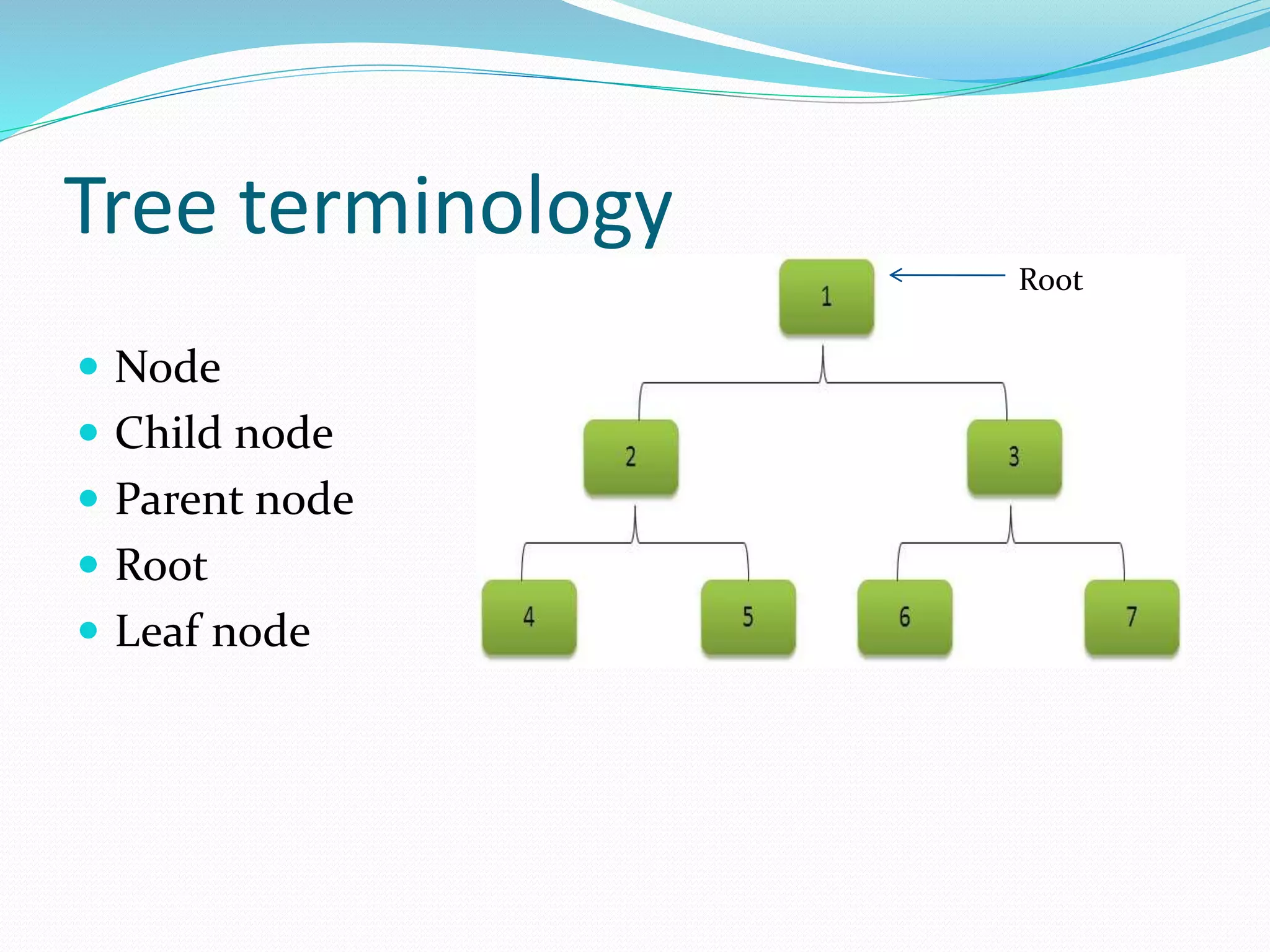
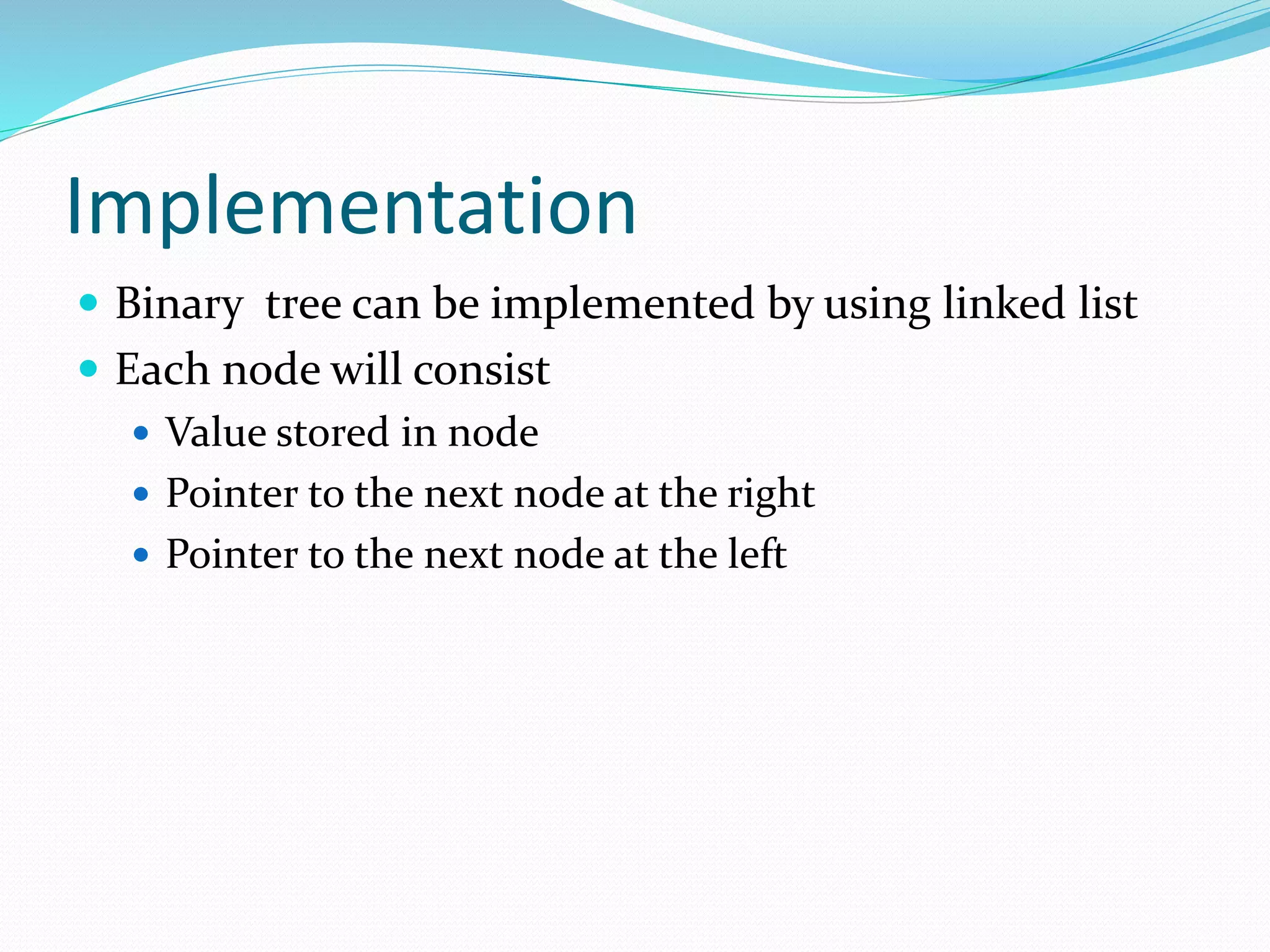
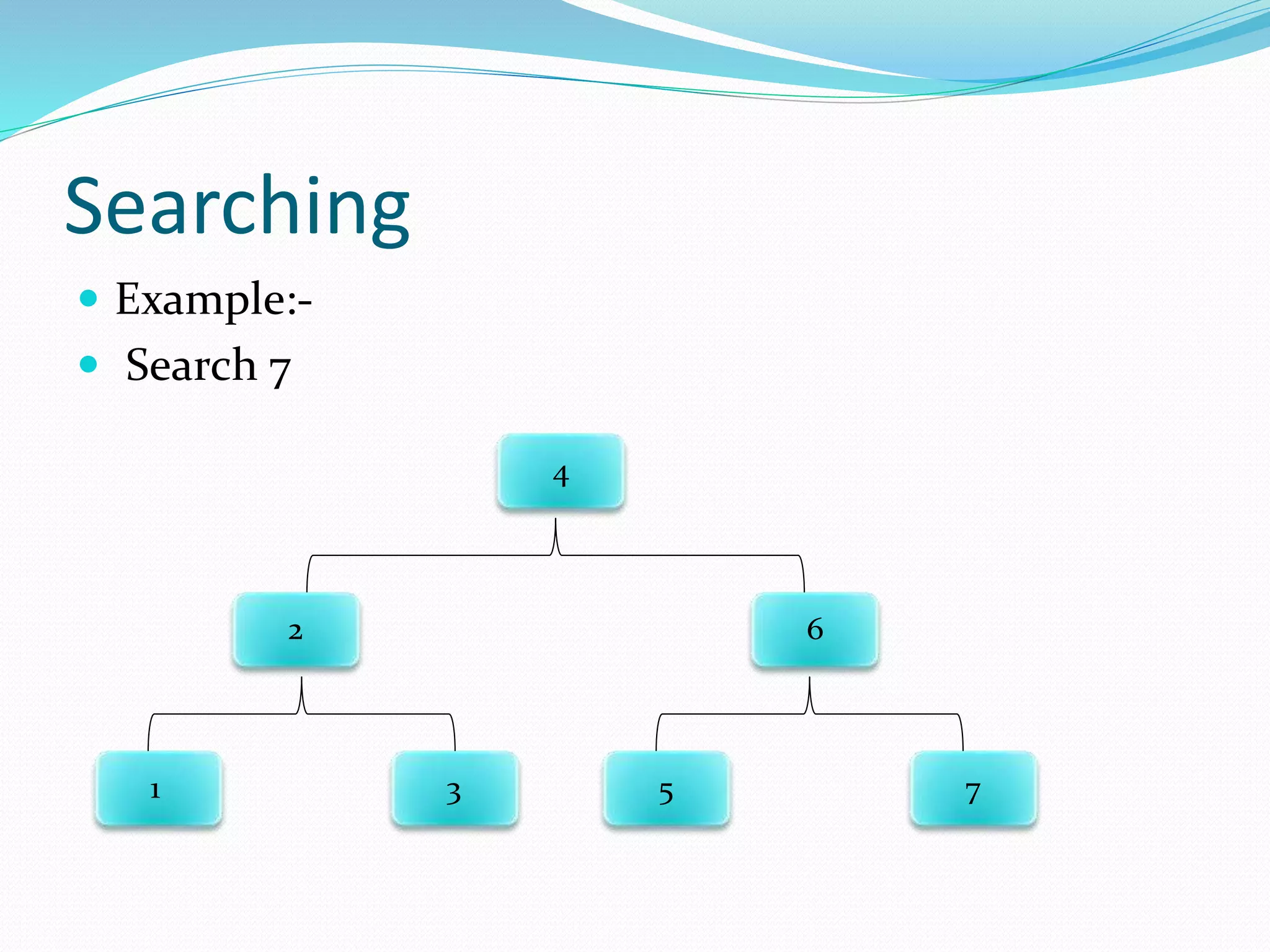
