Isomerism types and examples
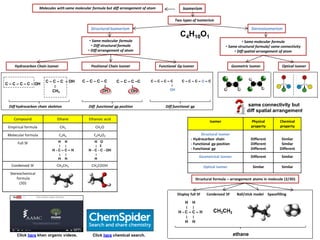
- 1. IsomerismMolecules with same molecular formula but diff arrangement of atom Two types of Isomerism Positional Chain Isomer Functional Gp Isomer C – C – C – C – OH C4H10O1 StructuralIsomerism • Same molecular formula • Diff structural formula • Diff arrangement of atom Diff hydrocarbon chain skeleton • Same molecular formula • Same structural formula/ same connectivity • Diff spatial arrangement of atom Stereoisomerism Hydrocarbon Chain Isomer Diff functional gp position Diff functional gp C – C – C – OH ׀ CH3 C – C – C –C ׀ OH C – C – C – C ׀ OH C – C – C – C ׀ OH C – C – C – O – C Optical IsomerGeometric Isomer Click here khan organic videos. Compound Ethane Ethanoic acid Empirical formula CH3 CH2O Molecular formula C2H6 C2H4O2 Full SF Condensed SF CH3CH3 CH3COOH Stereochemical formula (3D) Isomer Physical property Chemical property Structural isomer - Hydrocarbon chain - Functional gp position - Functional gp Different Different Different Similar Similar Different Geometrical isomer Different Similar Optical isomer Similar Similar H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – H ׀ ׀ H H H O ׀ ‖ H - C - C - OH ׀ H Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule (2/3D) H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – H ׀ ׀ H H CH3CH3 ethane Display full SF Condensed SF Ball/stick model Spacefilling Click here chemical search. same connectivity but diff spatial arrangement
- 2. Geometric Isomers OpticalIsomers Same chemical property– Same functional gp • Diff physical property – Diff spatial arrangement (Diff density, solubility, melting pt/boiling pt) • Same chemical property – Same functional gp • Same physical property (Same density, solubility, melting pt/boiling pt) Vs Enantiomer Mirror image of each other Enantiomer Mirror image of each other Stereoisomerism Molecules with same molecular formula but diff spatial arrangement • Same molecular formula • Same structuralformula /same connectivity • Diff spatial arrangement ofatom Cis Isomer Atom on same side Trans Isomer Atom on diff side click here for optical rotation sugar click here for polarimeter click here opical rotation corn syrupclick here polarimeter Pasco Demo Mirror image Right handed Left handed Non superimposable Chiral/asymmetrical/stereocentre carbon (4 diff groups) same connectivity but diff spatial arrangement
- 3. Isomers with same Molecular Formula and Structural Formula but diff spatial arrangement • At least 1 asymmetric / chiral carbon / stereocentre , bonded to 4 diff gp • NH2CH(R)COOH show optical isomerism • Optical isomers/mirror images call enantiomers (cannot superimpose on each other) • Similar physical and chemical property except for the effect on rotation of plane of polarised light • Optically active – enantiomer rotate plane polarised light to one direction (clockwise / anticlockwise) • Optically inactive – enantiomer present in equal amt (equimolar) – racemic mix and rotation cancel out each other Optical Isomers chiral carbon – 4 diff gp Optically inactive – Rotation cancel out each other Enantiomer (R) - rotate clockwise Enantiomer (S) – rotate anticlock wise 50% 50% 70% 30% Optically active – Net Rotation clockwise Non superimposable Non superimposable
- 4. 1. Light pass through 1st polariser – plane polarised light produced 2. Sample introduce to tube. Sample is optically active Rotate plane of polarised light to one direction 3. Turn analyzereither clockwise/anticlock wise to give light of max intensity again 4. If sample rotate light 120 clockwise – Analyzer need to rotate anticlock wise 120 5. If one enantiomer rotate light 120 clockwise Another enantiomer rotate light anticlock wise 120 How polarimeter detect optical isomer ? 