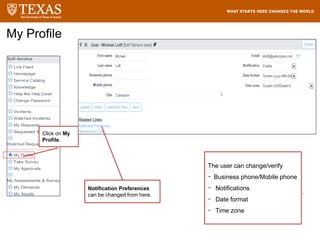
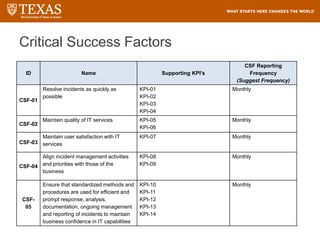
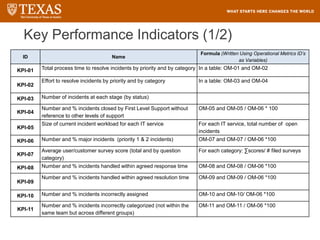
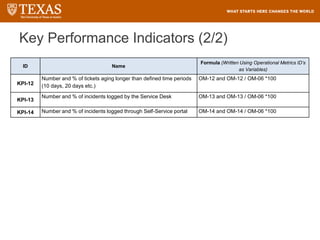
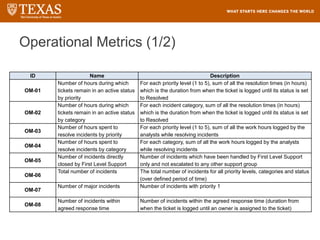
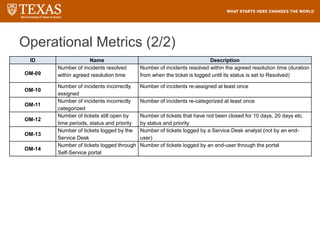
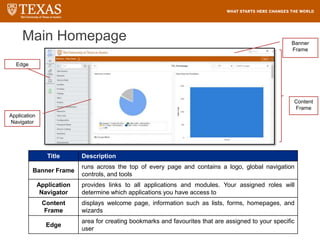
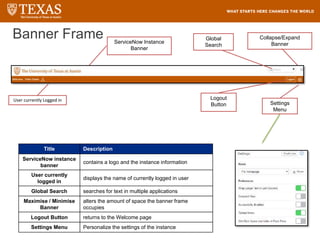
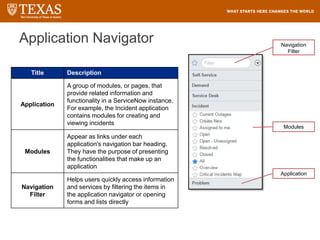
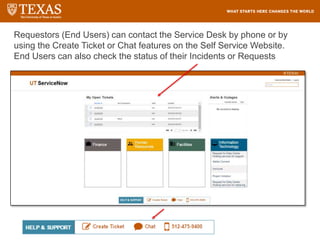
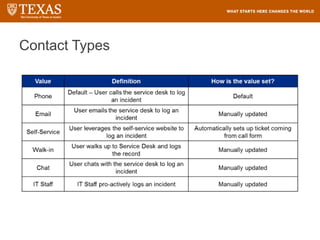
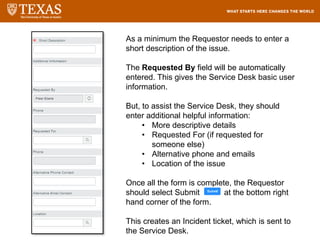
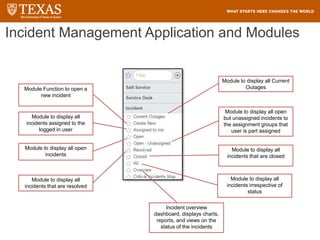
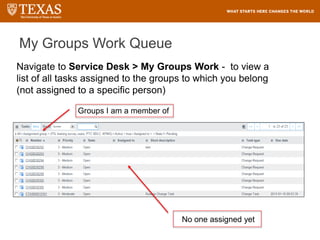
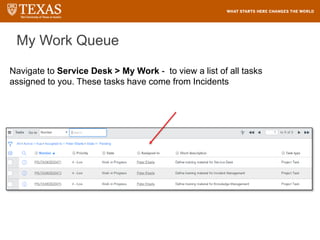
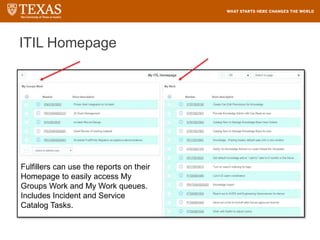
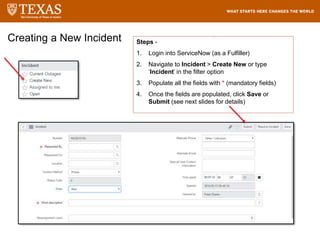
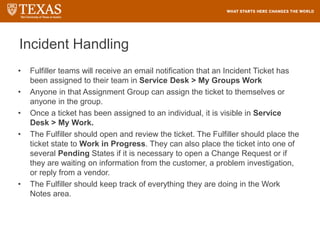
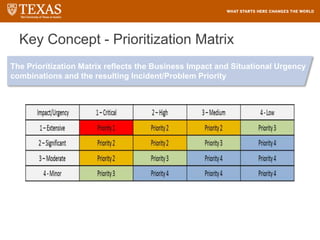
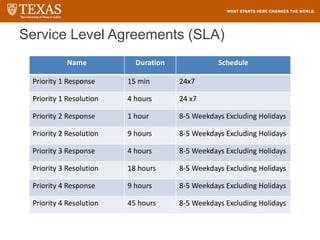
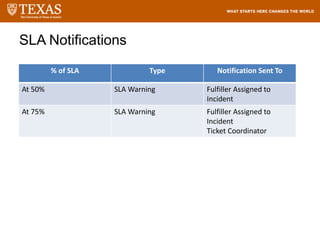
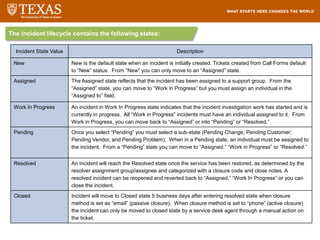
