Anatomy & Physiology - LYMPHATIC SYSTEM PPT By wincy Thirumurugan
- 1. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF LYMPHATIC SYSTEM BY.MRS.WINCY THIRUMURUGAN PROFESSOR.
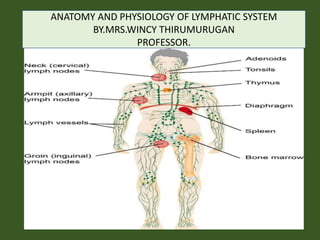
- 2. OVERVEIW: Lymphatic system is considered as a part of both the circulatory and immune systems. The lymphatic system begins with the lymphatic capillary meshwork that collects the excessive fluid from the tissues.. The lymphatic system involves many organs, including the tonsils, adenoids, spleen, and thymus. Lymph nodes filter out bacteria and cancer cells and create white blood cells to fight infection. These nodes are found throughout the body (neck, armpits, groin, chest, and abdomen).
- 3. DEFINITION: The lymphatic system is a network of vessels and organs that regulates the amount of fluid in the human body and defends it against infections. OR The lymphatic system consists of lymphatic vessels, a fluid called lymph, lymph nodes, the thymus, and the spleen. The lymphatic system is a system of specialized vessels and organs whose main function is to return the lymph from the tissues back into the bloodstream.
- 4. Lymph Lymph is a transudative fluid that is transparent and yellow. It is formed when fluid leaves the capillary bed in tissues due to hydrostatic pressure. Roughly 10% of blood volume becomes lymph.It is created as a result of the filtration of the plasma. The plasma from the blood diffuses through the porous capillary wall into the tissues to deliver nutrients. After feeding the hungry cells on the periphery, the majority of fluid gets reabsorbed back into the blood vessels, while around 10% of the fluid stays in the tissue. That amount of residual fluid in the tissues is called the interstitial fluid. When the interstitial fluid gets absorbed into the lymphatic capillaries it becomes the lymph.
- 5. LYMPHATIC VESSELS : THE TUBAL STRUCTURES CARRY THE LYMPH FLUID FROM THE TISSUE TO THE BLOOD STREAM. The lymph travels from the tissues through larger lymph vessels until it reaches its destination point; the bloodstream. On the way, it traverses lymphoid organs filled with immune cells that monitor if there are any pathogens in the incoming lymph. TYPES OF VESSELS : AFFERENT VS EFFERENT LYMPH VESSELS: Lymphatic vessels that carry lymph towards the lymph node are known as afferent, whereas the vessels that carry lymph away from the lymph node are called efferent lymphatic vessels.
- 7. Lymphatic capillaries Lymphatic capillaries are the smallest lymphatic vessels that collect the interstitial fluid from the tissues. They are organized in networks called lymphatic plexuses. Plexuses converge to make larger lymphatic vessels that carry the lymph away from the tissues and into the bloodstream. There are also special types of lymphatic capillaries called lacteals. These capillaries absorb nutrients from the small intestine.
- 10. COMPOSITION OF THE LYMPH FLUID: The composition of lymph is fairly similar to that of blood plasma, with the majority of the volume (around 95%) comprised of water. The remaining 5% is composed of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates (mainly glucose), various ions and some cells (mainly lymphocytes), although this can vary depending on where in the body the lymph is produced. For example, chyle (lymph that is produced in the gastrointestinal system) is particularly rich in fats. VOLUME OF LYMPH : The average adult produces between 3-4 litres of lymphatic fluid each day, although this can vary in illness.
- 11. Lymphatic pathway/circulation: The lymphatic system (also called the lymphoid system) is part of the immune system. The system moves lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells from the tissue through afferent lymphatic vessel,lymph nodes,efferent lymphatic vessels,lymphatic trunk,lymphatic duct and the right subclavian vein into the superior venacava and mix with the venous blood.
- 12. Lymphatic pathway/circulation: lymph from the tissue through afferent lymphatic vessel, lymph nodes efferent lymphatic vessels, lymphatic trunk lymphatic duct the right subclavian vein the right subclavian vein superior venacava mix with the venous blood.
