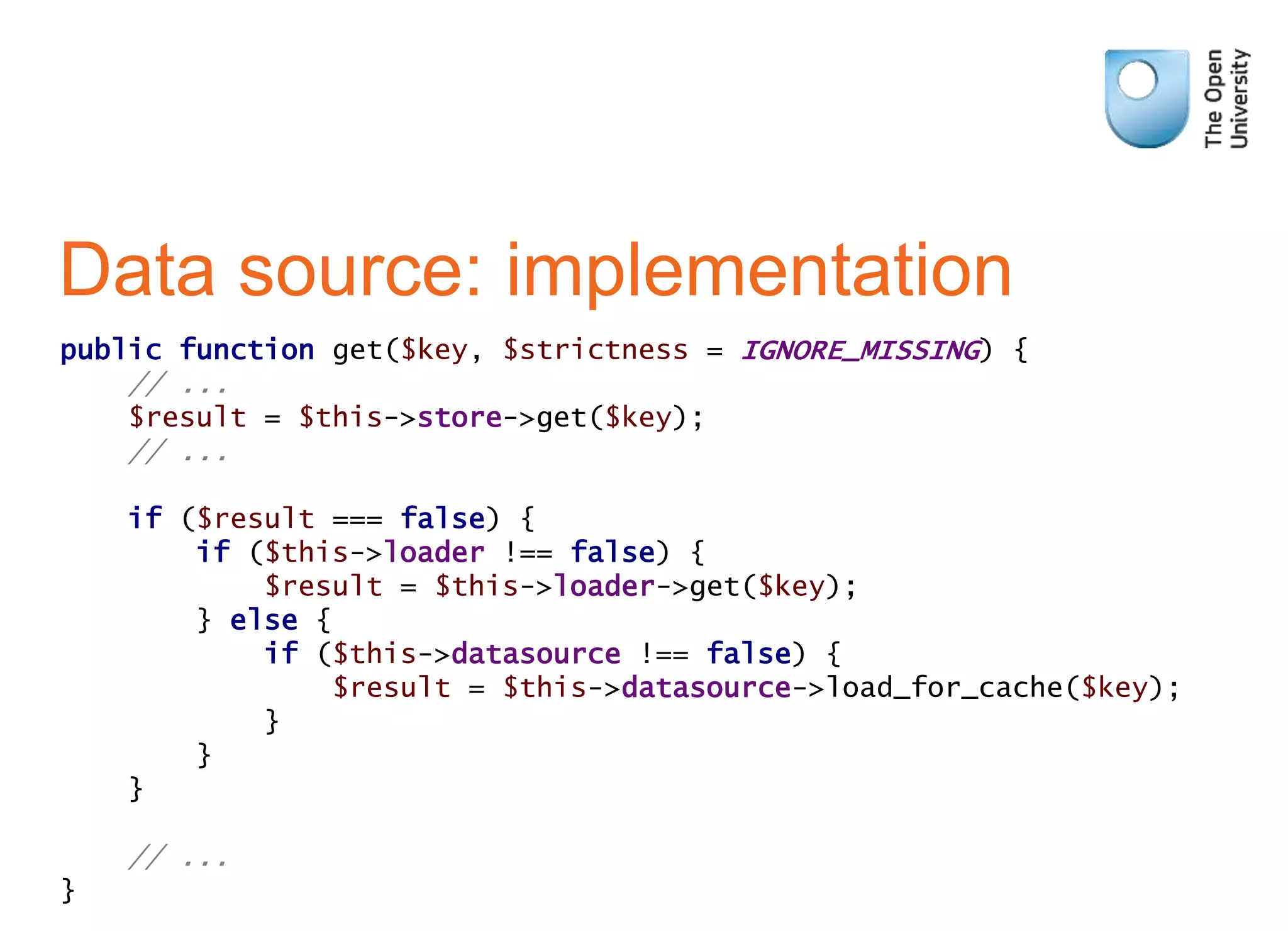
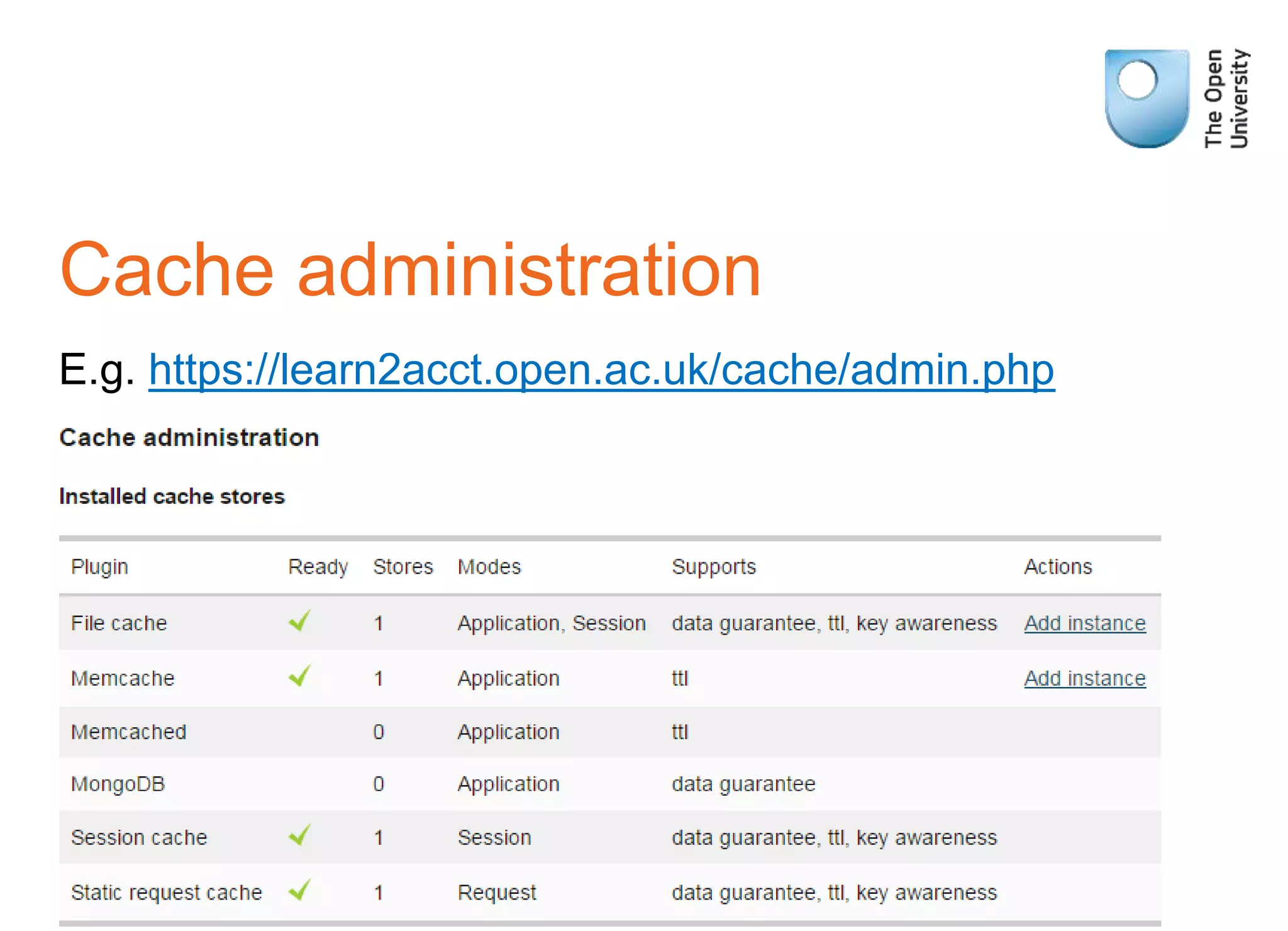
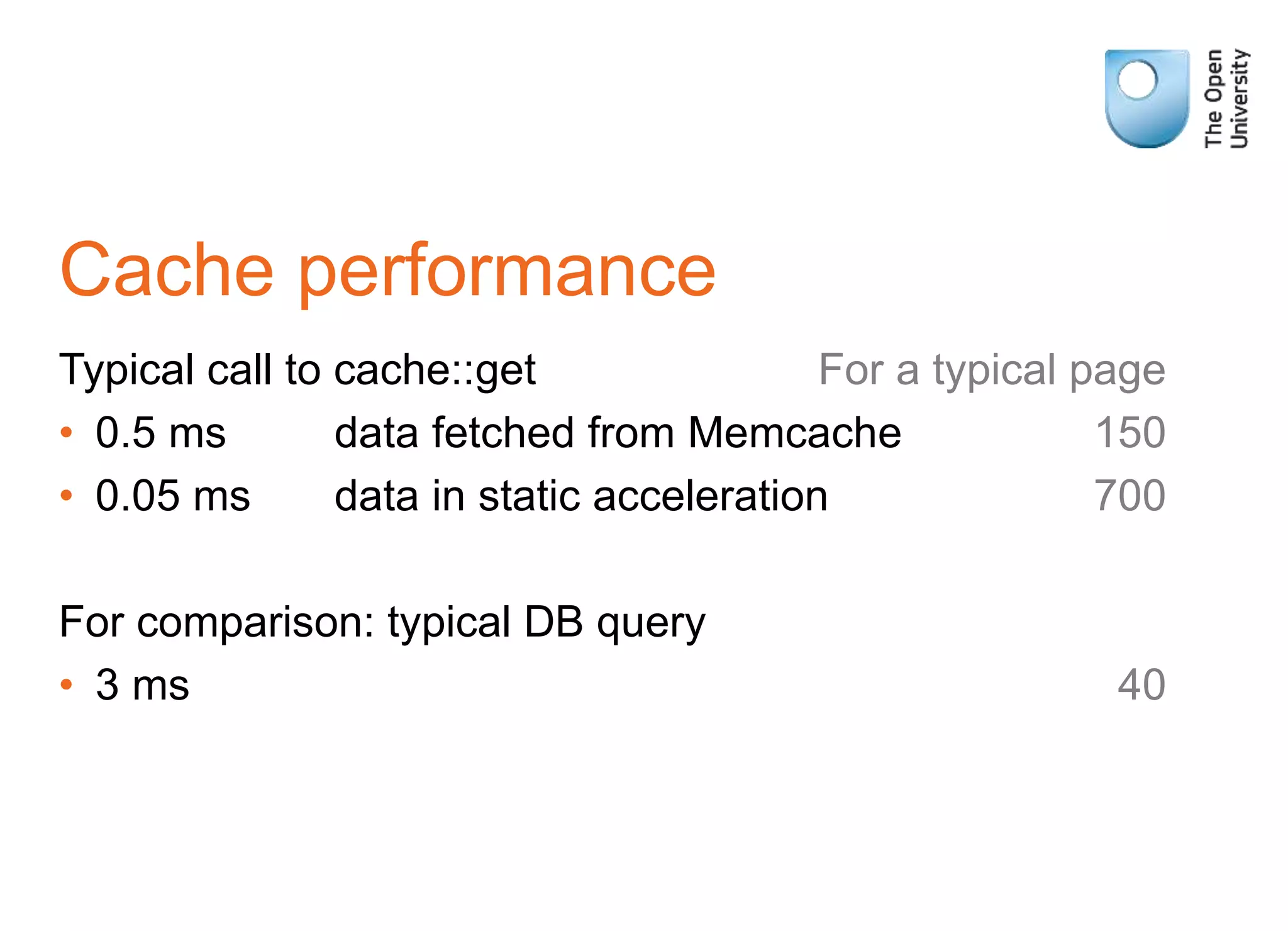
MUC (Moodle Universal Cache) is a caching system that allows storing and retrieving frequently accessed data to improve performance. It supports storing cached data in different backends like Memcache, Redis. The cache stores derived data identified by keys rather than real data. Developers can define different caches for application-wide, session-specific, or request-specific data. It provides APIs to get, set, delete cached data and clear caches. Data sources can be defined to load data if not found in cache. Cache administration tools allow monitoring cached data. Some issues include Memcache purging wiping all caches and complex keys hurting performance.






![Defining your cache
In db/caches.php in your plugin. E.g. from lib/db/caches.php
$definitions = array(
// Used to store processed lang files.
// Keys used are revision, lang and component of the string file.
// Static acceleration size is based on student access of the site.
'string' => array(
'mode' => cache_store::MODE_APPLICATION,
'simplekeys' => true,
'simpledata' => true,
'staticacceleration' => true, // Metadata helps cache
'staticaccelerationsize' => 30, // system handle the data
'canuselocalstore' => true, // efficiently.
),
);
$string['cachedef_string'] = 'Language string cache';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016-12muc-161208162952/75/MUC-Moodle-Universal-Cache-8-2048.jpg)


![Bulk actions
$cache->get_many(['key1', 'key2']);
// ['key1' => 'value1', 'key2' => 'value2']
$cache->set_many(
['key1' => 'value1', 'key2' => 'value2']);
$cache->delete_many(['key1', 'key2']);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016-12muc-161208162952/75/MUC-Moodle-Universal-Cache-11-2048.jpg)