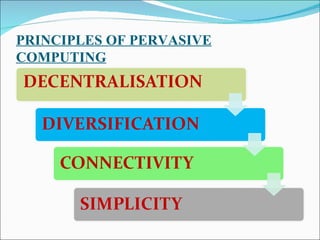
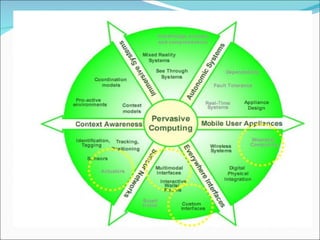
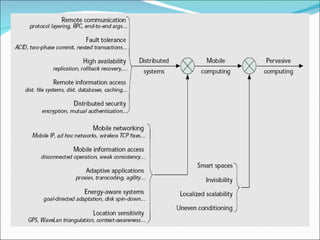
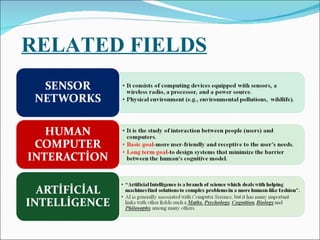
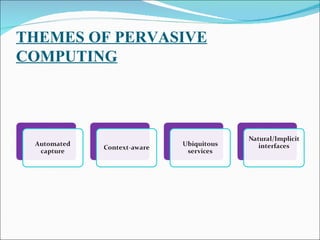
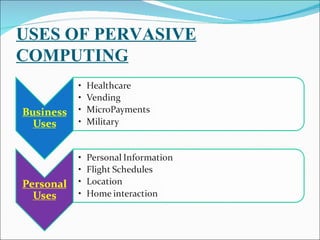
The document discusses pervasive computing, which refers to microprocessors being embedded everywhere and computing being available anywhere. It is enabled by technologies like mobile internet access, wireless communication, and Bluetooth. Pervasive computing allows access from any device, on any network, with any data. It aims to spread intelligence and connectivity to more or less everything, from ships and aircrafts to coffee mugs and the human body. Some principles of pervasive computing include anytime/anywhere access, physical integration between computing nodes and the physical world, and instantaneous interoperation between devices. Examples of applications include smart clothing, interactive flexible posters, and pill cameras.