- 13. TYPES OF LYMPHATIC VESSELS SUPERFICIAL AND DEEP LYMPHATIC VESSELS. The superficial vessels are located in the subcutaneous layer of the skin where they collect the lymph from the superficial structures of the body. They tend to follow the drainage of the venous system and in the end, drain into deep lymphatic vessels. The deep lymphatic vessels carry lymph from internal organs. In contrast to the superficial vessels, the deep vessels are accompanied by the arteries. These arteries lean onto the walls of the deep lymphatic vessels, putting pressure upon them and helping the flow of the lymph. Along the way, both superficial and deep lymphatic vessels go through lymph nodes that monitor the content of the lymph.
- 15. LYMPHATIC TRUNKS: The efferent vessels empty into the lymphatic trunks. The lymphatic trunks are named according to the region of the body that they drain the lymph from. There are four pairs of trunks: 1. Lumbar, 2. Bronchomediastinal, 3. Subclavian and 4. Jugular. There is also one unpaired intestinal lymph trunk, that drains lymph from the majority of organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The duct opens in the cisterna chyli which is the dilated origin of the thoracic duct.
- 17. LYMPHATIC DUCT: The lymphatic trunks then converge into the two lymphatic ducts; the right lymph duct and thoracic duct. The RIGHT LYMPHATIC DUCT collects lymph from the right upper limb and the right side of the head and chest. The THORACIC DUCT is a larger vessel and collects lymph from the rest of the body. The lymphatic ducts take the lymph into the right and left subclavian veins, which flow into the superior vena cava.
- 18. Lymphatic vessels vs. blood vessels The lymphatic vessels should not be confused with blood vessels. First of all, the lymphatic system is a one-way street starting blindly in the tissues and opening into the circulatory system on the other end. On the other hand, the venous and arterial vessels of the circulatory system vessels are connected by capillary networks and thus the blood flows in circles. The lymphatic system doesn’t have a pump that can regulate the pressure of the flow of the lymph like the circulatory system has (the heart). Instead, the lymph flows thanks to the movements of the body, pulsation of the arteries and contractions of skeletal muscles.
- 19. Lymphatic vessels vs. blood vessels The lymphatic vessels have valves that prevent the lymph flowing backwards. Lymphatic vessels are located throughout the whole body but note that some tissues and organs are lacking the lymphatic vessels(e.g. epidermis, cartilage, bone marrow, the structures of the eye). For a long time, it has been believed that the central nervous system doesn't contain lymph vessels. Now there is convincing evidence that the lymphatics do exist in some parts of the central nervous system.
- 20. Lymphoid organs : The Lymphoid organs are the sites where the maturation and proliferation of lymphocytes occur and help carry out various immune functions. OR the Lymphoid organs are specialized tissues that provide the typical anatomic location and microenvironment, which helps in attaining maturity of lymphocytes and thus, activates them.
- 22. Types of Lymphoid Organs The lymphatic system is composed of three types of lymphoid organs which are as follows: 1. Primary lymphoid Organs 2. Secondary lymphoid Organs 3. Tertiary lymphoid Organs
- 23. 1. Primary Lymphoid Organs I. Primary lymphoid organs are those organs where B and T-lymphocytes mature and acquire antigen-specific receptors. II. These organs are the sites of origin and proliferation of lymphocytes. Thus, they are also called central lymphoid organs. III. After the maturation of lymphocytes, they migrate to the secondary lymphoid organs. IV. These organs include bone marrow and thymus (and the bursa of Fabricius in birds).
- 24. a) Bone Marrow 1) It is a sponge-like tissue found inside the long bones. 2) The red bone marrow is involved in the immune system working. 3) It is the main lymphoid organ where all blood cells, including lymphocytes, are produced and multiply. 4) At the time of birth, many bones contain red bone marrow, which actively creates immune system cells. In adulthood, only a few of our bones contain red bone marrow, including the ribs, breastbone, and pelvis. 5) Bone marrow is primarily responsible for both the creation of T-cell precursors and the production and maturation of B cells. 6) Maturation of B-lymphocytes completes in the bone marrow only. On the contrary, T-cells travel from the bone marrow to the thymus, where they develop further and mature. 7) From the bone marrow, B cells immediately join the circulatory system and travel to secondary lymphoid organs in search of pathogen
- 26. b) Thymus 1) The thymus is a bi-lobed, pinkish-grey organ located behind the breastbone and above the heart. 2) It is quite large in size at the time of birth but keeps reducing with age. It reaches full maturity only in children and then slowly transforms into fatty tissue. 3) It is the site where T-lymphocytes mature. T-cells begin as hematopoietic precursors from the bone marrow and eventually migrate to the thymus, where they are referred to as thymocytes. 4) T-cells mediate the cell-mediated immune response (CMIR). 5) Thymus also secretes a family of hormones collectively known as thymosin which is essential for the normal functioning of the immune system.