6. Racemic Mix = enantiomers in equal amt (equimolar) , cancel each other rotation 1st polarizer 1st polarizer sample optically active sample optically inactive= Optical activity ability- to rotate plane of polarised light Optically active isomers –presence of asymmetrical/chiral centre - carbon bond to 4 diff gp Product from natural sources/catalysed by enzyme • give 1 pure optically active enantiomer • chiral and found in single enantiomer – optically active Products synthesised chemically • give 2 enantiomer in equal amt /racemic mix • optically inactive rotation cancel out each other Light source 1st polarizer Tube containing sample which able to rotate polarized light 2nd polarizer (Analyzer) Polarizer tube Rotated clockwise How Polarimeter works ? R – inactive Racemate mix ibuprofen S – active Racemate mix ibuprofenIbuprofen (painkiller) Click here notes isomers R limonene S limonene CH3 CH3 CH3
- 5. Product from natural source/catalysed by enzyme • give 1 pure optically active enantiomer • chiral and found in single enantiomer – optically active Product synthesised chemically • give 2 enantiomer in equal amt /racemic mix • optically inactive rotation cancel out each other R – inactive Racemate mix ibuprofen S – active Racemate mix ibuprofen Ibuprofen (painkiller) R limonene S limonene CH3 CH3 CH3 Stereoisomerism Mirror image / enantiomers Same chemical/physical property except rotation of polarized light Source/smell orange Source/smell lemon Mirror image / enantiomers Same chemical/physical property except rotation of polarized light R carvone S carvone Mirror image / enantiomers Same chemical/physical property except rotation of polarized light Source/smell spearmint Source/smell caraway seed R Thalidomide (sedative) S Thalidomide (teratogenic) • Drug company make drug with R and S (racemic mix) • Thalidomide exist as optical isomers • Enantiomers (R) and (S) • (R) effective against morning sickness • S teratogenic, birth and limb defect Our body synthesise enzyme which have active site for only one enantiomer Mirror image / enantiomers Thalidomide (pregnancy) • (S) cause limb defect / shortening of arm /leg • (R) is effective drug • Body convert (R) to (S) by racemisation process, produce racemic mix (R)/(S) • Most drug in racemic mix equal (R) and (S) • Cheaper to synthesise racemic mix than pure enantiomer • Single enantiomer appear to be more effective than racemic mix • Clinical trial is essential to ensure no harmful side effect (S), effective as pain relief (R) has no side effect!
- 6. Asymmetric/chiralcarbon/ stereocentre ,bondedto 4 diff gp Amino acid Amino acid – pair enantiomers Stereochemistryin protein Biologically-active moleculeare chiral, Most are L- amino acid – tasteless Synthesize D aminoacid – sweet Due to taste receptorin our body Chiral carbon D amino acid Enantiomer(R) Rotate clockwise L amino acid Enantiomer(S) Rotate anticlock wiseLD Cis Isomer Atom on same side Trans Isomer Atom on diff side Stereochemistryin lipids Geometric Isomers Long hydrocarbon fatty acid chain Saturated (No C = C) Unsaturated ( C = C) Fatty acid Saturated,unsaturated and polyunsaturated Presence cis /trans isomers Naturally fatty acids – cis form
- 7. Cis Isomer Atom on same side Trans Isomer Atom on diff side Stereochemistryin lipids Geometric Isomers Long hydrocarbon fatty acid chain Saturated (No C = C) Unsaturated ( C = C) Fatty acid Saturated,unsaturatedandpolyunsaturated Presence cis /trans isomers Naturally fatty acids – cis form Cis fatty acid Kink/ bend – unable to pack closely Weaker intermolecularforcesattraction VDF lower – m/p lower - liquid Trans fatty acid Straight chain – close packed together Strong intermolecularforcesattraction VDF higher –m/p high - Solid Solidify in arteries – risk heart attack (artherosclerosis) Good fatty acid Mono unsaturated (1 C =C ) Cis transform to transform Trans able to pack close together High m/p – solid form more stable to temp/oxi High risk – heart attack Increase level LDL (bad cholesterol) Polyunsaturated (> 2C = C) Trans fats (straight) Convert H2 Ni catalyst Cis (bend) complete hydrogenation partial hydrogenation