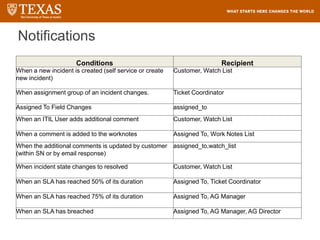
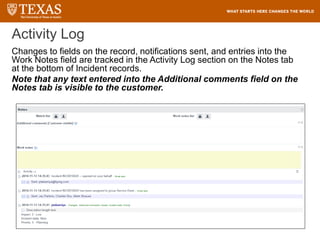
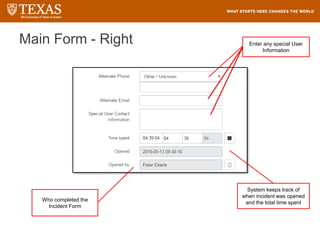
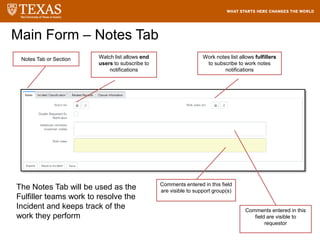
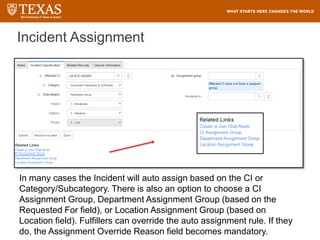
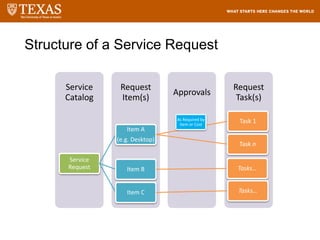
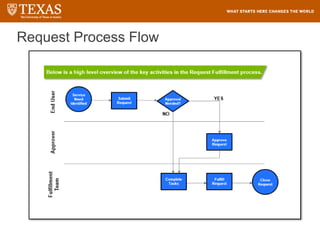
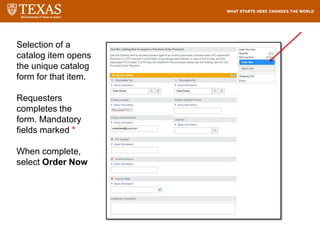
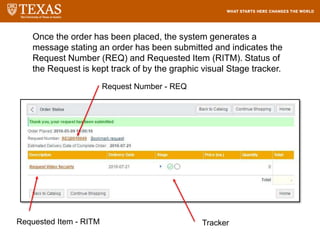
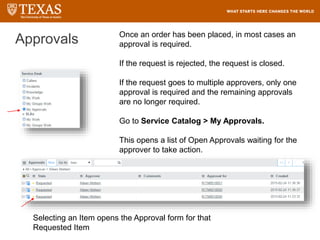
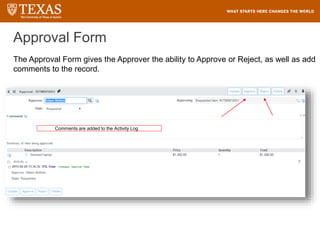
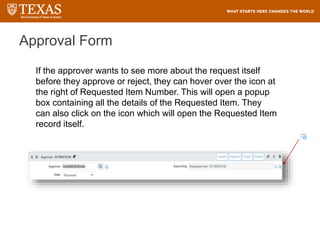
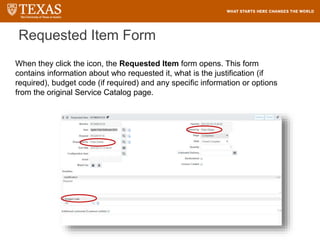
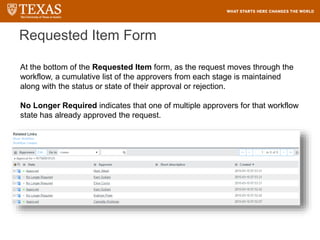
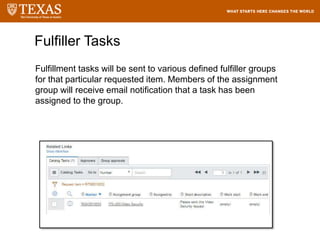
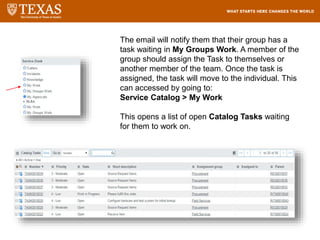
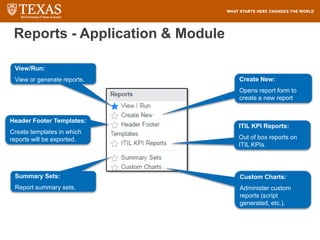
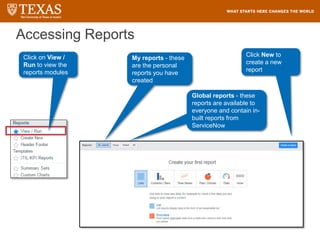
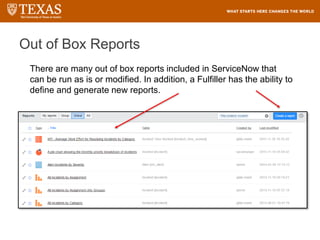
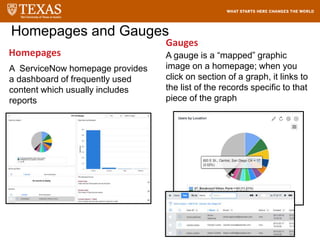
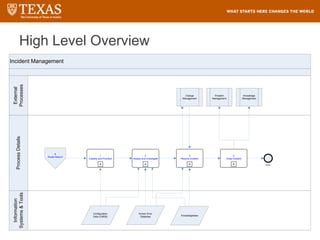
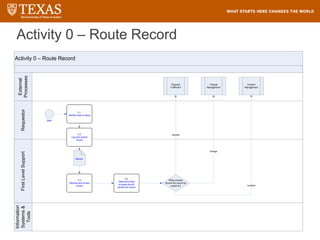
