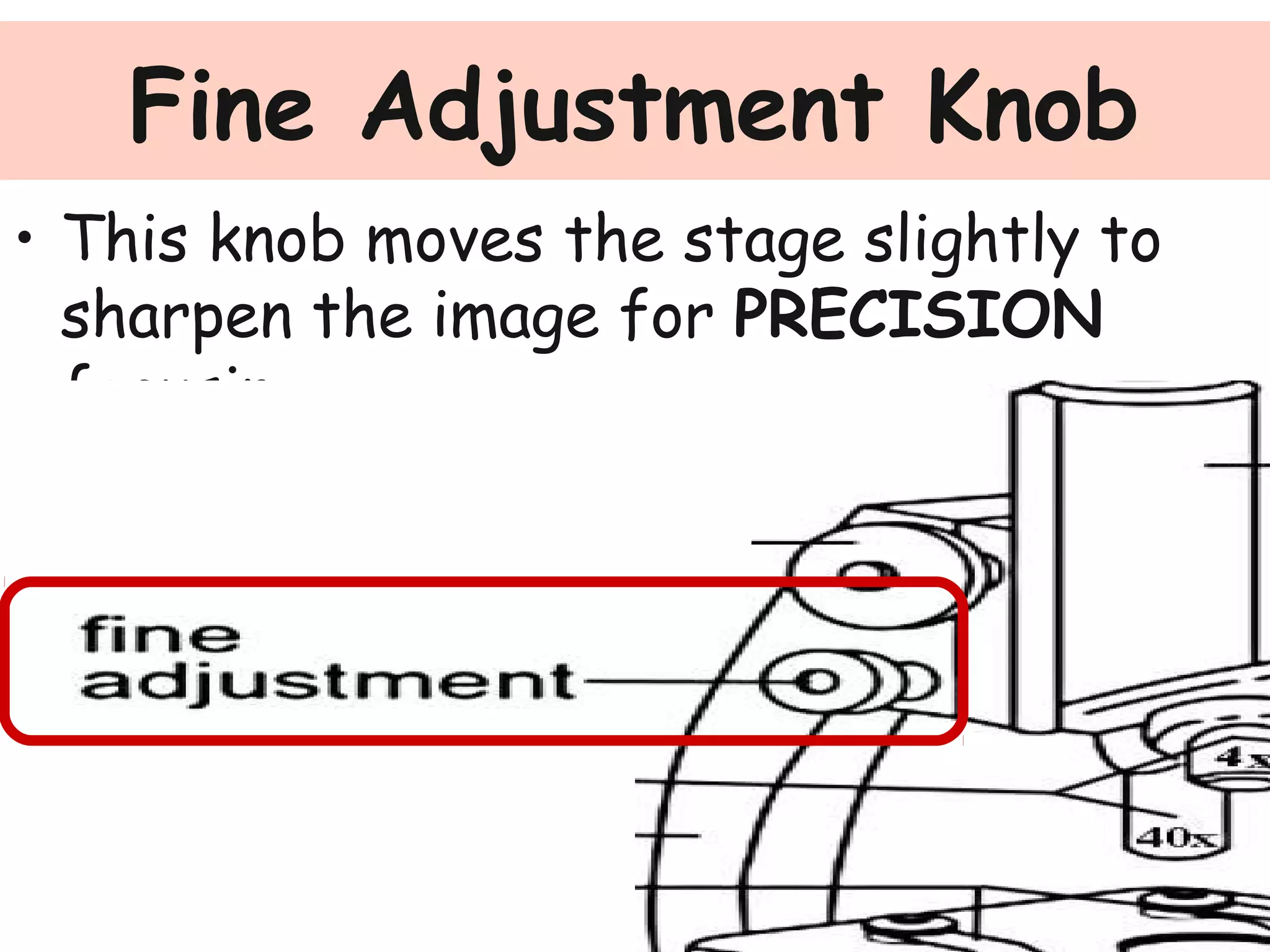
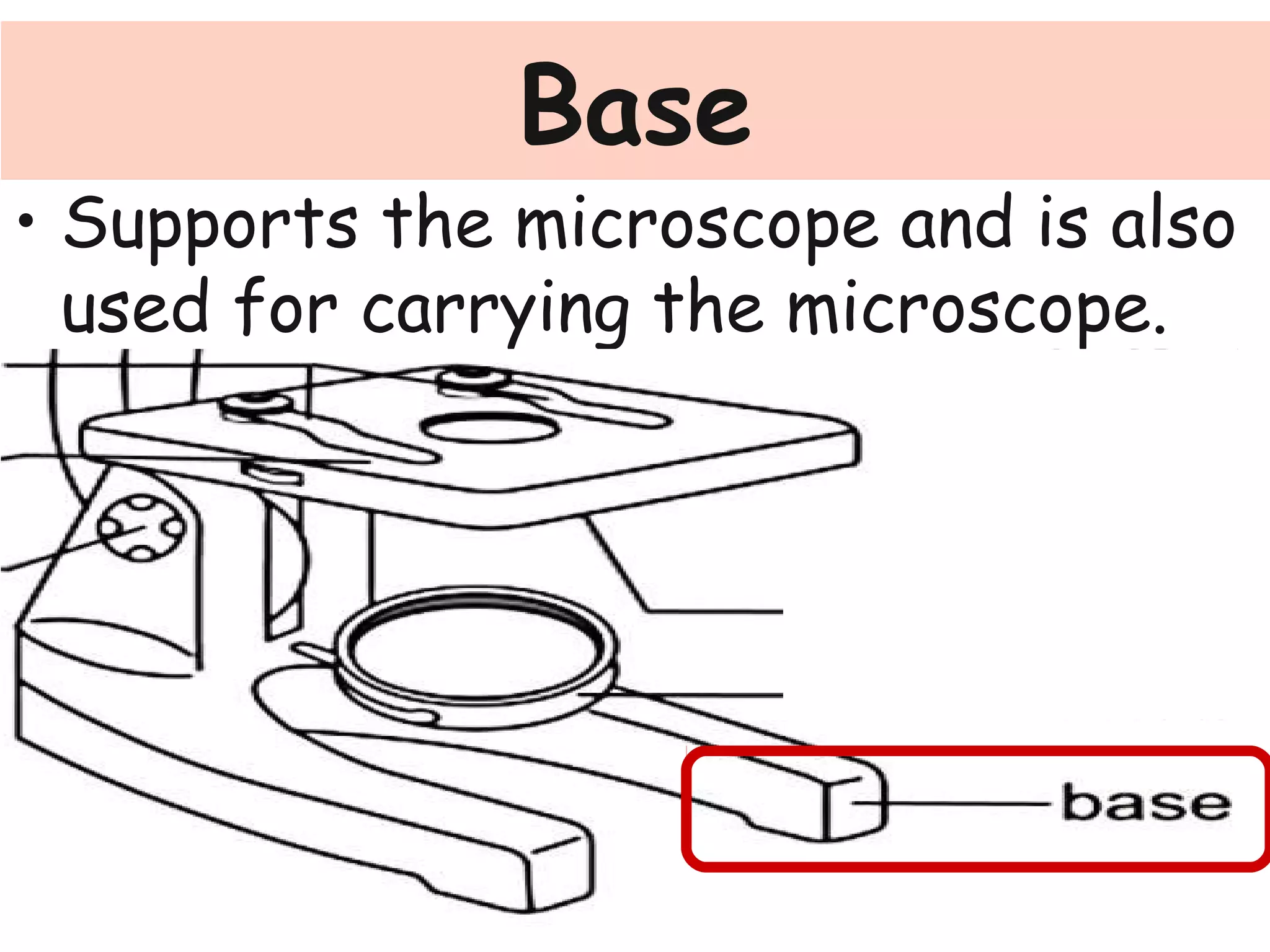
Convex lenses are curved glass that are used in microscopes and glasses to bend and focus light. A microscope uses two convex lenses, an objective lens that gathers and magnifies the light from the specimen, focusing the image inside the body tube. The ocular lens at the top of the microscope then further magnifies this image for viewing. Turning the nose piece changes the objective lens, altering the magnification of the specimen.