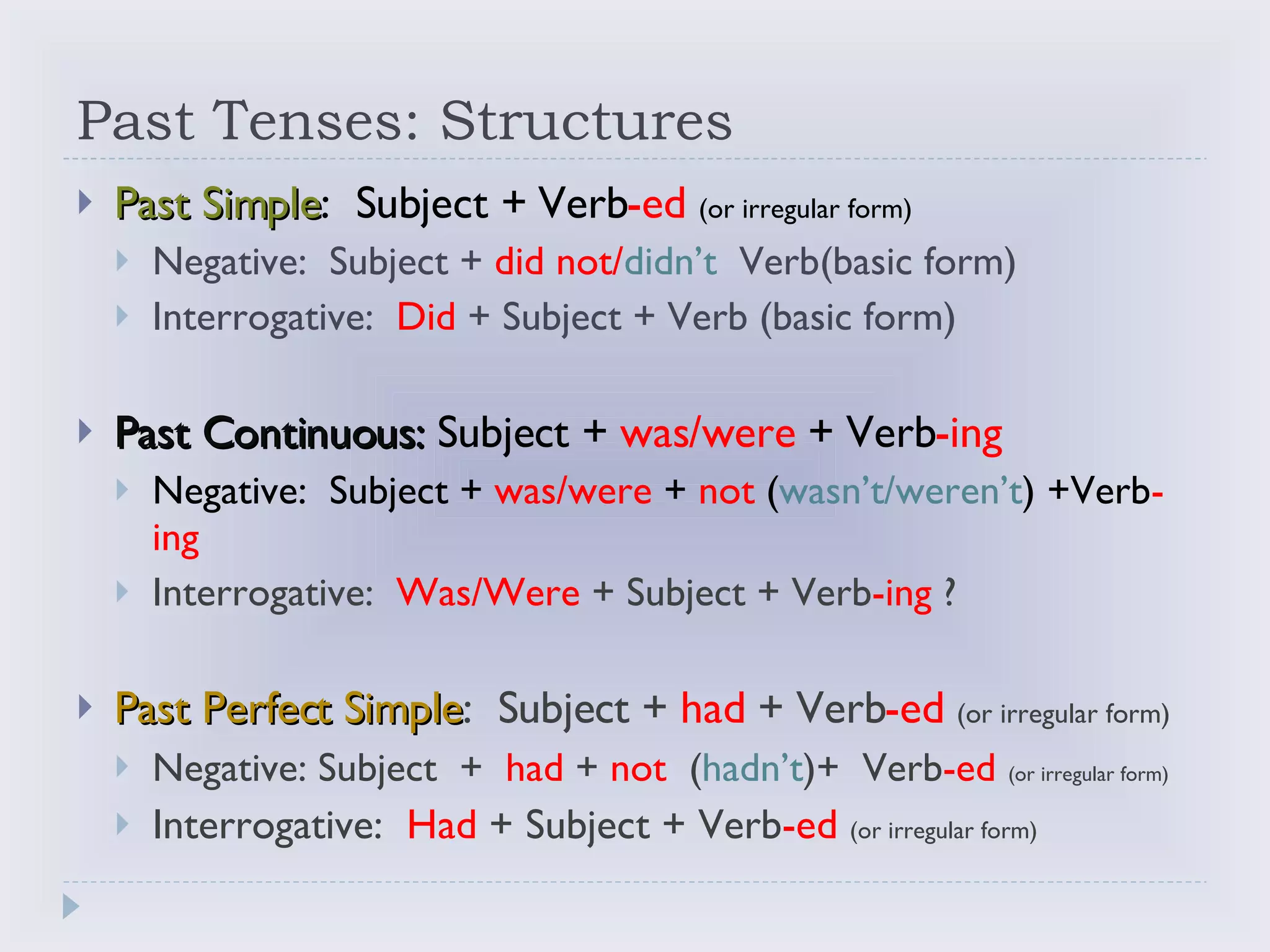
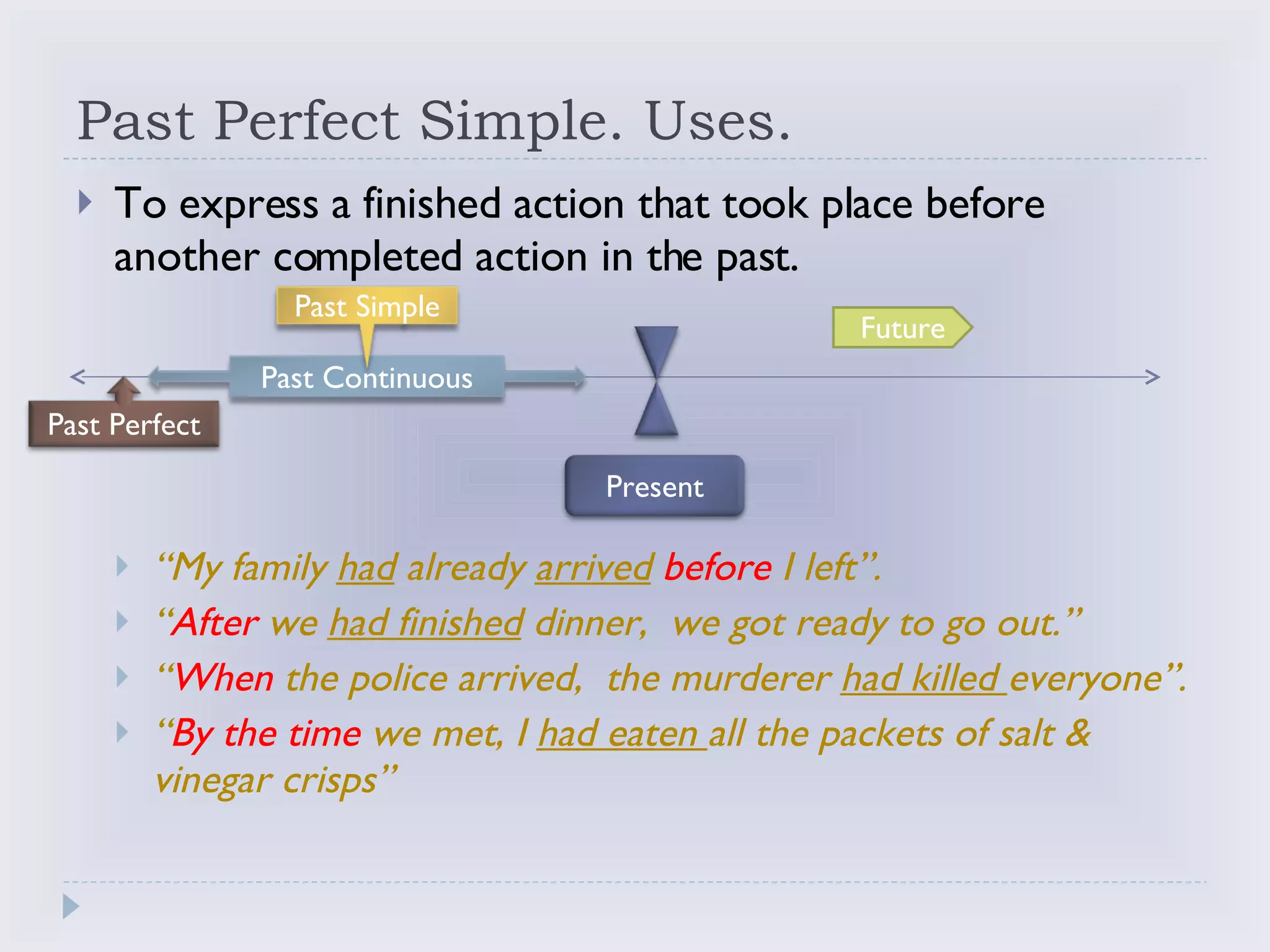
The document discusses different past verb tenses in English including their structures, uses, and formation rules. It covers the past simple tense, past continuous tense, and past perfect simple tense. For each tense it provides the basic structure, negative and interrogative forms, common uses to describe finished or ongoing past actions, and examples for clarification.