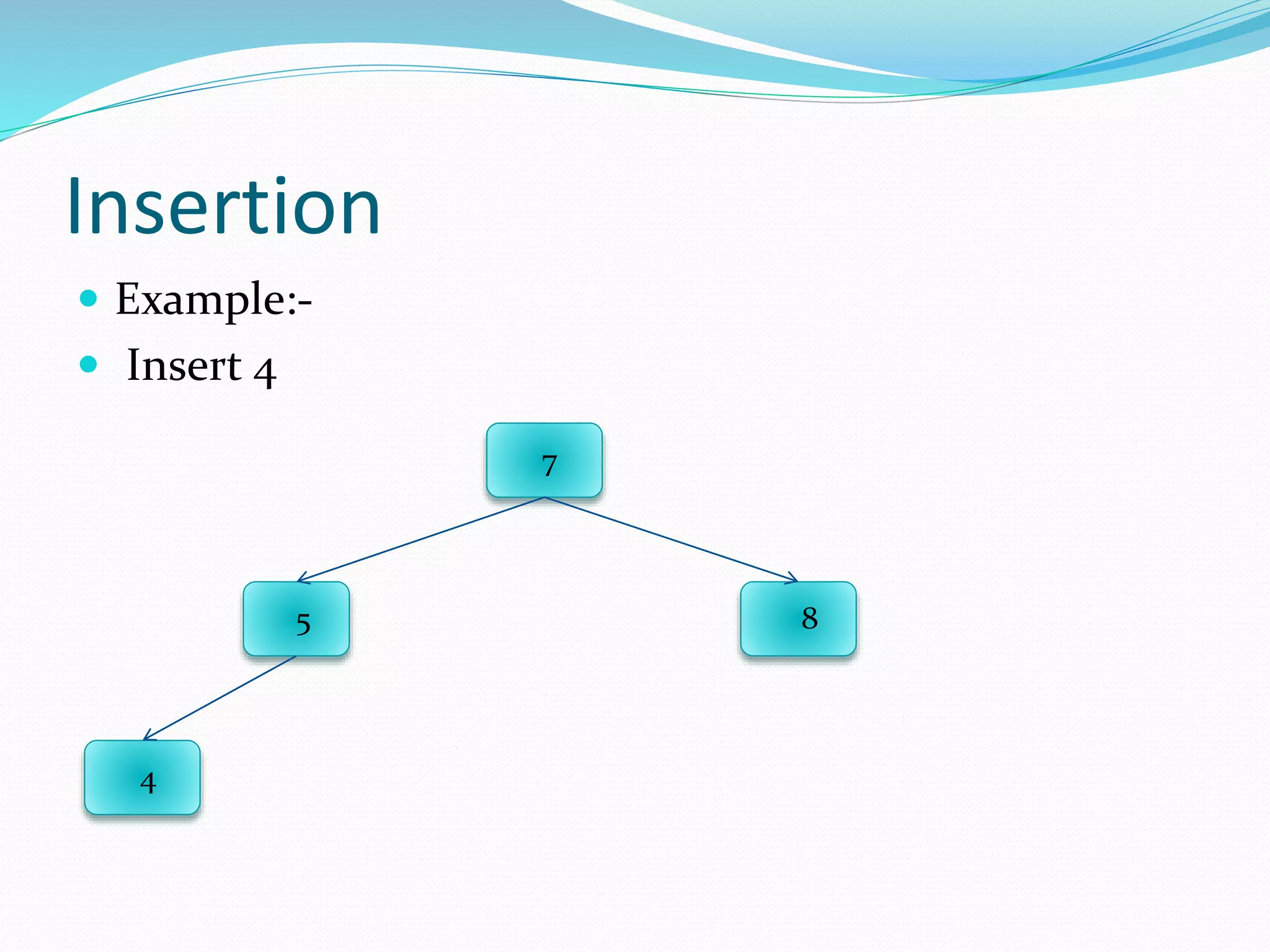
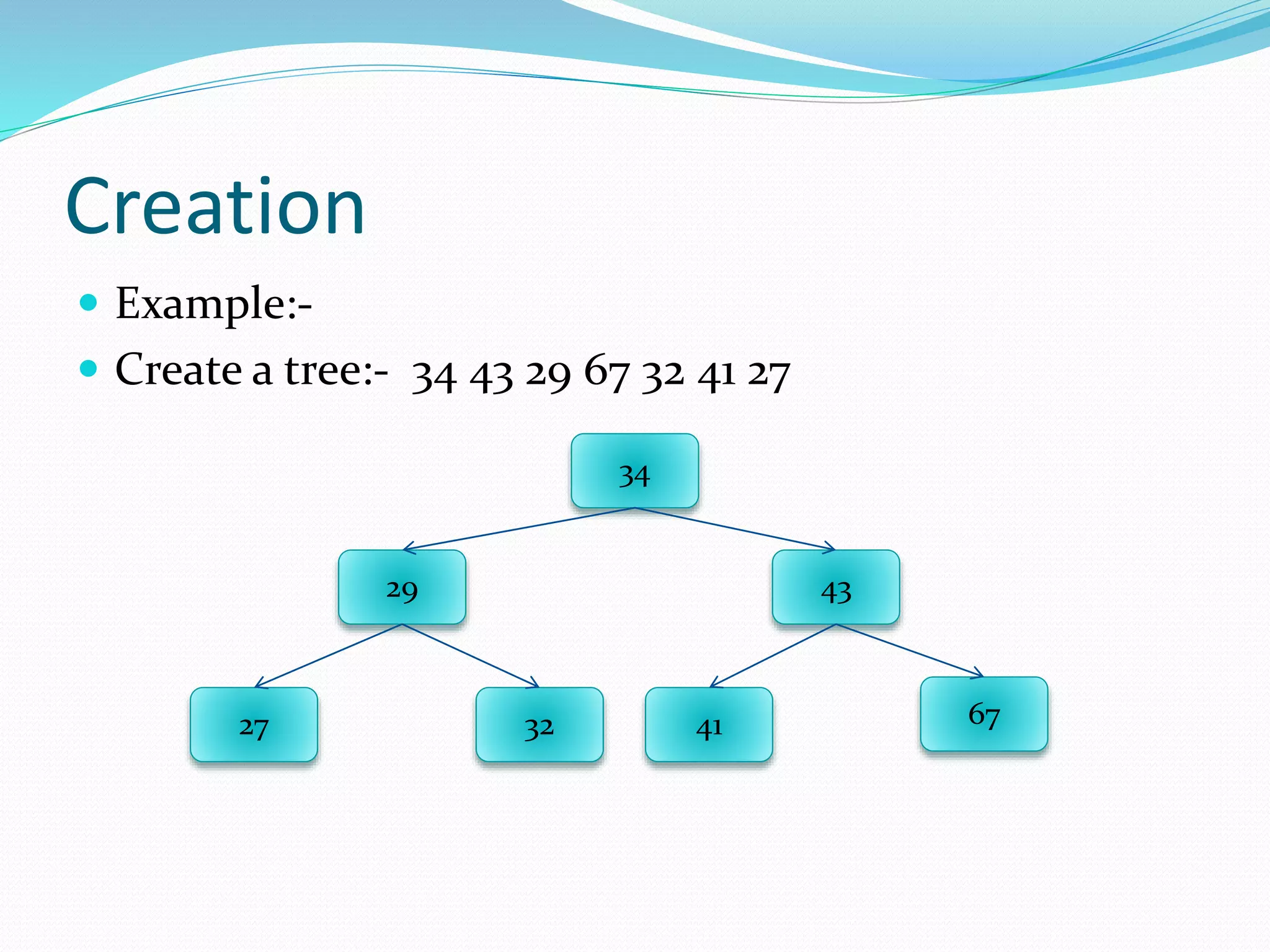
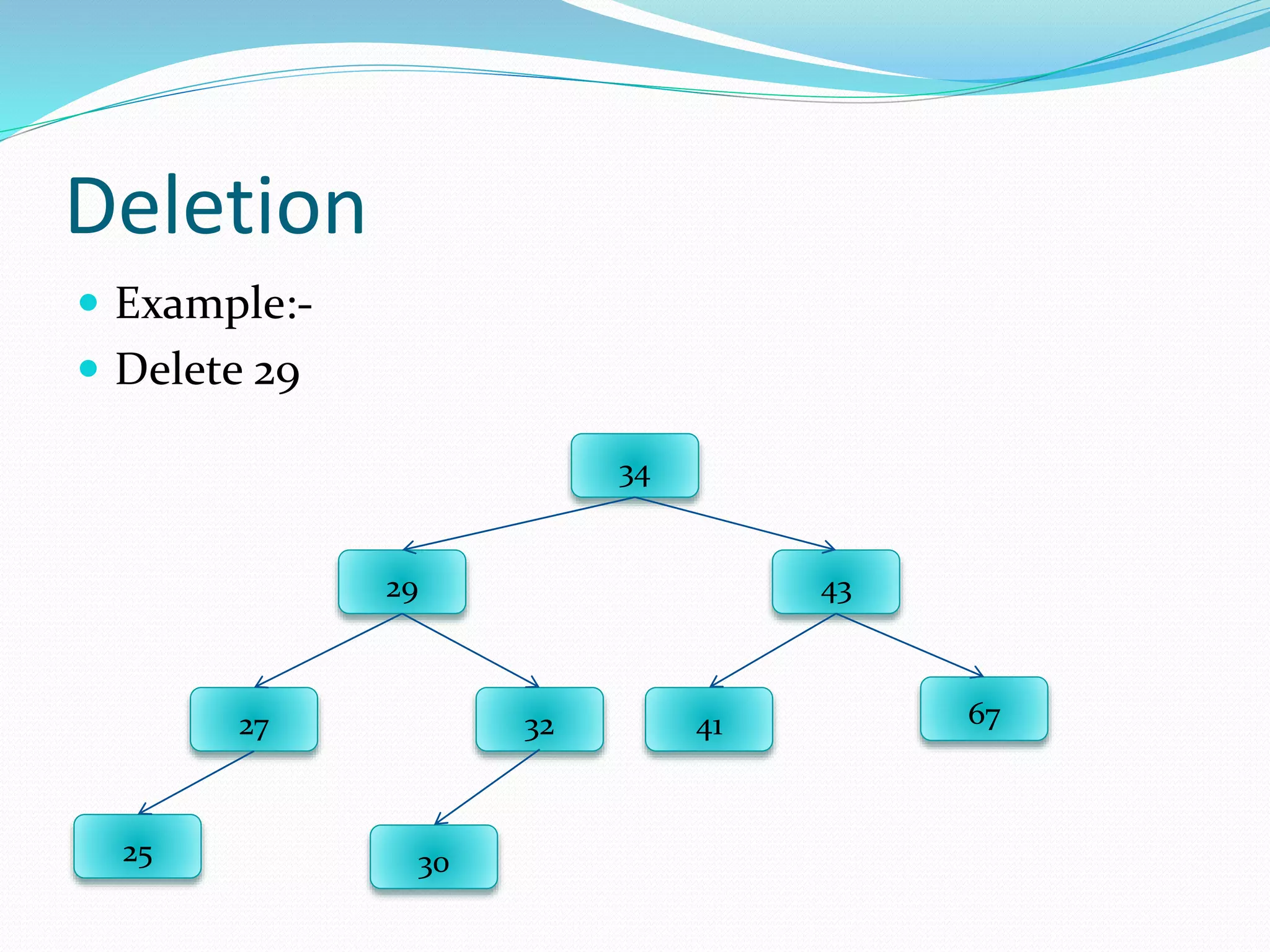
