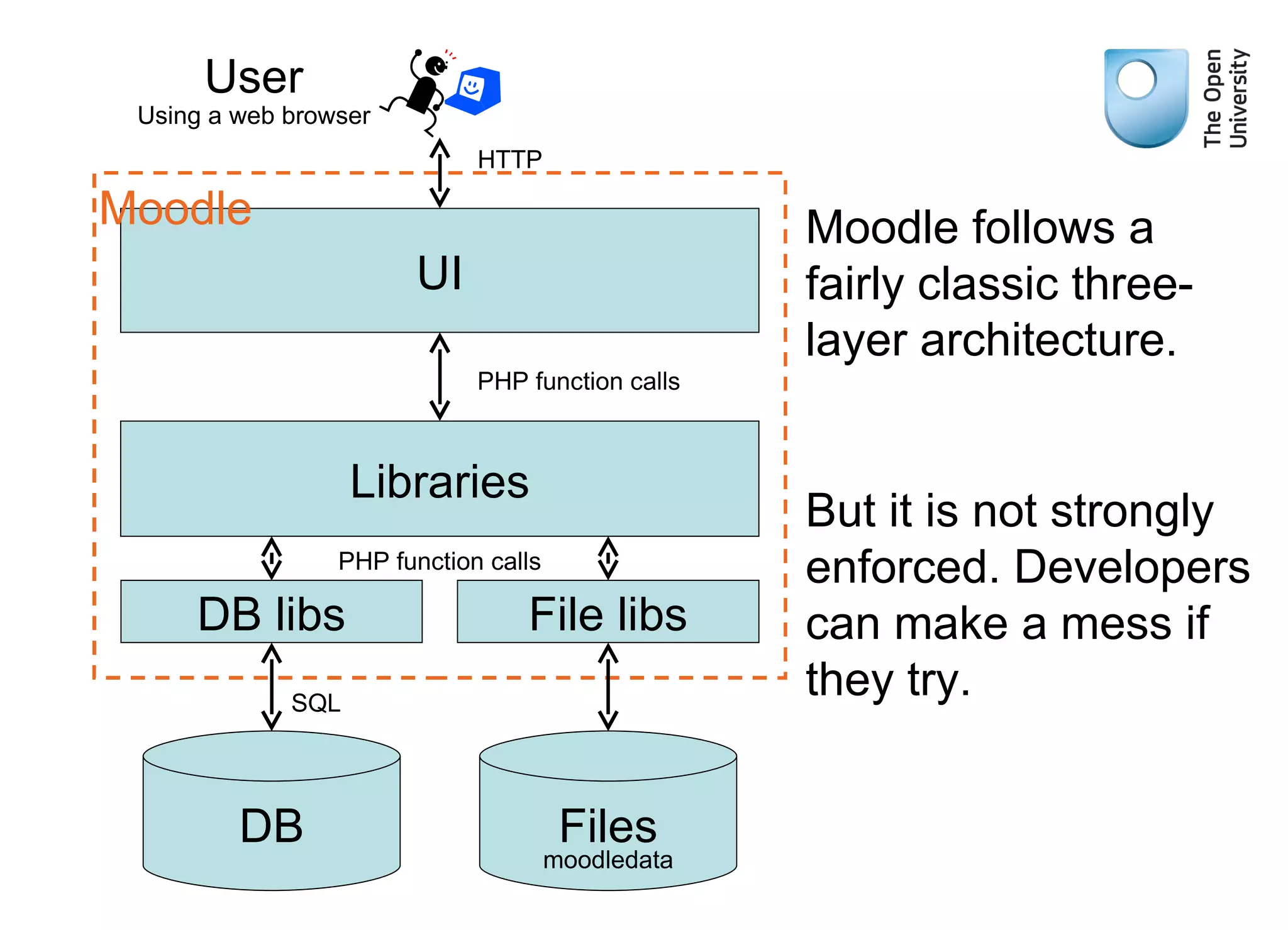
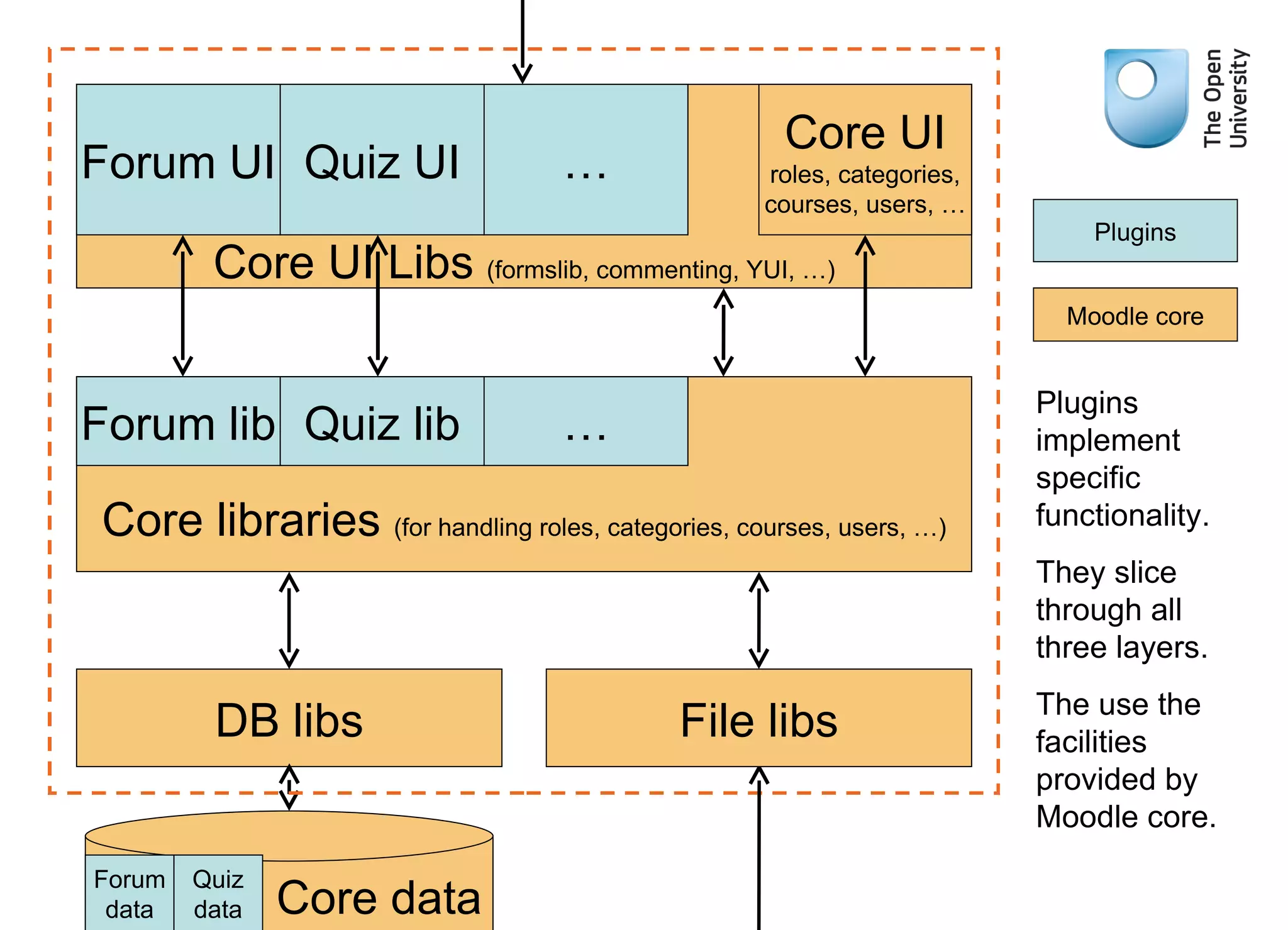
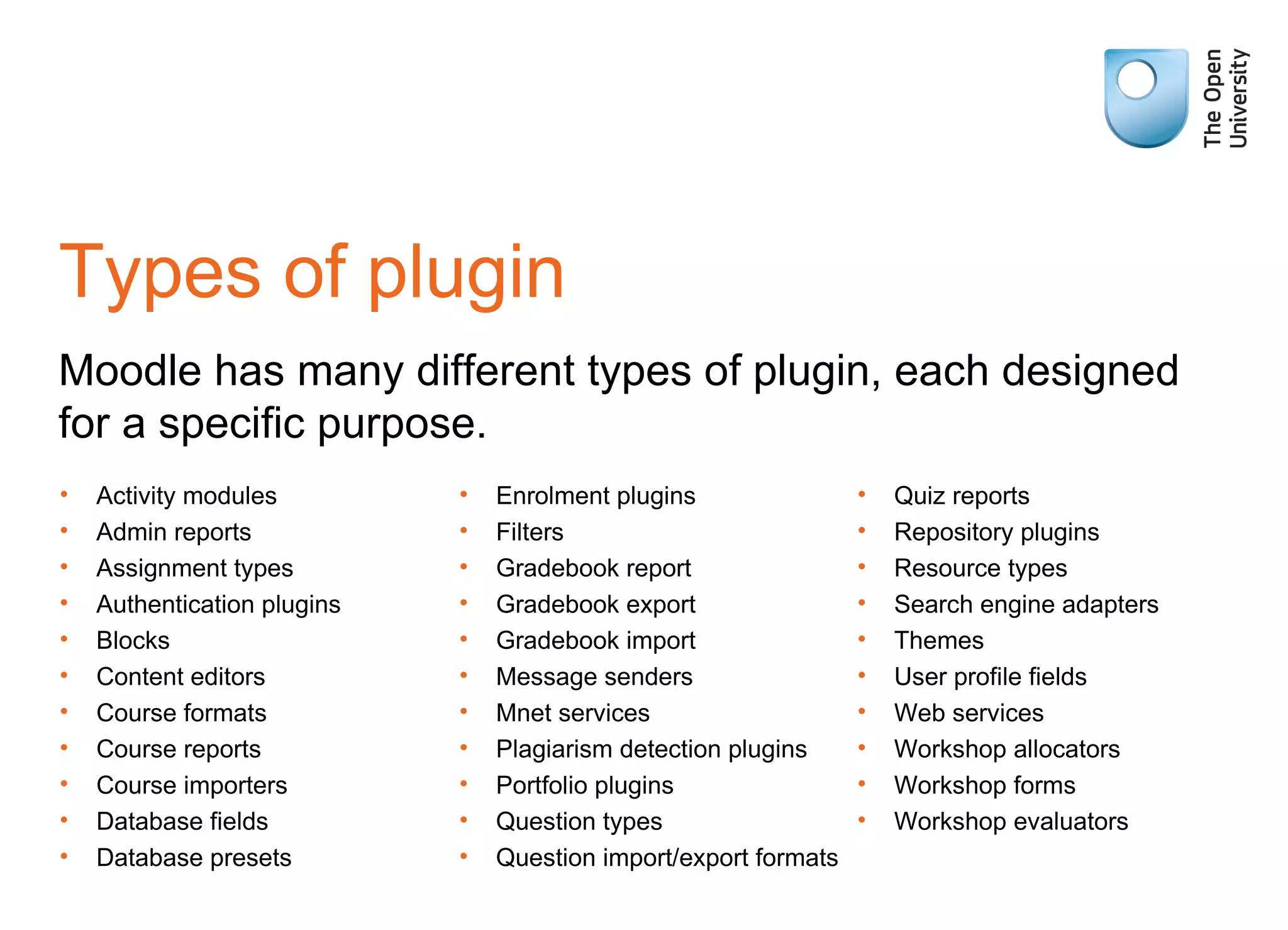