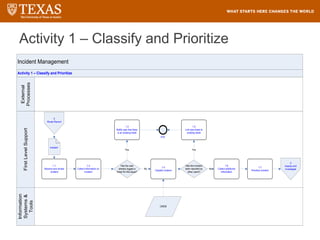
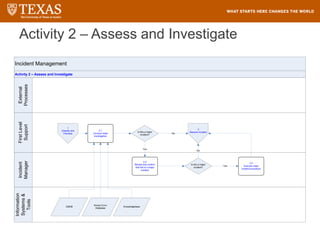
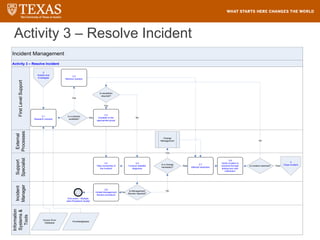
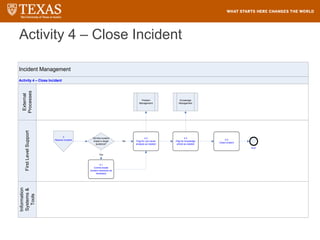
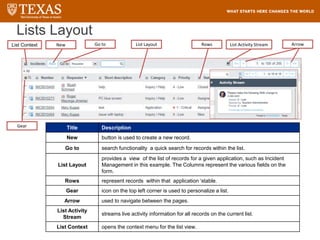
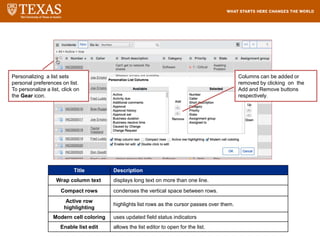
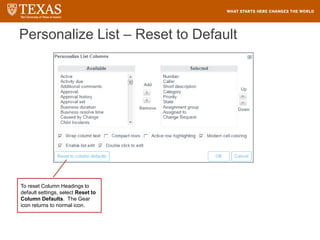
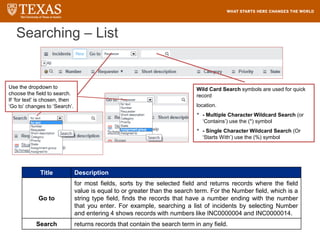
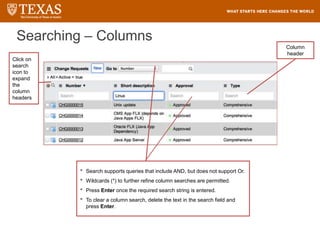
The document provides training information for ServiceNow fulfillers working for the UT Service Desk. It discusses the benefits of ServiceNow for UT, including adopting leading service management processes to improve service delivery. Fulfillers will learn general navigation in ServiceNow as well as the incident management process. Tickets in ServiceNow will be handled through the incident application, with fulfillers resolving incidents by keeping work notes, updating states, and documenting resolution in closure notes.























