This document provides an overview of basic computer skills, including:
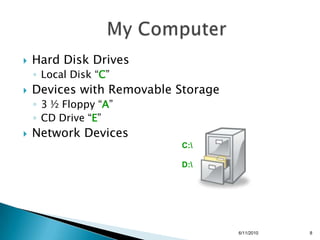
- Computer hardware components like the monitor, keyboard, mouse, hard drive, and disk drives.
- The difference between hardware and software.
- Types of computers like laptops, desktops, and handheld devices.
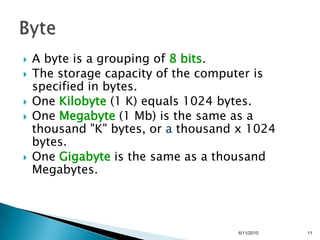
- Units of digital information like bits and bytes.
- Common software programs in Microsoft Office.
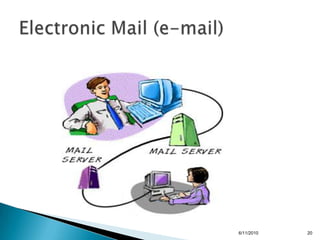
- How the internet works, including browsers, web pages, email addresses, and internet service providers.
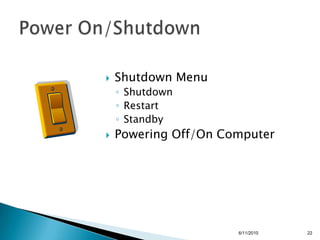
- How to power on and shut down a computer.
- Useful educational links and resources.