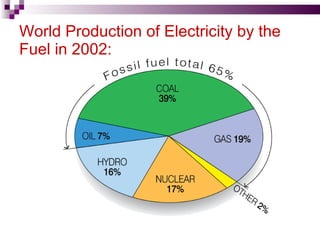
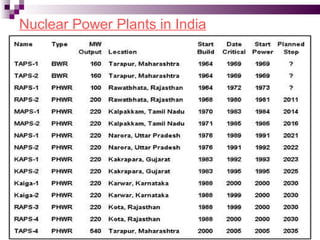
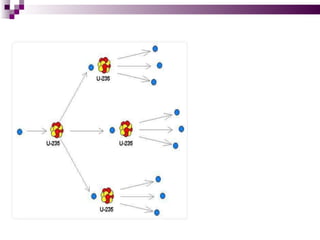
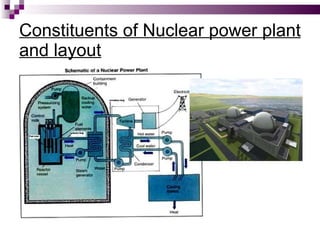
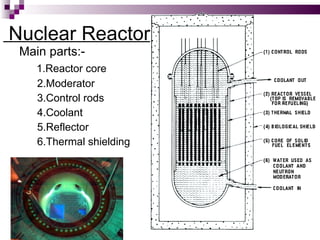
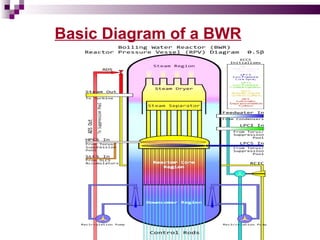
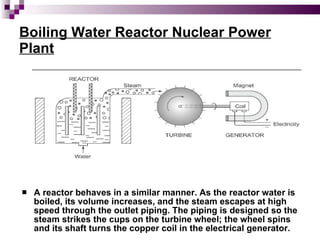
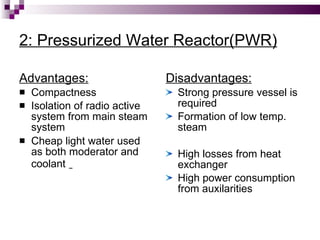
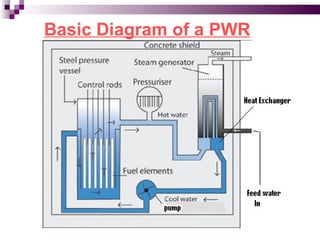
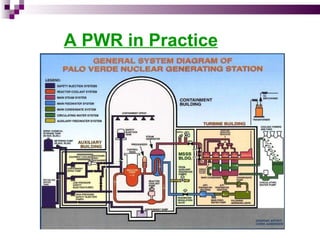
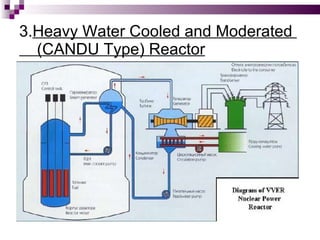
The document discusses the importance of nuclear power plants in India. It provides details on the basic concepts of nuclear reactions, fission, and chain reactions. It then describes the key components of a nuclear power plant including the reactor core, moderator, control rods, coolant, and reflector. Several types of power reactors are discussed - boiling water reactors, pressurized water reactors, and heavy water reactors. The document outlines India's nuclear program and goals to increase nuclear power generation to meet the country's energy needs.