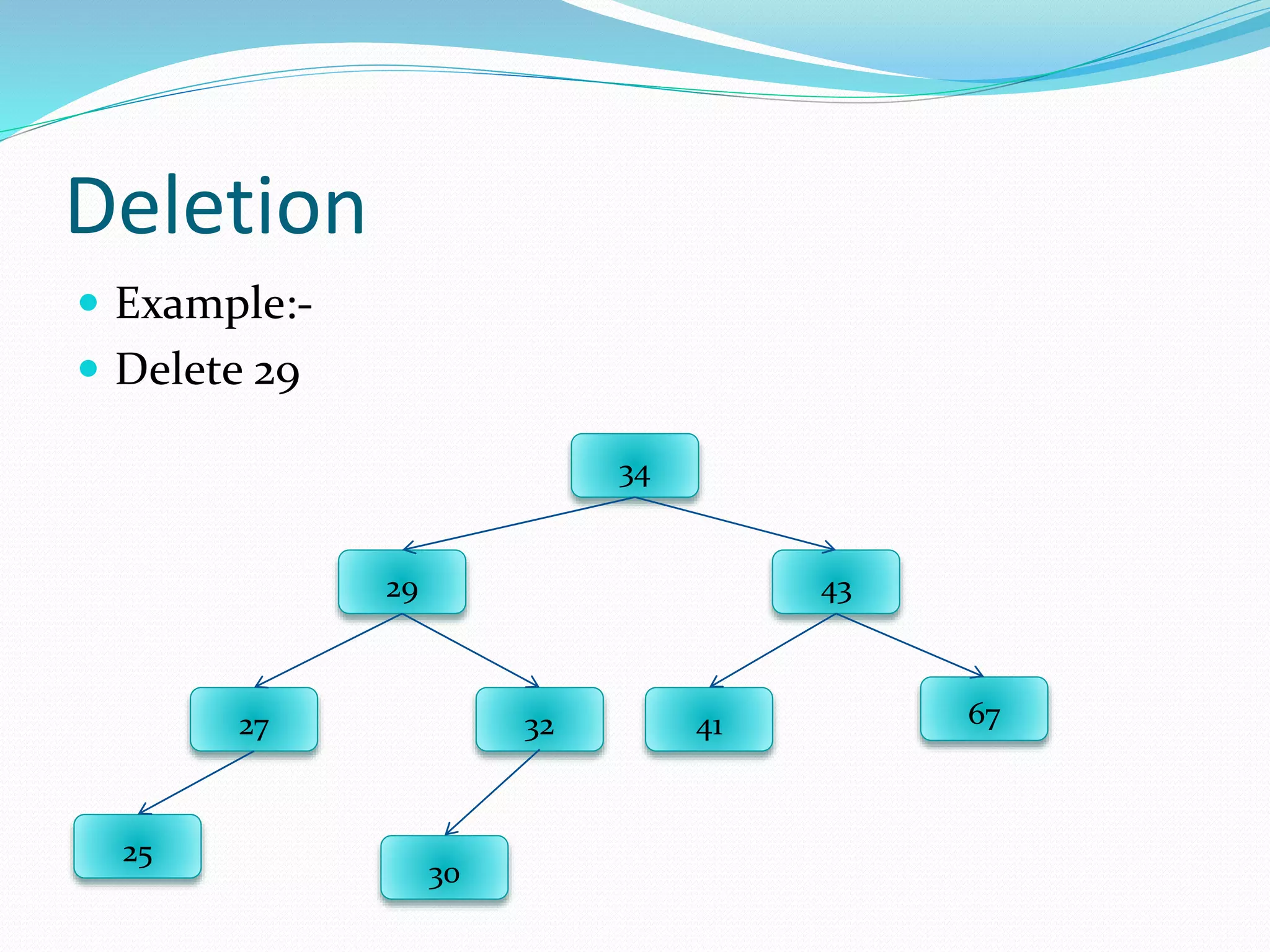
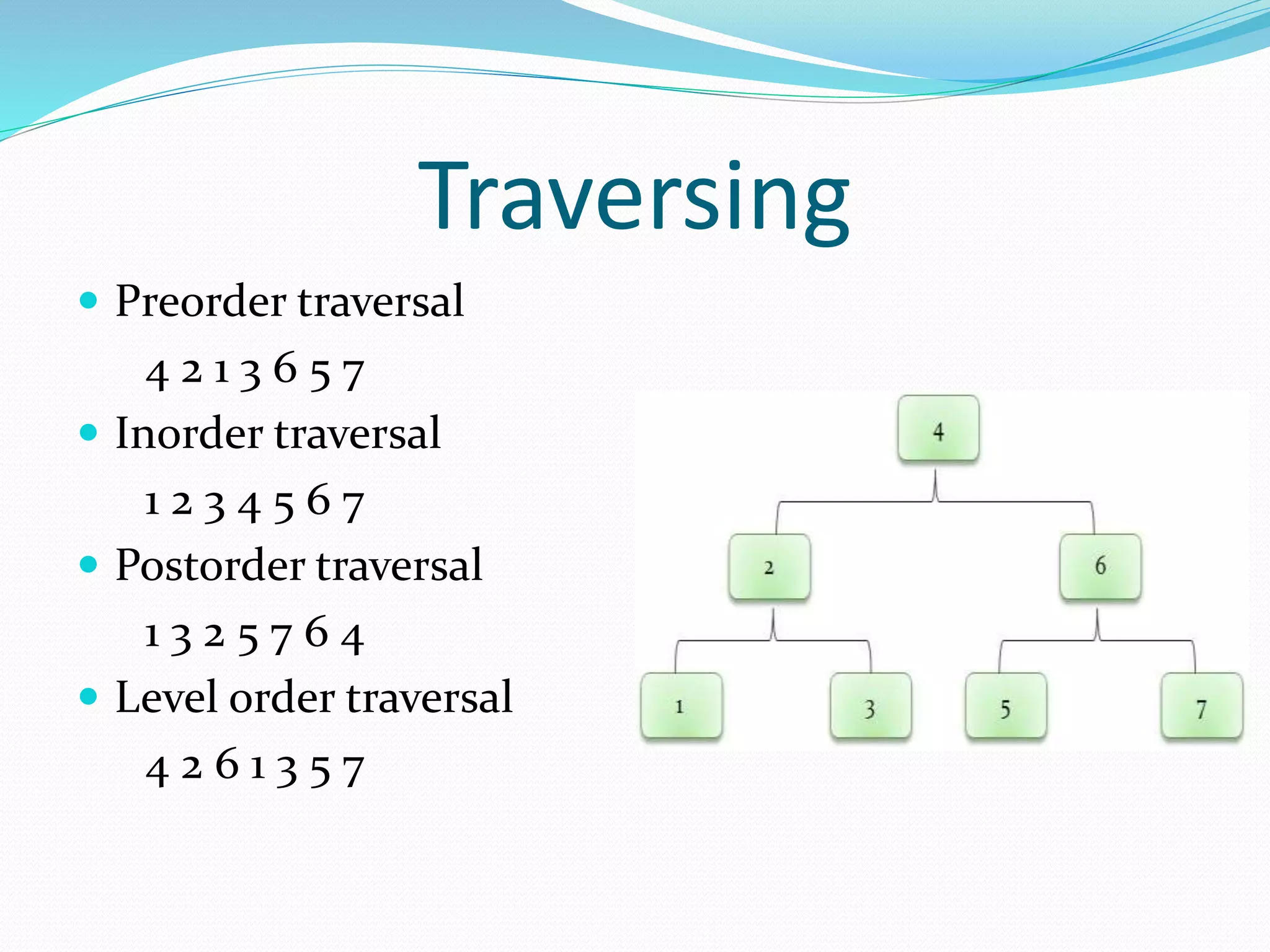
The document discusses binary trees, including their terminology, implementation, operations, and traversal methods. It lists the group members and then defines key binary tree concepts like nodes, children, parents, roots, and leaf nodes. It explains that a binary tree has at most two children per node, and describes how to implement one using linked lists. Common binary tree operations like searching, insertion, deletion, creation, and traversing are then covered with examples. The different traversal orders - preorder, inorder, postorder, and level order - are defined along with examples.