- 28. 2. Secondary Lymphoid Organs I. Secondary lymphoid organs are the sites where B and T-lymphocytes undergo proliferation and differentiation. II. They interact with the antigens and become effector cells. They are also called the peripheral lymphoid organs. III. They are associated with the initiation of the adaptive immune response. IV. In the secondary lymphoid tissues, the lymphocytes move from one lymphoid organ to another through blood and lymph. V. These organs include lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, Peyer’s patches of the small intestine, and Mucosal associated lymphoid tissues
- 29. a) Lymph Nodes 1) These are small bean-shaped tissues found at intervals along the lymphatic system composed of lymphoid tissue. 2) These are an organized collection of lymphoid tissue, through which the lymph passes on its way back to the blood. 3) These are the first organized lymphoid structures that encounter the antigens entering the tissue spaces. 4) In the germinal centre of these lymph nodes, the selection of B lymphocytes occurs. 5) They act as filters for the lymph, preventing foreign particles or germs from entering the bloodstream and also activate the production of special antibodies in the blood. It also produces lymphocytes and plasma cells. 6) Swollen or painful lymph nodes indicate that the immune system is active, i.e., fighting against an infection.
- 30. LYMPH NODES Lymph nodes are kidney shaped structures which act to filter foreign particles from the blood, and play an important role in the immune response to infection. On average, an adult has around 400 to 450 different lymph nodes spread throughout the body – with the majority located within the abdomen. Each node contains immune cells they are exposed to the fluid as it passes through the node, and can mount an immune response if they detect the presence of a pathogen. This immune response often recruits more inflammatory cells into the node – which is why lymph nodes are palpable during infection. Lymph fluid enters the node through afferent lymphatic
- 33. b) Spleen 1) It is a large bean-shaped organ located in the left upper abdomen and beneath the diaphragm. It is the largest lymphoid organ. This appears due to more blood flow through it. 2) In the foetus, the spleen produces all types of blood cells, but in adults, it only produces lymphocytes and phagocytes. 3) It is a large reservoir of erythrocytes (or RBCs). At maturity, it removes particulate matter and aged blood cells, mainly red blood cells. 4) The spleen is involved in the synthesis of antibodies in its white pulp. By way of blood and lymph node circulation, the spleen is also involved in the removal of antibody-coated bacteria and antibody-coated blood cells. 5) If the spleen is removed completely, then the other immune systems can carry out their functions.
- 34. The lymph nodes are secondary lymphoid organs distributed throughout the whole body, grouped according to the body regions they are in (e.g. axillary, pelvic, mediastinal lymph nodes). The lymph nodes house lymphocytes and other immune cells (e.g. macrophages, plasmocytes, dendrocytes). Macrophages located within the sinuses of the lymph node act to filter foreign particles out of the fluid as it travels through and the lymph nodes serve as a filtration point for the lymph that travels towards the venous system. In case the immunocytes detect a foreign particle in the lymph (e.g. microorganism), they will start the immune response to prevent the harming particle from
- 36. c) Tonsils 1) The tonsils (also called palatine tonsils) are a pair of soft tissue masses located at the rear of the throat (pharynx). 2) Since they are located at the throat and the palate regions, they can stop the germs from entering the body through the mouth or the nose. 3) There are different types of tonsils like palatine tonsils, adenoids, and the lingual tonsil, which are sometimes together called Waldeyer’s ring because they form a ring around the opening to the throat from the mouth and nose. 4) They act as filters to protect the body from bacteria and viruses and also contain white blood cells, which are responsible for killing germs.
- 38. d) Peyer’s Patches 1) Peyer’s patches are small clusters of lymphoid follicles found throughout the mucus membrane of the small intestine, especially along the ileum. They are also called aggregated lymphoid nodules. 2) These are an important part of gut associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). They are located within both the small and large intestines of many mammalian species. 3) Pathogenic microorganisms, any form of antigens, etc. which enter the intestinal tract come across the macrophages, dendritic cells, B-lymphocytes, and T-lymphocytes found in Peyer’s patches. 4) T cells, B-cells and memory cells are stimulated when antigens come in contact with Peyer’s patches. 5) They play an important role in the immune system by monitoring the intestinal bacteria populations and thus preventing the growth of pathogenic bacteria in the intestines.