- 8. Lipids chemistry Rancidityof lipids Condensation– Form triglyceride + Hydrolysis – Glyceroland Fatty acids Hydrolytic rancidity Oxidative rancidity Presence H2O/heat Hydrolysis rxn – (water)- ester link broken Presence O2/light/enzymes Oxidative rxn- react with C=C (unsaturation) Free radical mechanism LDL vs HDL LDL High ratio lipid to protein More lipid/Less protein Carry lipid/cholesterolto artery Bad cholesterol lipid protein HDL High ratio protein to lipid More protein/Less lipid Carry cholesterol from artery to liver Good cholesterol VS lipid protein
- 9. Stereochemistryin lipids Presence cis /trans isomers Naturally fatty acids – cis form Cis fatty acid Kink/ bend – unable to pack closely Weaker intermolecularforcesattraction VDF lower – m/p lower - liquid Good fatty acid Mono unsaturated (1 C =C ) Polyunsaturated (> 2C = C) Omega3 fatty acid Omega 6 fatty acid Omega-3fattyacid reduce bloodtriglyceride IncreaseHDL level - HDL as "goodcholesterol"they transport cholesterol out of bloodartery walls, and transport back to liver Cholesterolcarryin HDL away from blood ALA alpha linolenic acid (3 cis C=C) EPA eicosapentaenoic acid (5 cis C=C) DHA Docosahexaenoicacid (6 cis C=C) 3 source omega 3 fatty acid Linoleic acid (2 cis C=C) Arachidonic acid (4 cis C=C) Double bond start at C3 Double bond start at C6 Fatty acid Molar mass C =C bond Melting point Linoleic acid 278 3 -11 Linoleic acid 280 2 -5 Oleic acid 282 1 16 Stearic acid 284 0 70 NumberC = C increase ↑ (unsaturation ↑) ↓ Lower ability to pack – Dueto kink/bend structure ↓ Lower IMF/VDF ↓ between molecule ↓ Melting point decrease ↓ (liquidform) Iodine number- Measure degree saturation Iodine number = number gram of I2 react with 100g fat 1 mol Fat – 1 mol I2 (254g I2) C = C – C = C + 2I2 → C – C – C – C 1 mol Fat – 2 mol I2 (508g I2) 1 C =C in fat 2 C =C in fat
- 10. Stereochemistryin lipids Fatty acid Molar mass C =C bond Melting point Linoleic acid 278 3 -11 Linoleic acid 280 2 -5 Oleic acid 282 1 16 Stearic acid 284 0 70 NumberC = C increase ↑ (unsaturation ↑) ↓ Lower ability to pack – Dueto kink/bend structure ↓ Lower IMF/VDF ↓ between molecule ↓ Melting point decrease ↓ (liquidform) Iodine number- Measure degree saturation Iodine number = number gram of I2 react with 100g fat Linoleic acid C18H32O2. Determine iodine number of linoleic acid 1 mol Fat – 1 mol I2 (254g I2) C = C – C = C + 2I2 → C – C – C – C 1 mol Fat – 2 mol I2 (508g I2) 1 C =C in fat 2 C =C in fat Linoleic acid (2 cis C=C) C = C – C = C + 2I2 → C – C – C – C 1 mol linoleic acid – 2 mol I2 (508g I2) (RMM 280) 280 g linoleic acid – 508 g I2 2 C =C in fat Iodine number = number gram I2 react with 100g fat 508 g I2 – 280 g linoleic acid 100 g I2 – (280 x 100)/508 g I2 Iodine number = 181 Sample fat contain 0.02 mol fatty acid react with 10.16 g I2 Determine number C =C bonds 0.02 mol acid – 0.04 mol I2 1 mol acid – 2 mol I2 2 C =C in acid RMM I2 = 253.8 Moles I2 = 10.16/253.8 = 0.04 mol I2 Nutrient Energy/kJg-1 Carbohydrates 17 Protein 17 Lipid 38 Fat - more C- H bond -more reduced Carbohydrates – more C-O bond–already oxidized More energy when oxidized/combusted
- 11. Stereochemistryin lipids Fatty acid Molar mass C =C bond Melting point Linoleic acid 278 3 -11 Linoleic acid 280 2 -5 Oleic acid 282 1 16 Stearic acid 284 0 70 3 C =C in linolenic Iodine number = number gram I2 react with 100g fat Iodine number = 274 274 g I2 – 100 g linoleic acid 761.7 g I2 – 274 g linoleic acid (1 mol) 1 mol linolenic acid – 3 mol I2 2 C =C in acid RMM I2 = 253.8Moles I2 = 761.7/253.8 = 3 mol I2 Iodine number palmitic acid (Mr = 256) is 0 Iodine number linolenic acid (Mr = 278) is 274. Determine number double bonds in linolenic acid Linoleic acid (Mr = 281) CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH Cal vol of 1.00MI2 