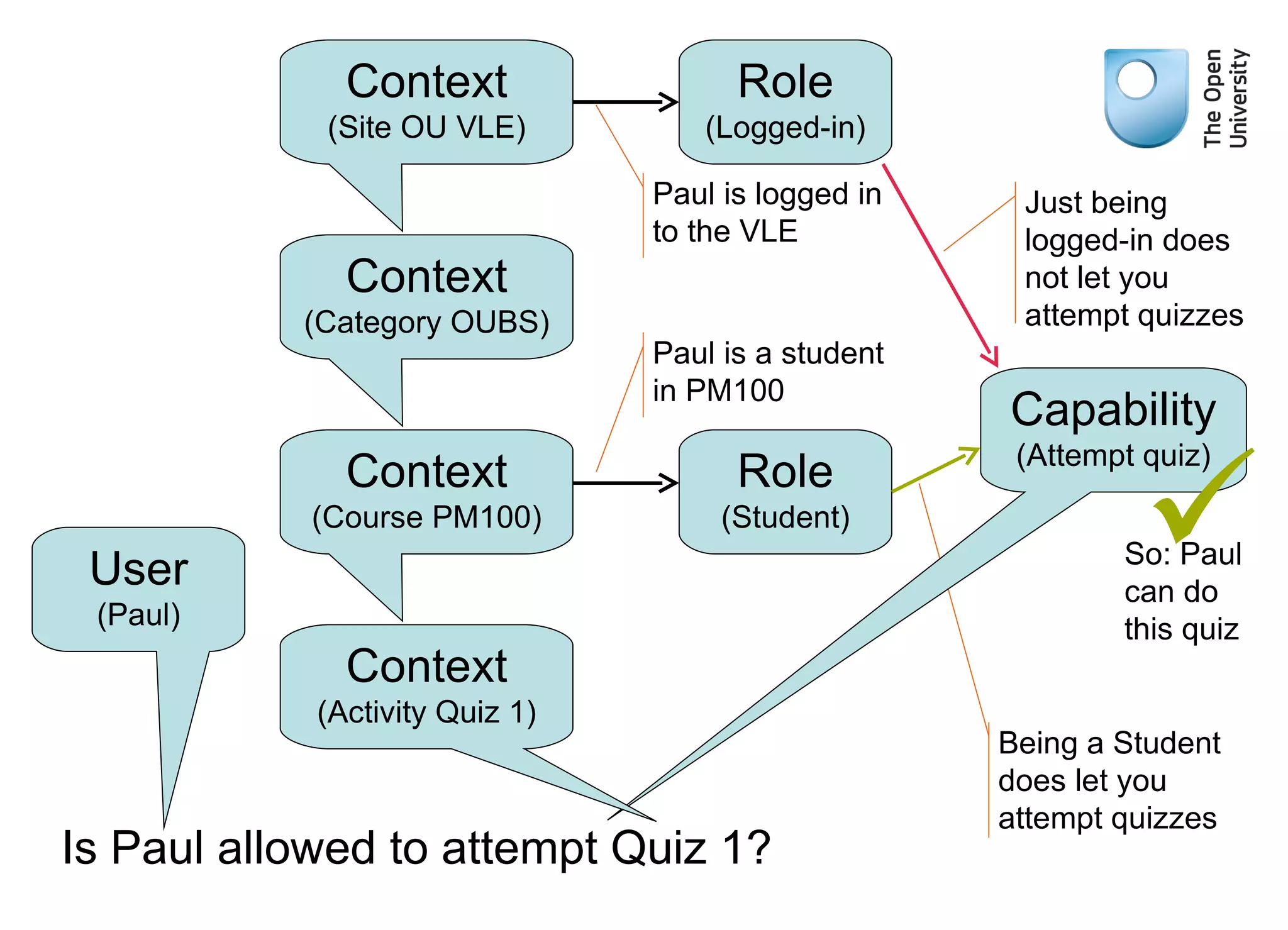
The document provides an overview of Moodle's architecture, emphasizing its three-layer system and the role of various libraries and plugins. It highlights the complexity of user roles, permissions, and group functionalities within the Moodle environment. Additionally, it suggests resources for further learning about using Moodle effectively.