- 40. e) Mucosal-Associated Lymphoid Tissues (MALT) 1) MALT is a significant aggregate of lymphoid tissues located in the mucosal lining of the major tracts like respiratory, digestive, and urinogenital tracts. 2) MALTs are concentrations of many lymphoid tissues found in the various submucosal membrane sites of the body, like the gastrointestinal tract, nasopharynx, thyroid, breast, lung, salivary glands, eye, and skin. 3) It constitutes about 50%50% of the lymphoid tissues in the human body. 4) They do not serve as the filters of lymph but are the centres of lymphocyte production. 5) Apart from B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes, phagocytic macrophages and dendritic cells are also present.
- 42. 3. Tertiary Lymphoid Organs I. Tertiary lymphoid organs are generally found at the sites of chronic inflammation in autoimmune diseases (like rheumatoid arthritis). II. These organized accumulations of T and B cells basically resemble secondary lymphoid organs and generate autoreactive effector cells. III. Tertiary lymphoid organs usually contain very few lymphocytes that assume their role when they encounter the antigens that cause inflammation. IV. These organs also play a prominent role in the immune response to cancer.
- 44. The Lymphoid Organs Functions The functions of lymphoid organs are as follows: 1. The main function of lymphoid organs is developing and providing immunity to the body. 2. The primary lymphoid organs, i.e., the bone marrow and thymus, are the sites where the proliferation and maturation of B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes take place. 3. Bone marrow is involved in the production of blood cells, i.e., RBCs (or erythrocytes), WBCs (or leucocytes), and Platelets (or thrombocytes). 4. The spleen helps in the removal of damaged red blood cells. In foetal conditions, this is also a haematopoietic organ. 5. Lymph nodes and spleen helps in filtering out and destroying the unwanted lymphocytes. They also help in maintaining the population of mature lymphocytes to enable the adaptive immune response to begin. 6. The tonsils prevent foreign materials and pathogens from entering the body.
- 45. Lymphocytes Lymphocytes are a type of WBC (leucocytes) that are the main components of our immune system. There are two types of lymphocytes, T-lymphocytes, and B-lymphocytes. The lymphocytes are one of the body's main immune cells. They arise from the stem cells in the primary lymphoid organs and belong to the part of the immune system called the acquired immunity. After maturation, the lymphocytes are distributed mainly in the secondary lymphoid organs. According to their histology and functional characteristics, the lymphocytes are divided into three major groups; B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells. Their main role is to establish a specific immune response to foreign particles (antigens). B lymphocytes destroy the antigens indirectly, by producing antigen- specific antibodies that attach to antigens and mark them for destruction. On the other hand, T lymphocytes and NK cells directly kill cells that are infected by viruses or become cancerous.
- 46. • Lymphocytes are white blood cells that help the body fight infection and disease. The normal range for an adults is between 1,000 and 4,800 lymphocytes in 1 microliter (µL) of blood. • In children, the normal range is between 3,000 and 9,500 lymphocytes in 1 µL of blood. • The immune system is a complex network of cells known as immune cells that include lymphocytes. These cells work together to defend the body against foreign substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells that can threaten its functioning.
- 48. TYPES OF B -LYMPHOCYTE: There are different types of B cells and T cells that have specific roles in the body and the immune system. B cells There are also several types of B cells: Memory B cells Memory B cells circulate in the body to start a fast antibody response when they find a foreign substance. They remain in the body for decades and become memory cells, which remember antigens and help the immune system respond faster to future attacks. Regulatory B cells Regulatory B cells, or Bregs, only account for a small number of B cells in healthy people. Although few in number, they have a vital role to play. Bregs have protective anti-inflammatory effects in the body and stop lymphocytes that cause inflammation. They also interact with several other immune cells and promote the production of regulatory T cells, or Tregs. Plasma cells Plasma cells are terminally differentiated B cells that produce antibodies and are responsible for antibody-mediated immunity. Terminally differentiated cells are cells that become specialized to a point after which they can no longer divide.