required to react with 1 g linoleic acid. Vol 1.0M I2 = 0.00712 dm3 or 71.2 cm3 mol linoleic acid 1/281 = 0.00356 mol Linoleic acid (2 cis C=C) 1 mol acid – 2 mol I2 (508g I2) 1 mol acid – 2 mol I2 0.00356 mol acid – 0.00712 mol I2 Find number C = C in linolenic acid, C18H30O2, given 7.7 g I2, react with 2.8 g of linolenic acid. 1– molg126.902 g7.7 1– molg278.48 g8.2 : 0.01 mol acid – 0.03 mol I2 1 mol acid – 3 mol I2 mol acid mol I2 3 C =C linolenic Find iodine number of linoleic acid. CH3(CH2)4(CH═CHCH2)2(CH2)6COOH Mr (280) Iodine number = number gram I2 react with 100g fat C = C – C = C + 2I2 → C – C – C – C 1 mol acid – 2 mol I2 (508g I2) 280 g – 508 g I2 100 g - (508 x 100)/280 = 181 g I2 Iodine number = 181
- 12. Natural occursugar –D form Glucose – 4 stereocenter C5 – chiralcenter furtherfrom C1 – OH on right - D form Enantiomers Diastereomers Same connectivity Have chiral carbon Non superimposable Mirror image each other Same connectivity Have chiral carbon Non superimposable No Mirror image diff chemical/physicalproperty 2 chiral centre 22 = 4 stereoisomer 3 chiral centre 23 = 8 stereoisomer same chemical/physicalproperty Mirror image Not Mirror image diff configuration at one or more of equivalent stereocenter chiral centre not mirror image same configuration mirror image diff configuration Enantiomer/mirror image 2n n = chiral centre D glucose L - glucose GlucoseIsomers Stereochemistryin carbohydrates OH at C1 – bottom ring α glucose * All chiral center diff configuration ↓ Mirror image α glucose β glucose OH at C1 – top ring β glucose equilibrium bet straight chain – ring form * * *
- 13. Enantiomers Diastereomers Same connectivity Have chiral carbon Non superimposable Mirror image each other Same connectivity Have chiral carbon Non superimposable No Mirror image diff chemical/physicalproperty 2 chiral centre 22 = 4 stereoisomer 3 chiral centre 23 = 8 stereoisomer same chemical/physicalproperty Mirror image Not Mirror image diff configuration at one or more of equivalent stereocenter chiral centre not mirror image same configuration mirror image diff configuration Enantiomer/mirror image 2n n = chiral centre D fructose L - fructose Natural occursugar –D form Fructose – 3 stereocenter C5 – chiralcenterfurtherfrom C1 – OH on right - D form FructoseIsomers Stereochemistryin carbohydrates OH at C2 – bottom ring α fructose * All chiral center diff configuration ↓ Mirror image α fructose β fructose OH at C2 – top ring β fructose equilibrium bet straight chain – ring form
- 14. Natural occursugar –D form Glucose – 4 stereocenter C5 – chiralcenter – OH on right - D form Enantiomer/mirror image D glucose L - glucose GlucoseIsomers Stereochemistryin carbohydrates *All chiral center diff configuration ↓ Mirror image equilibrium bet straight chain – ring form Starch/glycogen- α glucose link together (1-4 α glycosidic link) Human – have α amylase recognise α glucose - can digest starch Starch α glucose α glucose α glucose (1-4 α glycosidic link) Cellulose Cellulose - β glucose link together – (1-4 β glycosidic link) Cow – have β cellulase recognise β glucose – can digest cellulose Cellulose – fibre to human – strong long chain - H2 bond bet chain All OH gp below (1-4 β glycosidic link) Β glucose β glucose β glucose β glucose OH gp alternate * * *
- 15. Isomers with same Molecular Formula and Structural Formula but diff spatial arrangement • At least 1 asymmetric / chiral carbon / stereocentre , bonded to 4 diff gp • NH2CH(R)COOH show optical isomerism • Optical isomers/mirror images call enantiomers (cannot superimpose on each other) Optical Isomers chiral carbon – 4 diff gp Non superimposable Non superimposable click here diastereomers OpticalIsomers Enantiomers Diastereomers Same connectivity Have chiral carbon Non superimposable Mirror image each other Same connectivity Have chiral carbon Non superimposable No Mirror image diff chemical/physicalproperty click here diastereomers same chemical/physicalproperty Mirror image Not Mirror image diff configuration at one or more of equivalent stereocentre chiral centre not mirror image same configuration mirror image diff configuration Video on diastereomers