![Notification Examples
Email Subject: [Task] [Number] has been opened on your behalf
To Whom It May Concern,
We have received your [Incident/Request][Number].
Summary: [Short Description of Incident/Request].
Click Here to view: [Link to Incident/Request]
Email Subject: [Task] [Number] has been updated by Requestor
To Whom It May Concern,
[Incident/Request][Number] has been updated by [Name].
Summary: [Short Description] [Work Notes/Comments Update]
Click here to view: [Link to Incident/Request]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/servicedeskfulfillertraining-220821082216-eea883c2/85/Service-Desk-Fulfiller-Training-pptx-49-320.jpg)


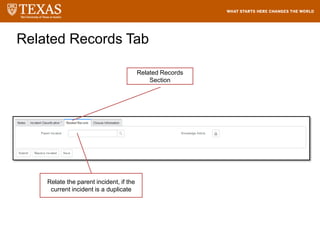

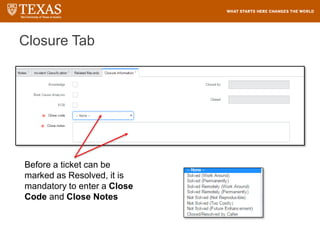
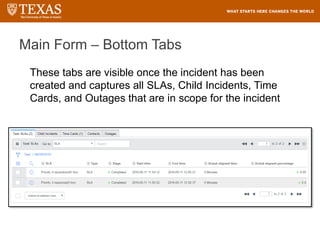


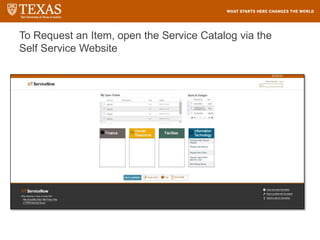














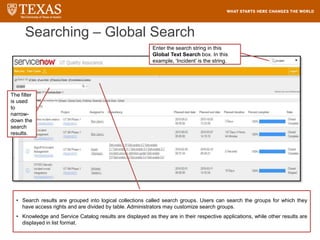
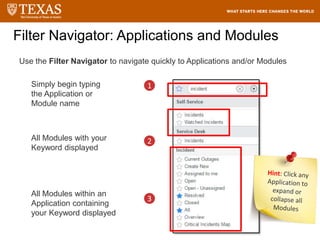
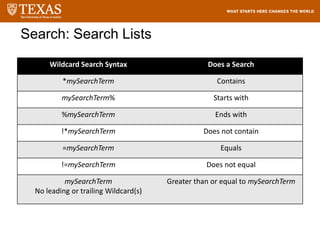
![Searching – Filter
The system will display breadcrumbs at the top of the
screen, displaying the applied conditions in the filter
and the filtered results
1. Click
on drop
down
icon to
expand
the filter.
2. Select a field
from the drop
down list, select
an operator, and
then enter or
select the value of
the field to filter
by.
Click the AND
condition or the
OR condition to
add more
relationships to
the filter
Click Delete [X] to
remove a
condition
3. Click on Run to view the
results.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/servicedeskfulfillertraining-220821082216-eea883c2/85/Service-Desk-Fulfiller-Training-pptx-112-320.jpg)