- 49. TYPES OF T- LYMPHOCYTE: There are several types of T cells: Killer T cells Killer, or cytotoxic, T cells scan the surface of cells in the body to see if they have become infected with germs or turned cancerous. If so, they kill these cells. Helper T cells Helper T cells “help” other cells in the immune system to start and control the immune response against foreign substances. There are different types of helper T cells, and some are more effective than others against different types of germs. Regulatory T cells, or Tregs Tregs control or suppress other cells in the immune system. They have both helpful and harmful effects. They maintain tolerance to germs, prevent autoimmune diseases, and limit inflammatory diseases. But they can also suppress the immune system from doing its job against certain antigens and tumors. Memory T cells Memory T cells protect the body against antigens that they have previously identified. They live for a long time after an infection is over, helping the immune system remember previous infections. If the same germ enters the body a second time, memory T cells remember it and quickly multiply, helping the body fight it more quickly.
- 50. FUNCTIONS /PHYSIOLOGY OF LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system has several crucial functions for maintaining body homeostasis which include: maintaining the body's fluid balance, transportation of large molecules and immune surveillance. The fluid balance is maintained by draining the extra fluid that remains after the exchange of blood and nutrients between the tissues and capillaries. If not regularly drained, this amount of fluid can accumulate and cause swelling (edemas). The lymphatic organs house numerous immune system cells which surveil the content of the lymph as it flows toward the venous system. If a foreign particle is detected, the immune cells start an immune response to destroy the pathogen and prevent the infection and damage. The lymphatic system filters the lymph by destroying pathogens, inactivating toxins, and removing particulate matter. Lymph nodes, small bodies interspersed along lymphatic vessels, act as cleaning filters and as immune response centers that defend against infection.
- 51. CONTI…… This system supplements and extends the cardiovascular system in the following ways:The lymphatic system collects excess fluids and plasma proteins from surrounding tissues (interstitial fluids) and returns them to the blood circulation. Because lymphatic capillaries are more porous than blood capillaries, they are able to collect fluids, plasma proteins, and blood cells that have escaped from the blood. The lymphatic system absorbs lipids and fat‐soluble materials from the digestive tract. Lymph also carries the molecules that are too large to diffuse through the capillary wall (e.g. proteins or lipids). This is why the small intestine has a vast lymphatic drainage, as it is the site where the lipids and proteins are absorbed from
- 52. Clinical Relevance lymphoma is one of a group of tumours developing from lymphatic cells. Lymphedema: This is an accumulation of lymph fluid in the body. It most commonly occurs in the arms and legs. It ranges from mild to very painful. It is common in people who have received cancer treatment. Lymphatic filariasis: Also called elephantiasis, this infection is caused by a parasite that infects the body through a mosquito bite. The worms invade the lymphatic system, resulting in a blocked lymphatic system and swelling, pain, and disfigurement. Lymphadenopathy: This is the medical term for swollen lymph nodes. Lymph nodes, themselves, can become infected, but swollen lymph nodes also indicate an infection within the body.
- 54. CONTI…… Lymphadenitis: This term refers to an infection of the lymph node(s). This infection often occurs due to germs that spread through the lymphatic system from one part of the body to the lymph nodes. Lymphangitis: Inflammation of the lymph vessels, which may result from some bacterial infections. Lymphocytosis: This condition is a higher than normal amount of lymphocytes, often a result of your body dealing with infection or inflammation. Castleman disease: This condition is an overgrowth of cells in the lymphatic system. An infection causes it. It may result in a full feeling in the abdomen, lumps in the armpits, groin, neck, and weight loss. Mesenteric lymphadenitis: This is inflammation of lymph nodes in the abdomen. An infection causes it, and it usually affects children and teenagers. Tonsillitis: An infection of the tonsils, resulting in a very sore throat.
- 55. TONSILLITIS
- 56. REFERENCE : 1. Available From :https://www.khanacademy.org/science/in-in-class-12- biology-india/xc09ed98f7a9e671b:in-in-human-health-and-disease/xc09ed 2. Available From :Lymphoid Organs: Definition, Types, Functions, Examples – Embibe 3. Available From:https://www.bing.com/images/search?view=detailV2&ccid=ATNqHuiN &id=377A360442C1E23C9DC6140D786AB2579E53D701&th 4. Available From :https://www.bing.com/images/search?view=detailV2&ccid=ATNqHuiN&id=3 77A360442C1E23C9DC6140D786AB2579E53D701&th