- 16. OpticalIsomers Enantiomers Diastereomers Same connectivity Have chiral carbon Non superimposable Mirror image each other Same connectivity Have chiral carbon Non superimposable No Mirror image diff chemical/physicalproperty 2 chiral centre 22 = 4 stereoisomer 3 chiral centre 23 = 8 stereoisomer same chemical/physicalproperty Mirror image Not Mirror image diff configuration at one or more of equivalent stereocentre chiral centre not mirror image same configuration mirror image diff configuration Enantiomersand Diastereomers Diastereomer/NOT mirror image Can separate by physical/chemical mean Enantiomer/mirror image Cant be separated by physical/chemical mean 3 sugar, same structural formula 2n n = chiral centre All chiral center diff configuration ↓ Mirror image Which of the followingare enantiomersand diastereomers? one chiral center diff configuration Diastereomer/NOT mirror image Can separate by physical/chemical mean two chiral center diff configuration
- 17. OpticalIsomers Enantiomers Diastereomers Same connectivity Have chiral carbon Non superimposable Mirror image each other Same connectivity Have chiral carbon Non superimposable No Mirror image diff chemical/physicalproperty 2 chiral centre 22 = 4 stereoisomer 3 chiral centre 23 = 8 stereoisomer click here to view diastereomers same chemical/physicalproperty Mirror image Not Mirror image diff configuration at one or more of equivalent stereocentre chiral centre not mirror image same configuration mirror image diff configuration 2, 3 - dibromopentane Diastereomers A B C D Enantiomer/mirror image Enantiomer/mirror image Diastereomer/NOT mirror image Enantiomer/mirror image Diastereomer/NOT mirror image 2n n = chiral centre
- 18. Stereochemistry in vitamins RODS Conjugated protein Rhodopsin Retina – 2 typeslight sensitive RODS (no colour)and CONES (colour) Light cause photo isomerization 11 cis retinal → all trans retinal (light) Cis fit into protein opsin Trans dissociate from protein opsin Nerve impulse trigger Rhodopsin made up of 11 cis retinal ↓ Bend ↓ Fit into Opsin all trans retinal ↓ Straight ↓ Dissociate from Opsin Light – PHOTO ISOMERIZATION – CIS to TRANS Opsin (protein) 11 cis retinal (conjugated chromophore) + visual cycle Vit A – source of retinal Lack Vit A – night blindness
- 19. Write structural formula isomers for C4H9OH, state which isomer show optical isomerism Butan -1-ol Butan-2-ol 2-methylpropan-2-ol 2-methylpropan-1-ol All structuralisomers Stereoisomers (Optical Isomers) Write structural formula of cyclic isomers for C3H4CI2, state type of isomerism Structuralformula Geometric Isomers Cis/Tans isomerism Optical Isomers Enantiomer,mirror image Cyclic ring geometric isomers CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3 ׀ OH CH3-CH2-CH-CH3 ׀ OH CH3 ׀ CH3-C-OH ׀ CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-OH ׀ CH3 chiral centre chiral centre CI CI CI CI H HHH H HHH CI CICICI Trans 1, 2 dichlorocyclopropaneCis 1, 2 dichlorocyclopropane Stereoisomers (Optical Isomers) CICI CICI H HHH chiral centre chiral centre * *
- 20. Optical Isomerism Which carbon has chiral center? Draw all stereoisomers CHBr=CHCH(OH)CH3 CHBr=CHCH(OH)CH3 Optical isomersGeometric isomers Chiral carbon with 4 diff gpDouble bond prevent bond rotation Cis / Z Trans / E CH3CH2C* H(CH3)(CI) CH3C* H(NH2)COOH CH3C* H(OH)CH2OH C2H5C* H(OH)CH2OH C2H5 H H ׀ ׀ C = C ׀ ׀ Br CH(OH)CH3 H CH(OH)CH3 ׀ ׀ C = C ׀ ׀ Br H H ׀ CHBr=CH-C–CH3 ׀ OH H ׀ CH3-C-CH=CHBr ׀ OH R (enantiomer) S (enantiomer) chiral centre Non chiral centre NOT mirrorimage superimposable χ rotate it They are same. Superimposable Mirror image Non superimposable chiral centre
